文章目录
背景
Focal Loss由何凯明提出,最初用于图像领域解决数据不平衡造成的模型性能问题。
交叉熵损失函数
L o s s = L ( y , p ^ ) = − y l o g ( p ^ ) − ( 1 − y ) l o g ( 1 − p ^ ) Loss=L(y,\hat{p})=-ylog(\hat{p})-(1-y)log(1-\hat{p}) Loss=L(y,p^)=−ylog(p^)−(1−y)log(1−p^)
其中,
p
^
\hat{p}
p^为预测概率大小。y为label,二分类中对应0和1。
L
c
e
(
y
,
p
^
)
=
{
−
l
o
g
(
p
^
)
,
if
y
=
1
−
l
o
g
(
1
−
p
^
)
,
if
y
=
0
L_{ce}(y,\hat{p})= \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} -log(\hat{p}), & \text{if } y = 1 \\ -log(1-\hat{p}), & \text{if }y=0 \end{array} \right.
Lce(y,p^)={−log(p^),−log(1−p^),if y=1if y=0
对于所有样本,需要求平均作为最终的结果:
L
=
1
N
∑
i
=
1
N
l
(
y
i
,
p
^
i
)
L=\frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^{N}l(y_i,\hat{p}_i)
L=N1i=1∑Nl(yi,p^i)
对于二分类问题,可以改写成:
L
=
1
N
(
∑
y
i
=
1
m
−
l
o
g
(
p
^
)
+
∑
y
i
=
0
n
−
l
o
g
(
1
−
p
^
)
)
L=\frac{1}{N}(\sum_{y_i=1}^{m}-log(\hat{p})+\sum_{y_i=0}^{n}-log(1-\hat{p}))
L=N1(yi=1∑m−log(p^)+yi=0∑n−log(1−p^))
其中,N为样本总数,m和n为正、负样本数,
m
+
n
=
N
m+n=N
m+n=N
当样本分布不平衡时,损失函数L的分布也会发生倾斜,若m>>n时,正样本就会在损失函数中占据主导地位,由于损失函数的倾斜,训练的模型会倾向于样本较多的类别,导致对较少样本类别的性能较差。
平衡交叉熵函数
对于样本不平衡造成的损失函数倾斜,最直接的方法就是添加权重因子,提高少数类别在损失函数中的权重,从而平衡损失函数的分布。还是以之前的二分类问题为例,我们添加权重参数
α
∈
[
0
,
1
]
\alpha∈[0,1]
α∈[0,1]
L
=
1
N
(
∑
y
i
=
1
m
−
α
l
o
g
(
p
^
)
+
∑
y
i
=
0
n
−
(
1
−
α
)
l
o
g
(
1
−
p
^
)
)
L=\frac{1}{N}(\sum_{y_i=1}^{m}-\alpha log(\hat{p})+\sum_{y_i=0}^{n}-(1-\alpha)log(1-\hat{p}))
L=N1(yi=1∑m−αlog(p^)+yi=0∑n−(1−α)log(1−p^))
其中,
α
1
−
α
=
n
m
\frac{\alpha}{1-\alpha}=\frac{n}{m}
1−αα=mn,权重大小由正负样本数量比来设置。
Focal Loss损失函数
Focal Loss从loss角度提供了一种样本不均衡的解决方案:
L
f
o
c
a
l
(
y
,
p
^
)
=
{
−
(
1
−
p
^
)
γ
l
o
g
(
p
^
)
,
if
y
=
1
−
p
^
γ
l
o
g
(
1
−
p
^
)
,
if
y
=
0
L_{focal}(y,\hat{p})= \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} -(1-\hat{p})^\gamma log(\hat{p}), & \text{if } y = 1 \\ -\hat{p}^\gamma log(1-\hat{p}), & \text{if }y=0 \end{array} \right.
Lfocal(y,p^)={−(1−p^)γlog(p^),−p^γlog(1−p^),if y=1if y=0
令
p
t
=
{
p
^
,
if
y
=
1
1
−
p
^
,
otherwise.
p_t= \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} \hat{p}, & \text{if } y = 1 \\ 1-\hat{p}, & \text{otherwise. } \end{array} \right.
pt={p^,1−p^,if y=1otherwise.
则表达式统一为:
L
f
o
c
a
l
=
−
(
1
−
p
t
)
γ
l
o
g
(
p
t
)
L_{focal}=-(1-p_t)^\gamma log(p_t)
Lfocal=−(1−pt)γlog(pt)
与交叉熵表达式对照:
L
c
e
=
−
l
o
g
(
p
t
)
L_{ce}=-log(p_t)
Lce=−log(pt),仅仅多了一个可变系数
(
1
−
p
t
)
γ
(1-p_t)^\gamma
(1−pt)γ.
其中, p t p_t pt反应了与ground truth的接近程度,越大表示分类越准。 γ > 0 \gamma>0 γ>0为调节因子。
对于分类不准确的样本, p t → 0 p_t→0 pt→0, ( 1 − p t ) γ → 1 (1-p_t)^\gamma→1 (1−pt)γ→1, L f o c a l → L c e L_{focal}→L_{ce} Lfocal→Lce;对于分类准确的样本, p t → 1 p_t→1 pt→1, ( 1 − p t ) γ → 0 (1-p_t)^\gamma→0 (1−pt)γ→0, L f o c a l → 0 L_{focal}→0 Lfocal→0;因此,Focal Loss对于分类不准确的样本,损失没有改变;对于分类准确的样本,损失会变小。整体来看,Focal Loss增加了分类不准确样本在损失函数中的权重。
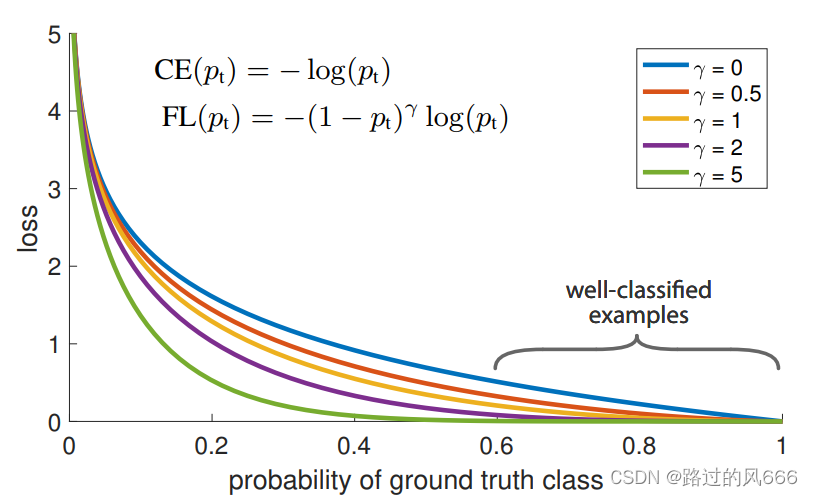
如下是不同调节因子 γ \gamma γ对应的Loss-proba分布图,可以看出Cross Entropy(CE)和Focal Loss(FL)之间的区别,Focal Loss使损失函数更倾向于难分的样本。
Focal Loss vs Balanced Cross Entropy
- Focal Loss是从样本分类难易程度出发,让Loss聚焦于难分类的样本;
- Balanced Cross Entropy是从样本分布角度对Loss添加权重因子。
- 缺点:仅仅考虑样本分布,有些难以区分的类别的样本数可能也比较多,此时被BCE赋予了较低的权重,会导致模型很难识别该类别!
Why does Focal Loss work?
Focal Loss从样本难易分类的角度出发,解决了样本不平衡导致模型性能较低的问题。
WHY?
样本不平衡造成的问题就是,样本数少的类别分类难度大,因此Focal Loss聚焦于难分样本,解决了样本少的类别分类精度不高的问题,对于难分样本中样本多的类别,也会被Focal Loss聚焦。因此,它不仅解决了样本不平衡问题,还提升了模型整体性能。
但是,要使模型训练过程中聚焦于难分类样本,仅仅将Loss倾向于难分类样本是不够的,因为模型参数更新取决于Loss的梯度:
w
=
w
−
α
∂
L
∂
w
w=w-\alpha\frac{\partial L}{\partial w}
w=w−α∂w∂L
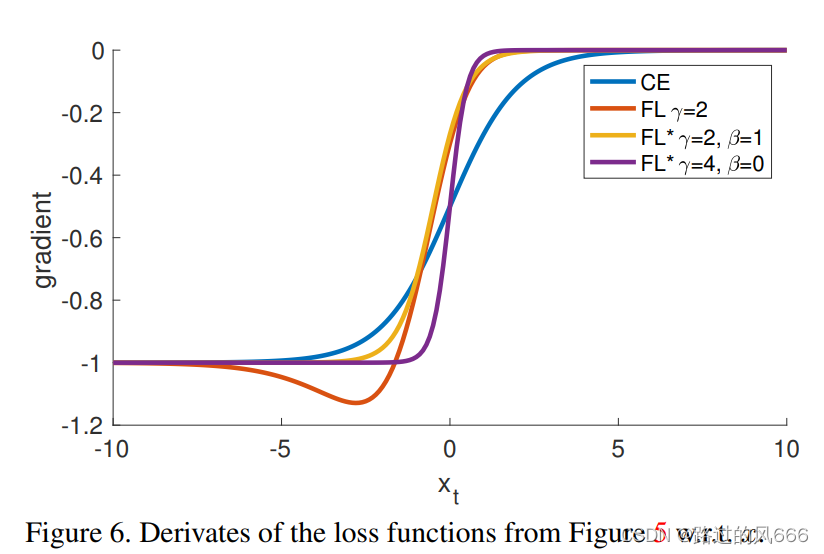
若Loss中难分类样本的权重较高,但是难分类样本的Loss梯度为0,难分类样本就不会影响到模型的参数更新。对于梯度问题,Focal Loss中的梯度与
x
t
x_t
xt的关系如下所示,其中
x
t
=
y
x
x_t=yx
xt=yx,
y
∈
{
−
1
,
1
}
y∈\{-1,1\}
y∈{−1,1}为类别,
p
t
=
σ
(
x
t
)
p_t=\sigma(x_t)
pt=σ(xt),对于易分样本,
x
t
>
0
x_t>0
xt>0,即
p
t
>
0.5
p_t>0.5
pt>0.5,由下图可知,此时的导数趋于0。对于难分样本,导数数值较大,因此,学习过程中更聚焦于难分样本。
难易分类样本是动态的, p t p_t pt在训练的过程中,可能会在难易之间相互转换。
在Loss梯度中,难训练样本起主导作用,参数朝着优化难训练样本的方向改变,变化之后可能会导致原本易训练的样本 p t p_t pt变化,即变成难训练样本。若发生了这种情况会导致模型收敛速度较慢。
为了防止这种难易样本的频繁变化,应该选择较小的学习率。
针对VidHOI数据集
因为VidHOI数据集中的一个人-物对会被多个交互标签同时标注,如< human,next to & watch & hold, cup >,所以会面临multi-class multi-label的分类问题。以往常常使用Binary cross-entropy,能够计算每个交互类别独立于其他类别的损失。但是,VidHOI数据集分布不均且具有长尾分布,为了解决这个不均衡问题同时避免过分强调最频繁类别的重要性,我们采用class-balanced Focal loss:
C
B
f
o
c
a
l
(
p
i
,
y
i
)
=
−
1
−
β
1
−
β
n
i
(
1
−
p
y
i
)
γ
l
o
g
(
p
y
i
)
w
i
t
h
p
y
i
=
{
p
i
,
if
y
i
=
1
1
−
p
i
,
otherwise.
CB_{focal}(p_i,y_i)=-\frac{1-\beta}{1-\beta^{n_i}}(1-p_{y_i})^{\gamma}log(p_{y_i}) \\ with \ p_{y_i} = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} p_i, & \text{if } y_i = 1 \\ 1-p_i, & \text{otherwise.} \end{array} \right.
CBfocal(pi,yi)=−1−βni1−β(1−pyi)γlog(pyi)with pyi={pi,1−pi,if yi=1otherwise.
其中的 − ( 1 − p y i ) γ l o g ( p y i ) -(1-p_{y_i})^{\gamma}log(p_{y_i}) −(1−pyi)γlog(pyi)是Lin提出的Focal loss, p i p_i pi表示预估为第i个类别的可能性, y i ∈ { 0 , 1 } y_i∈\{0,1\} yi∈{0,1}表示Ground Truth的label。变量 n i n_i ni表示第i个类别在Ground Truth下的样本量, β ∈ [ 0 , 1 ) \beta∈[0,1) β∈[0,1)是可调节参数。所有类别的平均损失作为一个预测的损失。
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from typing import Optional
class FocalBCEWithLogitLoss(nn.modules.loss._Loss):
"""Focal Loss with binary cross-entropy
Implement the focal loss with class-balanced loss, using binary cross-entropy as criterion
Following paper "Class-Balanced Loss Based on Effective Number of Samples" (CVPR2019)
Args:
gamma (int, optional): modulation factor gamma in focal loss. Defaults to 2.
alpha (int, optional): modulation factor alpha in focal loss. If a integer, apply to all;
if a list or array or tensor, regard as alpha for each class; if none, no alpha. Defaults to None.
weight (Optional[torch.Tensor], optional): weight to each class, !not the same as alpha. Defaults to None.
size_average (_type_, optional): _description_. Defaults to None.
reduce (_type_, optional): _description_. Defaults to None.
reduction (str, optional): _description_. Defaults to "mean".
"""
def __init__(
self,
gamma=2,
alpha=None,
weight: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
size_average=None,
reduce=None,
reduction: str = "mean",
pos_weight: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
):
super(FocalBCEWithLogitLoss, self).__init__(size_average, reduce, reduction)
self.gamma = gamma
# a number for all, or a Tensor with the same num_classes as input
if isinstance(alpha, (list, np.ndarray)):
self.alpha = torch.Tensor(alpha)
else:
self.alpha = alpha
self.register_buffer("weight", weight)
self.register_buffer("pos_weight", pos_weight)
self.weight: Optional[torch.Tensor]
self.pos_weight: Optional[torch.Tensor]
def forward(self, input: torch.Tensor, target: torch.Tensor):
if self.alpha is not None:
if isinstance(self.alpha, torch.Tensor):
alpha_t = self.alpha.repeat(input.shape[0], 1)
else:
alpha_t = torch.ones_like(input) * self.alpha
else:
alpha_t = None
# 二元交叉熵
ce = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(input, target, reduction="none")
# pt = torch.exp(-ce)
# modulator = ((1 - pt) ** self.gamma)
# following author's repo https://github.com/richardaecn/class-balanced-loss/blob/master/src/cifar_main.py#L226-L266
# explaination https://github.com/richardaecn/class-balanced-loss/issues/1
# A numerically stable implementation of modulator.
if self.gamma == 0.0:
modulator = 1.0
else:
# e^(-gamma*target*input - gamma*log(1+e^(-input)))
modulator = torch.exp(-self.gamma * target * input - self.gamma * torch.log1p(torch.exp(-input)))
# focal loss
fl_loss = modulator * ce
# alpha
if alpha_t is not None:
alpha_t = alpha_t * target + (1 - alpha_t) * (1 - target)
fl_loss = alpha_t * fl_loss
# pos weight
if self.pos_weight is not None:
fl_loss = self.pos_weight * fl_loss
# reduction
if self.reduction == "mean":
return fl_loss.mean()
elif self.reduction == "sum":
return fl_loss.sum()
else:
return fl_loss
C B f o c a l ( p i , y i ) = − 1 − β 1 − β n i ( 1 − p y i ) γ l o g ( p y i ) w i t h p y i = { p i , if y i = 1 1 − p i , otherwise. CB_{focal}(p_i,y_i)=-\frac{1-\beta}{1-\beta^{n_i}}(1-p_{y_i})^{\gamma}log(p_{y_i}) \\ with \ p_{y_i} = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} p_i, & \text{if } y_i = 1 \\ 1-p_i, & \text{otherwise.} \end{array} \right. CBfocal(pi,yi)=−1−βni1−β(1−pyi)γlog(pyi)with pyi={pi,1−pi,if yi=1otherwise.
原始版本的代码:
def focal_loss(labels, logits, alpha, gamma):
"""Compute the focal loss between `logits` and the ground truth `labels`.
Focal loss = -alpha_t * (1-pt)^gamma * log(pt)
where pt is the probability of being classified to the true class.
pt = p (if true class), otherwise pt = 1 - p. p = sigmoid(logit).
Args:
labels: A float32 tensor of size [batch, num_classes].
logits: A float32 tensor of size [batch, num_classes].
alpha: A float32 tensor of size [batch_size]
specifying per-example weight for balanced cross entropy.
gamma: A float32 scalar modulating loss from hard and easy examples.
Returns:
focal_loss: A float32 scalar representing normalized total loss.
"""
with tf.name_scope('focal_loss'):
logits = tf.cast(logits, dtype=tf.float32)
cross_entropy = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(
labels=labels, logits=logits)
# positive_label_mask = tf.equal(labels, 1.0)
# probs = tf.sigmoid(logits)
# probs_gt = tf.where(positive_label_mask, probs, 1.0 - probs)
# # With gamma < 1, the implementation could produce NaN during back prop.
# modulator = tf.pow(1.0 - probs_gt, gamma)
# A numerically stable implementation of modulator.
if gamma == 0.0:
modulator = 1.0
else:
modulator = tf.exp(-gamma * labels * logits - gamma * tf.log1p(
tf.exp(-1.0 * logits)))
loss = modulator * cross_entropy
weighted_loss = alpha * loss
focal_loss = tf.reduce_sum(weighted_loss)
# Normalize by the total number of positive samples.
focal_loss /= tf.reduce_sum(labels)
return focal_loss
Reference
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/266023273
- https://github.com/nizhf/hoi-prediction-gaze-transformer
- https://github.com/richardaecn/class-balanced-loss/blob/master/src/cifar_main.py#L226-L266