SpringAop
aop定义
AOP:Aspect Oriented Programming(面向切面编程、面向方面编程),其实说白了,面向切面编程就是面向特定方法编程
AOP的优势主要体现在以下四个方面:
- 减少重复代码:不需要在业务方法中定义大量的重复性的代码,只需要将重复性的代码抽取到AOP程序中即可。
- 代码无侵入:在基于AOP实现这些业务功能时,对原有的业务代码是没有任何侵入的,不需要修改任何的业务代码。
- 提高开发效率
- 维护方便
核心概念
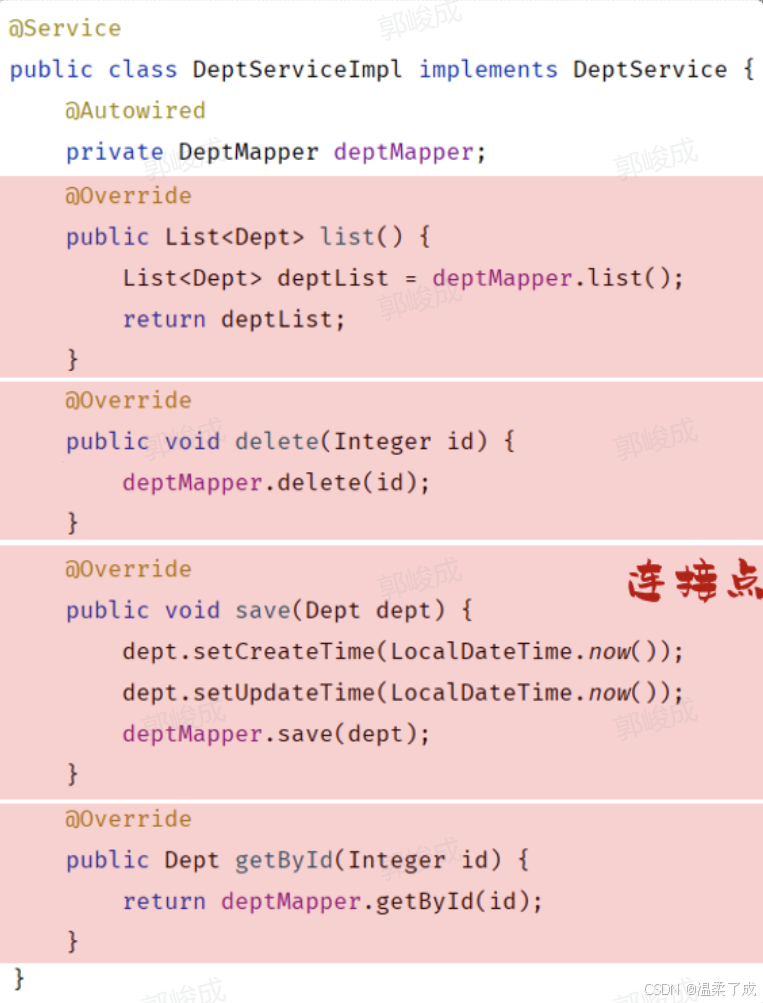
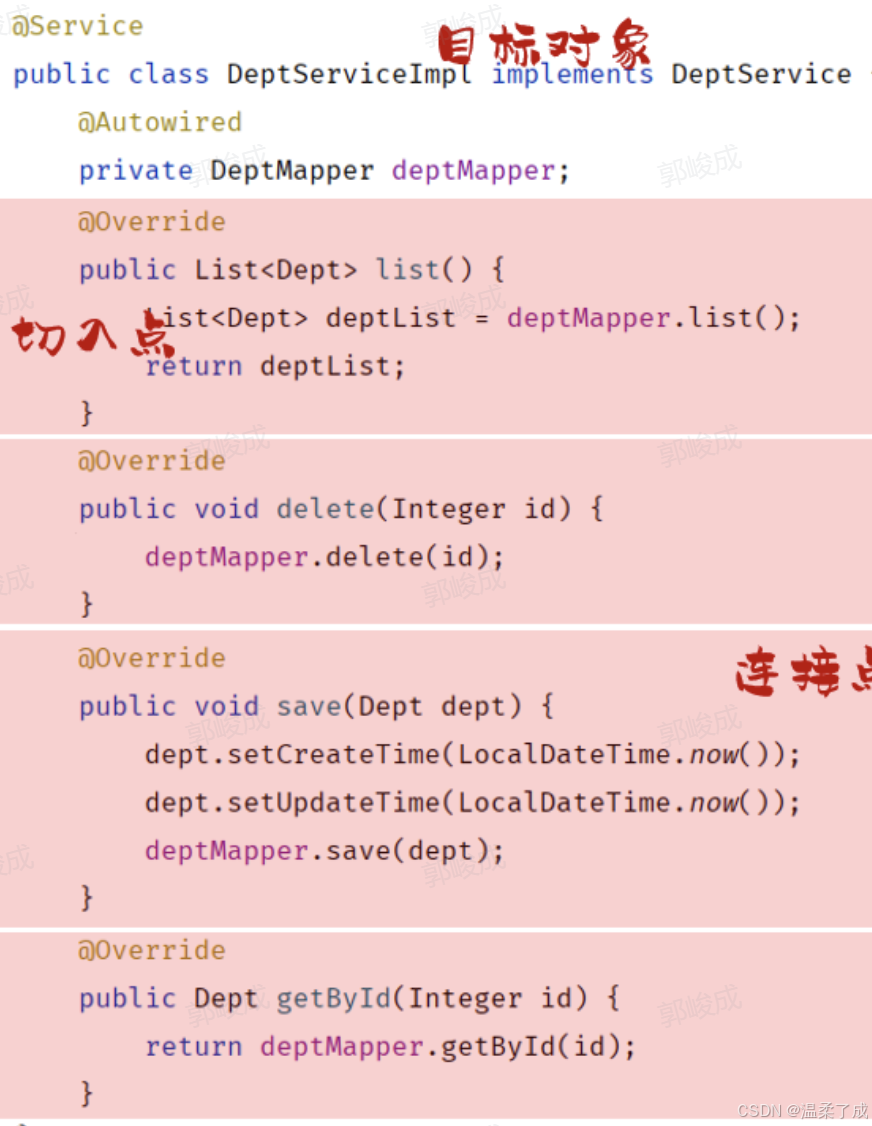
1. 连接点:JoinPoint,可以被AOP控制的方法(暗含方法执行时的相关信息)
- 连接点指的是可以被aop控制的方法。例如:入门程序当中所有的业务方法都是可以被aop控制的方法。
- 在SpringAOP提供的JoinPoint当中,封装了连接点方法在执行时的相关信息
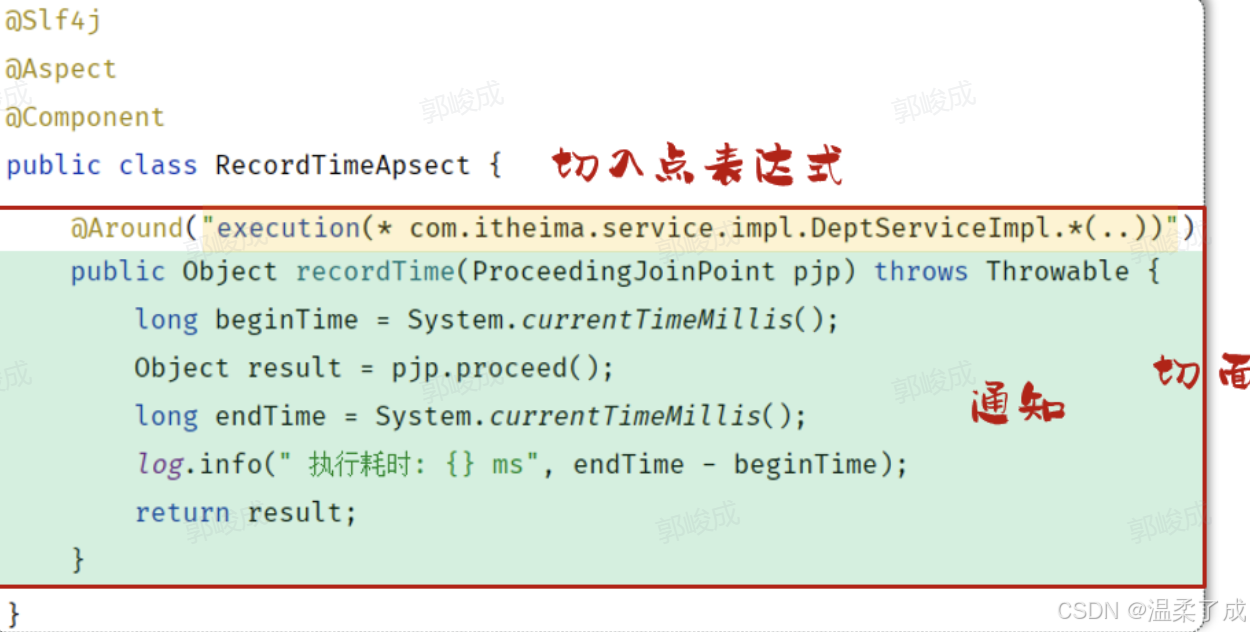
2.通知:Advice,指哪些重复的逻辑,也就是共性功能(最终体现为一个方法)
- 在入门程序中是需要统计各个业务方法的执行耗时的,此时我们就需要在这些业务方法运行开始之前,先记录这个方法运行的开始时间,在每一个业务方法运行结束的时候,再来记录这个方法运行的结束时间。
- 是在AOP面向切面编程当中,我们只需要将这部分重复的代码逻辑抽取出来单独定义。抽取出来的这一部分重复的逻辑,也就是共性的功能。
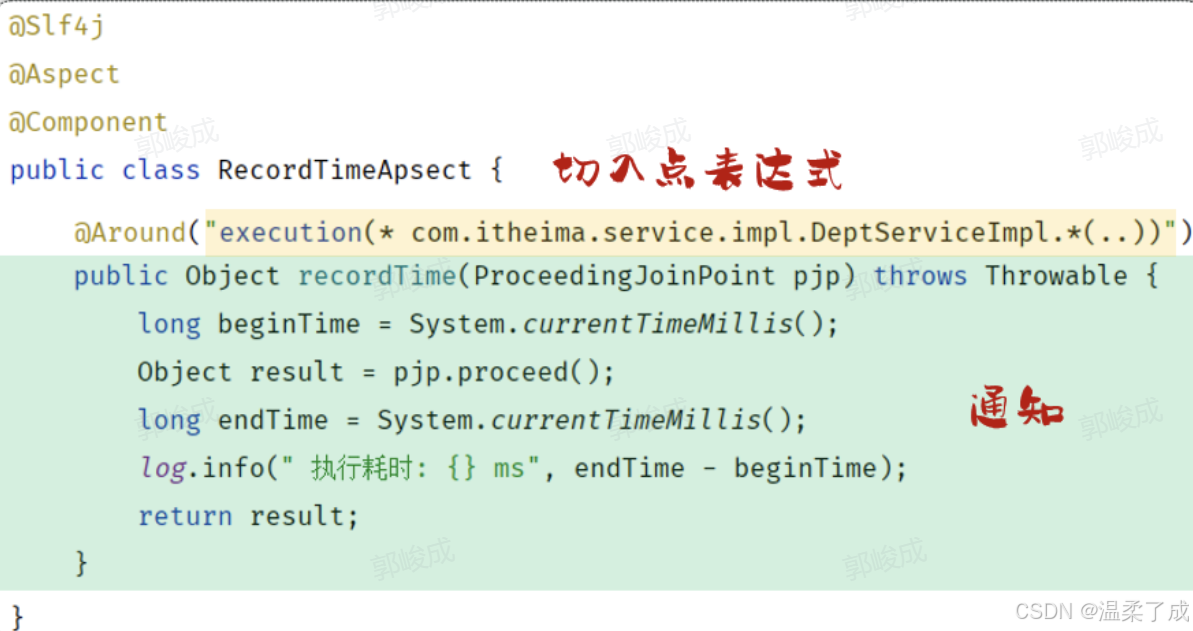
**3.切入点:**PointCut,匹配连接点的条件,通知仅会在切入点方法执行时被应用。
- 在通知当中,我们所定义的共性功能到底要应用在哪些方法上?此时就涉及到了切入点pointcut概念。切入点指的是匹配连接点的条件。通知仅会在切入点方法运行时才会被应用
**4.切面:**Aspect,描述通知与切入点的对应关系(通知+切入点)
当通知和切入点结合在一起,就形成了一个切面。通过切面就能够描述当前aop程序需要针对于哪个原始方法,在什么时候执行什么样的操作
切面所在的类,称之为切面类(被@Aspect注解标识的类)。
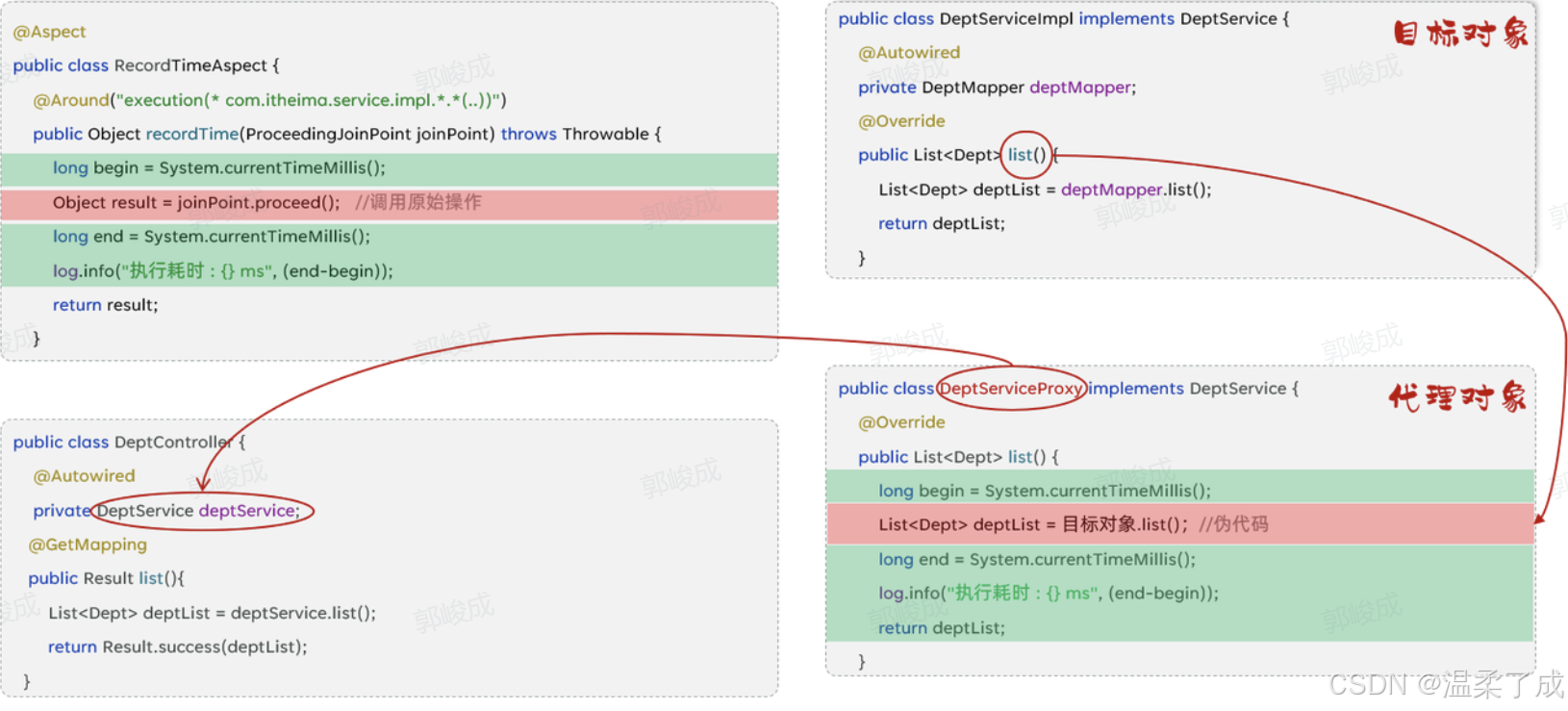
**5.目标对象:**Target,通知所应用的对象
目标对象指的就是通知所应用的对象,我们就称之为目标对象
aop基础实现
导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
aop方法
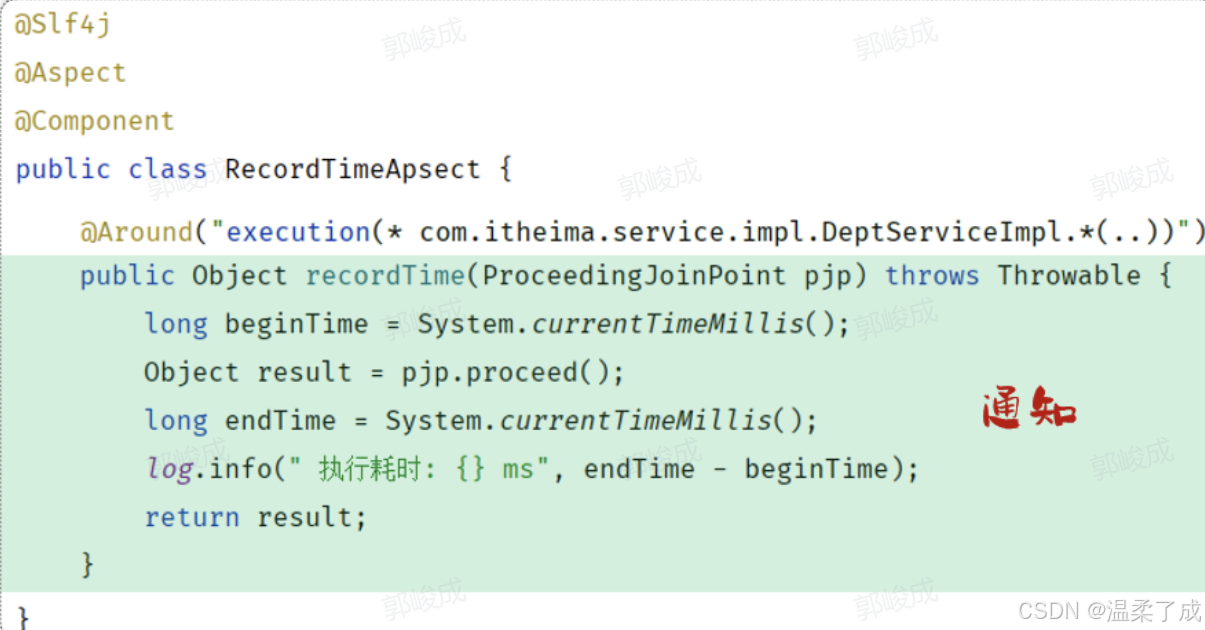
@Component
@Aspect //当前类为切面类
@Slf4j
public class RecordTimeAspect {
@Around("execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.DeptServiceImpl.*(..))")
public Object recordTime(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
//记录方法执行开始时间
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
//执行原始方法
Object result = pjp.proceed();
//记录方法执行结束时间
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
//计算方法执行耗时
log.info("方法执行耗时: {}毫秒",end-begin);
return result;
}
}
执行流程
Spring的AOP底层是基于动态代理技术来实现的,也就是说在程序运行的时候,会自动的基于动态代理技术为目标对象生成一个对应的代理对象。在代理对象当中就会对目标对象当中的原始方法进行功能的增强。
aop进阶
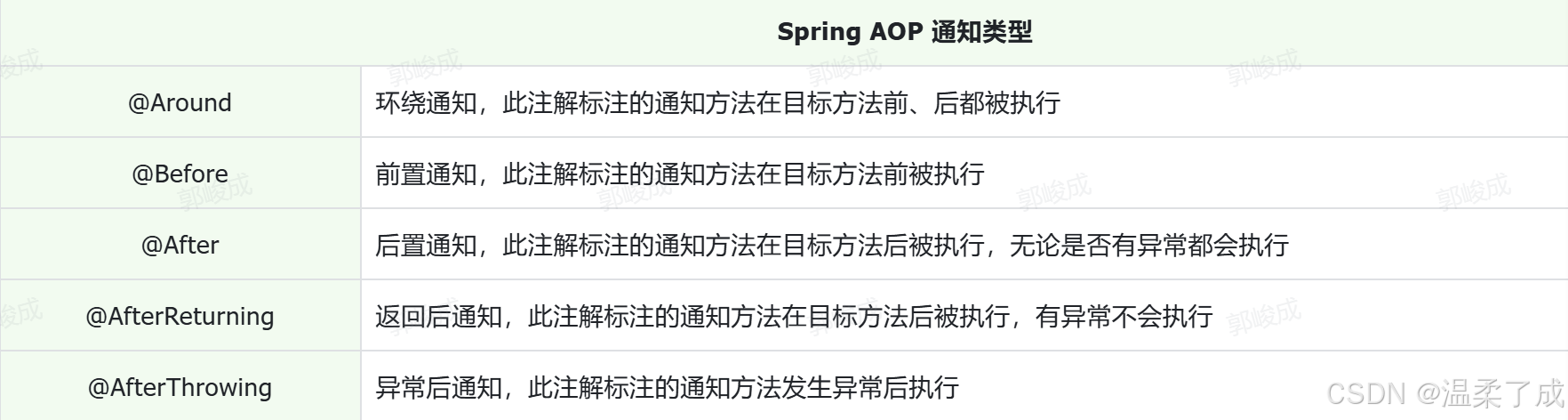
通知类型
@Slf4j
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspect1 {
//前置通知
@Before("execution(* com.itheima.service.*.*(..))")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
log.info("before ...");
}
//环绕通知
@Around("execution(* com.itheima.service.*.*(..))")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
log.info("around before ...");
//调用目标对象的原始方法执行
Object result = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
//原始方法如果执行时有异常,环绕通知中的后置代码不会在执行了
log.info("around after ...");
return result;
}
//后置通知
@After("execution(* com.itheima.service.*.*(..))")
public void after(JoinPoint joinPoint){
log.info("after ...");
}
//返回后通知(程序在正常执行的情况下,会执行的后置通知)
@AfterReturning("execution(* com.itheima.service.*.*(..))")
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint){
log.info("afterReturning ...");
}
//异常通知(程序在出现异常的情况下,执行的后置通知)
@AfterThrowing("execution(* com.itheima.service.*.*(..))")
public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint){
log.info("afterThrowing ...");
}
}
注意事项:
- @Around环绕通知需要自己调用 ProceedingJoinPoint.proceed() 来让原始方法执行,其他通知不需要考虑目标方法执行
- @Around环绕通知方法的返回值,必须指定为Object,来接收原始方法的返回值,否则原始方法执行完毕,是获取不到返回值的
切入点表达式的抽取
可以使用 @Pointcut注解,对切入点表达式进行抽取
//切入点方法(公共的切入点表达式)
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.service.*.*(..))")
private void pt(){}
//前置通知(引用切入点)
@Before("pt()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
log.info("before ...");
}
通知的执行顺序
- 目标方法前的通知方法:字母排名靠前的先执行
- 目标方法后的通知方法:字母排名靠前的后执行
如果我们想控制通知的执行顺序有两种方式:
- 修改切面类的类名(这种方式非常繁琐、而且不便管理)
- 使用Spring提供的@Order注解
@Slf4j
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(2) //切面类的执行顺序(前置通知:数字越小先执行; 后置通知:数字越小越后执行)
public class MyAspect2 {
//前置通知
@Before("execution(* com.itheima.service.*.*(..))")
public void before(){
log.info("MyAspect2 -> before ...");
}
//后置通知
@After("execution(* com.itheima.service.*.*(..))")
public void after(){
log.info("MyAspect2 -> after ...");
}
}
- 不同的切面类当中,默认情况下通知的执行顺序是与切面类的类名字母排序是有关系的
- 可以在切面类上面加上@Order注解,来控制不同的切面类通知的执行顺序
切入点表达式
切入点表达式:描述切入点方法的一种表达式
- 作用:主要用来决定项目中的哪些方法需要加入通知
- 常见形式:
1.execution(……):根据方法的签名来匹配
2.@annotation(……) :根据注解匹配
@execution方式实现
语法格式:
execution(访问修饰符? 返回值 包名.类名.?方法名(方法参数) throws 异常?)
@annotation注解方式实现
第一步:自定义注解
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface LogOperation{
}
第二步:给接入点加注解,表示这是目标方法
@Override
@LogOperation //自定义注解(表示:当前方法属于目标方法)
public void delete(Integer id) {
//1. 删除部门
deptMapper.delete(id);
}
示例
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface AuthCheck {
/**
* 用户权限: admin ,user
**/
String mustRole() default "";
}
@Aspect
@Component
public class AuthInterceptor {
@Resource
private UserService userService;
/**
* 执行拦截
*
* @param joinPoint 切入点
* @param authCheck 权限校验注解
*/
//@Around("@annotation(authCheck)")
@Around("@annotation(authCheck)")
public Object doInterceptor(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, AuthCheck authCheck) throws Throwable {
String mustRole = authCheck.mustRole();
RequestAttributes requestAttributes = RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) requestAttributes).getRequest();
// 获取当前登录用户
User loginUser = userService.getLoginUser(request);
UserRoleEnum mustRoleEnum = UserRoleEnum.getEnumByValue(mustRole);
// 如果不需要权限,放行
if (mustRoleEnum == null) {
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
// 以下的代码:必须有权限,才会通过
UserRoleEnum userRoleEnum = UserRoleEnum.getEnumByValue(loginUser.getUserRole());
if (userRoleEnum == null) {
throw new BusinessException(ErrorCode.NO_AUTH_ERROR);
}
// 要求必须有管理员权限,但用户没有管理员权限,拒绝
if (UserRoleEnum.ADMIN.equals(mustRoleEnum) && !UserRoleEnum.ADMIN.equals(userRoleEnum)) {
throw new BusinessException(ErrorCode.NO_AUTH_ERROR);
}
// 通过权限校验,放行
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
}