系列目录:【Vue.js设计与实现】阅读笔记目录
当新旧vnode 的子节点都是一组节点时,为了以最小的性能开销完成更新操作,需要比较两组子节点,用于比较的算法就叫作 Diff 算法。
9.1 减少 DOM 操作的性能开销
核心 Diff 只关心新旧虚拟节点都存在一组子节点的情况。
假设有新旧DOM如下:
const oldVNode = {
type: "div",
children: [
{ type: "p", children: "1" },
{ type: "p", children: "2" },
{ type: "p", children: "3" },
],
};
const newVNode = {
type: "div",
children: [
{ type: "p", children: "4" },
{ type: "p", children: "5" },
{ type: "p", children: "6" },
],
};
节点标签都一样,只是文本内容不同,可以直接更新。
patch就是更新的方法。
const patchChildren = (n1, n2, container) => {
if (typeof n2.children === "string") {
// ...
} else if (Array.isArray(n2.children)) {
//
const oldChildren = n1.children;
const newChildren = n2.children;
const oldLen = oldChildren.lengt,
newLen = newChildren.length;
const commonLength = Math.min(oldLen, newLen);
for (let i = 0; i < commonLength; i++) {
patch(oldChildren[i], newChildren[i], container);
}
// 有新的要挂载
if (newLen > oldLen) {
for (let i = commonLength; i < newLen; i++) {
patch(null, newChildren[i], container);
}
}
// 有旧的要卸载
else if (newLen < oldLen) {
for (let i = commonLength; i < oldLen; i++) {
unmount(oldChildren[i]);
}
}
} else {
// ...
}
};
9.2 DOM 复用与 key 的作用
假设新旧DOM的type不完全一样:
const oldChildren = [
{ type: "p", children: "1" },
{ type: "div", children: "2" },
{ type: "span", children: "3" },
];
const newChildren = [
{ type: "span", children: "4" },
{ type: "p", children: "5" },
{ type: "div", children: "6" },
];
可以通过 DOM 的移动来完成子节点的更新,这要比不断地执行子节点的卸载和挂载性能更好。
需要引入额外的key作为vnode的标识:key相当于一个节点的身份证号,如果两个虚拟节点具有相同的key和vnode.type,这意味着在更新时可以复用DOM,即只需要通过移动来完成更新。
const patchChildren2 = (n1, n2, container) => {
if (typeof n2.children === "string") {
// ...
} else if (Array.isArray(n2.children)) {
//
const oldChildren = n1.children;
const newChildren = n2.children;
const oldLen = oldChildren.lengt,
newLen = newChildren.length;
// 遍历新的children
for (let i = 0; i < newLen; i++) {
const newVNode = newChildren[i];
for (let j = 0; j <= oldLen; j++) {
const oldVNode = oldChildren[j];
// key相同:可以复用,但要更新内容
if (newVNode.key === oldVNode.key) {
patch(oldVNode, newVNode, container);
break; // 找到了唯一可以复用的
}
}
}
} else {
// ...
}
};
9.3 找到需要移动的元素
先逆向思考,在什么情况下节点不需要移动?
答:当新旧两组节点的顺序不变时,就不需要额外的移动操作。
有例子如下:
旧:14523
新:12345
则新的节点对应的旧节点的索引是(为了方便,这里从1开始):
14523
我们找索引的递增。 索引不是递增的就要在后面插入。
上述例子的旧节点的123不需要移动,45要从旧的位置移动到新位置,即4在3的后面,5在4的后面。就得到了新节点。
使用lastIndex变量存储最大索引值:
const patchChildren3 = (n1, n2, container) => {
if (typeof n2.children === "string") {
// ...
} else if (Array.isArray(n2.children)) {
//
const oldChildren = n1.children;
const newChildren = n2.children;
// 最大索引值
let lastIndex = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < newChildren.length; i++) {
const newVNode = newChildren[i];
for (let j = 0; j < oldChildren.length; j++) {
const oldVNode = oldChildren[i];
if (newVNode.key === oldVNode.key) {
patch(oldVNode, newVNode, container);
if (j < lastIndex) {
// 说明不是递增,这里需要移动
} else {
// 在递增,更新lastIndex
lastIndex = j;
}
break;
}
}
}
} else {
// ...
}
};
9.4 如何移动元素
const el=n2.el=n1.el
使用赋值语句对DOM元素进行复用。在复用了 DOM 元素之后,新节点也将持有对真实 DOM 的引用:
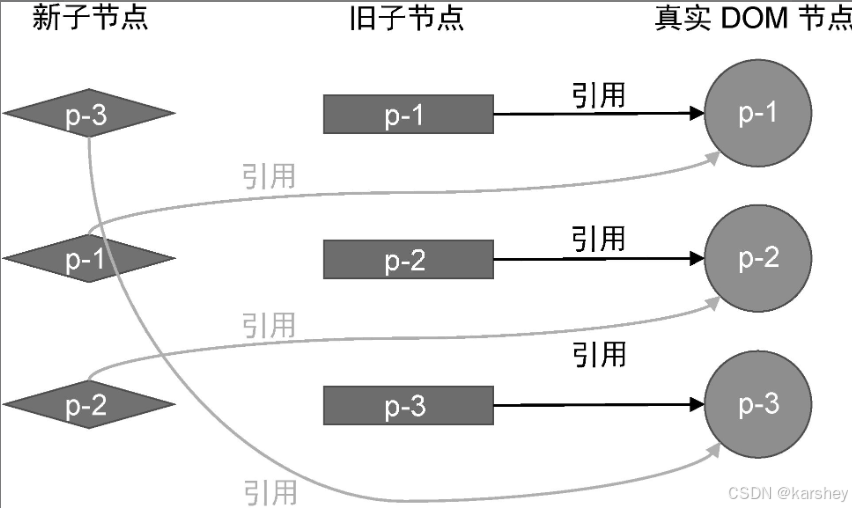
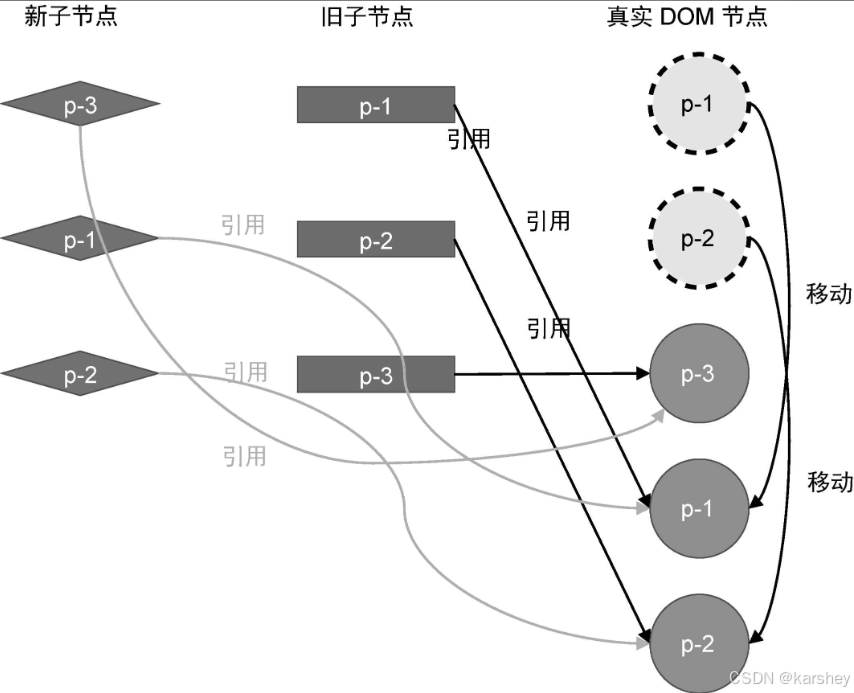
根据上一节所属,新子节点对应旧子节点索引递增的不变。
上图新子节点对应旧子节点的索引为:
2 0 1
因此p-1和p-2要移动:p-1加在p-3后,p-2加在p-1后:
9.5 添加新元素
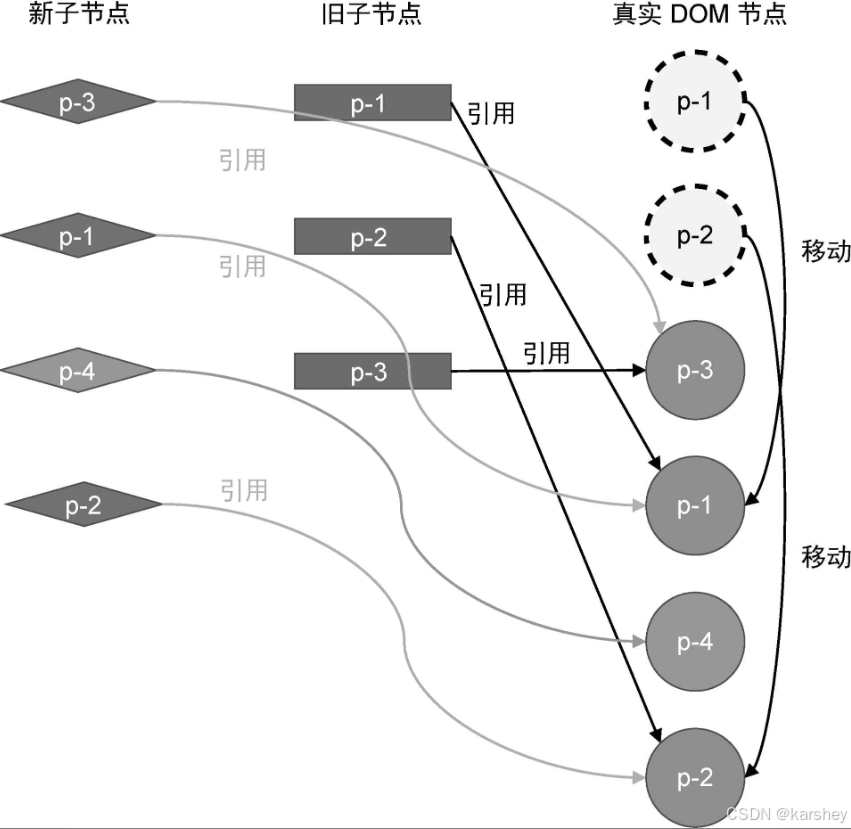
新节点没有在旧节点找到,说明这是新元素。直接添加。
preVnode 是当前要添加节点的前一个。anchor 是要加节点的位置。
if (!find) {
const preVnode = newChildren[i - 1];
let anchor = null;
if (preVnode) {
anchor = preVnode.el.nextSibling; // 前一个的后一个
} else {
// 是第一个节点
anchor = container.firstChild;
}
// 挂载
patch(null, newVNode, container, anchor);
}
如图,这里的preVnode是p-1
9.6 移除不存在的元素
直接删除不存在的节点。
完整的代码:
const patchChildren4 = (n1, n2, container) => {
if (typeof n2.children === "string") {
// ...
} else if (Array.isArray(n2.children)) {
//
const oldChildren = n1.children;
const newChildren = n2.children;
let lastIndex = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < newChildren.length; i++) {
const newVNode = newChildren[i];
let j = 0;
let find = false; // 是否找到可复用的节点
for (j; j < oldChildren.length; j++) {
const oldVNode = oldChildren[j];
if (newVNode.key === oldVNode.key) {
find = true;
patch(oldVNode, newVNode, container);
if (j < lastIndex) {
// 代码运行到这里,说明newVNode的真实DOM需要移动
const preVNode = newChildren[i - 1];
// 如果preVNode不存在,说明当前newVNode是第一个节点,不需要移动
if (preVNode) {
// 我们要将newVNode对应的真实DOM移到preVNode对应的真实DOM后面
const anchor = preVNode.el.nextSibling;
// 调用insert将newVNode对应的DOM插入到锚点前,即preNode对应的真实DOM后
insert(newVNode.el, container, anchor);
}
} else {
lastIndex = j;
}
break;
}
}
// 新节点
if (!find) {
const preVnode = newChildren[i - 1];
let anchor = null;
if (preVnode) {
anchor = preVnode.el.nextSibling;
} else {
// 是第一个节点
anchor = container.firstChild;
}
// 挂载
patch(null, newVNode, container, anchor);
}
// 删除要删除的节点
for (let i = 0; i < oldChildren.length; i++) {
const oldVNode = oldChildren[i];
const has = newChildren.find(
(vnode) => vnode.key === oldVNode.key
);
if (!has) {
unmount(oldVNode);
} else {
// ...
}
}
}
} else {
// ...
}
};