如果有了解过yolo网络,那肯定也听说过anchors,当然anchors这个概念布置在YOLO里面才有,在其他的目标检测中也存在anchors这个概念。对于anchors计算的一些公式这篇文章就不进行讲解了,这篇文章主要是讲在训练网络模型过程中anchors执行的流程,并将这个抽象的概念具体化,便于更深的理解yolo。
-
1. anchors是什么?
答:anchors其实就是在训练之前人为设定的先验框,网络输出结果的框就是在anchors的基础上进行调整的。所以说先验框设定的好坏对于模型的输出效果影响还是挺大的。在yolo中一般设定一个物体的先验框的个数一般是9个,例如:
anchors = np.array(
[[27., 183.], [87., 31.], [51., 62.], [139., 95.], [53., 50.], [60., 54.5], [87., 55.], [161., 41.], [49.5, 44.]])这个先验框anchors一共有9个元素,每一个元素代表一个先验框的宽高。例如【27,183】就表示第一个先验框的宽为27,高为183。
-
2.一张图片有多少个先验框?
答:先验框的个数与图片是哪个的物体的个数有关系,一个物体默认会设定9个先验框。
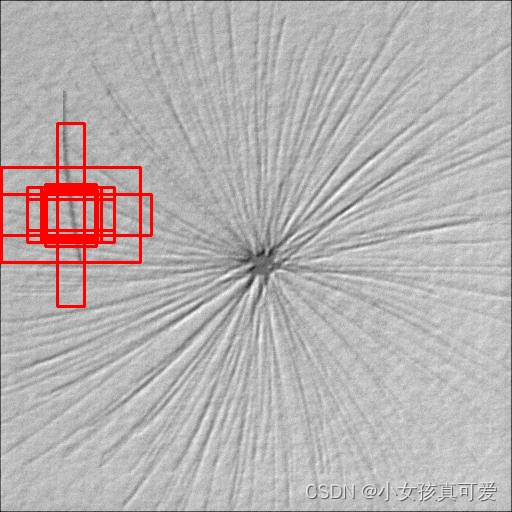
在标注的时候会用一个矩形框来将物体标注出来,这样子我们可以根据标注信息来获取物体的左上角(x1, y1)和右下角(x2,y2)坐标,然后计算出物体的中心坐标[(x2-x1)/2, (y2-y1)/2]。 这样子就可以把ancors表示出来了。下面就是原图与画了先验框的图片的对比:
3.先验框在哪一步会进行调整?
答:在YOLO网络里面,一张图片进入模型编码之后会输出三个feature map(特征层),分别用
小特征层(20,20)、中特征层(40,40)和大特征层(80,80)来表示。其中小特征层用于检测大物体,中特征层用于检测中等物体,大特征层用于检测小物体。(因为小特征层的尺寸比较小,也就是压缩的倍数多,小物体经过多次压缩的话在小特征层上面可能就不明显甚至没有,所以小特征用于检测大的物体)。anchors是在特征层上进行调整的,但最开始的anchors是相对于原图的,我们需要将anchors的大小以及物体的中心也对应到feature map上。我们可以从feature map上获取到物体中心以及框的宽高的偏移量offset_x, offset_y, offset_w, offset_h, 然后根据偏移量对先验框进行调整。
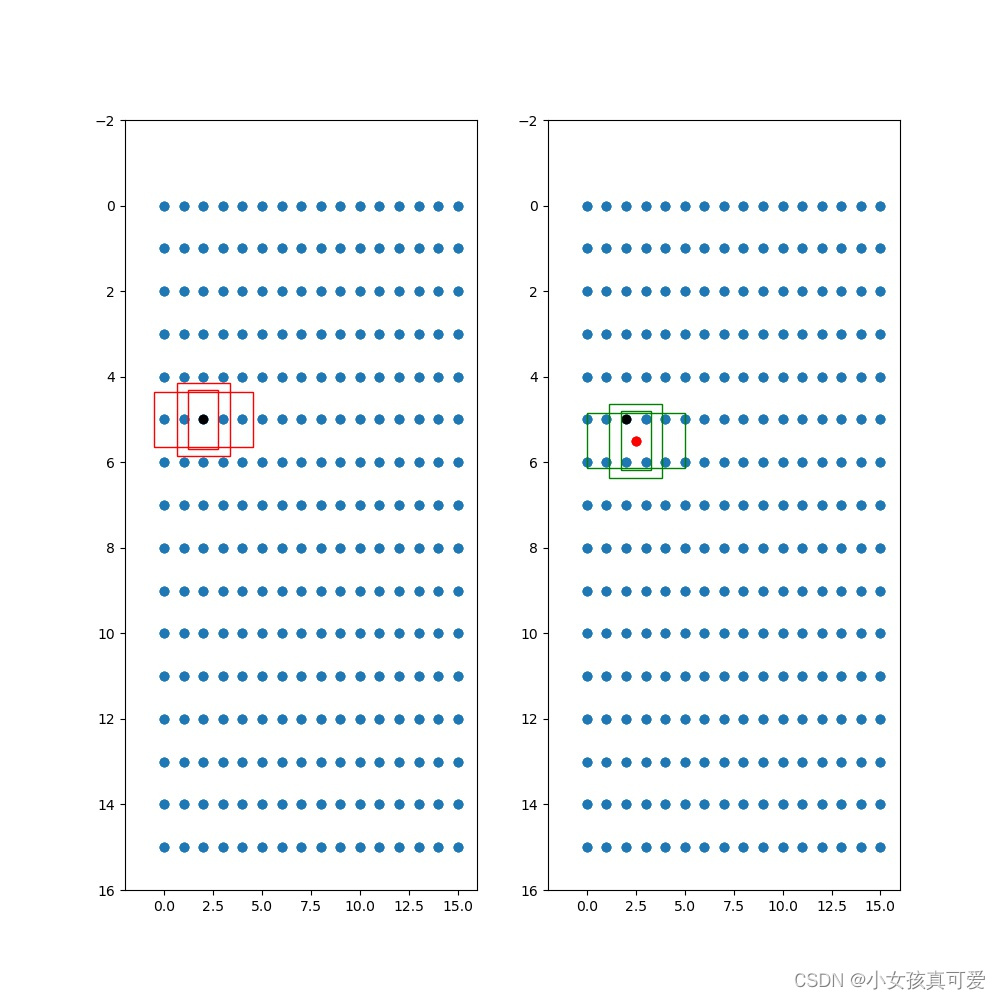
下面是先验框的可视化展示:
原图上:
特征层上:一共9个anchors,有3层特征层, 所以每层3个先验框
左边的红框是先验框没调整之前在特征层上的位置,黑点表示中心位置
右边的绿框是中心点和先验框调整之后在特征层上的位置
opt:懒得打字但又想记录一下的部分。
在训练过程中,对anchors的调整是在求loss前会对anchors进行调整,然后用调整后的anchors和真实框来计算loss_iou。
yolo过了模型之后有三个feature map,所以每个feature map上一个物体有三个anchor,在对anchors进行调整的时候会吧feature map的值调整到0~1之间,这是因为在feature map上每个网格的长度默认为1.
Last:代码实现部分:
代码引用到的YoloDataset, yolo_dataset_collate这两个函数在:
YoloDataset, yolo_dataset_collate:
YoloBody是网络结构,可以用YOLO系列的网络
import os
import random
import cv2
import torch
import numpy as np
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from algorithm_code.yolov6.yolo_net import YoloBody
from algorithm_code.yolov6.yolo_dataloader import YoloDataset, yolo_dataset_collate
import os
os.environ["KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK"] = "TRUE"
def sigmoid(x):
s = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
return s
def get_anchors_and_decode(feats, anchors, center, num_classes, j):
feat1 = feats.new(feats.shape)
feats = feat1.cpu().numpy()
x, y = center
plt_w, plt_h = feats.shape[1:3]
# feats [batch_size, h, w, 3 * (5 + num_classes)]
num_anchors = len(anchors)
grid_shape = np.shape(feats)[1:3]
# 获得各个特征点的坐标信息。生成的shape为(h, w, num_anchors, 2)
grid_x = np.tile(np.reshape(np.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[1]), [1, -1, 1, 1]), [grid_shape[0], 1, num_anchors, 1])
grid_y = np.tile(np.reshape(np.arange(0, stop=grid_shape[0]), [-1, 1, 1, 1]), [1, grid_shape[1], num_anchors, 1])
grid = np.concatenate([grid_x, grid_y], -1)
# 将先验框进行拓展,生成的shape为(h, w, num_anchors, 2)
anchors_tensor = np.reshape(anchors, [1, 1, num_anchors, 2])
anchors_tensor = np.tile(anchors_tensor, [grid_shape[0], grid_shape[1], 1, 1])
# 将预测结果调整成(batch_size,h,w,3,nc+5)
feats = np.reshape(feats, [-1, grid_shape[0], grid_shape[1], num_anchors, num_classes + 5])
box_xy = sigmoid(feats[..., :2]) + grid
box_wh = np.exp(feats[..., 2:4]) * anchors_tensor
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10., 10.,))
ax = fig.add_subplot(121)
plt.ylim(-2, plt_h)
plt.xlim(-2, plt_w)
plt.scatter(grid_x, grid_y)
plt.scatter(x, y, c='black')
plt.gca().invert_yaxis()
anchor_left = grid_x - anchors_tensor / 2
anchor_top = grid_y - anchors_tensor / 2
print(np.shape(anchor_left))
rect1 = plt.Rectangle([anchor_left[y, x, 0, 0], anchor_top[y, x, 0, 1]], anchors_tensor[0, 0, 0, 0],
anchors_tensor[0, 0, 0, 1], color="r", fill=False)
rect2 = plt.Rectangle([anchor_left[y, x, 1, 0], anchor_top[y, x, 1, 1]], anchors_tensor[0, 0, 1, 0],
anchors_tensor[0, 0, 1, 1], color="r", fill=False)
rect3 = plt.Rectangle([anchor_left[y, x, 2, 0], anchor_top[y, x, 2, 1]], anchors_tensor[0, 0, 2, 0],
anchors_tensor[0, 0, 2, 1], color="r", fill=False)
ax.add_patch(rect1)
ax.add_patch(rect2)
ax.add_patch(rect3)
ax = fig.add_subplot(122)
plt.ylim(-2, plt_h)
plt.xlim(-2, plt_w)
plt.scatter(grid_x, grid_y)
plt.scatter(x, y, c='black')
plt.scatter(box_xy[0, y, x, :, 0], box_xy[0, y, x, :, 1], c='r')
plt.gca().invert_yaxis()
pre_left = box_xy[..., 0] - box_wh[..., 0] / 2
pre_top = box_xy[..., 1] - box_wh[..., 1] / 2
rect1 = plt.Rectangle([pre_left[0, y, x, 0], pre_top[0, y, x, 0]], box_wh[0, y, x, 0, 0], box_wh[0, y, x, 0, 1],
color="g", fill=False)
rect2 = plt.Rectangle([pre_left[0, y, x, 1], pre_top[0, y, x, 1]], box_wh[0, y, x, 1, 0], box_wh[0, y, x, 1, 1],
color="g", fill=False)
rect3 = plt.Rectangle([pre_left[0, y, x, 2], pre_top[0, y, x, 2]], box_wh[0, y, x, 2, 0], box_wh[0, y, x, 2, 1],
color="g", fill=False)
ax.add_patch(rect1)
ax.add_patch(rect2)
ax.add_patch(rect3)
plt.savefig(r"C:\Users\HJ\Desktop\demo\%s_%s.jpg" % (i, j))
plt.close()
anchors = np.array(
[[27., 183.], [87., 31.], [51., 62.], [139., 95.], [53., 50.], [60., 54.5], [87., 55.], [161., 41.], [49.5, 44.]])
anchors_mask = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]]
data_line = ['E:/私人文件/V3软件标注/定位/tags/1/1/1_00000001.jpg 42,74,113,289,0 228,236,306,308,1']
train_dataset = YoloDataset(data_line, [512, 512], 10, anchors, False, False)
gen_train = DataLoader(train_dataset, shuffle=True, batch_size=1, num_workers=0, pin_memory=True, drop_last=False,
collate_fn=yolo_dataset_collate)
model = YoloBody(num_classes=10).to("cuda")
for iteration, batch in enumerate(gen_train):
images, targets, y_trues = batch[0], batch[1], batch[2]
print("image shape:", images.shape)
boxes = targets[0].cpu().numpy()
boxes_center = [((box[0] + box[2]) / 2, (box[1] + box[3]) / 2) for box in boxes]
print("boxes:", boxes_center)
img_h, img_w = images.shape[2:4]
print("img_wh:", img_w, img_h)
with torch.no_grad():
images = images.to("cuda")
targets = [ann.to("cuda") for ann in targets]
y_trues = [ann.to("cuda") for ann in y_trues]
outputs = model(images)
for i, feat in enumerate(outputs):
input_anchor = anchors[anchors_mask[i]]
# print("input anchor:", input_anchor)
feat = feat.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
print("feat.shape:", feat.shape)
# 1.获取feat 的高和宽
feat_h, feat_w = feat.shape[1:3]
# 2.有了原图大小和feat大小,就可以求出步长
stride_h, stride_w = img_h / feat_h, img_w / feat_w
print("stride:", stride_h, stride_w)
# 3.anchors是相对于原图的,而我们读取数据的到的image是经过resize之后得到的图片,所以我们要先把anchors对应到resize之后的图片,然后再映射到feature map
# 由于我这里原图是512,512. resize的大小也是512,512所以就不需要将anchor从原图映射到resize之后的图片,也就是少做了一个除法
feat_anchors = input_anchor / np.array([stride_w, stride_h]) # 把anchors从热size之后的图映射到feature map上
# 4.根据原图的坐标信息我们可以求出物体的中心位置,有了步长之后局可以求出物体在feature map上面的位置
for j, center in enumerate(boxes_center):
feat_x, feat_y = int(center[0] / stride_w), int(center[1] / stride_h)
print("第%s特征的x, y:" % i, feat_x, feat_y)
# 5.现在feature map,中心,anchors都有了,就可以画出anchors的图片了
get_anchors_and_decode(feat, feat_anchors, (feat_x, feat_y), 10, j)
print("==============================")