目录
二叉搜索树的概念
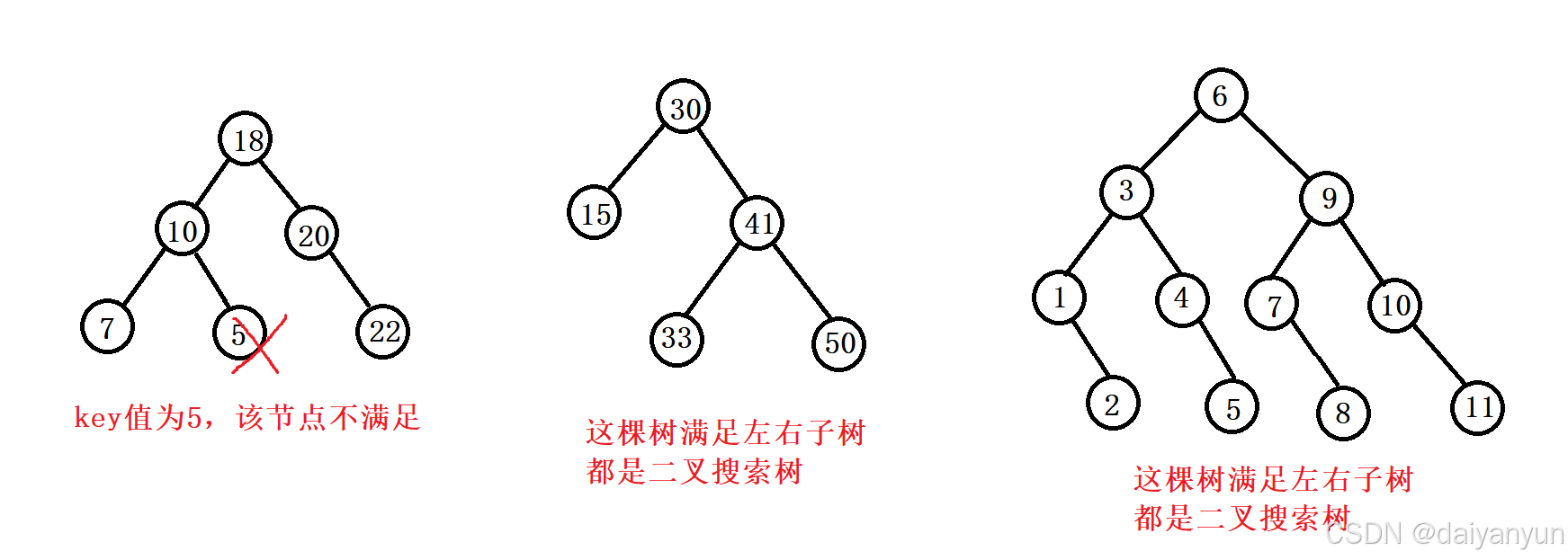
二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有以下性质的二叉树:
若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
注意:二叉搜索树key值不能相同。
二叉搜索树中序遍历是有序的,因为二叉搜索树的定义决定了左子树节点值小于根节点值、右子树节点值大于等于根节点值(每一颗子树也满足),而中序遍历先左子树、再根节点、后右子树的方式使得遍历结果自然有序。
二叉搜索树的实现
基本结构
二叉搜索树中的每个节点包含两个指针,分别指向左子树和右子树,以及一个存储关键值(key 值)的数据域。这种结构使得二叉搜索树能够以二叉树的形式组织数据,并通过比较节点的关键值来进行高效的查找、插入和删除操作。
二叉搜索树不能修改里面的key值,如果修改了就会破坏二叉搜索树的结构。
//节点的定义
template<class K>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K>* _left; //左节点
BSTreeNode<K>* _right; //右节点
K _key; //存储 key 值
BSTreeNode(const K& key) //构造函数完成初始化
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_key(key)
{}
};
template <class K> //key 关键字,进行比较
class BSTree //Binary Search Tree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
private:
Node* _root = nullptr; //在类内进行成员初始化
};插入
1,当树是空树的时候
直接定义一个节点把该节点给 _root。
2,当树不为空的时候
不是空树,去找这个需要插入的位置,插入一定是找一个空的位置,不可能替代某个位置。
如果插入时是相同的元素,则插入失败,因为二叉搜索树不允许出现相同的 key 值。
#pragma once
//节点的定义
template<class K>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K>* _left; //左节点
BSTreeNode<K>* _right; //右节点
K _key; //存储 key 值
BSTreeNode(const K& key) //构造函数完成初始化
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_key(key)
{}
};
template <class K> //key 关键字,进行比较
class BSTree //Binary Search Tree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
//1,根为空的时候
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
}
//2,根不为空的时候
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (key > cur->_key) //插入的key比当前节点大就往右边走
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (key < cur->_key) //插入的key比当前节点小就往左边走
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false; //插入的key和当前节点相等,就插入失败
}
}
cur = new Node(key);
return true;
}
//中序遍历
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr; //在类内进行成员初始化
};
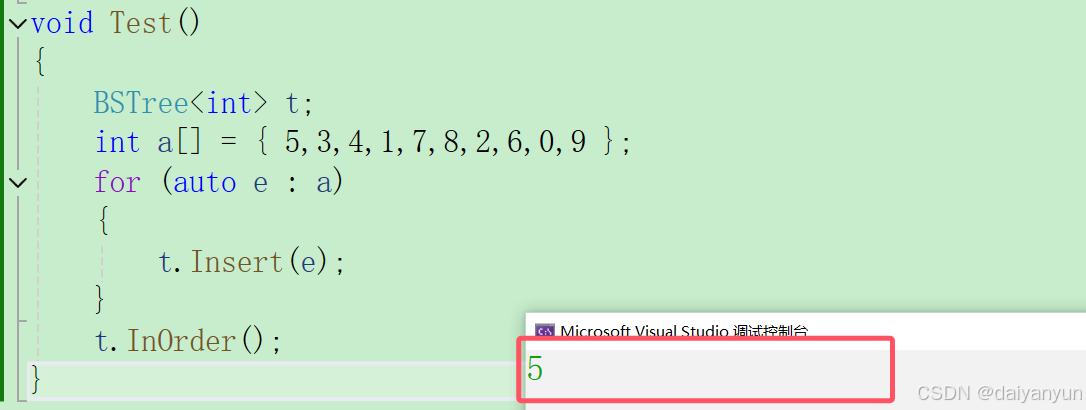
void Test()
{
BSTree<int> t;
int a[] = { 5,3,4,1,7,8,2,6,0,9 };
for (auto e : a)
{
t.Insert(e);
}
t.InOrder();
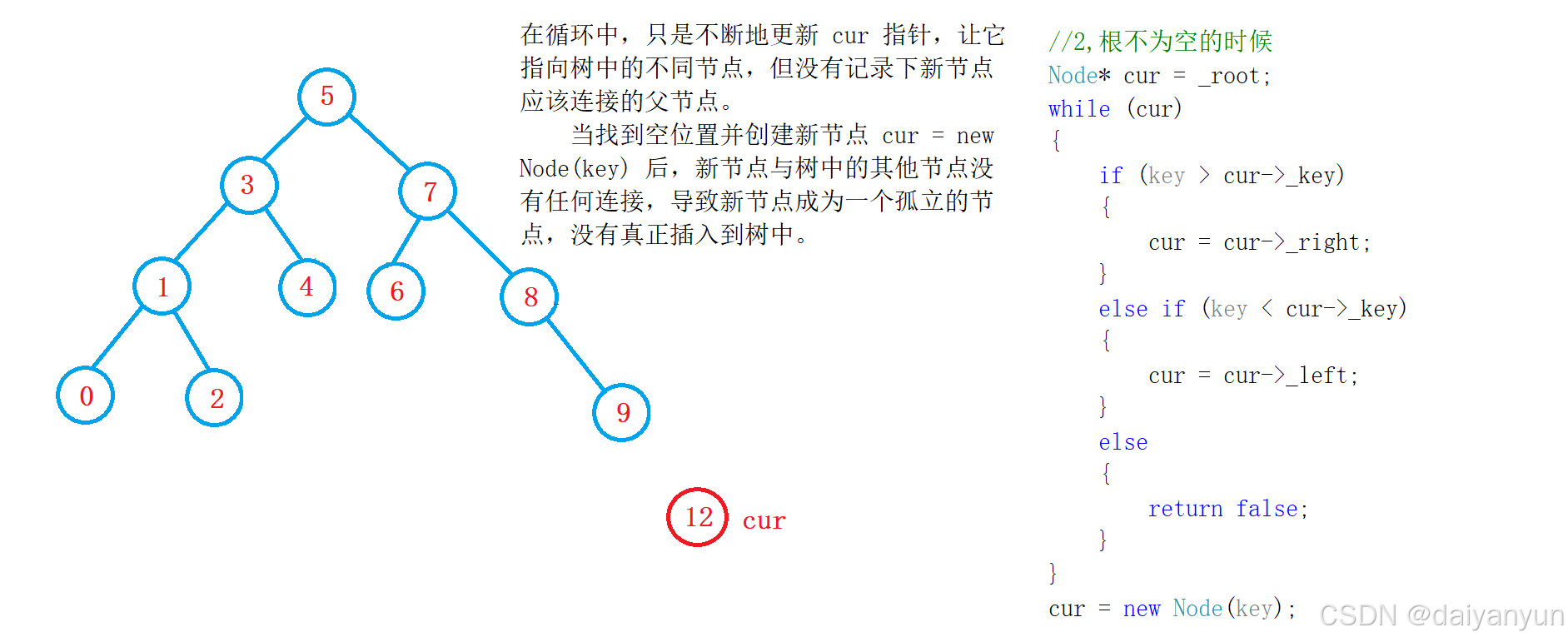
}通过测试我们会发现,这里只有 5 插入成功了,也就是根节点插入成功,那么这段代码存在一定的问题,如何解决呢???
问题:在循环中,只是不断地更新 cur 指针,让它指向树中的不同节点,但没有记录下新节点应该连接的父节点。
当找到空位置并创建新节点 cur = new Node(key) 后,新节点与树中的其他节点没有任何连接,导致新节点成为一个孤立的节点,没有真正插入到树中。改进:
- 添加一个
parent指针来记录新节点的父节点。在循环中,当更新cur指针时,也同时更新parent指针。- 在找到插入位置后,根据
key与parent->_key的大小关系,将新节点连接到父节点的左子树或右子树。
3,纠正后的代码
#pragma once
//节点的定义
template<class K>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K>* _left; //左节点
BSTreeNode<K>* _right; //右节点
K _key; //存储 key 值
BSTreeNode(const K& key) //构造函数完成初始化
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_key(key)
{}
};
template <class K> //key 关键字,进行比较
class BSTree //Binary Search Tree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
//当树是空树的时候
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
//树不为空的时候
Node* parent = nullptr; //用一个节点来记录cur的父亲
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (key > cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (key < cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key);
if (key > parent->_key) //判断到底是属于父亲的左树还是右树
parent->_right = cur;
else
parent->_left = cur;
return true;
}
//中序遍历
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr; //在类内进行成员初始化
};
void Test()
{
BSTree<int> t;
int a[] = { 5,3,4,1,7,8,2,6,0,9 };
for (auto e : a)
{
t.Insert(e);
}
t.InOrder();
}查找
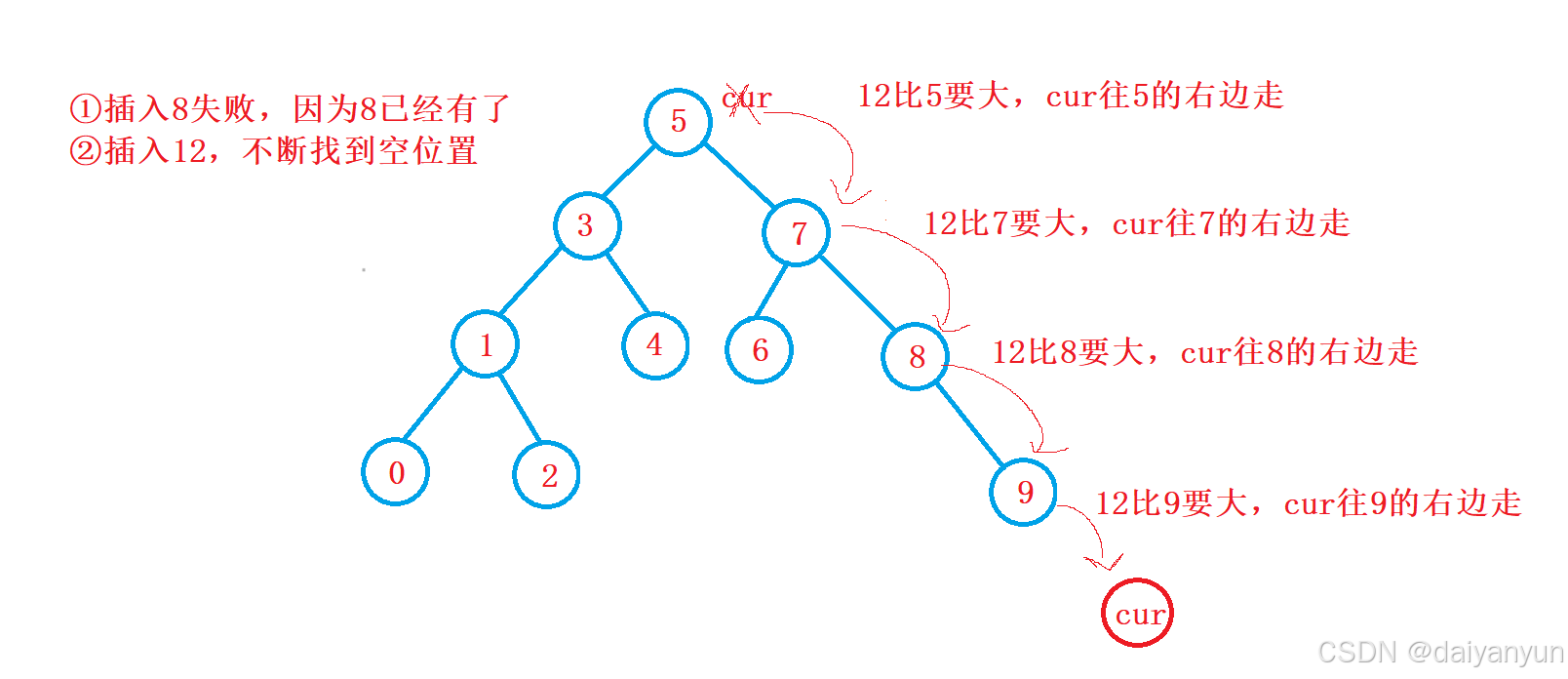
查找和插入类似,如果比当前节点小就往左边找,如何比当前节点大就往右边找,不断更新cur,直到找返回 true,如果没有找到,返回 false。
//查找
bool Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (key > cur->_key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (key < cur->_key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}删除
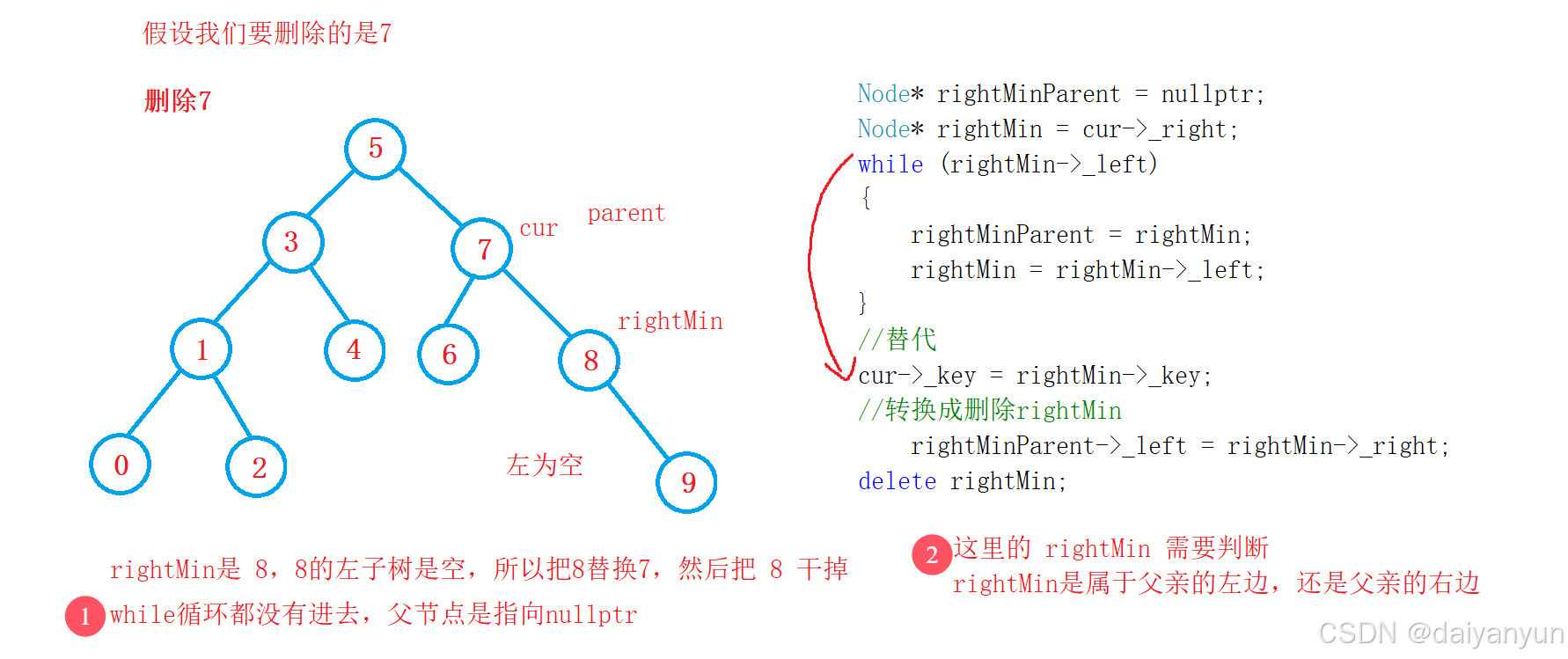
二叉搜索树重点在于删除操作,也比较简单。
在实现Erase的时候我们不能使用Find,因为我们还需用到它的父亲,所以这里还是使用双指针。
当我们试删除这些节点,我们可以发现可以存在这些情况:
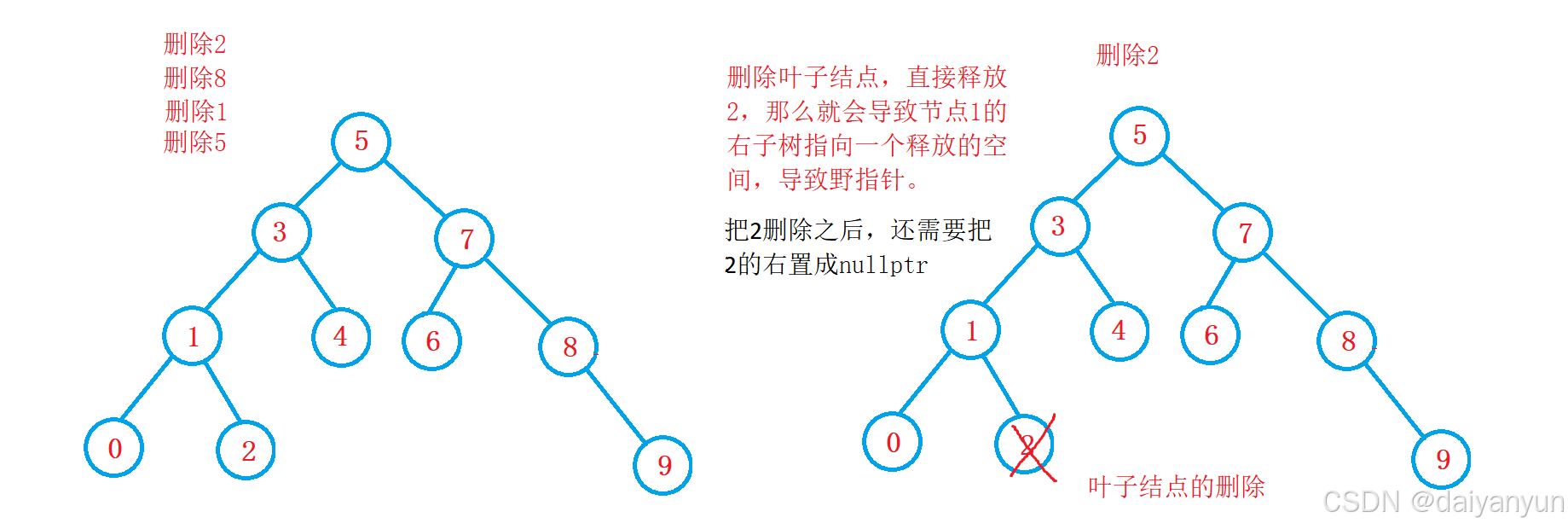
1,删除2最好删,把2删除之后,还需要把2的右置成nullpt,不然就是野指针了。
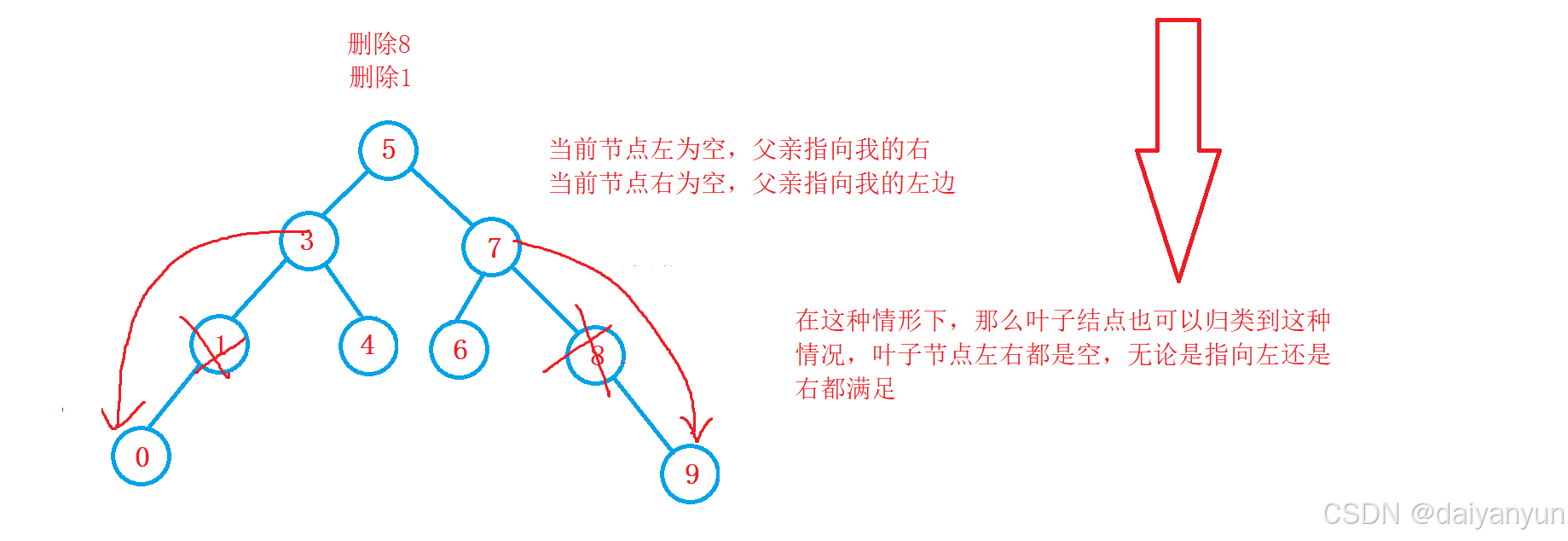
2, 当前节点左为空,父亲指向我的右,当前节点右为空,父亲指向我的左边。
3,叶子结点也可以归类到这种左为空或者右为空,让父亲指向左/右。
3,当左右都不为空的时候不能直接删除,用替换法删除
可以找左子树的最大节点(最右节点)或者右子树的最小节点最左节点)替代它综上所述:
① 左为空
② 右为空
③ 左右都不为空
1,左为空或右为空
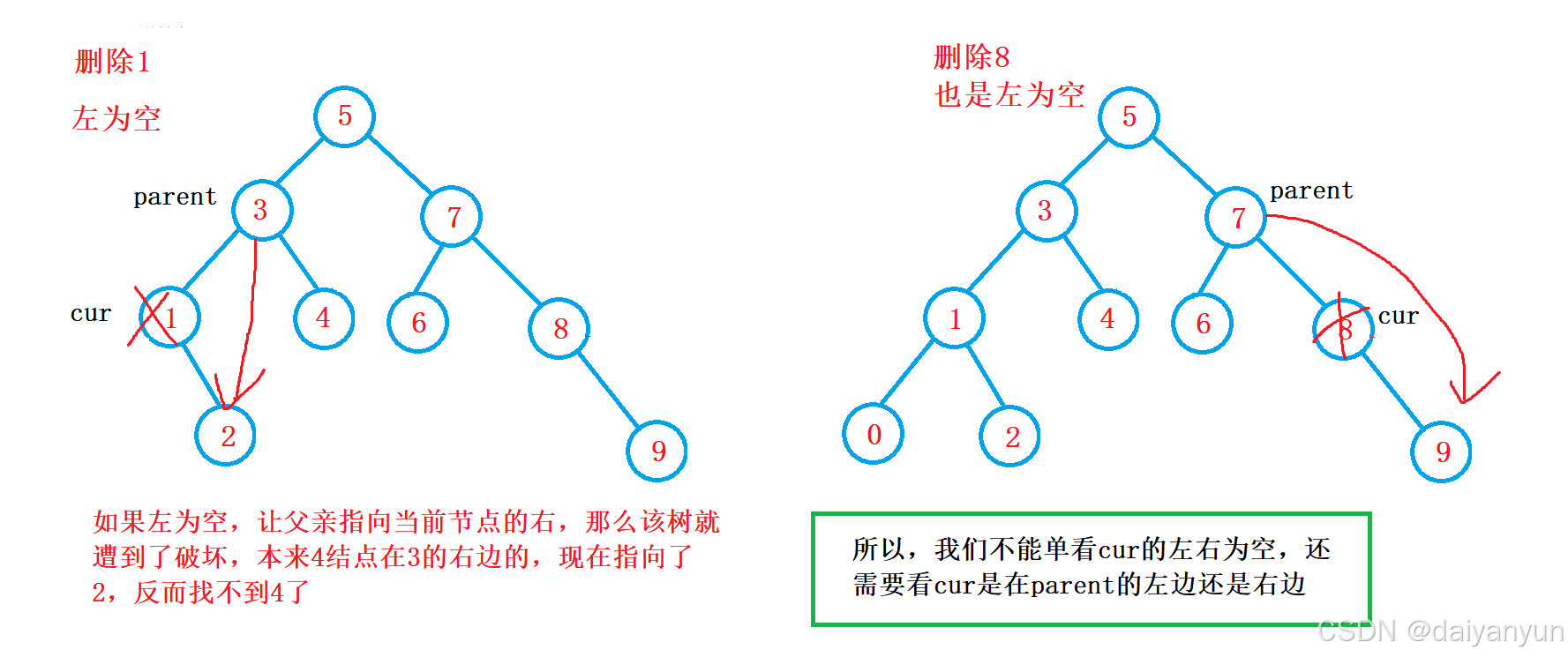
我们不能单单只看cur的左右是否为空,然后直接用parent去指向cur的左右,而是我们需要去观察 cur 属于parent 左边还是右边,如果在左边就用 parent 的左边去指向cur的左或者右,如果在右边就用 parent 的右边去指向cur的左或者右。
右为空和左为空同理。
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (key > cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (key < cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
//找到了
//1,左边为空
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (parent->_right == cur)
parent->_right = cur->_right;
else
parent->_left = cur->_right;
delete cur;
}
//2,右边为空
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (parent->_left = cur)
parent->_left = cur->_left;
else
parent->_right = cur->_left;
delete cur;
}
else //3,左右都不为空
{
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
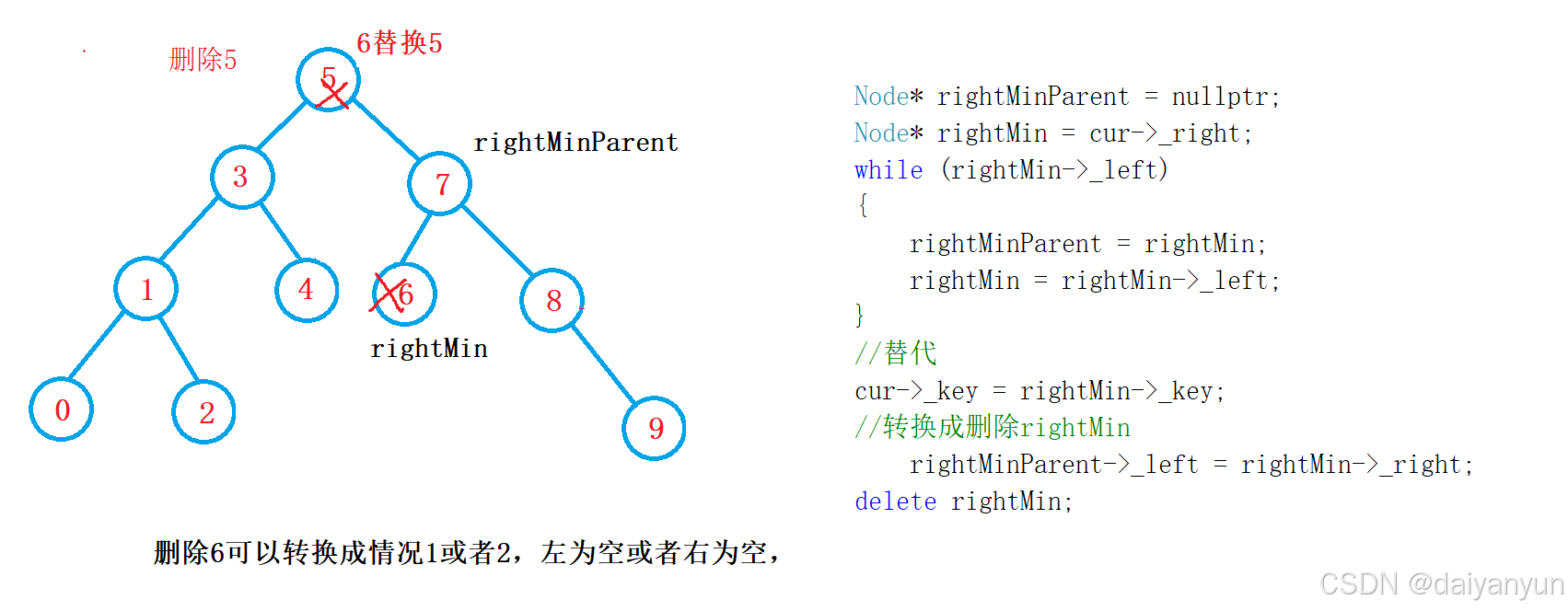
2,左右都不为空
左右都不为空:找左树的最大节点,或者右树的最小节点,也就是左子树的最右节点,或者右子树的最左节点
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (key > cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (key < cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
//找到了
//1,左边为空
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (parent->_right == cur)
parent->_right = cur->_right;
else
parent->_left = cur->_right;
delete cur;
}
//2,右边为空
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (parent->_left = cur)
parent->_left = cur->_left;
else
parent->_right = cur->_left;
delete cur;
}
else //3,左右都不为空
{
Node* rightMinParent = nullptr;
Node* rightMin = cur->_right;
while (rightMin->_left)
{
rightMinParent = rightMin;
rightMin = rightMin->_left;
}
//替代
cur->_key = rightMin->_key;
//转换成删除rightMin
rightMinParent->_left = rightMin->_right;
delete rightMin;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
假设我一上来就删除 7 这棵树存在问题
纠正后的代码:
Node* rightMinParent = cur;
Node* rightMin = cur->_right;
while (rightMin->_left)
{
rightMinParent = rightMin;
rightMin = rightMin->_left;
}
//替代
cur->_key = rightMin->_key;
//转换成删除rightMin (rightMin是左为空,父亲指向它的右边)
if (rightMin == rightMinParent->_left)
rightMinParent->_left = rightMin->_right;
else
rightMinParent->_right = rightMin->_right;
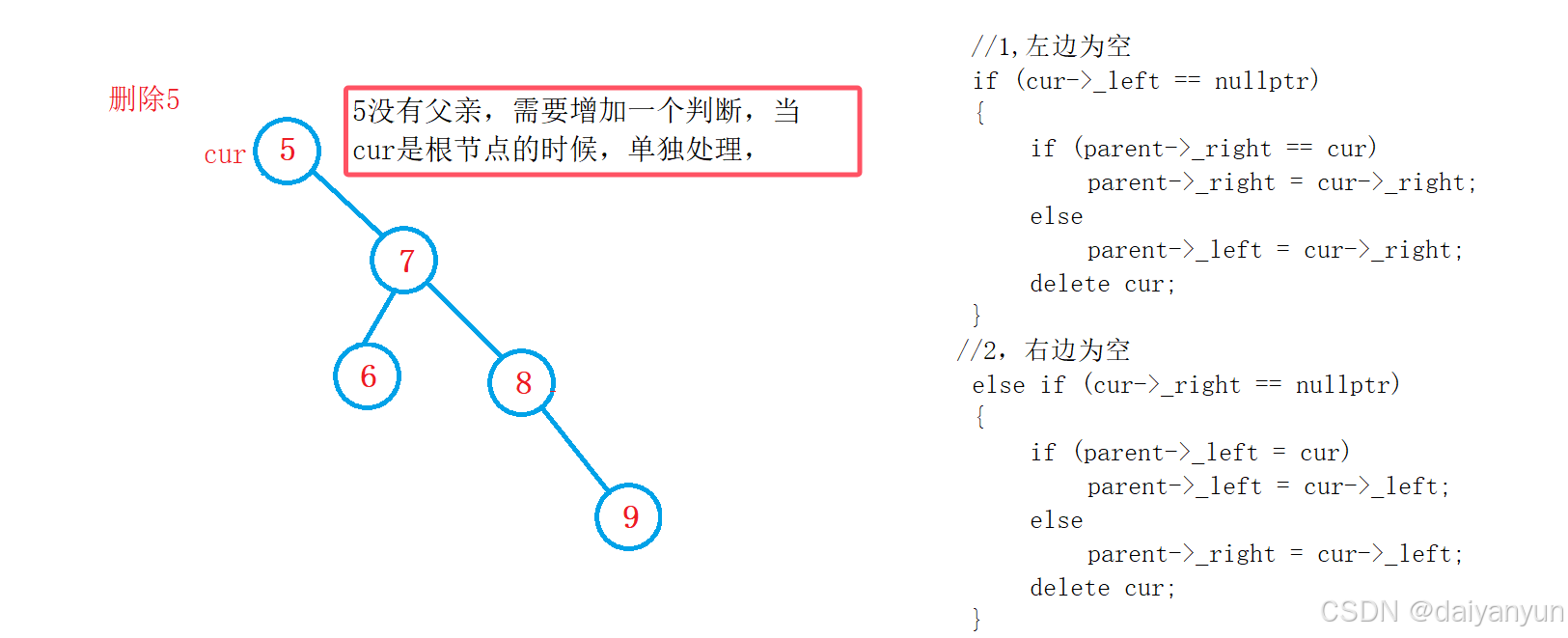
delete rightMin;如果把这棵树删空也会存在问题
纠正后的代码:
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root) //当删除的是根节点的时候
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (parent->_right == cur)
parent->_right = cur->_right;
else
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
delete cur;
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root) //当删除的是根节点的时候
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (parent->_left == cur)
parent->_left = cur->_left;
else
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
delete cur;
}3,删除的完整代码:
//删除
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (key > cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (key < cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
//找到了,开始删除
// 1、左为空
// 2、右为空
// 3、左右都不为空
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (parent->_right == cur)
parent->_right = cur->_right;
else
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
delete cur;
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (parent->_left == cur)
parent->_left = cur->_left;
else
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
delete cur;
}
else
{
Node* rightMinParent = cur;
Node* rightMin = cur->_right;
while (rightMin->_left)
{
rightMinParent = rightMin;
rightMin = rightMin->_left;
}
//替代
cur->_key = rightMin->_key;
//转换成删除rightMin (rightMin是左为空,父亲指向它的右边)
if (rightMin == rightMinParent->_left)
rightMinParent->_left = rightMin->_right;
else
rightMinParent->_right = rightMin->_right;
delete rightMin;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}二叉搜索树的完整代码
BSTree.h
#pragma once
template<class K>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K>* _right;
K _key;
BSTreeNode(const K& key)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_key(key)
{}
};
template <class K> //key 关键字,进行比较
class BSTree //Binary Search Tree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
public:
//插入
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
//当树是空树的时候
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
//树不为空的时候
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (key > cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (key < cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key);
if (key > parent->_key)
parent->_right = cur;
else
parent->_left = cur;
return true;
}
//查找
bool Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (key > cur->_key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (key < cur->_key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//删除
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (key > cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (key < cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
//找到了,开始删除
// 1、左为空
// 2、右为空
// 3、左右都不为空
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (parent->_right == cur)
parent->_right = cur->_right;
else
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
delete cur;
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (parent->_left == cur)
parent->_left = cur->_left;
else
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
delete cur;
}
else
{
Node* rightMinParent = cur;
Node* rightMin = cur->_right;
while (rightMin->_left)
{
rightMinParent = rightMin;
rightMin = rightMin->_left;
}
//替代
cur->_key = rightMin->_key;
//转换成删除rightMin (rightMin是左为空,父亲指向它的右边)
if (rightMin == rightMinParent->_left)
rightMinParent->_left = rightMin->_right;
else
rightMinParent->_right = rightMin->_right;
delete rightMin;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//中序遍历
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
void TestBSTree()
{
BSTree<int> t;
int a[] = { 5,3,4,1,7,8,2,6,0,9 };
for (auto e : a)
{
t.Insert(e);
}
t.InOrder();
//1.上来我就删除7,有问题
t.Erase(7);
t.InOrder();
t.Erase(8);
t.InOrder();
//2.把这棵树删空,也会存在问题
/*for (auto e : a)
{
t.Erase(e);
}
t.InOrder();*/
叶子
t.Erase(2);
t.InOrder();
左为空或者右为空
t.Erase(8);
t.Erase(1);
t.InOrder();
左右都不为空
t.Erase(5);
t.InOrder();
}
test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include "BSTree.h"
int main()
{
TestBSTree();
return 0;
}
二叉搜索树的应用
Key 模型
- 在 Key 模型中,数据主要围绕一个关键标识符(Key)来组织。通常这个 Key 是一个唯一的标识,用于快速检索数据。例如,在一个简单的学生信息系统中,学生的学号可以作为 Key。系统可以根据学号快速查找对应的学生信息,但是可能存储的信息相对比较单一,主要就是和这个 Key 直接相关的内容。
- 它类似于一个索引,重点在于通过这个唯一的标识来定位某个特定的数据项。
- 以上二叉搜索树的实现使用的就是key模型
Key-Value 模型
- Key - Value 模型则是由一个 Key 和一个与之对应的 Value 组成的键值对。Key 仍然用于检索,但是 Value 可以是各种各样的数据结构,如字符串、数字、对象、数组等。比如在一个缓存系统中,Key 可以是一个 URL,Value 则是这个 URL 对应的网页内容。
- 这种模型更强调数据的关联性,Key 和 Value 共同构成了一个完整的数据单元,Value 的内容可以非常丰富,并且 Key 和 Value 之间存在一种明确的对应关系。
- Key 通常是设计为唯一的标识符,用于精确地定位和区分不同的键值对。而 Value 可以是相同的。例如,在一个记录用户购物偏好的系统中,Key 可以是用户的唯一标识(如用户 ID),Value 是用户喜欢的商品类别。多个用户(不同的 Key)可能都喜欢相同的商品类别(相同的 Value)。
- 实际中 Key-Value模型应用广泛。
改造二叉搜索树为KV结构
BSTree.h
#pragma once
// Key-Value 模型
template<class K, class V>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K, V>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K, V>* _right;
K _key;
V _value;
BSTreeNode(const K& key, const V& value)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _key(key)
, _value(value)
{}
};
template <class K, class V> //key 关键字,进行比较
class BSTree //Binary Search Tree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
//插入
bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value)
{
//当树是空树的时候
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key, value);
return true;
}
//树不为空的时候
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (key > cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (key < cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key, value);
if (key > parent->_key)
parent->_right = cur;
else
parent->_left = cur;
return true;
}
//查找
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (key > cur->_key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (key < cur->_key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
//删除
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (key > cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (key < cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
//找到了,开始删除
// 1、左为空
// 2、右为空
// 3、左右都不为空
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (parent->_right == cur)
parent->_right = cur->_right;
else
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
delete cur;
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (parent->_left == cur)
parent->_left = cur->_left;
else
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
delete cur;
}
else
{
Node* rightMinParent = cur;
Node* rightMin = cur->_right;
while (rightMin->_left)
{
rightMinParent = rightMin;
rightMin = rightMin->_left;
}
//替代
cur->_key = rightMin->_key;
//转换成删除rightMin (rightMin是左为空,父亲指向它的右边)
if (rightMin == rightMinParent->_left)
rightMinParent->_left = rightMin->_right;
else
rightMinParent->_right = rightMin->_right;
delete rightMin;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//中序遍历
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << ":" << root->_value << endl;
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
void TestBSTree()
{
//输入单词,查找单词对应的中文翻译
/*BSTree<string, string> dict;
dict.Insert("sort", "排序");
dict.Insert("string", "字符串");
dict.Insert("tree", "树");
dict.Insert("insert", "插入");
string str;
while (cin >> str)
{
BSTreeNode<string, string>* ret = dict.Find(str);
if (ret)
{
cout << ret->_value << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "无此单词" << endl;
}
}*/
//以后很常用,统计水果的个数
string strArr[] = { "西瓜","西瓜" ,"樱桃","苹果","香蕉","西瓜" ,"西瓜","哈密瓜" ,"西瓜" ,"西瓜" };
BSTree<string, int> countTree;
for (auto str : strArr)
{
BSTreeNode<string, int>* ret = countTree.Find(str);
if (ret == nullptr)
{
countTree.Insert(str, 1);
}
else
{
ret->_value++;
}
}
countTree.InOrder();
}
test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include "BSTree.h"
int main()
{
TestBSTree();
return 0;
}
二叉搜索树的性能分析
最好情况:
- 对于平衡的二叉搜索树,插入操作首先需要找到插入位置。因为树是平衡的,这个查找过程类似于查找操作,时间复杂度为 O(logN)。
- 找到位置后,插入新节点的操作本身时间复杂度为O(1) (只需要修改指针来连接新节点)。所以,整体插入操作在最好情况下的时间复杂度为O(logN)。
最坏情况:
- 当二叉搜索树退化为链表时,插入操作需要先遍历链表找到合适的插入位置。例如,若按照从小到大的顺序插入节点,要插入一个新的最大值,需要遍历到链表的末尾。此时,插入操作的时间复杂度为 O(N)。
问题:如果退化成单支树,二叉搜索树的性能就失去了。那能否进行改进,不论按照什么次序插入关键码,二叉搜索树的性能都能达到最优?那么就有我们后续学习的AVL树和红黑树。