AOP
一、什么是AOP
AOP:面向切面编程,对面向对象编程的一个补充;是使用动态代理来实现,将系统级别的功能提取出来形成一个切面(Java中的类);像这样的公共功能就好维护了;
面向对象,基于对象,高内聚低耦合,每个对象都相对独立,每个对象都是一个垂直体系,有些功能是系统级别的,该功能会涉及多个对象,例如,日志,事务等等,就需要通过面向切面的方案解决系统级别的功能,将系统级的功能定义在切面类中通过动态代理的方式,在不改变现有对象的基础上,为现有对象附加额外功能。
二、AOP中的相关概念
1.目标类(targetClass):被代理的对象,需要增加额外功能的对象
2.代理类(proxyClass):拥有目标类中的功能,并且附加了额外功能
3.连接点(JoinPoint):可以被附加额外功能的点,字段、方法等等(在Java中,目前只有方法可以作为连接点)
4.切点(pointcut):本质上是一个表达式,通过表达式筛选连接点,只有符合该表达式的连接点才会被附加额外功能
5.通知(advice):通知就是一个方法,该方法中定义了额外的功能:
-
前置通知(before):在核心方法之前
-
后置通知(after-returning):在核心方法无误的执行完成之后
-
异常通知(after-throwing):在核心方法产生异常时会执行
-
最终通知(after):核心方法执行之后执行,不论有没有异常都会执行
-
环绕通知(around):最强大的通知,他可以实现以上4个通知的效果
6.切面(aspect):Java中的一个类,通知就定义在此类中
7.织入(weaving):将额外功能和代理对象结合的过程
8.引入(introduction):在运行时为现有接口或者类增加额外的字段和方法
AOP的实现方案
AOP实现方案
1.配置文件
2.注解
配置文件实现AOP
1.导入aop相关依赖
<!-- spring核心依赖,会将spring-aop传递进来-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.29</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 切入点表达式依赖,目的是找到切入方法,也就是要找到增强的方法-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.3.29</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.创建目标类
public class Target {
public void add(){
System.out.println("-----------添加方法-----------");
}
public int delete(int id){
System.out.println("-----------删除方法------------");
return id;
}
}
3.创建切面类
//切面类
public class MyAspect {
//前置通知
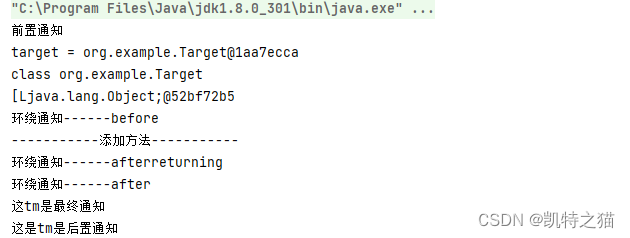
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("前置通知");
//可以通过在此方法获取目标类
Object target = joinPoint.getTarget();
System.out.println("target = " + target);
//目标对象的类型
System.out.println(joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringType());
//获取方法的参数
System.out.println(joinPoint.getArgs());
}
public void afterReturning(){
System.out.println("这是tm是后置通知");
}
public void afterThrowing(){
System.out.println("这是tm是异常通知");
}
public void after(){
System.out.println("这tm是最终通知");
}
//环绕通知,可实现以上所有功能
//参数为连接点对象,该参数是用来执行目标类中的方法
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
//执行目标类中的方法,proceed方法的返回值,就是目标方法的返回值
try {
System.out.println("环绕通知------before");
Object returnValue = joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕通知------afterreturning");
return returnValue;
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("环绕通知------afterthrowing");
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
System.out.println("环绕通知------after");
}
}
}
4.配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- 将目标类和代理类加载到ioc容器中-->
<bean id="target" class="org.example.Target"></bean>
<bean id="myaspect" class="org.example.MyAspect"></bean>
<!-- 配置aop-->
<aop:config>
<!-- 配置切点-->
<!--
execution(访问控制符 返回值类型 包名.类名.方法名(参数类型列表))
execution(public void com.lanou.service.MyService.add(int))
1.访问控制符部分可以省略,代表任意的访问控制都可以
execution( void com.lanou.service.MyService.add(int))
2.返回值类型不可以省略,但是可以使用*来代表任意返回值
3.类名和方法名亦可以使用*代表任意类和任意方法
execution( * com.lanou.service.MyService.add(int))
4.指定包以及其他子孙包
execution( * com.lanou.service..*.*(int))
5.任意参数
execution( * com.lanou.service..*.*(..))
-->
<aop:pointcut id="pd" expression="execution(* org.example.Target.*(..))"/>
<!-- 配置切面 ref:切面对象id值,引用了IOC容器中已注册的切面对象-->
<aop:aspect id="pc" ref="myaspect">
<!-- 配置通知
method是切面中的方法
pointcut-ref是切点
-->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pd"></aop:before>
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturning" pointcut-ref="pd"></aop:after-returning>
<aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowing" pointcut-ref="pd"></aop:after-throwing>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pd"></aop:after>
<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="pd"></aop:around>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
5.生成代理类
public class App
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
ApplicationContext context =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//此处获取的就是代理对象了
Target target = context.getBean("target",Target.class);
//调用方法就能看到aop的效果了
target.add();
}
}
运行结果
通过注解实现AOP
1.导入依赖,和上面相同
2.创建配置文件,开启注解
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="org.example"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 开启事务注解-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
</beans>
3.创建目标类,通知注解将目标类注册到spring容器中
@Component
public class App
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
ApplicationContext context =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//此处获取的就是代理对象了
Target target = context.getBean("target",Target.class);
//调用方法就能看到aop的效果了
target.add();
}
}
4.创建切面类,通过注解实现通知和注册
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspect2 {
//前置通知
@Before(value = "execution( * org.example.Target.*(..))")
public void before(){
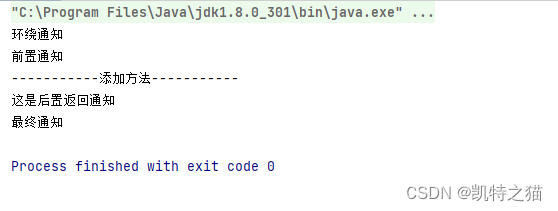
System.out.println("前置通知");
}
//可以定义一个切点
@Pointcut(value = "execution( * org.example.Target.*(..))")
public void pointcut(){}
//引用已存在的切点
@AfterReturning(value = "pointcut()",returning = "re")
public void afterRetrun(Object re){
System.out.println("这是后置返回通知");
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "pointcut()",throwing = "throwable")
public void afterThrowing(Throwable throwable){
System.out.println("这是后置异常通知" + throwable);
}
@After("pointcut()")
public void after(){
System.out.println("最终通知");
}
@Around(value = "pointcut()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("环绕通知");
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
}
5.生成代理类
public class App
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
ApplicationContext context =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext2.xml");
//此处获取的就是代理对象了
Target target = context.getBean("target",Target.class);
//调用方法就能看到aop的效果了
target.add();
}
}
运行结果