这是educoder平台,机器学习-实验四-编程实现基于信息增益进行划分选择的决策树算法的代码详解与解决过程详解,创造不易,请大家点点赞,收藏藏!
目录
1.导包 加载数据
from math import log
import operator
def loaddata():
dataSet = [[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 'yes'],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 'yes'],
[2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 'yes'],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 'no'],
[0, 2, 2, 0, 2, 1, 'no'],
[2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 0, 'no'],
[2, 0, 0, 2, 2, 1, 'no'],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 'no'],
[2, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 'no'],
[1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 'no'],
[2, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0, 'no'],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 'no']]
feature_name = ['a1', 'a2', 'a3', 'a4', 'a5', 'a6']
return dataSet, feature_name2. 计算信息熵
def entropy(dataSet):
# 数据集条数
m = len(dataSet)
# 保存所有的类别及属于该类别的样本数
labelCounts = {}
for featVec in dataSet:
currentLabel = featVec[-1]
if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys():
labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0
labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1
# 保存熵值
e = 0.0
# 补充计算信息熵的代码
for key in labelCounts:
prob = float(labelCounts[key]) / m
e -= prob * log(prob, 2)
return e3.对数据进行划分
def splitDataSet(dataSet, axis, value):
# 补充按给定特征和特征值划分好的数据集的代码
# axis对应的是特征的索引;
retDataSet = []
# 遍历数据集
for featVec in dataSet:
if featVec[axis] == value:
reduceFeatVec = featVec[:axis]
reduceFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis + 1:])
retDataSet.append(reduceFeatVec)
return retDataSet4.计算信息的熵,条件熵,信息增益来保存最好的属性
def chooseBestFeature(dataSet):
n = len(dataSet[0]) - 1
# 计数整个数据集的熵
baseEntropy = entropy(dataSet)
bestInfoGain = 0.0;
bestFeature = -1
# 遍历每个特征
for i in range(n):
# 获取当前特征i的所有可能取值
featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet]
uniqueVals = set(featList)
newEntropy = 0.0
# 遍历特征i的每一个可能的取值
for value in uniqueVals:
# 按特征i的value值进行数据集的划分
subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, i, value)
# 补充计算条件熵的代码
prob = len(subDataSet) / float(len(dataSet))
newEntropy += prob * entropy(subDataSet)
# 计算信息增益
infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy
# 保存当前最大的信息增益及对应的特征
if (infoGain > bestInfoGain):
bestInfoGain = infoGain
bestFeature = i
return bestFeature5.对数据进行排序处理
def classVote(classList):
# 定义字典,保存每个标签对应的个数
classCount = {}
for vote in classList:
if vote not in classCount.keys():
classCount[vote] = 0
classCount[vote] += 1
# 排序
sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
return sortedClassCount[0][0]6.进行划分,生成决策树 (核心代码)
def trainTree(dataSet, feature_name):
classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet]
# 所有类别都一致
if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList):
return classList[0]
# 数据集中没有特征
if len(dataSet[0]) == 1:
return classVote(classList)
# 选择最优划分特征
bestFeat = chooseBestFeature(dataSet)
bestFeatName = feature_name[bestFeat]
myTree = {bestFeatName: {}}
featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet]
uniqueVals = set(featValues)
# 遍历uniqueVals中的每个值,生成相应的分支
for value in uniqueVals:
sub_feature_name = feature_name[:]
# 生成在dataSet中bestFeat取值为value的子集;
sub_dataset = splitDataSet(dataSet, bestFeat, value)
# 根据得到的子集,生成决策树
myTree[bestFeatName][value] = trainTree(sub_dataset, sub_feature_name)
return myTree7.编写预测函数
def predict(inputTree, featLabels, testVec):
firstStr = list(inputTree.keys())[0]
secondDict = inputTree[firstStr]
featIndex = featLabels.index(firstStr)
key = testVec[featIndex]
valueOfFeat = secondDict[key]
if isinstance(valueOfFeat, dict):
classLabel = predict(valueOfFeat, featLabels, testVec)
else:
classLabel = valueOfFeat
return classLabel8.测试代码,进行测试代码的正确
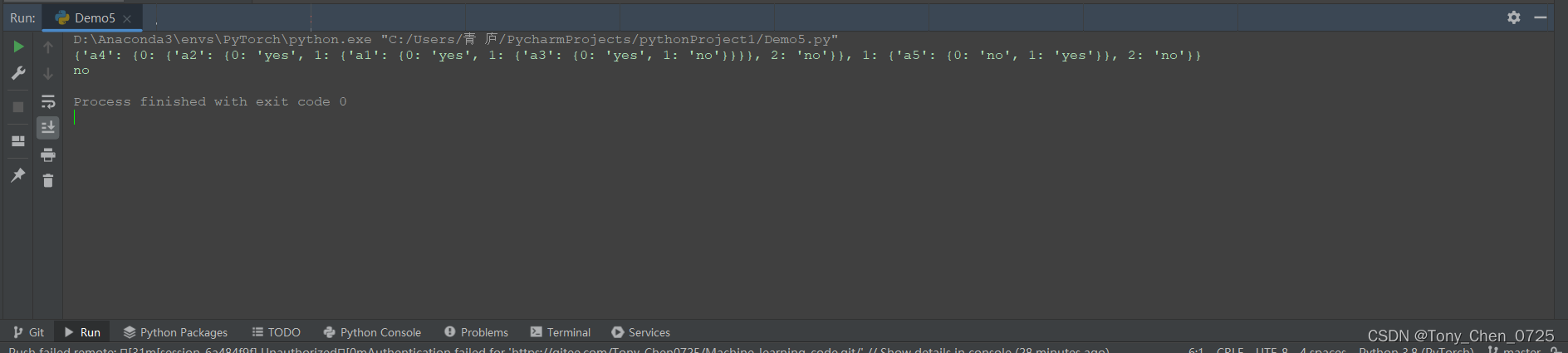
myDat, feature_name = loaddata()
myTree = trainTree(myDat, feature_name)
print(myTree)
print(predict(myTree, feature_name, [1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0]))