1.vue3简单介绍
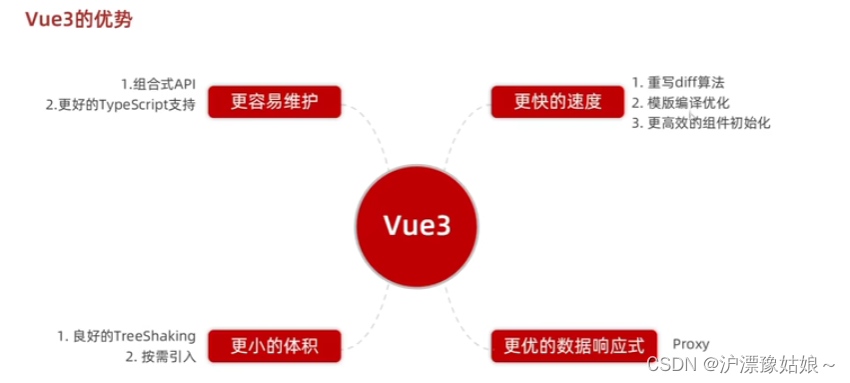
1.1 vue3的优势
1.2 vue3 VS vue2
需求:点击按钮,使数值+1
- vue2
<script>
export defaule{
data(){
return{
count:0
}
},
methods:{
addCount(){
this.count++
}
}
}
</script>
- vue3
<script setup>
import {ref} from 'vue'
const count=ref(0) //声明数据,声明一个0
const addCount=()=>count.value++
</script>
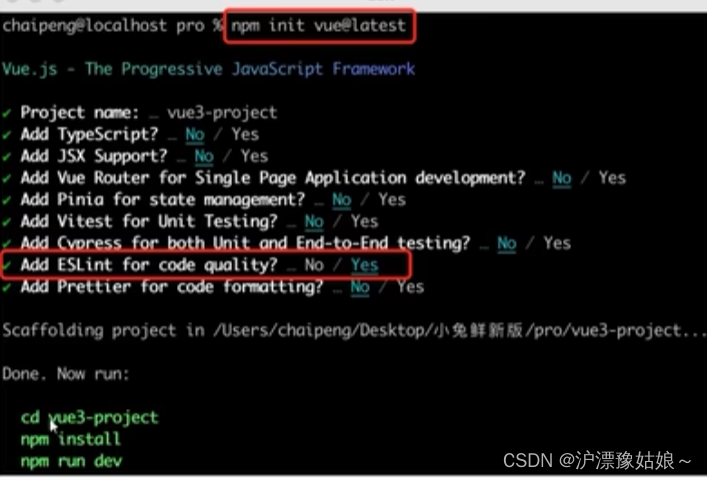
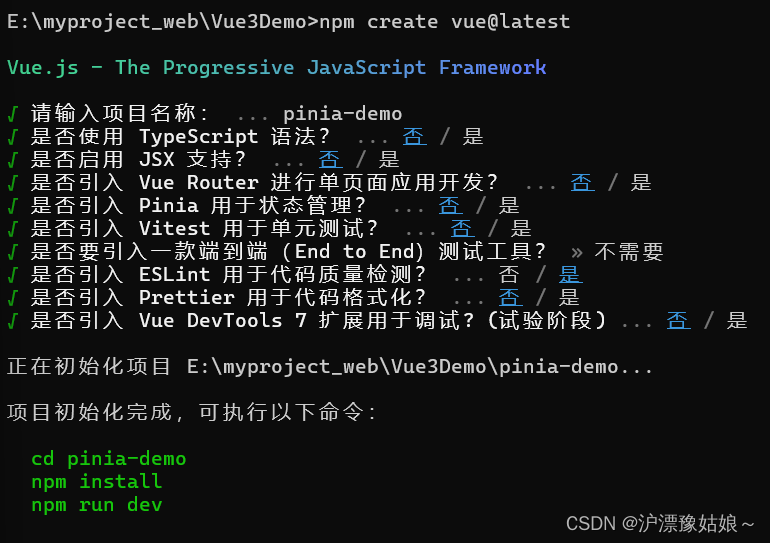
2.使用create-vue搭建vue3项目
2.1 认识create-vue
create-vue是Vue官方新的脚手架工具,底层切换到了vite(下一代构建工具),为开发提供极速响应。
2.2 使用create-vue创建项目
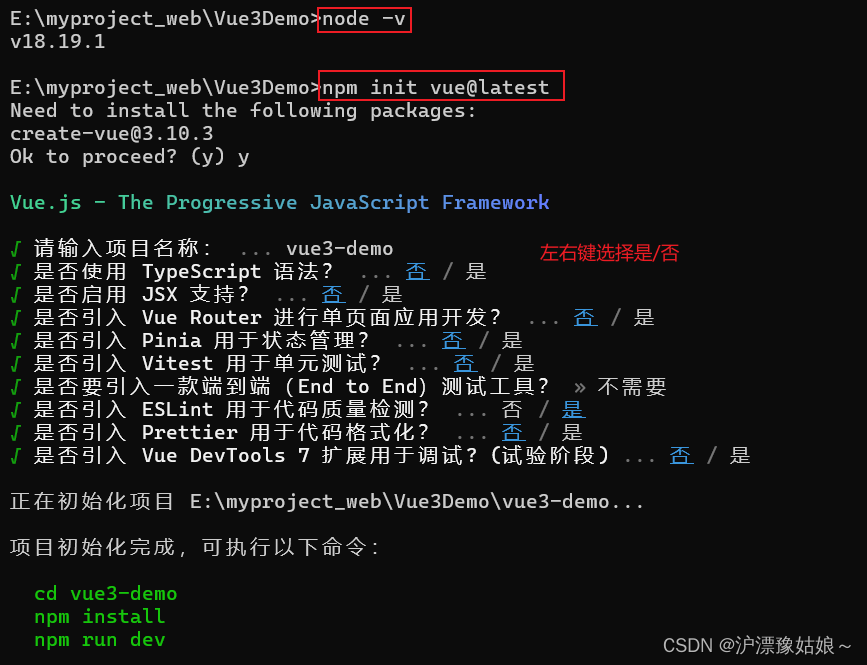
2.2.1 前提环境条件
已安装16.0或更高版本的Node.js
node -v
2.2.2 创建一个Vue应用
npm init vue@latest //这一指令将会安装并执行create-vue
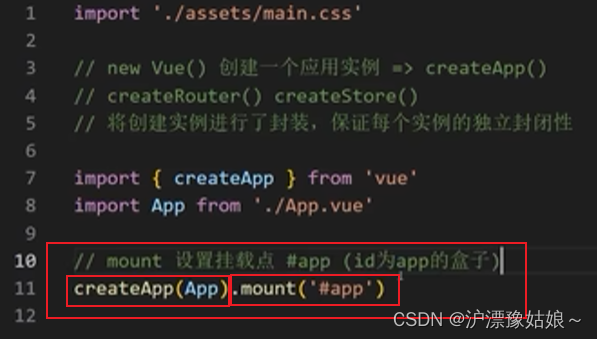
3.熟悉项目目录和关键文件
main.js
4.组合式API
4.1 组合式API - setup选项
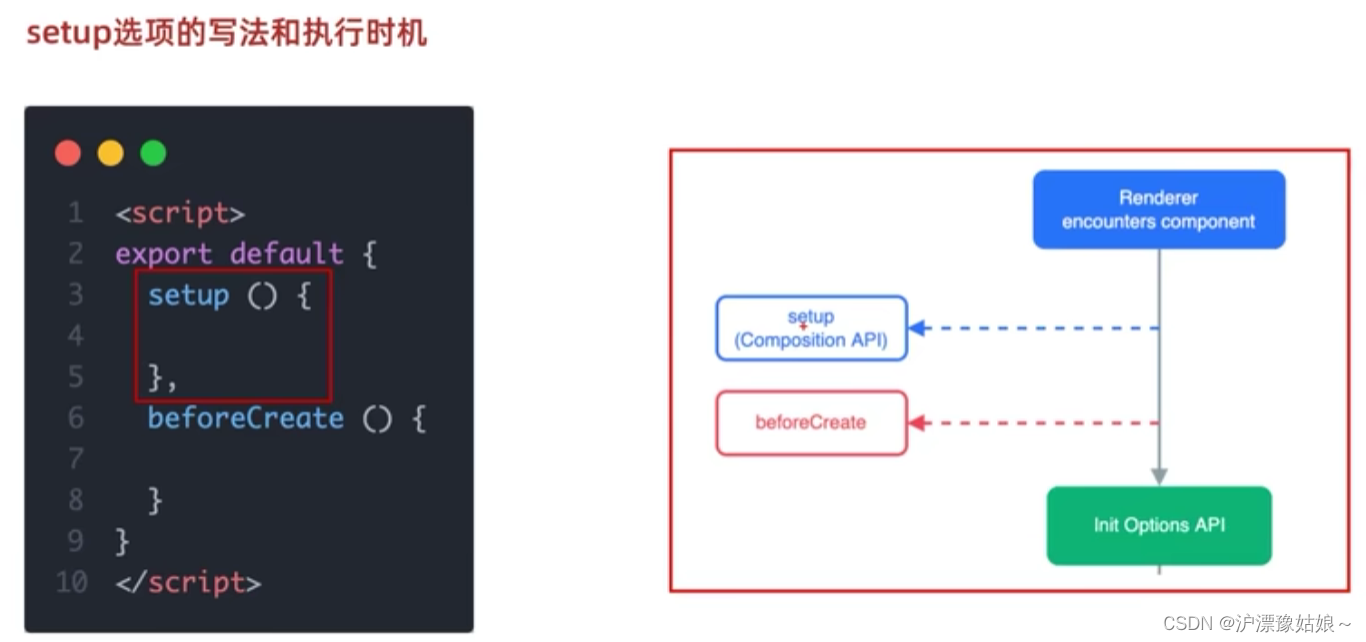
组合式API:可理解成一系列函数,通过调用这些函数来书写逻辑;
setup选项:组合式API的入口,只有写setup,才可以写组合式API函数
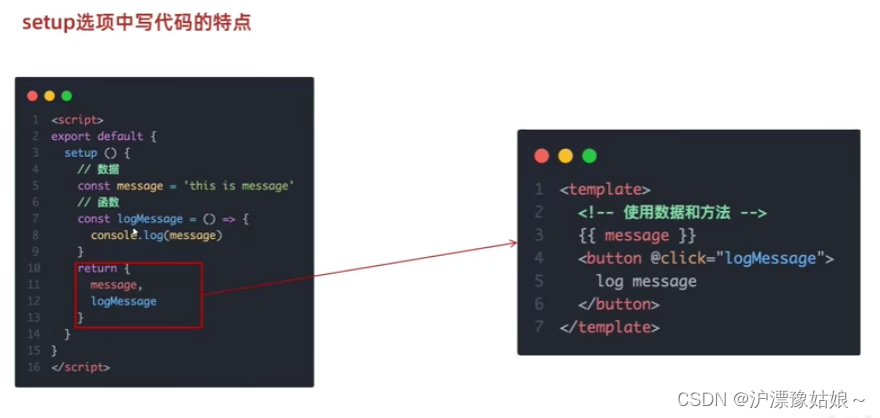
setup选项中写代码的特点
setup中的内容需要return:setup中可定义变量、函数,但这些都需要return,后面模板中才可以使用
<!--setup
1.执行时机比beforeCreate还要早
2.setup函数中,获取不到this(this是undefined)
3.数据和函数,需要在setup最后return,才能在模板中应用
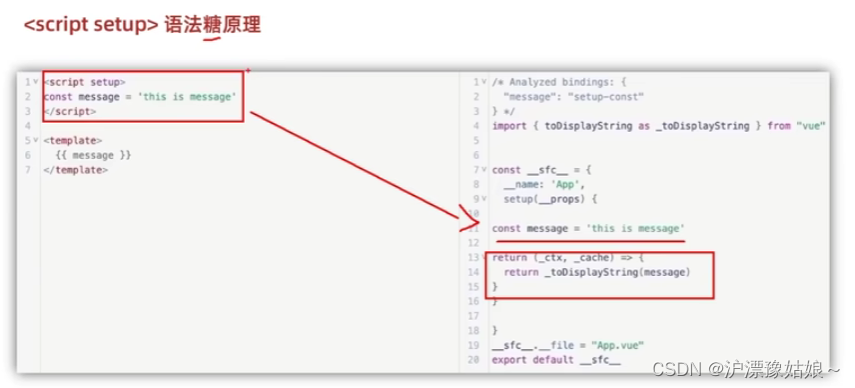
问题:每次都要对setup中的数据或函数进行return 太麻烦?
解决:直接在script标签中加个setup语法糖,如<script setup>后,不用再写return返回setup中的数据或函数
4.通过setup语法糖简化代码
-->
<!--<script>
export default {
setup() {
// console.log("setup函数",this)
// 数据
const message = "hello vue3"
// 函数
const logMessage = () => {
console.log(message)
}
return {
message,
logMessage
}
},
beforeCreate() {
console.log("beforeCreate函数")
}
}
</script>-->
<!--setup语法糖简化-->
<script setup>
// 数据
const message = "hello vue3"
// 函数
const logMessage = () => {
console.log(message)
}
</script>
<template>
<div>{{ message }}</div>
<button @click="logMessage">按钮</button>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
4.2 组合式API - reactive和ref函数
4.2.1 reactive() 处理对象类型数据
作用:接收对象类型数据的参数传入并返回一个响应式的对象;
4.2.2 ref() 处理简单类型或对象类型的数据
作用:接收简单类型或对象类型的数据传入并返回一个响应式的对象;
<!--
1.reactive():接收一个对象类型的数据,返回一个响应式的对象
问题:reactive是接收一个对象类型的数据,如果是简单类型的数据,应该怎么办?
解决:使用ref()函数处理简单类型数据
2.ref():接收一个简单类型 或 复杂类型,返回一个响应式的对象
本质:是再原有传入数据的基础上,外层包了一层,包成了复杂类型
底层:包成复杂类型之后,再借助reactive()实现响应式
注意:
1.在script脚本中访问数据,需要通过.value;
2.在template模板中访问数据,不需要加.value(帮我们扒了一层)
推荐:以后声明数据,统一使用ref=>统一了编码规范
-->
<script setup>
//1.reactive()
/*import {reactive} from "vue";
const state = reactive({
count: 100
})
const setCount = () => {
state.count++
}*/
//2.ref()
import {ref} from "vue";
const count=ref(0)
// console.log(count.value)
const addCount=()=>{
count.value++
}
const subCount=()=>{
count.value--
}
</script>
<template>
<div>
<div>{{ count }}</div>
<button @click="addCount">+1</button>
<button @click="subCount">-1</button>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
4.3 组合式API - computed计算属性函数
计算属性基本思想和Vue2的完全一致,组合式API下的计算属性只是修改了写法;
<!--
computed:计算属性基本思想和Vue2的完全一致,组合式API下的计算属性只是修改了写法;
-->
<script setup>
//基本语法:
//const 计算属性 = computed(()=>{return 计算返回的结果})
import {computed,ref} from "vue";
//声明数据
const list = ref([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
//基于list派生一个计算属性,要求从list中过滤出>2
const computedList = computed(() => {
return list.value.filter(item => item > 2)
})
//定义修改数组的方法
const addFn = (() => {
list.value.push(888)
})
</script>
<template>
<div>
<div>原始数据:{{ list }}</div>
<div>计算后的数据:{{ computedList }}</div>
<button type="button" @click="addFn">修改</button>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
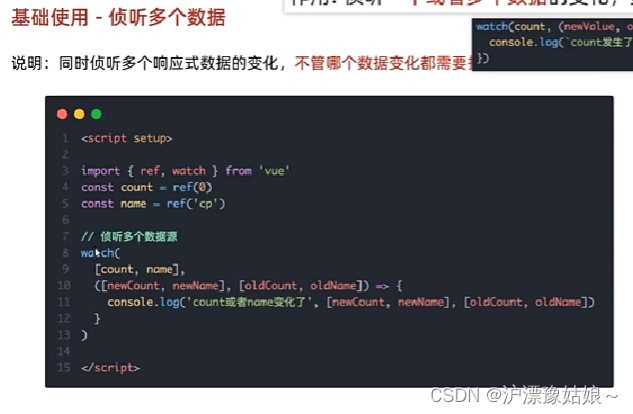
4.4 组合式API - watch
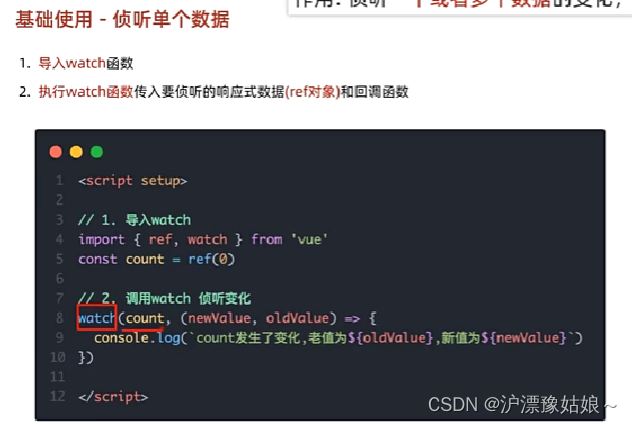
1.基础使用 - 侦听单个数据
<script setup>
//1.导入watch函数
import {ref,watch} from "vue";
//声明数据
const count = ref(0)
//2.调用watch侦听变化
//基本语法:
//watch(ref对象,回调函数),该watch侦听的作用,一旦count值发生变化,后面的回调函数就会自动执行
watch(count,(newValue,oldValue)=>{
console.log(`count发生了变化,老值为${oldValue},新值为${newValue}`)
})
</script>
- 基础使用 - 侦听多个数据
<script setup>
//(2)侦听多个数据
import {ref, watch} from 'vue'
const count = ref(0)
const name = ref('cp')
const updateCount=()=>{
count.value++
}
const updateName=()=>{
name.value="沪漂豫姑娘~"
}
//ref多个对象用数组包裹
watch([count, name], ([newCount, newName], [oldCount, oldName]) => {
console.log(`count或name变化了`, [newCount, newName], [oldCount, oldName])
})
</script>
<template>
<div>
<div>{{ count }}</div>
<button @click="updateCount"><span>+1</span></button>
<div>{{ name }}</div>
<button @click="updateName">改昵称</button>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
- 额外参数 - immediate
<script>
//(3)immediate 立刻执行
import {ref, watch} from "vue";
const count = ref(0)
const name = ref('张三')
const updateCount=()=>{
count.value++
}
const updateName=()=>{
name.value="沪漂豫姑娘~"
}
watch(count, (newValue,oldValue) => {
console.log(newValue,oldValue)
}, {
immediate: true
})
</script>
- 额外参数 - deep
<script>
//(4)deep 深度监视,默认的watch进行的是浅层监视,但如果需要监视复杂对象中的子属性数据的变化,可使用deep监视
//如果 const ref1=ref(简单类型),可以直接监视
//如果 const ref2=ref(复杂类型),监视不到复杂类型内部数据的变化(如果对象内部属性数据发生变化,但监视不到)
import {ref, watch} from "vue";
const userInfo = ref({
name: 'zs',
age: 18
})
const setUserInfo = () => {
// 修改了userInfo.value修改了对象的地址,才能监视到
// userInfo.value={name:'豫姑娘~',age:19}
userInfo.value.age++
}
watch(userInfo, (newValue) => {
console.log(newValue)
}, {
deep: true
})
</script>
- 精确侦听对象中的某个属性
<script>
// 需求:在不开启deep的前提下,侦听age的变化,只有age变化时才执行回调
import {ref, watch} from "vue";
const userInfo = ref({
name: 'zs',
age: 18
})
const setUserInfo = () => {
// 修改了userInfo.value修改了对象的地址,才能监视到
// userInfo.value={name:'豫姑娘~',age:19}
userInfo.value.age++
// userInfo.value.name="沪漂~"
}
watch(
() => userInfo.value.age, //监听对象中的指定属性,固定写法
(newValue,oldValue) => console.log(newValue,oldValue))
</script>
注意:
(1)作为watch函数的第一个参数,ref对象需要添加.value吗?
答:不需要,第一个参数就是传ref对象
(2)watch只能侦听单个数据吗?
答:单个或多个
(3)不开启deep,直接监视 复杂类型,修改属性能触发回调吗?
答:不能,默认是浅层监听(只可以监听简单类型的数据,不可以监听对象类型的数据)
(4)不开启deep,精确侦听对象的某个属性?
答:可以把第一个参数写成函数的写法,返回要监听的具体属性;
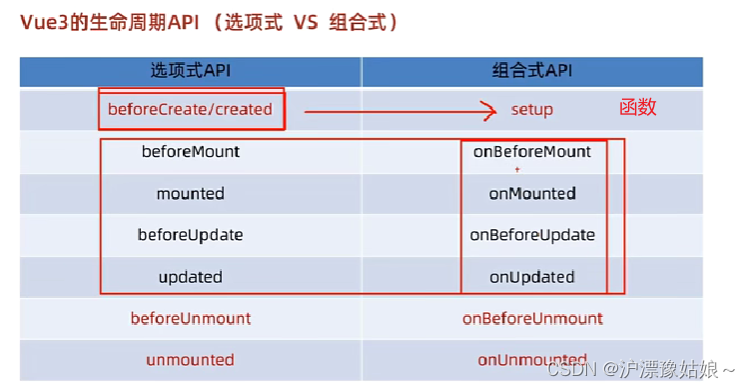
4.5组合式API - 生命周期函数
<!--组合式API - 生命周期函数
-->
<script setup>
//beforeCreate 和 created 的相关代码
//一律放到setup中执行
import {onMounted} from "vue";
const getList = () => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('发送请求,获取数据')
}, 2000)
}
//一进入页面,就会发送该请求
getList()
//如果有些代码需要在mounted生命周期中执行
onMounted(()=>{
console.log('mounted生命周期函数 - 逻辑1')
})
//写成函数的调用方式,可以调用多次,并不会冲突,而是按照顺序依次执行
onMounted(()=>{
console.log('mounted生命周期函数 - 逻辑2')
})
</script>
<template>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
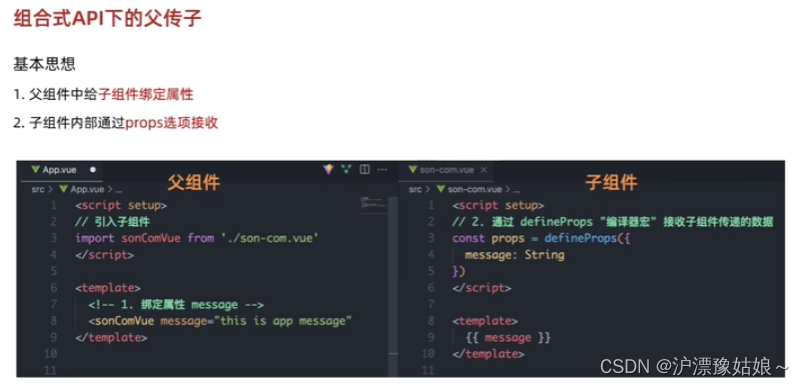
4.6 组合式API - 父子通信
4.6.1 父传子
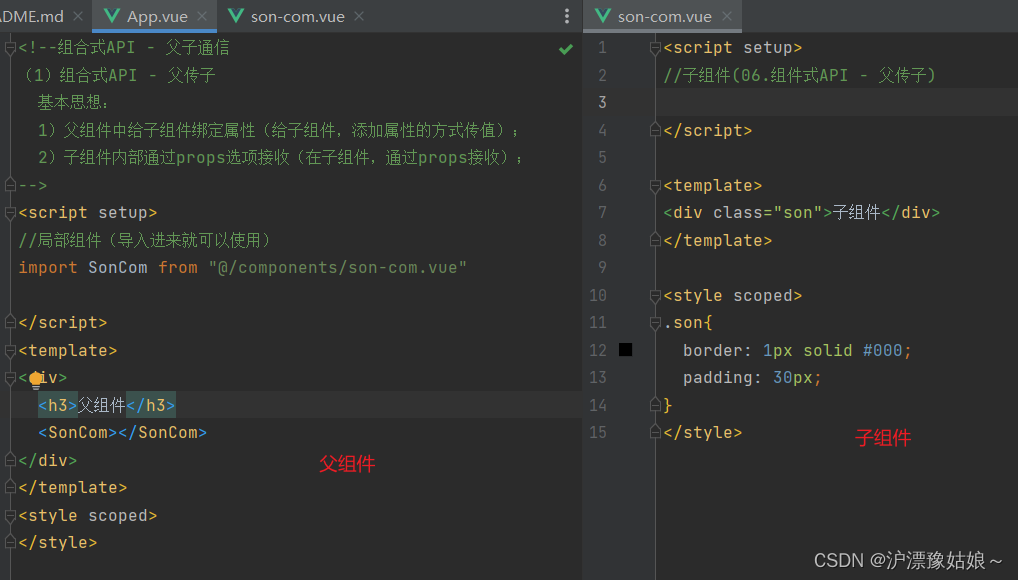
- 父组件 (App.vue)
<!--组合式API - 父子通信
(1)组合式API - 父传子
基本思想:
1)父组件中给子组件绑定属性(给子组件,添加属性的方式传值);
2)子组件内部通过props选项接收(在子组件,通过props接收);
-->
<script setup>
import {ref} from 'vue'
//局部组件(导入进来就可以使用)
import SonCom from "@/components/son-com.vue"
const money = ref(100)
const getMoney = () => {
money.value += 10
}
</script>
<template>
<div>
<h3>父组件 - {{ money }}
<button @click="getMoney">挣钱</button>
</h3>
<!-- 给子组件,添加属性的方式传值-->
<!-- :money="money将数据动态的传入给子组件-->
<SonCom car="宝马车" :money="money"></SonCom>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
- 子组件 (son-com.vue)
<script setup>
//子组件(06.组件式API - 父传子)
//注意:
//(1)由于写了 setup,所以无法直接配置props选项,此处需要借助于“ 编译器宏 ”函数defineProps(),接收子组件传递的数据
//(2)在脚本(script)中,调用父组件传过来的数据props,需要props.属性名进行使用,而在模板(template)中使用父组件传过来的数据props,可以直接使用(不用加props前缀)
const props=defineProps({
// 在此处写配置项,接收父组件穿过来的数据
car: String,
money: Number
})
// 使用props.属性名使用父组件传过来的数据
console.log(props.car)
console.log(props.money)
</script>
<template>
<!-- 直接使用父组件传过来props中的数据-->
<div class="son">子组件 - {{car}} - {{money}}</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
.son{
border: 1px solid #000;
padding: 30px;
}
</style>
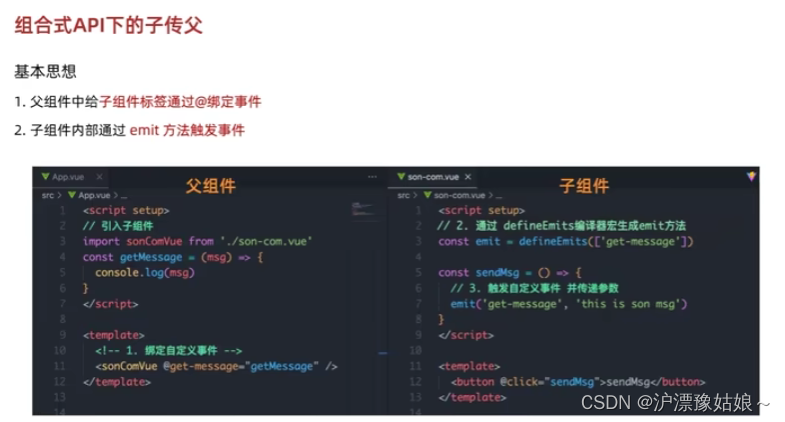
组合式API - 子传父
基本思想:
1)在子组件内部,通过emit方法触发事件(emit是通过编译器宏获取);
2)在父组件中,给子组件标签通过@绑定事件(通过@进行监听);
-->
<script setup>
import {ref} from 'vue'
//局部组件(导入进来就可以使用)
import SonCom from "@/components/son-com.vue"
const money = ref(100)
const getMoney = () => {
money.value += 10
}
//监听子组件发出的请求后,做出的处理函数
const changeFn=(newMoney)=>{
money.value=newMoney
}
</script>
<template>
<div>
<h3>父组件 - {{ money }}
<button @click="getMoney">挣钱</button>
</h3>
<!-- 给子组件,添加属性的方式传值-->
<!-- :money="money将数据动态的传入给子组件-->
<!-- @changeMoney="changeFn":是监听事件-->
<SonCom
@changeMoney="changeFn"
car="宝马车"
:money="money"></SonCom>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
- 子组件 (son-com.vue)
<script setup>
//子组件(06.组件式API - 父传子)
//注意:
//(1)由于写了 setup,所以无法直接配置props选项,此处需要借助于“ 编译器宏 ”函数defineProps(),接收子组件传递的数据
//(2)在脚本(script)中,调用父组件传过来的数据props,需要props.属性名进行使用,而在模板(template)中使用父组件传过来的数据props,可以直接使用(不用加props前缀)
const props=defineProps({
// 在此处写配置项,接收父组件穿过来的数据
car: String,
money: Number
})
//定义emit事件
const emit=defineEmits(["changeMoney"])
// 使用props.属性名使用父组件传过来的数据
console.log(props.car)
console.log(props.money)
//子传父
const buy=()=>{
// 需要emit触发事件(emit是通过defineProps编译器宏定义,如编译器定义的changeMoney)
// 直接使用编译器定义的事件,后面是传入的值,例如:5
emit("changeMoney",5)
}
</script>
<template>
<!-- 直接使用父组件传过来props中的数据-->
<div class="son">子组件 - {{car}} - {{money}}
<button @click="buy">花钱</button>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
.son{
border: 1px solid #000;
padding: 30px;
}
</style>
4.7 组合式API - 模板引用
vue3中的模板引用
- test-com.vue
<script setup>
const count=999
const sayHi=()=>{
console.log("hello")
}
//默认情况下,在setup语法糖下组件内部的属性和方法是不开放给父组件访问的
// 可通过defineExpose编译宏指定哪些数据和方法允许访问
//通过defineExpose编译宏指定的数据和方法,在父组件中导入该子组件后就可以直接使用defineExpose指定的数据和方法
defineExpose({
count,
sayHi
})
</script>
<template>
<div>
测试组件 - {{count}}
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
- App.vue
<!--组合式API - 模板引用
//模板引用(可以获取dom,也可以获取组件)
通过ref表示获取真实的dom对象或组件实例对象
1.调用ref函数生成一个ref对象;
2.通过ref标识绑定ref对象到标签;
3.通过ref对象,value即可访问到绑定元素(必须在渲染完成后,才可以拿到);
-->
<script setup>
//导入子组件,在该组件中可以使用导入的子组件中的defineExpose中的属性和方法
import TestCom from "@/components/test-com.vue"
import {onMounted, ref} from 'vue'
//模板引用(可以获取dom,也可以获取组件)
//1.调用ref函数生成一个ref对象
const inp = ref(null)
//生命周期钩子 onMounted
onMounted(() => {
console.log('页面打开自动聚焦')
inp.value.focus() //一进页面就聚焦
// clickFn()
})
const clickFn = () => {
console.log("点击按钮,进行聚焦")
inp.value.focus()
}
//-----------------------------
const testRef=ref(null)
const getCom=()=>{
console.log(testRef.value.count)
// console.log(testRef.value.sayHi())
testRef.value.sayHi()
}
</script>
<template>
<div>
<!-- 2.通过ref标识绑定ref对象-->
<!-- <h1 ref="inp">我是dom标签h1</h1>-->
<input ref="inp" type="text">
<button @click="clickFn">点击聚焦输入框</button>
</div>
<TestCom ref="testRef"></TestCom>
<button @click="getCom">获取组件</button>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
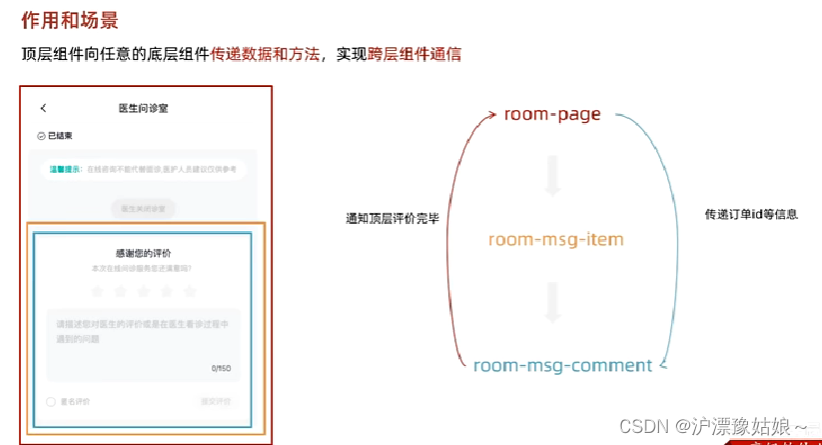
4.8 组合式API - provide 和 inject
1.顶部组件(APP.vue)
<!--
组合式API - provide和inject
跨层传递普通数据
1.顶层组件通过provide函数提供数据;
2.底层组件通过inject函数获取数据
-->
<script setup>
import {onMounted, provide, ref} from 'vue'
import CenterCom from "@/components/center-com.vue"
//1.跨层传递普通数据
provide("theme-color",'pink')
//2.跨层传递复杂数据
provide('userInfo',{
name:'豫姑娘~',
age:18
})
//3.跨层传递响应式数据
const count=ref(100)
provide("count",count)
//4.跨层传递函数=>给子孙后代传递可以修改数据的方法
provide("changeCount",(num)=>{
count.value=count.value+num
})
</script>
<template>
<div>
<h1>顶层组件</h1>
<CenterCom></CenterCom>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
- 中间组件(center-com.vue)
<script setup>
import centerCom from "@/components/bottom-com.vue"
</script>
<template>
<div>
<h2>中间组件</h2>
<center-com></center-com>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
- 底部组件(bottom-com.vue)
<script setup>
import {inject} from "vue";
const color = inject('theme-color')
const userInfo = inject("userInfo")
const count = inject("count")
//祖先组件传入的修改数据的方法
const changeCount = inject("changeCount")
const clickFn = (num) => {
changeCount(num)
}
</script>
<template>
<div>
<h3>底部组件</h3>
<p>普通数据:{{ color }}</p>
<p>复杂数据:{{ userInfo.name }}------{{ userInfo.age }}</p>
<p>响应式数据count:{{ count }}</p>
<button @click="clickFn(100)">+100</button>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
5.vue3新特性
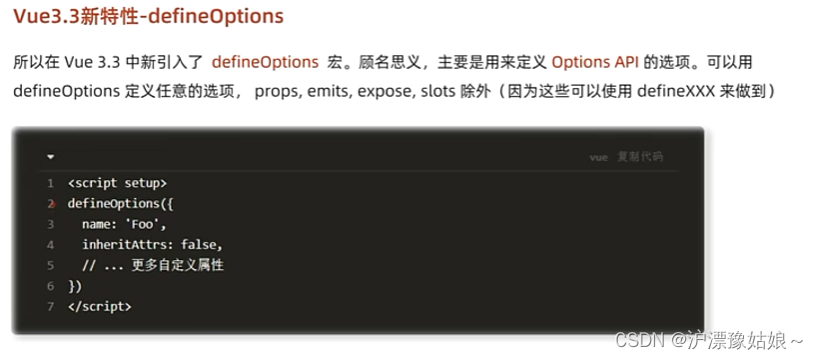
5.1 defineOptions
在script标签中使用defineOptions编译器方法给组件命名
<script setup>
defineOptions({
//给组件命名
name:'RegisterIndex'
})
</script>
给views/login/index.vue对应组件重新命名
<script setup>
defineOptions({
//给组件命名
name:'RegisterIndex'
})
</script>
<template>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
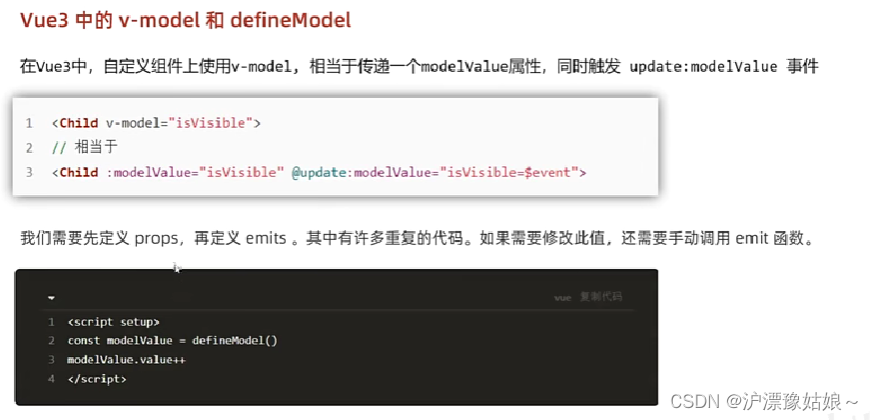
5.2 defineModel
- APP.vue
<!--
vue3新特性 - defineModel
-->
<script setup>
import inputCom from '@/components/input-com.vue'
import {ref} from "vue";
const txt = ref('vue3新特性,defineModel')
</script>
<template>
<div>
<inputCom v-model="txt"></inputCom>
{{ txt }}
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
- input-com.vue(input-com-copy.vue简写)
<script setup>
import {defineModel} from "vue";
//vue3新特性
const modelValue = defineModel()
</script>
<template>
<div>
<input type="text"
:value="modelValue"
@input="e=>modelValue=e.target.value">
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
- input-com-copy.vue
<script setup>
defineOptions({
name:"input-com",
//接收modelValue传入的数据
modelValue:String
})
//使用defineEmits定义当前emit方法
const emit=defineEmits(['update:modelValue'])
</script>
<template>
<div>
<input type="text"
:value="modelValue"
@input="e=>emit('update:modelValue',e.target.value)">
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
- vite.config.js
import { fileURLToPath, URL } from 'node:url'
import { defineConfig } from 'vite'
import vue from '@vitejs/plugin-vue'
// https://vitejs.dev/config/
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [
vue({
script:{
defineModel:true //声明使用defineModel
}
}),
],
resolve: {
alias: {
'@': fileURLToPath(new URL('./src', import.meta.url))
}
}
})
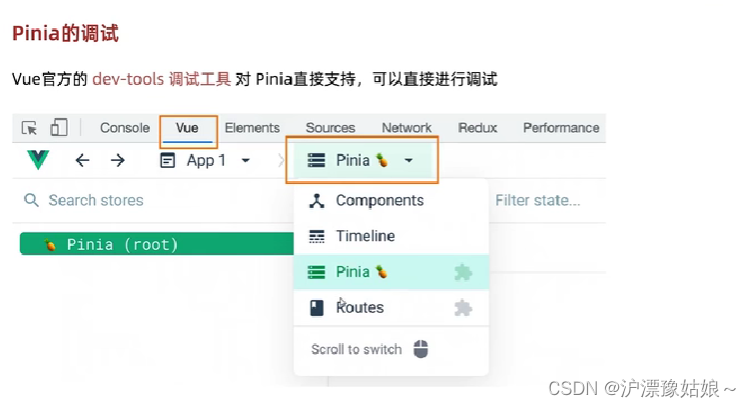
6.Pinia快速入门
6.1 什么是Pinia?
6.2 手动将Pinia添加到项目中?
将Pinia添加到项目中的整体步骤:
(1)新建一个vue3项目;
(2)在项目中安装pinia;
npm install pinia //在项目中安装pinia
(3)在main.js中导入pinia;
(4)在各组件中使用;
- main.js
import {createApp} from 'vue'
import {createPinia} from 'pinia'
import App from './App.vue'
const pinia=createPinia() //创建Pinia实例
const app=createApp(App) //创建根实例
app.use(pinia) //pinia插件的安装配置
app.mount('#app') //视图的挂载
- App.vue
<script setup>
import Son1Com from "@/components/son1-com.vue"
import Son2Com from "@/components/son2-com.vue"
</script>
<template>
<div>
<h1>App.vue根组件 - 0</h1>
<Son1Com></Son1Com>
<Son2Com></Son2Com>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
- son1-com.vue
<script setup>
defineProps({
name:"Son1Com"
})
</script>
<template>
<div>son1Com - 0 - <button>+</button></div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
- son2-com.vue
<script setup>
defineOptions({
name:"son2Com"
})
</script>
<template>
<div>Son2Com - 0 - <button>-</button></div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
6.3 Pinia基本语法
Pinia基础使用 - 计数器案例
1). 定义store;
2). 组件使用store;
- App.vue
<script setup>
import Son1Com from "@/components/son1-com.vue"
import Son2Com from "@/components/son2-com.vue"
//使用store中仓库的值
import {useCounterStore} from "@/store/count.js"
const countStore = useCounterStore() //获取store中的对象
const countStoreCount=countStore.count //获取store中对象的值
const countStoreMsg=countStore.msg //获取store对象中的值
</script>
<template>
<div>
<h1>App.vue根组件 - 0</h1>
<h2>{{countStoreCount}} --- {{countStoreMsg}}</h2>
<Son1Com></Son1Com>
<Son2Com></Son2Com>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
- store/count.js(store仓库,该仓库中的数据可以提供给多个组件使用)
import {defineStore} from "pinia";
import {ref,computed} from 'vue'
//定义store仓库数据(多组件可以共享的数据)
// defineStore(仓库的唯一标识(参数1),()=>{...}(参数2))
/**
* useCounterStore 基于该名使用仓库中的值
* export 导出
* @type {StoreDefinition<"counter", _ExtractStateFromSetupStore<{msg: Ref<UnwrapRef<string>>, count: Ref<UnwrapRef<number>>}>, _ExtractGettersFromSetupStore<{msg: Ref<UnwrapRef<string>>, count: Ref<UnwrapRef<number>>}>, _ExtractActionsFromSetupStore<{msg: Ref<UnwrapRef<string>>, count: Ref<UnwrapRef<number>>}>>}
*/
// 1.创建仓库,基于useCounterStore就可以获取函数,进而使用该仓库中的值
export const useCounterStore = defineStore("counter", () => {
// 声明数据 state - count
const count = ref(100)
// 声明操作数据的方法 action(普通函数)
const addCount = () => {
count.value++
}
const subCount = () => {
count.value--
}
// 声明基于数据派生的的计算属性 getters(computed)
const double = computed(() =>
count.value * 2
)
// 声明数据 state - msg
const msg = ref("hello pinia")
return {
count, //count属性
double, //计算属性
addCount, //方法1
subCount, //方法2
msg
}
})
- son1-com.vue(调用count.js仓库中的数据)
<script setup>
defineProps({
name:"Son1Com"
})
import {useCounterStore} from "@/store/count.js";
const countStore=useCounterStore() //获取仓库中的数据对象
const count=countStore.count //获取仓库对象中的值
const msg=countStore.msg
const double=countStore.double
</script>
<template>
<!-- 注意:当在js脚本中将对象中的属性分离出来时,在修改原对象中的值时,无法修改分离出的对象属性值不被修改-->
<div>son1Com(获取js模块中分离出的对象中的各属性值)
- {{count}} -{{msg}} - {{double}}
- <button @click="countStore.addCount">+</button></div>
<div>son1Com(直接根据对象引用其中的值)
- {{countStore.count}} -{{countStore.msg}} - {{countStore.double}}
- <button @click="countStore.subCount">-</button></div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
6.4 Pinia - action异步写法
- store/channel.js(仓库数据)
import {defineStore} from 'pinia'
import axios from "axios";
import {ref} from 'vue'
//仓库变量的命名(use+仓库名+Store)
export const useChannelStore=defineStore("channel",()=>{
// 声明数据
const channelList=ref([])
// 声明操作数据的方法
const getList=async ()=>{
// 支持异步({data:{data}}是解构返回的数据)
const {data:{data}}=await axios.get("http://geeek.itheima.net/v1_0/channels")
channelList.value=data.channels
console.log(data.channels)
}
// 声明getters相关
// 返回数据及方法
return {
channelList,
getList
}
})
- App.vue(引用channel.js中的数据)
<script setup>
import Son1Com from "@/components/son1-com.vue"
import Son2Com from "@/components/son2-com.vue"
//使用store中仓库的值
import {useCounterStore} from "@/store/count.js"
import {useChannelStore} from "./store/channel.js"
const countStore = useCounterStore() //获取store中的counter对象
const channelStore=useChannelStore() //获取store中的channel对象
const countStoreCount=countStore.count //获取store中对象的值
const countStoreMsg=countStore.msg //获取store对象中的值
</script>
<template>
<div>
<h1>App.vue根组件 - 0</h1>
<h2>{{countStoreCount}} --- {{countStoreMsg}}</h2>
<Son1Com></Son1Com>
<Son2Com></Son2Com>
<hr>
<button @click="channelStore.getList()">获取频道数据</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="item in channelStore.channelList">新闻</li>
<li>音乐</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
6.5 Pinia - storeToRefs方法
App.vue
<script setup>
//导入storeToRefs方法,避免直接解构会失去响应式
import {storeToRefs} from 'pinia'
import Son1Com from "@/components/son1-com.vue"
import Son2Com from "@/components/son2-com.vue"
//使用store中仓库的值
import {useCounterStore} from "@/store/count.js"
import {useChannelStore} from "./store/channel.js"
const countStore = useCounterStore() //获取store中的counter对象
const channelStore=useChannelStore() //获取store中的channel对象
//此时,直接解构,不处理,数据会丢失响应式(希望解构后仍保持响应式)
// const {count,msg} = counterStore
//使用storeToRefs保持解构后数据的响应式
/**
* 对数据的解构处理
*/
const {count,msg} = storeToRefs(countStore)
const {channelList} = storeToRefs(channelStore)
/**
* 对方法的解构处理
*/
const {getList} = channelStore
// const countStoreCount=countStore.count //获取store中对象的值
// const countStoreMsg=countStore.msg //获取store对象中的值
</script>
<template>
<div>
<h1>App.vue根组件 - 0</h1>
<h2>{{count}} --- {{msg}}</h2>
<Son1Com></Son1Com>
<Son2Com></Son2Com>
<hr>
<button @click="getList">获取频道数据</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="item in channelList" :key="item.id">新闻</li>
<li>音乐</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>
6.6 Pinia - 持久化
在对数据进行处理之后,保持着最新的数据,即使刷新页面,其数据也保持处理后的值。
(内部原理:修改数据时,将修改后的数据存放到本地,刷新页面时,首先从本地查询)

//导入持久化插件
import piniaPluginPersistedstate from 'pinia-plugin-persistedstate'
(2)在main.js中使用持久化插件
app.use(pinia.use(piniaPluginPersistedstate)) //pinia插件的安装配置
(3)在仓库中对数据进行持久化操作
defineStore(仓库的唯一标识(参数1),()=>{…}(参数2),导入的持久化(piniaPluginPersistedstate):true(开启当前模块数据的持久化))
// 1.创建仓库,基于useCounterStore就可以获取函数,进而使用该仓库中的值
export const useCounterStore = defineStore("counter", () => {
// 声明数据 state - count
const count = ref(100)
// 声明操作数据的方法 action(普通函数)
const addCount = () => {
count.value++
}
const subCount = () => {
count.value--
}
// 声明基于数据派生的的计算属性 getters(computed)
const double = computed(() =>
count.value * 2
)
// 声明数据 state - msg
const msg = ref("hello pinia")
return {
count, //count属性
double, //计算属性
addCount, //方法1
subCount, //方法2
msg
}
}, {
piniaPluginPersistedstate: true //开启当前模块的持久化
})
- main.js
import {createApp} from 'vue'
import {createPinia} from 'pinia'
import App from './App.vue'
//导入持久化插件
import piniaPluginPersistedstate from 'pinia-plugin-persistedstate'
const pinia=createPinia() //创建Pinia实例
const app=createApp(App) //创建根实例
app.use(pinia.use(piniaPluginPersistedstate)) //pinia插件的安装配置
app.mount('#app') //视图的挂载
- count.js
import {defineStore} from "pinia";
import {computed, ref} from 'vue'
//定义store仓库数据(多组件可以共享的数据)
// defineStore(仓库的唯一标识(参数1),()=>{...}(参数2),导入的持久化(piniaPluginPersistedstate):true(开启当前模块的持久化))
/**
* useCounterStore 基于该名使用仓库中的值
* export 导出
* @type {StoreDefinition<"counter", _ExtractStateFromSetupStore<{msg: Ref<UnwrapRef<string>>, count: Ref<UnwrapRef<number>>}>, _ExtractGettersFromSetupStore<{msg: Ref<UnwrapRef<string>>, count: Ref<UnwrapRef<number>>}>, _ExtractActionsFromSetupStore<{msg: Ref<UnwrapRef<string>>, count: Ref<UnwrapRef<number>>}>>}
*/
// 1.创建仓库,基于useCounterStore就可以获取函数,进而使用该仓库中的值
export const useCounterStore = defineStore("counter", () => {
// 声明数据 state - count
const count = ref(100)
// 声明操作数据的方法 action(普通函数)
const addCount = () => {
count.value++
}
const subCount = () => {
count.value--
}
// 声明基于数据派生的的计算属性 getters(computed)
const double = computed(() =>
count.value * 2
)
// 声明数据 state - msg
const msg = ref("hello pinia")
return {
count, //count属性
double, //计算属性
addCount, //方法1
subCount, //方法2
msg
}
}, {
// piniaPluginPersistedstate: true //开启当前模块的持久化
piniaPluginPersistedstate: {
key:'piniaData' , //key是持久化数据往本地存放时的key值(本地存储的唯一标识),此时key作为键值,持久化数据作为值
paths:['count'] //指定持久化数据(对模块中特定数据进行持久化)(无此项则表示对该模块中的数据全部进行持久化)
}
})