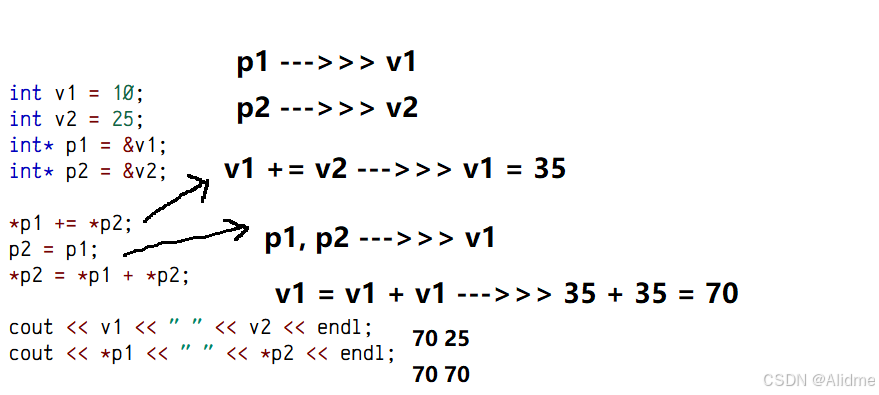打卡cs106x(Autumn 2017)-lecture13
(以下皆使用SPL实现,非STL库,后续课程结束会使用STL实现)
1、v1v2p1p2
The following code C++ uses pointers and produces two lines of output. What is the output?
int v1 = 10;
int v2 = 25;
int* p1 = &v1;
int* p2 = &v2;
*p1 += *p2;
p2 = p1;
*p2 = *p1 + *p2;
cout << v1 << " " << v2 << endl;
cout << *p1 << " " << *p2 << endl;解答:
70 25
70 70
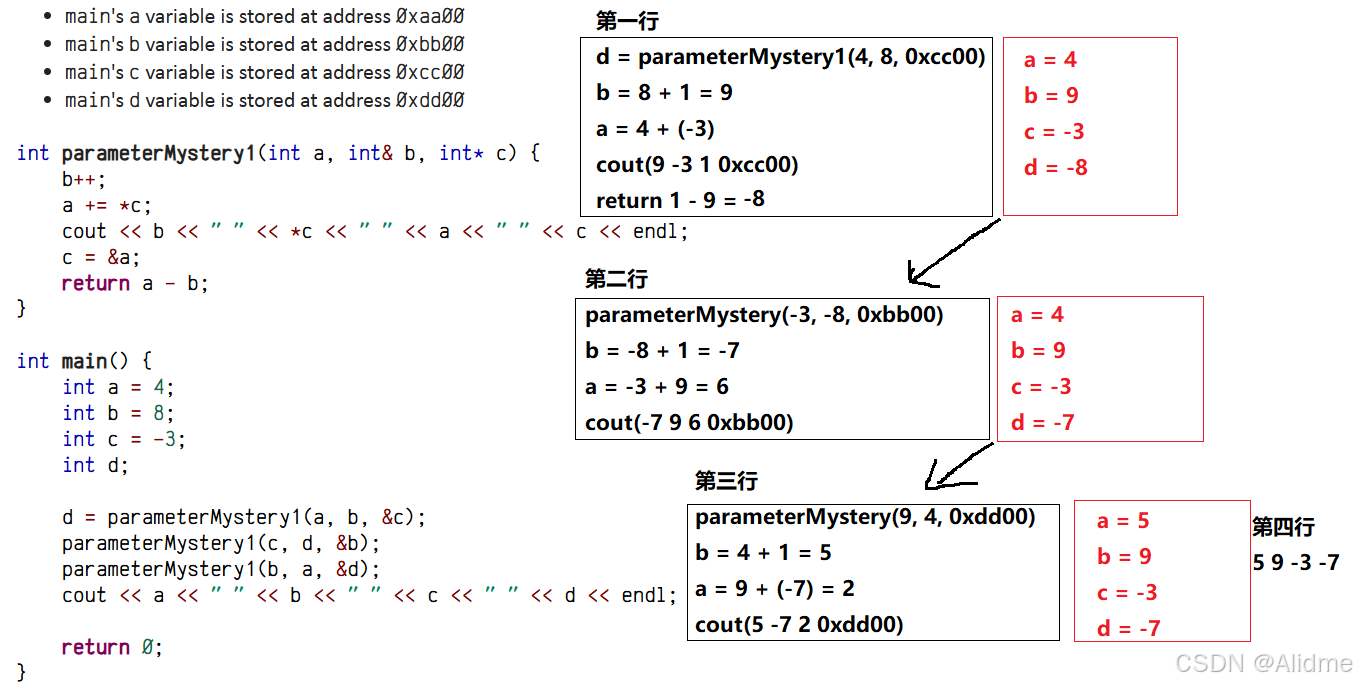
2、parameterMystery1
The following code produces 4 lines of output. What is the output? Write each line of output as it would appear on the console.
For the purposes of this problem, assume that the variables in main are stored at the following memory addresses:
main'savariable is stored at address0xaa00main'sbvariable is stored at address0xbb00main'scvariable is stored at address0xcc00main'sdvariable is stored at address0xdd00
解答:
| line 1 | 9 -3 1 0xcc00 |
| line 2 | -7 9 6 0xbb00 |
| line 3 | 5 -7 2 0xdd00 |
| line 4 | 5 9 -3 -7 |
3、12-123
Write the code that will produce the given "after" result from the given "before" starting point by modifying links between the nodes shown and/or creating new nodes as needed. Assume that the nodes have already been declared and initialized to match the "before" figure below. There may be more than one way to write the code, but do NOT change any existing node's data field value.
If a variable does not appear in the "after" picture, it doesn't matter what value it has after the changes are made. If a given node object does not appear in the "After" picture, you must free its memory to avoid a memory leak.
| Before | list: 1 -> 2 / |
|---|---|
| After | list: 1 -> 2 -> 3 / |
Assume that you are using the following ListNode structure:
struct ListNode {
int data; // data stored in this node
ListNode* next; // a link to the next node in the list
ListNode(int data = 0, ListNode* next = nullptr) { ... } // constructor
};解答:
ListNode* node3 = new ListNode(3);
node3->next = nullptr;
list->next->next = node3;4、12-312
Write the code that will produce the given "after" result from the given "before" starting point by modifying links between the nodes shown and/or creating new nodes as needed. Assume that the nodes have already been declared and initialized to match the "before" figure below. There may be more than one way to write the code, but do NOT change any existing node's data field value.
If a variable does not appear in the "after" picture, it doesn't matter what value it has after the changes are made. If a given node object does not appear in the "After" picture, you must free its memory to avoid a memory leak.
| Before | list: 1 -> 2 / |
|---|---|
| After | list: 3 -> 1 -> 2 / |
Assume that you are using the following ListNode structure:
struct ListNode {
int data; // data stored in this node
ListNode* next; // a link to the next node in the list
ListNode(int data = 0, ListNode* next = nullptr) { ... } // constructor
};解答:
//ListNode* list = new ListNode(1);
//list->next = new ListNode(2);
//list->next->next = nullptr;
ListNode* node3 = new ListNode(3);
node3->next = list;
list = node3;