解释
利用springboot可以方便的实现资源的上传与下载,文件的上传与下载也是诸如:头像上传,资源获取等问题的基础。
Springboot上传下载文件
准备
只需导入下面两个依赖即可
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
首先在templates文件夹下创建index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh,en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, user-scalable=0">
<title>文件的上传与下载</title>
</head>
<body style="text-align: center">
<h1>文件的上传与下载</h1>
<hr>
<h2>上传单个文件</h2>
<!-- 上传文件只能用post,切记加属性enctype -->
<form action="/upload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
文件:<input type="file" name="myfile"/><br>
<input type="submit" value="上传"/>
</form>
<hr>
<h2>上传多个文件</h2>
<!-- 多个文件的name属性必须相同 -->
<form action="/upload_multi" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
文件1:<input type="file" name="files"/><br>
文件2:<input type="file" name="files"/><br>
<input type="submit" value="上传"/>
</form>
<hr>
<h2>下载刚刚上传的文件</h2>
<a href="/download">下载文件</a>
</body>
</html>
创建FileController书写接口
/upload接口
/**
* 上传文件
* @param myfile springmvc接受到的文件
* @return 返回是否成功
*/
@SneakyThrows
@RequestMapping("/upload")
public String uploadFile(MultipartFile myfile){
System.out.println("前端上传时input——name属性为:"+myfile.getName());
String fileName = myfile.getOriginalFilename();
System.out.println("文件名:"+fileName);
String suffix = fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf("."));
System.out.println("文件后缀:"+suffix);
System.out.println("文件是否为空:"+myfile.isEmpty());
// 下面开始在服务器保存上传的文件
if(myfile.isEmpty()){
return "文件为空";
}
// 以绝对路径构建存储文件的地址,不要用相对路径,相对路径会报错
String path = "E:/upload/";
// 构建一个文件对象,参数为保存的地址加文件名
File dest = new File(path+fileName);
if(!dest.getParentFile().exists()){ //判断父文件夹是否存在
dest.getParentFile().mkdir();
}
System.out.println("文件上传绝对路径:"+dest.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("文件上传父绝对路径:"+dest.getParentFile().getAbsolutePath());
try {
// 内部实现:参数=需要上传的文件夹和文件名
myfile.transferTo(dest);
} catch (IOException e) {
return "上传失败"+e.getMessage();
}
return "上传成功";
}
/upload_multi接口
/**
* 上传多个
* @param request 收到的请求
* @return 返回是否成功
*/
@SneakyThrows
@RequestMapping("/upload_multi")
public String uploadMultiFile(HttpServletRequest request){
List<MultipartFile> files = ((MultipartHttpServletRequest) request).getFiles("files");
// 设置上传路径,不能是相对路径
String path = "E:/upload/";
for (MultipartFile file : files) {
File dest = new File(path+file.getOriginalFilename());
try {
file.transferTo(dest);
} catch (IOException e) {
return "上传失败"+e.getMessage();
}
}
return "上传成功";
}
/download接口
/**
* 下载文件
* @param request 请求
* @param response 响应
* @return 返回是否成功下载
*/
@SneakyThrows
@RequestMapping("/download")
public String download(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
// 要下载的文件,具体开发中需要指定
String path = "E:/upload/加菲人.jpg";
String fileName = "加菲人.jpg";
File file = new File(path);
FileInputStream fis = null;
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
byte[] buffer = new byte[10240];
if(file.exists()){
/*
服务端向客户端游览器发送文件时,如果是浏览器支持的文件类型,一般会默认使用浏览器打开,比如txt、jpg等,
会直接在浏览器中显示,如果需要提示用户保存,就要利用Content-Disposition进行一下处理,关键在于一定要
加上attachment:Response.AppendHeader("Content-Disposition","attachment;filename=FileName.txt");
备注:这样浏览器会提示保存还是打开,即使选择打开,也会使用相关联的程序比如记事本打开,而不是浏览器直接打开了。
*/
response.addHeader("Content-Disposition","attachment;fileName="+ URLEncoder.encode(fileName,"UTF-8"));
// 文件的下载要用到io流
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
// 一次性读取buffer.length个字节,返回读取的字节数,当读取完毕时会返回-1
int read = bis.read(buffer);
while(read!=-1){
// 让浏览器以流的形式将此文件下载到客户端
response.getOutputStream().write(buffer,0,read);
read = bis.read(buffer);
}
fis.close();
bis.close();
}
return "下载成功";
}
代码的解释都写在了注释里,当开启服务后,访问index.html页面,即可进行操作
资源路径映射与跨域
假设我现在有这样一个需求,用户想要上传自己的头像并持久化,我们有两种方案,一种是将图片存储在数据库中,一种是将图片存放在服务器中,数据库中存放图片的url地址。
第一种方案,对数据库的要求较高,并且开发较麻烦,因此我们采用第二种方案。
现在我们看下第二种方案的逻辑
- 我们把用户上传的头像存放在本地磁盘中某个文件中,例如
E:/upload/ - 我们开启服务器时,只能通过
localhost:8080访问资源 - 创建一个接口,让此接口能和
E:/upload/下的资源建立关联,假设此接口为download - 需要一种方案,将
http://localhost:8080/download/映射成file:///E:/upload/
将两个不同协议的建立关联,或者说,让这两个不同协议的资源路径可以实现资源共享,这就牵扯到了跨域问题,好在Springboot提供了一个类
org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurationSupport
我们只需要继承这个类,然后重写两个方法,就可以解决跨域和资源路径映射。
什么是跨域
Url的一般格式:
协议 + 域名(子域名 + 主域名) + 端口号 + 资源地址
只要协议,子域名,主域名,端口号这四项组成部分中有一项不同,就可以认为是不同的域,不同的域之间互相访问资源,就被称之为跨域。
下面是演示代码:
新建一个WebMvcConfig类
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.CorsRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurationSupport;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
/**
* @author
* @description
*/
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
/*
设置资源映射,将localhost:8080/download/下的资源映射为file:///E:/upload/下的资源
*/
@Override
protected void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
// 这个file:///是文件传输协议必须要加上
registry.addResourceHandler("/download/**").addResourceLocations("file:///E:/upload/");
super.addResourceHandlers(registry);
}
/*
跨域需要进行请求配置,规定那个请求允许跨域访问
*/
@Override
protected void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
//设置允许跨域的路径
registry.addMapping("/download/**")
//设置允许跨域请求的域名,这里设置为文件域
.allowedOrigins("file:///E:/upload/")
//允许带上cookie信息,服务器将发送cookie
.allowCredentials(true)
//设置允许的方法
.allowedMethods("GET", "POST", "PUT", "DELETE")
//跨域允许时间
.maxAge(3600);
}
/**
* 全局设置编码格式
* @return
*/
@Bean
public HttpMessageConverter<String> responseBodyConverter() {
return new StringHttpMessageConverter(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
}
}
我的磁盘中有这样一张图片
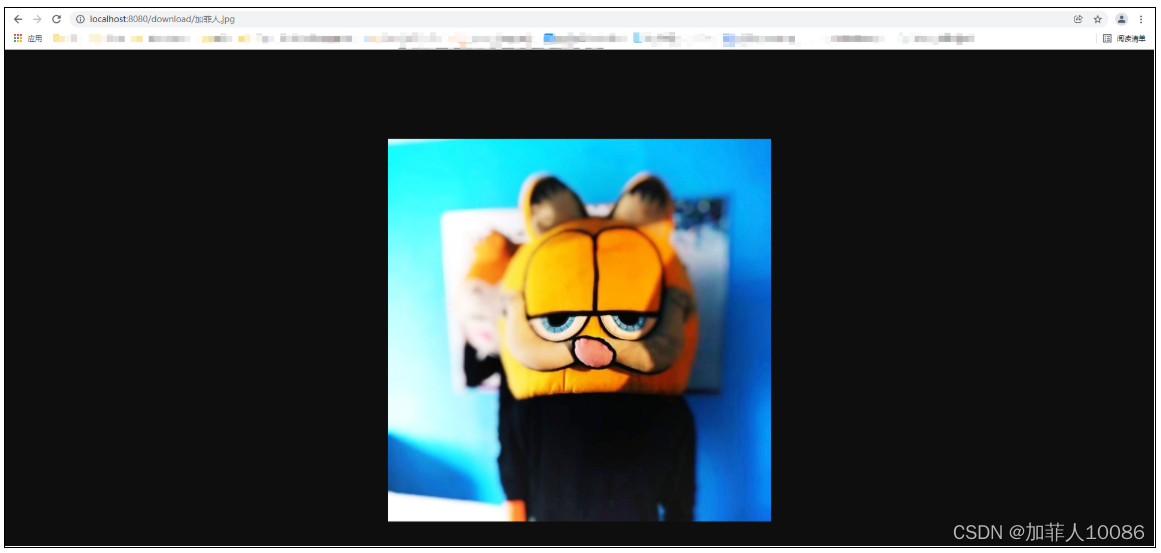
然后我开启springboot,输入http://localhost:8080/download/加菲人.jpg
这样全局设置了localhost:8080/download/下的资源共享,但只设置了file域可以访问,如果不是前后端真正分离,是不需要设置其他域名的。
由此可见,磁盘的路径成功和服务器的资源路径建立了映射,并实现了跨域的资源共享!!
不得不说,springboot真是YYDS