一 简介
头文件<mutex>
template< class Mutex >
class lock_guard;The class lock_guard is a mutex wrapper that provides a convenient RAII-style mechanism for owning a mutex for the duration of a scoped block.
When a lock_guard object is created, it attempts to take ownership of the mutex it is given. When control leaves the scope in which the lock_guard object was created, the lock_guard is destructed and the mutex is released.
The lock_guard class is non-copyable.
即: 类 lock_guard 是互斥封装器,为在作用域块期间占有互斥提供了一种方便的RAII风格机制。
创建lock_guard对象时,它试图接收给定互斥的所有权。控制离开创建lock_guard对象的作用域时,销毁lock_guard并释放互斥。
lock_guard 类不可复制。
二 举例
例子1
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <iostream>
int g_i = 0;
std::mutex g_i_mutex; // 保护 g_i
void safe_increment() {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(g_i_mutex);
++g_i;
std::cout << std::this_thread::get_id() << ": " << g_i << '\n';
// g_i_mutex 在锁离开作用域时自动释放
}
int main() {
std::cout << "main: " << g_i << '\n';
std::thread t1(safe_increment);
std::thread t2(safe_increment);
t1.join();
t2.join();
std::cout << "main: " << g_i << '\n';
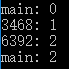
}结果:
例子2
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
std::mutex g_mutex; // 保护 vc
std::vector<int> vc;
void func() {
// std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(g_mutex); 注意此句
for(int i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
{
vc.emplace_back(i);
}
std::cout << std::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;
// g_mutex 在锁离开作用域时自动释放
}
int main() {
std::cout << "main: " << vc.size() << '\n';
std::thread t1(func);
std::thread t2(func);
t1.join();
t2.join();
std::cout << "main: " << vc.size() << '\n';
getchar();
return 0;
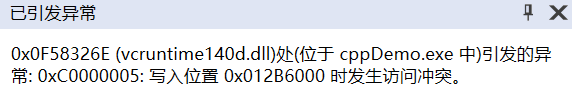
}若不加锁,此时由于数据竞争,运行报错
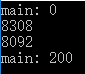
若将 func 函数第一句代码放开,则运行正确:
三 参考