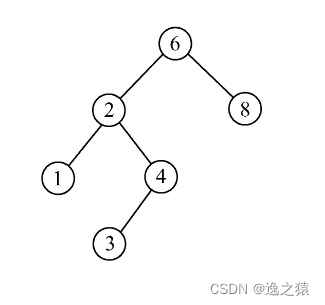
一、顺序查找
顺序查找又称线性查找,对于顺序表和链表都适用。对于顺序表,可通过数组下标递增来顺序扫描每个元素;对于链表,则通过指针next来依次扫描每个元素。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct{
ElemType *elem; //整形指针,申请的堆空间的起始地址存入elem
int TableLen; //存储动态数组里边元素的个数
}SSTable;
void ST_Init(SSTable &ST,int len){
//多申请一个位置,存哨兵
ST.TableLen=len+1;
ST.elem=(ElemType *)malloc(sizeof(ElemType)*ST.TableLen);
int i;
srand(time(NULL)); //随机数生成
for(i=1;i<ST.TableLen;i++){
ST.elem[i]=rand()%100;
}
}
void ST_print(SSTable ST){
int i;
for(i=1;i<ST.TableLen;i++){
printf("%3d",ST.elem[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int Search_Seq(SSTable ST,ElemType key){
ST.elem[0]=key; //key存在零号位置,作为哨兵,在循环时,可以少些i>=0
int i;
for(i=ST.TableLen-1;ST.elem[i]!=key;i--);
return i;
}
//顺序查找
int main(){
SSTable ST;
ST_Init(ST,10);
ST_print(ST);
ElemType key;
printf("please input search key:\n");
scanf("%d",&key);
int pos;
pos=Search_Seq(ST,key);
if(pos){
printf("find pos,pos=%d\n",pos);
}
else{
printf("not find\n");
}
return 0;
}二、折半查找
折半查找又称二分查找,仅适用于有序的顺序表。
基本思想:首先将给定值key与表中中间位置的元素比较,若相等则查找成功,返回该元素的存储位置,若不等,则所需查找的元素只能中间元素以外的前半部分或后半部分。然后缩小范围继续进行同样的查找。
1、初始化顺序表,随机10个元素
2、使用qsort进行排序,排序完毕后,打印
3、输入要查找的元素值,存入变量key中
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct{
ElemType *elem; //整形指针,申请的堆空间的起始地址存入elem
int TableLen; //存储动态数组里边元素的个数
}SSTable;
void ST_Init(SSTable &ST,int len){
ST.TableLen=len;
ST.elem=(ElemType *)malloc(sizeof(ElemType)*ST.TableLen);
int i;
srand(time(NULL)); //随机数生成
for(i=0;i<ST.TableLen;i++){
ST.elem[i]=rand()%100;
}
}
void ST_print(SSTable ST){
int i;
for(i=1;i<ST.TableLen;i++){
printf("%3d",ST.elem[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int BinarySearch(SSTable L,ElemType key){
int low=0;
int high=L.TableLen-1;
int mid;
while(low<=high){
mid=(low+high)/2;
if(key>L.elem[mid]){
low=mid+1;
}
else if(key<L.elem[mid]){
high=mid-1;
}
else{
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
//函数名中存储的是函数的入口地址,也是一个指针,是函数指针类型
//qsort规定,如果left指针指向的值大于right指针指向的值,返回正值;小于,返回负值
int compare(const void *left,const void *right){
return *(int*)left-*(int*)right; //从小到大
}
//二分查找
int main(){
SSTable ST;
ST_Init(ST,10);
ST_print(ST);
qsort(ST.elem,ST.TableLen,sizeof(ElemType),compare);
ST_print(ST);
ElemType key;
printf("please input search key:\n");
scanf("%d",&key);
int pos;
pos=BinarySearch(ST,key);
if(pos!=-1){
printf("find pos,pos=%d\n",pos);
}
else{
printf("not find\n");
}
return 0;
}三、二叉排序树
二叉排序树(二叉查找树)或是一颗空树,或是具有下列特性的二叉树:
1、若左子树非空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于根结点的值
2、若右子树非空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于根结点的值
3、左、右子树也分别是一颗二叉排序树
二叉排序树的最大查找次数是树的高度
二叉排序树新建,中序遍历,查找 ,删除
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int KeyType;
typedef struct BSTNode{
KeyType key;
struct BSTNode *lchild,*rchild;
}BSTNode,*BiTree;
//递归
int BST_Insert(BiTree &T,KeyType k){
if(T==NULL){
//为新结点申请空间,第一个结点作为树根,后面递归再进入的不是树根,是叶子结点
T=(BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BSTNode));
T->key=k;
T->lchild=T->rchild=NULL;
return 1; //代表插入成功
}
else if(k==T->key){
return 0; // 发现相同元素,就不插入
}
else if(k<T->key){
return BST_Insert(T->lchild,k);
}
else{
return BST_Insert(T->rchild,k);
}
}
void Create_BST(BiTree &T,KeyType str[],int len){
int i;
for(i=0;i<len;i++){
BST_Insert(T,str[i]); //把某一个结点放入二叉查找树
}
}
//中序遍历
void InOrder(BiTree T){
if(T!=NULL){
InOrder(T->lchild); //打印左子树
//putchar(p->c);
printf("%3d",T->key);
InOrder(T->rchild); //打印右子树
}
}
BiTree BST_Search(BiTree T,KeyType k,BiTree &parent){
parent=NULL;
while(T!=NULL&&k!=T->key){
parent=T;
if(k>T->key){
T=T->rchild;
}
else{
T=T->lchild;
}
}
return T;
}
void DeleteNode(BiTree &root,KeyType x){
if(root==NULL){
return;
}
if(root->key>x){
DeleteNode(root->lchild,x);
}
else if(root->key<x){
DeleteNode(root->rchild,x);
}
else{ // 查找到了删除结点
if(root->lchild==NULL){ // 左子树为空,右子树直接顶上去
BiTree tempNode=root; // 临时存着,一会儿free
root=root->rchild;
free(tempNode);
}
else if(root->rchild==NULL){ // 右子树为空,左子树直接顶上去
BiTree tempNode=root;
root=root->lchild;
free(tempNode);
}
else{ // 左右子树都不为空
//左子树的最大数据(右子树的最小数据)代替要删除的结点
BiTree tempNode=root->lchild;
while(tempNode->rchild!=NULL){ // 向右找到最大的
tempNode=tempNode->rchild;
}
root->key=tempNode->key; // 把tempNode对应的值替换到要删除的值的位置上
DeleteNode(root->lchild,tempNode->key); //在左子树上找到tempNode值,把其删除
}
}
}
//二叉排序树新建,中序遍历,查找 ,删除
int main(){
BiTree T=NULL; // 树根
BiTree parent; // 存储父亲结点的地址值
KeyType str[7]={54,20,66,40,28,79,58}; // 将要进入二叉排序树的元素值
Create_BST(T,str,7);
InOrder(T);
printf("\n");
BiTree search;
search=BST_Search(T,40,parent);
if(search){
printf("find key %d\n",search->key);
}
else{
printf("not find\n");
}
DeleteNode(T,40);
InOrder(T);
return 0;
}