文章目录
本文的学习文链接: http://t.csdn.cn/tjweo
1.修改集合中的值map
传入一个函数,函数的形参即为集合中的每一个值,该函数会对集合中的每一个元素进行函数体中的操作,最后返回一个新的值,修改或代替集合中的元素
分为两种情况:直接修改原来集合中的数据,生成一个新的集合。
高级玩法:可以直接在map中传入Student::getAge或personList.stream().map(p -> p.getAge()) , 获取到集合中所有对象的所有age,然后链式对属性操作,返回值也由集合中的对象类型变为对象的对应的属性类型。
//直接修改原来的数据 所有学生的年龄加2
List<Student> list1 = Arrays.asList(new Student("a",1),new Student("b",2),new Student("c",3));
List<Student> studentAgeAdd1 = list1.stream().map(x -> {
x.setAge(x.getAge() + 2);
return x;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("list1 = " + list1);
System.out.println("studentAgeAdd1 = " + studentAgeAdd1);
//生成新的集合 所有学生的年龄加2
List<Student> list2 = Arrays.asList(new Student("a",1),new Student("b",2),new Student("c",3));
List<Student> studentAgeAdd2 = list2.stream().map(x -> {
return new Student(x.getUsername(), x.getAge()+2);
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("list2 = " + list2);
System.out.println("studentAgeAdd2 = " + studentAgeAdd2);
//结果
Student(username=null, age=null)
list1 = [Student(username=a, age=3), Student(username=b, age=4), Student(username=c, age=5)]
studentAgeAdd1 = [Student(username=a, age=3), Student(username=b, age=4), Student(username=c, age=5)]
list2 = [Student(username=a, age=1), Student(username=b, age=2), Student(username=c, age=3)]
studentAgeAdd2 = [Student(username=a, age=3), Student(username=b, age=4), Student(username=c, age=5)]
2.过滤集合中符合条件的值filter
传入一个函数,函数的形参即为集合中的每一个值,该函数会对集合中的每一个元素进行函数体中的操作,函数体为一个条件判断,最后返回一个boolean值,为true则保留该元素为,false则去掉。最后生成一个新的集合。不改变原来的集合。
//保留年龄大于等于3的学生
List<Student> list1 = Arrays.asList(new Student("a",1),new Student("b",2),new Student("c",3));
List<Student> studentAgeAdd1 = list1.stream().filter((x) -> {
return x.getAge() >= 2;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("list1 = " + list1);
System.out.println("studentAgeAdd1 = " + studentAgeAdd1);
找集合中的最大/小的值,及操作后元素的个数max()/min()/count()
list.stream().max().get();
list.stream().min().get();
list.stream().filter().count();//操作后的个数
//获取学生年龄最大的那个
List<Student> list1 = Arrays.asList(new Student("a",1),new Student("b",2),new Student("c",3));
Student student = list1.stream().max(Comparator.comparing(Student::getAge)).get();
Student student1 = list1.stream().max((a, b) -> {
return a.getAge() - b.getAge();
}).get();
System.out.println(student);
System.out.println(student1);
//输出
Student(username=c, age=3)
Student(username=c, age=3)
//统计过滤后的数量
List<Student> list1 = Arrays.asList(new Student("a",1),new Student("b",2),new Student("c",3));
long count = list1.stream().filter(x -> x.getAge() >= 2).count();
//输出
2
归约:对集合中所有元素进行自定义计算获取最终值reduce()
reduce 、
//将所有对象中某元素的值相加
List<Student> list1 = Arrays.asList(new Student("a",1),new Student("b",2),new Student("c",3));
Integer sumAge = list1.stream().map(Student::getAge).reduce(Integer::sum).get();
System.out.println(sumAge);
//获取集合中所有元素和
List<Integer> intList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3);
Integer integer = intList.stream().reduce((sum, item) -> {
sum += item;
return sum;
}).get();
System.out.println(integer);
collect
流不存储数据,那么在流中的数据完成处理后,需要将流中的数据重新归集到新的集合里。
toList/toSet/toMap
例:list->map
List<Student> list1 = Arrays.asList(new Student("a",1),new Student("b",2),new Student("c",3));
Map<String, Student> collect = list1.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Student::getUsername, p -> p));
for (Map.Entry<String, Student> studentEntry : collect.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(studentEntry);
}
//打印
a=Student(username=a, age=1)
b=Student(username=b, age=2)
c=Student(username=c, age=3)
Collectors提供了一系列用于数据统计的静态方法:
计数:count
平均值:averagingInt、averagingLong、averagingDouble
最值:maxBy、minBy
求和:summingInt、summingLong、summingDouble
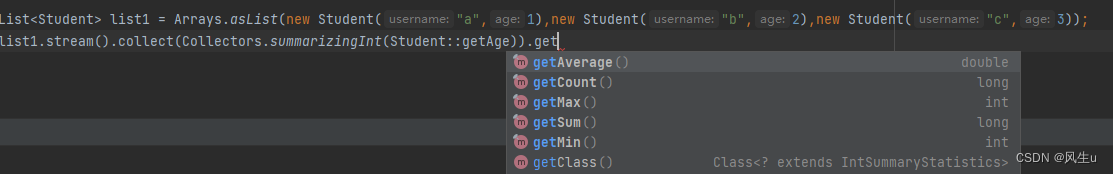
统计以上所有:summarizingInt、summarizingLong、summarizingDouble(包括计数,平均值,最值,和)
分组(partitioningBy/groupingBy)
partitioningBy():条件分组
groupingBy():根据集合内相同的元素进行分组
public class StreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<Person>();
personList.add(new Person("Tom", 8900, "male", "New York"));
personList.add(new Person("Jack", 7000, "male", "Washington"));
personList.add(new Person("Lily", 7800, "female", "Washington"));
personList.add(new Person("Anni", 8200, "female", "New York"));
personList.add(new Person("Owen", 9500, "male", "New York"));
personList.add(new Person("Alisa", 7900, "female", "New York"));
// 将员工按薪资是否高于8000分组
Map<Boolean, List<Person>> part = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(x -> x.getSalary() > 8000));
// 将员工按性别分组
Map<String, List<Person>> group = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getSex));
// 将员工先按性别分组,再按地区分组,嵌套分组
Map<String, Map<String, List<Person>>> group2 = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getSex, Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getArea)));
System.out.println("员工按薪资是否大于8000分组情况:" + part);
System.out.println("员工按性别分组情况:" + group);
System.out.println("员工按性别、地区:" + group2);
}
}
//输出结果
员工按薪资是否大于8000分组情况:{false=[mutest.Person@2d98a335, mutest.Person@16b98e56, mutest.Person@7ef20235], true=[mutest.Person@27d6c5e0, mutest.Person@4f3f5b24, mutest.Person@15aeb7ab]}
员工按性别分组情况:{female=[mutest.Person@16b98e56, mutest.Person@4f3f5b24, mutest.Person@7ef20235], male=[mutest.Person@27d6c5e0, mutest.Person@2d98a335, mutest.Person@15aeb7ab]}
员工按性别、地区:{female={New York=[mutest.Person@4f3f5b24, mutest.Person@7ef20235], Washington=[mutest.Person@16b98e56]}, male={New York=[mutest.Person@27d6c5e0, mutest.Person@15aeb7ab], Washington=[mutest.Person@2d98a335]}}
修改集合中元素之间的连接符join
public class StreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<Person>();
personList.add(new Person("Tom", 8900, 23, "male", "New York"));
personList.add(new Person("Jack", 7000, 25, "male", "Washington"));
personList.add(new Person("Lily", 7800, 21, "female", "Washington"));
String names = personList.stream().map(p -> p.getName()).collect(Collectors.joining(","));
System.out.println("所有员工的姓名:" + names);
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("A", "B", "C");
String string = list.stream().collect(Collectors.joining("-"));
System.out.println("拼接后的字符串:" + string);
}
}
提取/组合
public class StreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] arr1 = { "a", "b", "c", "d" };
String[] arr2 = { "d", "e", "f", "g" };
Stream<String> stream1 = Stream.of(arr1);
Stream<String> stream2 = Stream.of(arr2);
// concat:合并两个流 distinct:去重
List<String> newList = Stream.concat(stream1, stream2).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
// limit:限制从流中获得前n个数据
List<Integer> collect = Stream.iterate(1, x -> x + 2).limit(10).collect(Collectors.toList());
// skip:跳过前n个数据
List<Integer> collect2 = Stream.iterate(1, x -> x + 2).skip(1).limit(5).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("流合并:" + newList);
System.out.println("limit:" + collect);
System.out.println("skip:" + collect2);
}
}
//输出
流合并:[a, b, c, d, e, f, g]
limit:[1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19]
skip:[3, 5, 7, 9, 11]