目录
关系型数据库:
建立在概念西模型基础之上 由多张相互链接的二维表组成的数据库 二维表:指的是由行 和 列 组成的表
二维表的优点:
-
使用表存储数据,格式统一,便于维护
-
使用SQL语言操作,标准统一,使用方便,可用于复杂查询
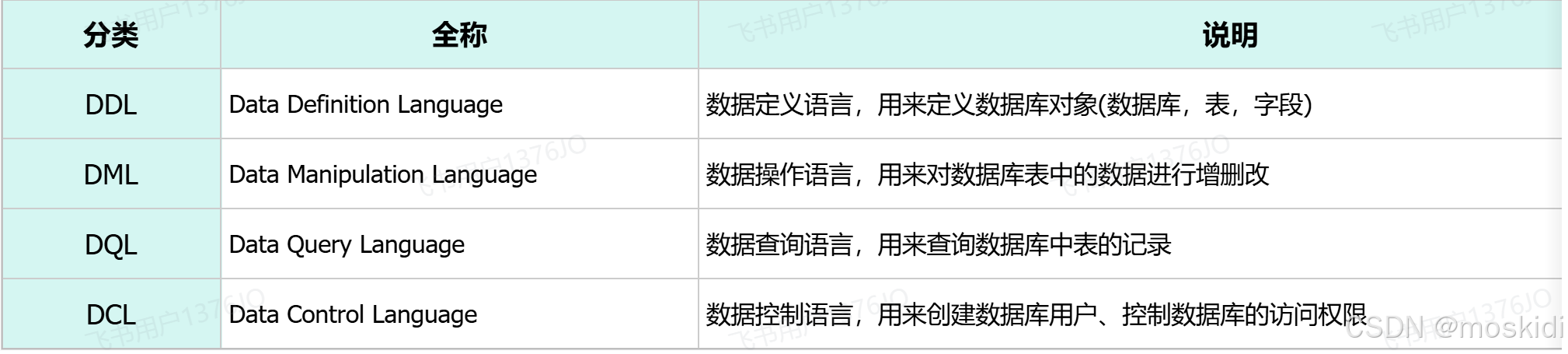
Sql 语句:
DDL definition 用来定义数据库对象 数据库 表 字段
DML Multiplication 用来操纵表 对表中的数据 进行增删改
DQL Query 用来查询 表中的数据
1.DDL:定义 数据库 表 字段:
数据库操作:
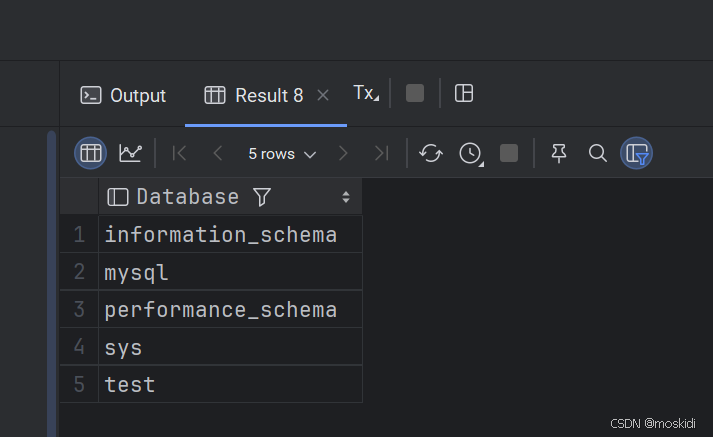
查询所有数据库:
show databases
查询当前正常使用的数据库:
select database();创建数据库:
create database itcast;使用数据库:
use 数据库名 ;删除数据库:
drop database [ if exists ] 数据库名 ;表操作:
创建表:
create table tb_user (
id int primary key auto_increment comment 'ID,唯一标识', #主键自动增长
username varchar(20) not null unique comment '用户名',
name varchar(10) not null comment '姓名',
age int comment '年龄',
gender char(1) default '男' comment '性别'
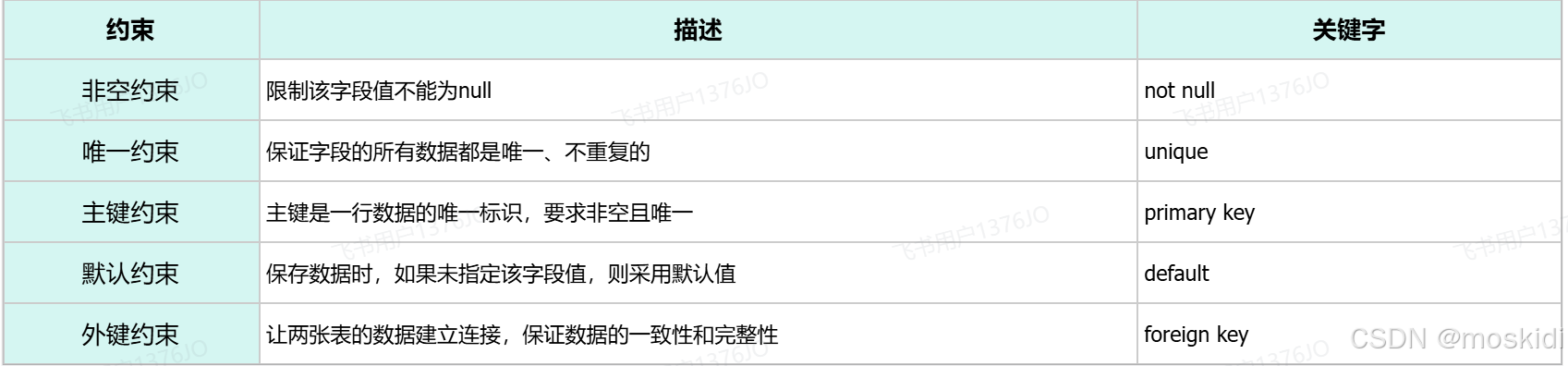
) comment '用户表';约束:
主键自增:auto_increment
-
每次插入新的行记录时,数据库自动生成id字段(主键)下的值
-
具有auto_increment的数据列是一个正数序列开始增长(从1开始自增)
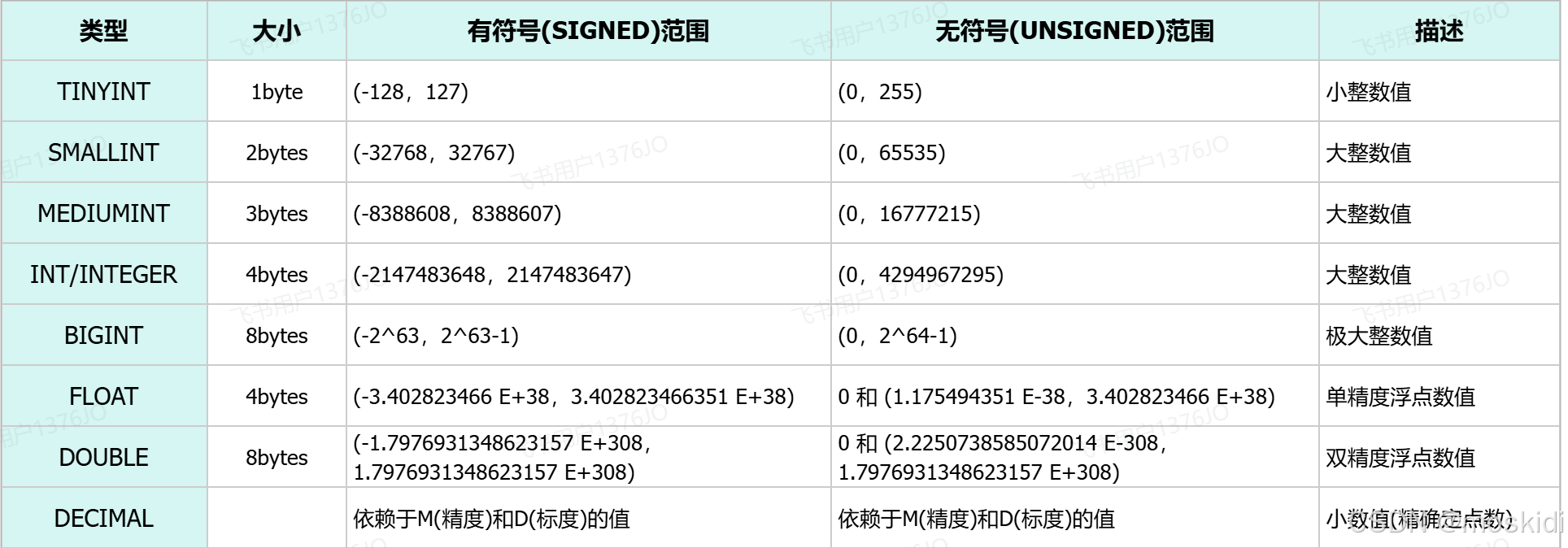
数据类型:
1). 数值类型
tinyint 1字节
smallint 2字节
mediumint 3字节
int/integer 4个字节
bigint 8个字节
double 8个字节
decimal(precision, scale)
precision:表示整个数值的最大位数(包括整数部分和小数部分)。例如,decimal(10, 2) 表示总共可以有10位数字,其中2位是小数。
scale:表示小数部分的位数。例如,decimal(10, 2) 表示小数部分有2位。
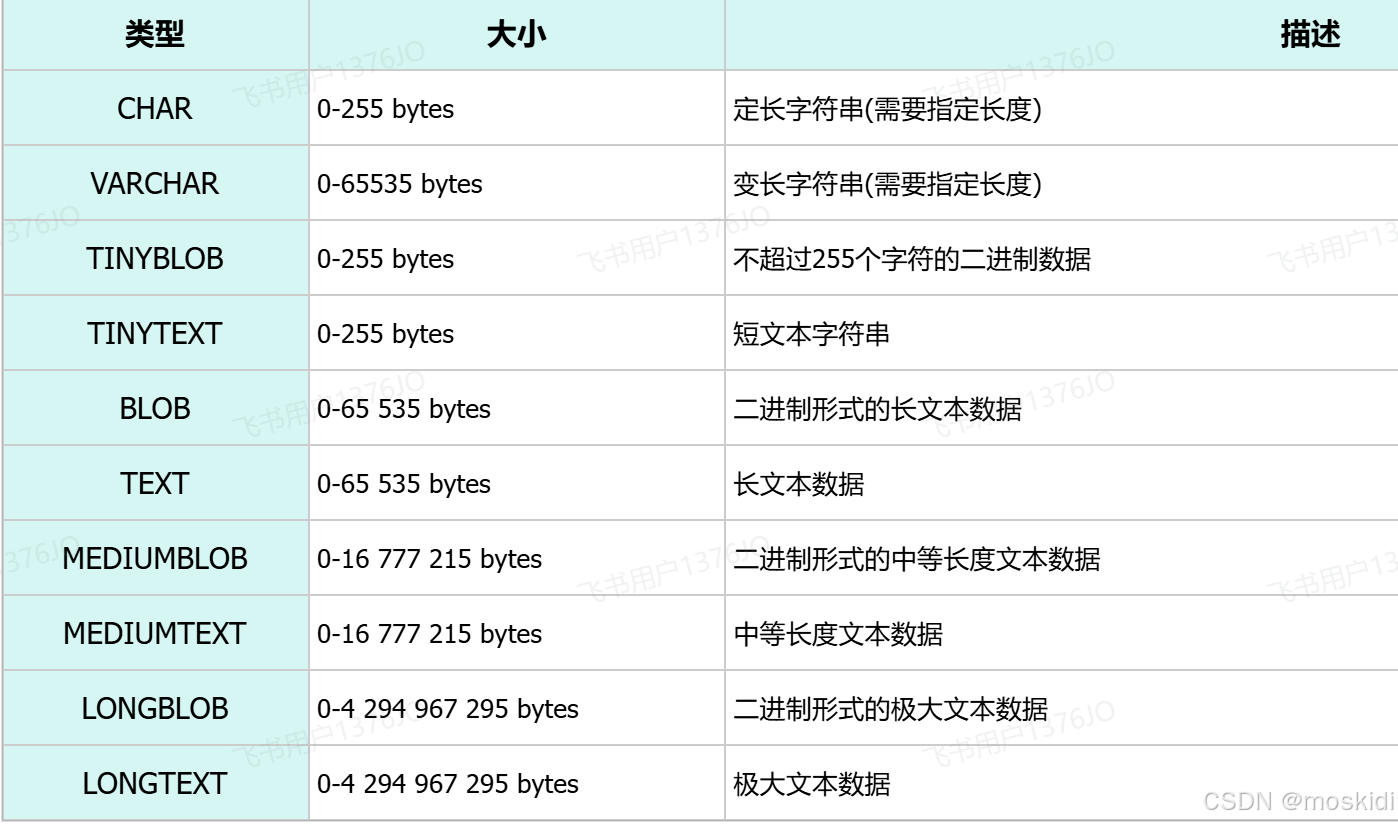
2). 字符串类型
char()定长字符串 永远开辟的是定长的空间
vachar(最大长度) char的性能会更高一些
char 与 varchar 都可以描述字符串,char是定长字符串,指定长度多长,就占用多少个字符,和字段值的长度无关 。而varchar是变长字符串,指定的长度为最大占用长度 。相对来说,char的性能会更高些。
create table tb_user (
id int primary key auto_increment comment 'ID,唯一标识', #主键自动增长
username varchar(20) not null unique comment '用户名',
name varchar(10) not null comment '姓名',
age int comment '年龄',
gender char(1) default '男' comment '性别'
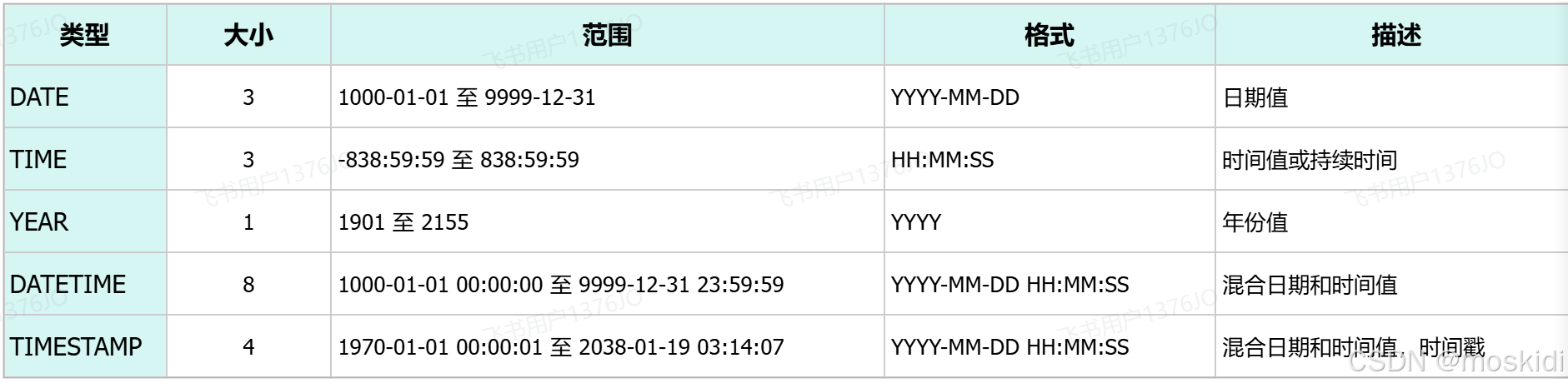
) comment '用户表';3). 日期时间类型
TimeStamp 只能显示到2038年 所以不用
示例:
生日字段 birthday ---生日只需要年月日
birthday date
创建时间 createtime --- 需要精确到时分秒
createtime datetime
案例:
create table emp(
id int unsigned primary key auto_increment comment 'ID,主键',
username varchar(20) not null unique comment '用户名',
password varchar(32) not null comment '密码',
name varchar(10) not null comment '姓名',
gender tinyint unsigned not null comment '性别, 1:男, 2:女',
phone char(11) not null unique comment '手机号',
job tinyint unsigned comment '职位, 1:班主任,2:讲师,3:学工主管,4:教研主管,5:咨询师',
salary int unsigned comment '薪资',
image varchar(255) comment '头像',
entry_date date comment '入职日期',
create_time datetime comment '创建时间',
update_time datetime comment '修改时间'
) comment '员工表';表的其他操作:
-- 查询当前数据库的所有表
show tables;
-- 查看指定的表结构
desc 表名 ; -- 可以查看指定表的字段、字段的类型、是否可以为NULL、是否存在默认值等信息
-- 查询指定表的建表语句
show create table 表名 ;修改表的结构:
增加列:
-- 添加字段
alter table 表名 add 字段名 类型(长度) [comment 注释] [约束];
-- 比如: 为tb_emp表添加字段qq,字段类型为 varchar(11)
alter table tb_emp add qq varchar(11) comment 'QQ号码';修改字段(列名):
-- 修改字段类型
alter table 表名 modify 字段名 新数据类型(长度);
-- 比如: 修改qq字段的字段类型,将其长度由11修改为13
alter table tb_emp modify qq varchar(13) comment 'QQ号码';修改字段名字:
-- 修改字段名,字段类型
alter table 表名 change 旧字段名 新字段名 类型(长度) [comment 注释] [约束];
-- 比如: 修改qq字段名为 qq_num,字段类型varchar(13)
alter table tb_emp change qq qq_num varchar(13) comment 'QQ号码';删除字段:
-- 删除字段
alter table 表名 drop 字段名;
-- 比如: 删除tb_emp表中的qq_num字段
alter table tb_emp drop qq_num;修改表名:
-- 修改表名
rename table 表名 to 新表名;
-- 比如: 将当前的emp表的表名修改为tb_emp
rename table emp to tb_emp;删除表:
-- 删除表
drop table [ if exists ] 表名;
-- 比如:如果tb_emp表存在,则删除tb_emp表
drop table if exists tb_emp; -- 在删除表时,表中的全部数据也会被删除。2.DML:对表的数据 进行 增 删 改:
插入数据:
向指定字段添加数据:
insert into 表名 (字段名1, 字段名2) values (值1, 值2);
insert into t_student(name,age) values ('张三',20);全部字段添加数据:
insert into 表名 values (值1, 值2, ...);
insert into t_student values (null,'李四',21);主键因为有自增所以直接 给nul就会自动赋值
批量添加数据(指定字段):
insert into 表名 (字段名1, 字段名2) values (值1, 值2), (值1, 值2);
insert into t_student(name,age) values ('王五',22),('Tom',22),('Cat',27);批量添加字段(全部数据):
insert into 表名 values (值1, 值2, ...), (值1, 值2, ...);
insert into t_student values (null,'kkl',20,'男',20000),(null,'ppd',21,'女',20000),(null,'ddf',22,'男',20000);insert操作的注意事项:
-
插入数据时,指定的字段顺序需要与值的顺序是一一对应的。
-
字符串和日期型数据应该包含在引号中。
-
插入的数据大小,应该在字段的规定范围内。
修改数据:
update 表名 set 字段名1 = 值1 , 字段名2 = 值2 , .... [where 条件] ;
update emp set name='张三', update_time=now() where id=1;
update emp set entry_date='2010-01-01', update_time=now();注意事项:
-
修改语句的条件可以有,也可以没有,如果没有条件,则会修改整张表的所有数据。
-
在修改数据时,一般需要同时修改公共字段update_time,将其修改为当前操作时间。
删除数据:
delete from 表名 [where 条件] ;
delete from emp where id = 1;
delete from tb_emp;如果不写 where 条件则删除所有的数据
DQL: 对数据表中的内容进行查询:
查询关键字:SELECT
DQL查询语句,语法结构如下:
SELECT
字段列表
FROM
表名列表
WHERE
条件列表
GROUP BY
分组字段列表
HAVING
分组后条件列表
ORDER BY
排序字段列表
LIMIT
分页参数基本查询:
select 字段1, 字段2, 字段3 from 表名;
select * from 表名;
select 字段1 [ as 别名1 ] , 字段2 [ as 别名2 ] from 表名;
--开发中as通常省略
-
去除重复记录
-
select distinct 字段列表 from 表名;
案例:
-- 方式1:
select name AS 姓名, entry_date AS 入职日期 from emp;
-- 方式2: 别名中有特殊字符时,使用''或""包含
select name AS '姓 名', entry_date AS '入职日期' from emp;
-- 方式3:
select name AS "姓名", entry_date AS "入职日期" from emp;条件查询:
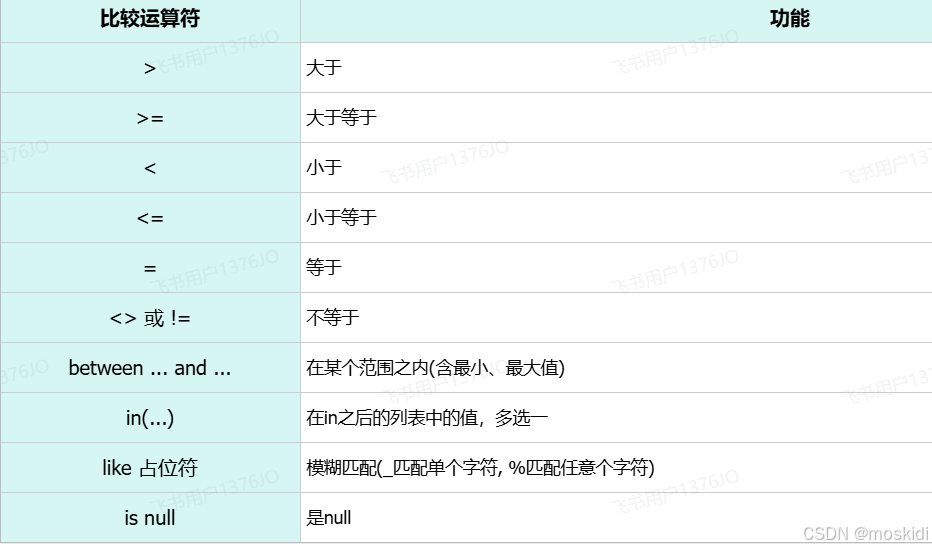
select 字段列表 from 表名 where 条件列表 ; -- 条件列表:意味着可以有多个条件比较运算符:
逻辑运算符:
-
案例2:查询 薪资小于等于 5000 的员工信息
select id, username, password, name, gender, phone, salary, job, image, entry_date, create_time, update_time
from emp
where salary <=5000;-
案例7:查询 入职时间 在 '2000-01-01' (包含) 到 '2010-01-01'(包含) 之间 且 性别为女 的员工信息
select id, username, password, name, gender, phone, salary, job, image, entry_date, create_time, update_time from emp where entry_date between '2000-01-01' and '2010-01-01'; and gender = 2;select username 名字,age 年龄,salary 薪资 from t_student where id>15 and age < 25;
用and也可表示范围
-
案例10:查询 姓 '张' 的员工信息
select id, username, password, name, gender, phone, salary, job, image, entry_date, create_time, update_time
from emp
where name like '张%'; # 通配符 "%" 代表任意个字符(0个 ~ 多个)张% 以张开头
%张% 包含张就可以
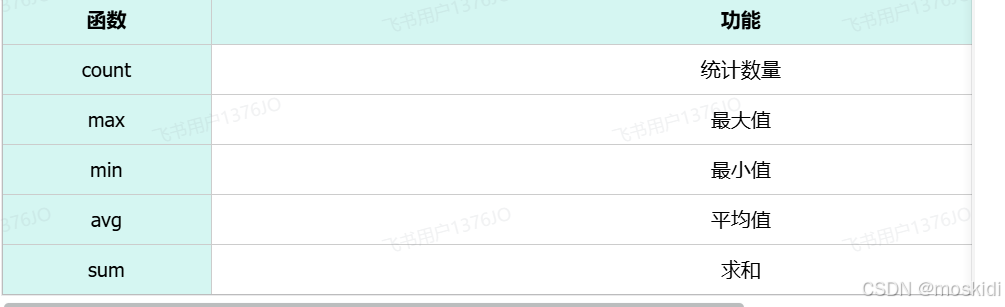
聚合函数:
select count(id) from emp;
-- count(*) 推荐此写法(MySQL底层进行了优化)
select count(*) from emp;
select avg(salary) from emp;
select min(salary) from emp;
select max(salary) from emp;
select sum(salary) from emp;分组查询:
select 字段列表 from 表名 [where 条件] group by 分组字段名 [having 分组后过滤条件];
-
案例1:根据性别分组 , 统计男性和女性员工的数量
select gender, count(*) from emp group by gender; -- 按照gender字段进行分组(gender字段下相同的数据归为一组)
-
案例2:查询入职时间在 '2015-01-01' (包含) 以前的员工 , 并对结果根据职位分组 , 获取员工数量大于等于2的职位
select job, count(*)
from emp
where entry_date <= '2015-01-01' -- 分组前条件
group by job -- 按照job字段分组
having count(*) >= 2; -- 分组后条件排序查询:
-
排序方式:
-
ASC :升序(默认值)
-
DESC:降序
-
-
案例1:根据入职时间对公司的员工进行升序排序,入职时间相同,再按照更新时间进行降序排序
select id, username, password, name, gender, phone, salary, job, image, entry_date, create_time, update_time
from emp
order by entry_date ASC , update_time DESC;分页查询:
select 字段列表 from 表名 limit 起始索引, 查询记录数 ;-
案例1:从起始索引0开始查询员工数据, 每页展示5条记录
select id, username, password, name, gender, phone, salary, job, image, entry_date, create_time, update_time
from emp
limit 0 , 5; -- 从索引0开始,向后取5条记录-
案例2:查询 第1页 员工数据, 每页展示5条记录
select id, username, password, name, gender, phone, salary, job, image, entry_date, create_time, update_time
from emp
limit 5; -- 如果查询的是第1页数据,起始索引可以省略,直接简写为:limit 条数-
案例3:查询 第2页 员工数据, 每页展示5条记录
select id, username, password, name, gender, phone, salary, job, image, entry_date, create_time, update_time
from emp
limit 5 , 5; -- 从索引5开始,向后取5条记录-
案例4:查询 第3页 员工数据, 每页展示5条记录
select id, username, password, name, gender, phone, salary, job, image, entry_date, create_time, update_time
from emp
limit 10 , 5; -- 从索引10开始,向后取5条记录-
起始索引从0开始。 计算公式 :起始索引 = (查询页码 - 1)* 每页显示记录数
-
分页查询是数据库的方言,不同的数据库有不同的实现,MySQL中是LIMIT
-
如果查询的是第一页数据,起始索引可以省略,直接简写为 limit 条数