1. 简介
1.1 创建springboot应用,选中我们需要的模块
1.2 springBoot已经默认将这些场景配置好了,只需要在配置文件中指定少量配置就可以运行起来
1.3 自己编写业务代码
顺便回顾下上一篇的自动装配
这个场景SpringBoot帮我们配置了什么?能不能修改?能修改哪些配置?能不能扩展?
2 springBoot对静态资源的映射规则
2.1 Springboot对静态资源的映射规则
WebMvcAuotConfiguration:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.resources", ignoreUnknownFields = false) public class ResourceProperties implements ResourceLoaderAware { //可以设置和静态资源有关的参数,缓存时间等 @Override public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) { if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) { logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled"); return; } Integer cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCachePeriod(); if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**")) { customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler("/webjars/**").addResourceLocations("classpath:/META‐INF/resources/webjars/").setCachePeriod(cachePeriod)); } String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern(); //静态资源文件夹映射 if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) { customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry. addResourceHandler(staticPathPattern).addResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()).setCachePeriod(cachePeriod)); } } / /配置欢迎页映射 @Bean public WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping( ResourceProperties resourceProperties) { return new WelcomePageHandlerMapping(resourceProperties.getWelcomePage(), this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern()); } //配置喜欢的图标 @Configuration @ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.mvc.favicon.enabled", matchIfMissing = true) public static class FaviconConfiguration { private final ResourceProperties resourceProperties; public FaviconConfiguration(ResourceProperties resourceProperties) { this.resourceProperties = resourceProperties; } @Bean public SimpleUrlHandlerMapping faviconHandlerMapping() { SimpleUrlHandlerMapping mapping = new SimpleUrlHandlerMapping(); mapping.setOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 1); //所有 **/favicon.ico mapping.setUrlMap(Collections.singletonMap("**/favicon.ico", faviconRequestHandler()); return mapping; } @Bean public ResourceHttpRequestHandler faviconRequestHandler() { ResourceHttpRequestHandler requestHandler = new ResourceHttpRequestHandler(); requestHandler.setLocations(this.resourceProperties.getFaviconLocations()); return requestHandler; } }2.2 所有/webjars/**,都去classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/ 找资源;
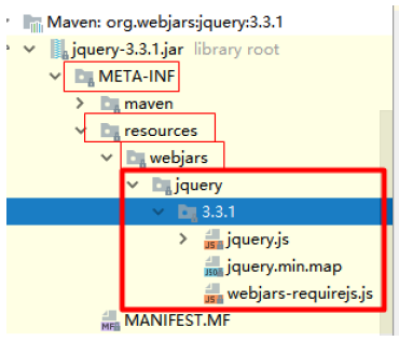
webjars:以jar包的方式引入静态资源;WebJars - Web Libraries in Jars
localhost:8080/webjars/jquery/3.3.1/jquery.js
2.3 那如何引入jquert-webjar呢?
在访问的时候只需要写webjars下面资源的名称即可
<!‐‐引入jquery‐webjar‐‐>在访问的时候只需要写webjars下面资源的名称即可 <dependency> <groupId>org.webjars</groupId> <artifactId>jquery</artifactId> <version>3.3.1</version> </dependency>2.4 "/**" 访问当前项目的任何资源,都去(静态资源的文件夹)找映射
"classpath:/META‐INF/resources/", "classpath:/resources/", "classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/" "/":当前项目的根路径localhost:8080/abc === 去静态资源文件夹里面找abc
2.5 欢迎页; 静态资源文件夹下的所有index.html页面;被"/**"映射;(localhost:8080/ 找index页面)
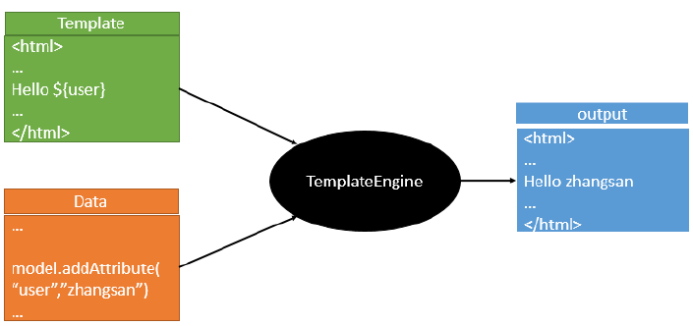
3. 模版引擎
JSP、Velocity、Freemarker、Thymeleaf
SpringBoot推荐的Thymeleaf;
语法更简单,功能更强大;
3.1 如何引入thymeleaf呢
在pom.xml中引入:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> </dependency>注意:
从spring父文件中能看到Springboot2.0.1所使用的thymeleaf版本是3.0.9
springBoot启动的时候会自动配置
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration
而从ThymeleafAutoConfiguration的源代码中我们可以得知ThymeleafProperties
中配置了Thymeleaf的规则
3.2 ThymeleafProperties中都配置了哪些呢?
public class ThymeleafProperties { private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING; public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/"; public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html"; private boolean checkTemplate = true; private boolean checkTemplateLocation = true; private String prefix = "classpath:/templates/"; private String suffix = ".html"; private String mode = "HTML"; private Charset encoding; private boolean cache;我们使用html作为模版,而且默认的前缀是放在classpath:/template/下,后缀是.html
当然这些属性我们都可以通过application.properties来修改。我们采用默认即可。
3.3 举个例子
3.3.1 在template下创建一个success.html
3.3.2 在html中引入thymeleaf的命名空间
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
3.3.3 创建一个Controller提供一个访问的方法
@RequestMapping("/success") public String hello(Model model){ model.addAttribute("hello","<h1>renliang</h1>"); return "success"; }3.3.4 在thymeleaf模板中取值
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div th:text="${hello}"> </div> </body> </html>
4. 现在来学习下Thymeleaf语法
4.1 变量表达式
变量表达式即OGNL表达式或Spring EL表达式(在Spring术语中也叫model attributes)。
如下所示: ${session.user.name}
它们将以HTML标签的一个属性来表示:
<span th:text="${book.author.name}">4.2 选择(星号作为表达式)
选择表达式很像变量表达式,不过它们用一个预先选择的对象来代替上下文变量容器(map)来执行,如下: *{customer.name}
被指定的object由th:object属性定义:
<div th:object="${book}"> ... <span th:text="*{title}">...</span> ... </div>4.3 文字国际化表达式
文字国际化表达式允许我们从一个外部文件获取区域文字信息(.properties),用Key索引Value,还可以提供一组参数(可选).
#{main.title}
4.4 URL表达式
URL表达式指的是把一个有用的上下文或回话信息添加到URL,这个过程经常被叫做URL
重写。不需要指定项目名字
@{/order/list}URL还可以设置参数:@{/order/details(id=${orderId})}
让我们看这些表达式:
<form th:action="@{/createOrder}"> <a href="main.html" rel="external nofollow" th:href="@{/main}" rel="external n4.5 表达式都支持哪些语法呢?
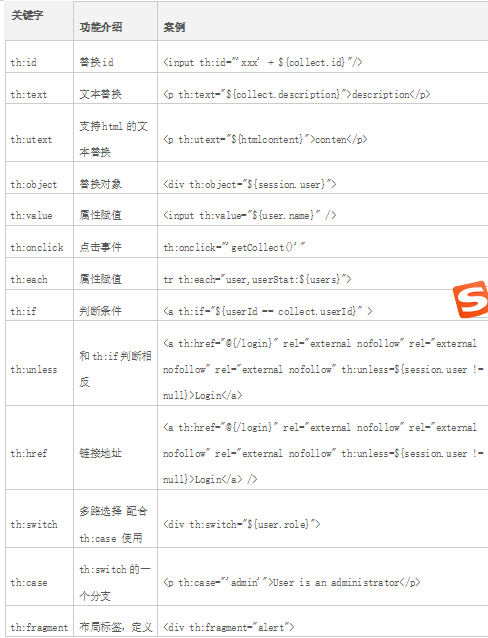
字面(Literals) 文本文字(Text literals): 'one text', 'Another one!',… 数字文本(Number literals): 0, 34, 3.0, 12.3,… 布尔文本(Boolean literals): true, false 空(Null literal): null 文字标记(Literal tokens): one, sometext, main,… 文本操作(Text operations) 字符串连接(String concatenation): + 文本替换(Literal substitutions): |The name is ${name}| 算术运算(Arithmetic operations) 二元运算符(Binary operators): +, -, *, /, % 减号(单目运算符)Minus sign (unary operator): - 布尔操作(Boolean operations) 二元运算符(Binary operators):and, or 布尔否定(一元运算符)Boolean negation (unary operator):!, not 比较和等价(Comparisons and equality) 比较(Comparators): >, <, >=, <= (gt, lt, ge, le) 等值运算符(Equality operators):==, != (eq, ne) 条件运算符(Conditional operators) If-then: (if) ? (then) If-then-else: (if) ? (then) : (else) Default: (value) ?: (defaultvalue) 例如:'User is of type ' + (${user.isAdmin()} ? 'Administrator' : (${user.type} ?: 'Unknown'))4.6 常用的thymeleaf标签
好了,最后整体来个例子吧!
模板:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <div th:text="${hello}" th:id="${hello.toUpperCase()}">xxxx</div> <input th:value="${user.getUsername()}"> <hr> <div th:object="${user}"> <span th:text="*{username}"></span> </div> <a th:href="" th:if="${user.getAge() == 2}" >年龄</a> <a th:class="${user.getAge() > 2}?'class1':'class2'" >年龄</a> <p th:if="${user.score >= 60 and user.score < 85}">B</p> <p th:if="${user.score < 60}">C</p> <p th:if="${user.score > 85}">优秀</p> <span th:switch="${user.gender}"> <p th:case="1">男</p> <p th:case="2">女</p> </span> <table> <tr th:each="a,aState:${uList}"> <td th:text="${a.username}"></td> <td th:text="${a.password}"></td> <td th:text="${aState.index}"></td> </tr> </table> </body> </html>Controller中给的数据:
@RequestMapping("/success") public String hello(HttpServletRequest req, HttpSession httpSession, Model model){ model.addAttribute("hello","<h1>renliang</h1>"); User user = new User(); user.setPassword("111"); user.setUsername("renliang"); user.setAge(1); user.setScore(78); user.setGender(2); List<User> uList = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){ User u = new User(); u.setUsername("renliang"+i); u.setPassword("111"+i); uList.add(u); } // httpSession.setAttribute("user", user); model.addAttribute("user", user); model.addAttribute("uList", uList); return "success"; }
5. Springboot整合springmvc
官网资料: https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.0.2.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#boot-features-spring-mvc
(学习springmvc和springboot的自动配置我们必须对springmvc的组件足够了解,起码知道怎么用。Springmvc的组件基本都被springboot来做了自动的配置。)
5.1 springmvc的自动配置管理
中央转发器(DispatcherServlet) 控制器 视图解析器 静态资源访问 消息转换器 格式化 静态资源管理5.2 中央转发器(DispatcherServlet)
注意
DispatcherServlet的自动注册: Spring Boot会自动注册并配置DispatcherServlet作为前端控制器,它是Spring MVC的核心组件,负责接收HTTP请求并分发到相应的处理器(Controller)XML不需要配置下面的
<servlet> <servlet-name>chapter2</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>chapter2</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>中央转发器被springboot自动接管,不再需要我们在web.xml中配置,我们现在的项目也不是web项目,也不存在web.xml,
在这里自动配置的哦 -》
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\
5.3 控制器(也就是Controller)
控制器Controller在springboot的注解扫描范围内自动管理
5.4 视图解析器自动管理
Inclusion of ContentNegotiatingViewResolver and BeanNameViewResolver beans.
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver:组合所有的视图解析器的
以前的配置文件无需配置
<bean id="de" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"></property> <property name="suffix" value="*.jsp"></property> </bean>源码:
public ContentNegotiatingViewResolver viewResolver(BeanFactory beanFactory) { ContentNegotiatingViewResolver resolver = new ContentNegotiatingViewResolver(); resolver.setContentNegotiationManager((ContentNegotiationManager)beanFactory.getBean(ContentNegotiationManager.class)); resolver.setOrder(-2147483648); return resolver; }注意:当我们做文件上传的时候我们也会发现multipartResolver是自动被配置好的
页面:
<form action="/upload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input name="pic" type="file"> <input type="submit"> </form>Controller:
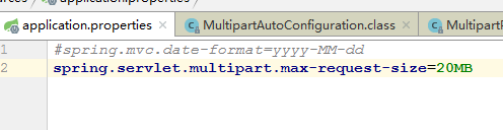
@ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/upload") public String upload(@RequestParam("pic")MultipartFile file, HttpServletRequest request){ String contentType = file.getContentType(); String fileName = file.getOriginalFilename(); /*System.out.println("fileName-->" + fileName); System.out.println("getContentType-->" + contentType);*/ //String filePath = request.getSession().getServletContext().getRealPath("imgupload/"); String filePath = "D:/imgup"; try { this.uploadFile(file.getBytes(), filePath, fileName); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception } return "success"; } public static void uploadFile(byte[] file, String filePath, String fileName) throws Exception { File targetFile = new File(filePath); if(!targetFile.exists()){ targetFile.mkdirs(); } FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(filePath+fileName); out.write(file); out.flush(); out.close(); }文件上传大小可以通过配置来修改---》打开application.properties, 默认限制是10MB,我们可以任意修改
5.5 消息转换和格式化
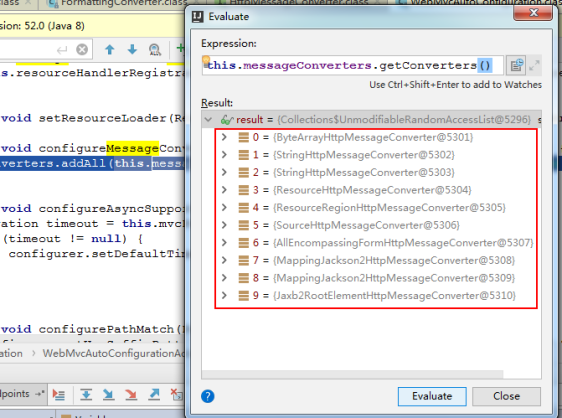
5.5.1 Springboot自动配置了消息转换器
格式化转换器的自动注册
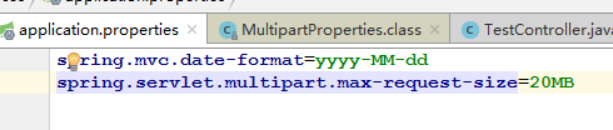
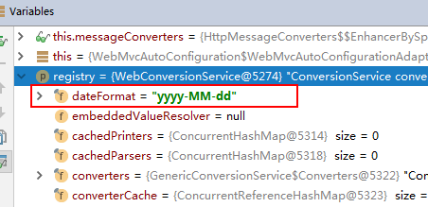
时间类型我们可以在这里修改
在配置文件中指定好时间的模式我们就可以输入了