ymal语法
创建application.yaml
-
application.properties
-
- 语法结构 :key=value
-
application.yml
-
- 语法结构 :key:空格 value
这种语言以数据作为中心,而不是以标记语言为重点!
说明:语法要求严格!
1、空格不能省略
2、以缩进来控制层级关系,只要是左边对齐的一列数据都是同一个层级的。
3、属性和值的大小写都是十分敏感的
基本语法:对空格要求很高
#k: v空格不能丢
#注入到我们的配置中
#对象
student:
name:ws
age:8
#行内写法
student2: {name: ws,age: 8}
#数组
pets:
-dog
-cat
-pig
pets2: [cat,dog.pig]
在application.properties中
k: v
student.name=ws
通过yaml给实体类赋值
实体类Person.java
package com.liu.pojo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Component
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Boolean happy;
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, Integer age, Boolean happy, Date birth, Map<String, Object> maps, List<Object> lists, Dog dog) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.happy = happy;
this.birth = birth;
this.maps = maps;
this.lists = lists;
this.dog = dog;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Boolean getHappy() {
return happy;
}
public void setHappy(Boolean happy) {
this.happy = happy;
}
public Date getBirth() {
return birth;
}
public void setBirth(Date birth) {
this.birth = birth;
}
public Map<String, Object> getMaps() {
return maps;
}
public void setMaps(Map<String, Object> maps) {
this.maps = maps;
}
public List<Object> getLists() {
return lists;
}
public void setLists(List<Object> lists) {
this.lists = lists;
}
public Dog getDog() {
return dog;
}
public void setDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", happy=" + happy +
", birth=" + birth +
", maps=" + maps +
", lists=" + lists +
", dog=" + dog +
'}';
}
}
Dog.java
package com.liu.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Dog {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Dog() {
}
public Dog(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
application.yaml
person:
name: 无双
age: 8
happy: ture
birth: 2022/4/21
maps:{k1: "ss",k2: "aa"}
lists:
-code
-gril
-game
dog:
name: 旺财
age: 3
在person中使用@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “person”)绑定
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-qnq5GErr-1650533441720)(C:\Users\TR\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20220421163659713.png)]
导入
<!-- 导入配置文件处理器,配置文件进行绑定就会有提示,需要重启 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
使用properties赋值
name=ws
使用@PropertySource(value=“classpath:wushuang.properties”)注解
并使用@Value(“${name}”)组合使用,javaConfig绑定可以使用这种方式
yaml配置文件还可以编写占位符生成随机数
person:
name: 无双${random.uuid}
age: ${random.int}
happy: true
birth: 2022/4/21
maps: {k1: a,k2: b}
lists:
-code
-gril
-game
dog:
name: ${person.hello:hello}_旺财
age: 3
对比小结
@Value这个使用起来并不友好!我们需要为每个属性单独注解赋值,比较麻烦;我们来看个功能对比图
1、@ConfigurationProperties只需要写一次即可 , @Value则需要每个字段都添加
2、松散绑定:这个什么意思呢? 比如我的yml中写的last-name,这个和lastName是一样的, - 后面跟着的字母默认是大写的。这就是松散绑定。可以测试一下
3、JSR303数据校验 , 这个就是我们可以在字段是增加一层过滤器验证 , 可以保证数据的合法性
4、复杂类型封装,yml中可以封装对象 , 使用value就不支持
结论:
配置yml和配置properties都可以获取到值 , 强烈推荐 yml;
如果我们在某个业务中,只需要获取配置文件中的某个值,可以使用一下 @value;
如果说,我们专门编写了一个JavaBean来和配置文件进行一一映射,就直接@configurationProperties,不要犹豫!
JSR303校检
松散绑定
dog.java
package com.liu.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "dog")
public class Dog {
private String firstName;
private Integer age;
public Dog() {
}
public Dog(String firstName, Integer age) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.age = age;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"firstName='" + firstName + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
yaml
dog:
first-name: 狗子
age: 3
303校验
开启验证支持
@Validated //数据校验
如检验
@Email()
如果爆红就导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency>
可以自定义messge提示
String message() default "{javax.validation.constraints.Email.message}";
只需要传入message即可
@Email(message = "邮箱格式错误")
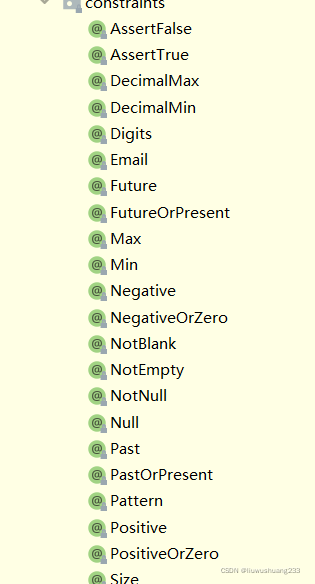
常见校验
常用的校验注解补充:
@NotBlank 检查约束字符串是不是Null还有被Trim的长度是否大于0,只对字符串,且会去掉前后空格. @NotEmpty 检查约束元素是否为NULL或者是EMPTY. @Length 被检查的字符串长度是否在指定的范围内 @CreditCardNumber信用卡验证 @Email 验证是否是邮件地址,如果为null,不进行验证,算通过验证。 @URL 验证是否是一个url地址
**注意:**一个字段可以标注多个校验注解。