一,写在前面
当Android原生控件无法满足开发需求时,需要自己来创造view,自定义控件。自定义控件分三步来完成:测量(onMeasure),布局(onLayout),绘制(onDraw)。今天主要介绍自定义流程的第一步-测量,通常一个布局文件的控件的简单嵌套,显示如下:

LinearLayout里面有两个子view:TextView,RelativeLayout(里面又有两个TextView)。
我们知道自定义控件无非是extends View, extends ViewGroup, extends 容器控件/非容器控件,因此提取出其中的View.java, FrameLayout.java, TextView.java进行分析。下面展示涉及类,方法的结构图,看不懂互相之间关系没事,可以看完后面的分析,然后再回过头来看结构图。 结构图:
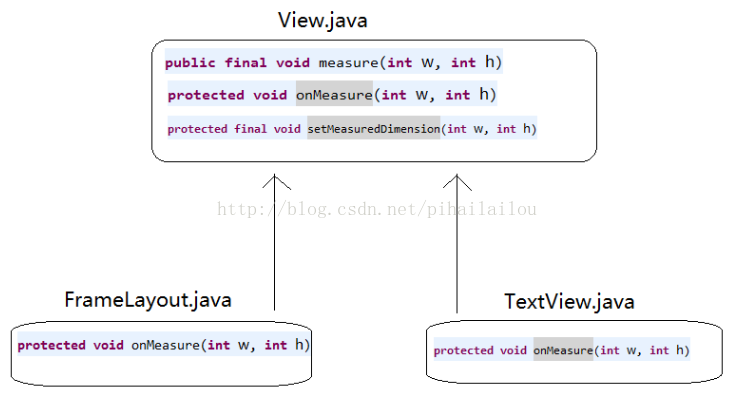
由上图可知,语法角度:子类可以重写onMeasure,只能继承View的measure,setMeasuredDimension方法。测量流程分为两种情况讨论:容器控件ViewGroup,原始的View(非容器控件)。原始的View测量,只需要测量自己的宽高;而容器控件需要先测量所有的子View的宽高,然后再测量自己的宽高。
看懂本篇文章,还需要大家自己先去研究下类View$MeasureSpec,相对比较简单,本文不描述MeasureSpec相关知识。
二,源码分析之View
先分析原始的View,打开View.java文件,查看measure方法:
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this);
if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) {
Insets insets = getOpticalInsets();
int oWidth = insets.left + insets.right;
int oHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom;
widthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.adjust(widthMeasureSpec, optical ? -oWidth : oWidth);
heightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.adjust(heightMeasureSpec, optical ? -oHeight : oHeight);
}
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT) == PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT ||
widthMeasureSpec != mOldWidthMeasureSpec ||
heightMeasureSpec != mOldHeightMeasureSpec) {
// first clears the measured dimension flag
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
resolveRtlPropertiesIfNeeded();
// measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// flag not set, setMeasuredDimension() was not invoked, we raise
// an exception to warn the developer
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) != PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) {
throw new IllegalStateException("onMeasure() did not set the"
+ " measured dimension by calling"
+ " setMeasuredDimension()");
}
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
}
mOldWidthMeasureSpec = widthMeasureSpec;
mOldHeightMeasureSpec = heightMeasureSpec;
}
主要分析measure(w,h)的两个关键点:
一,字段mPrivateFlags
1.1 字段mPrivateFlags在调用onMeasure(w,h)前,执行mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET,设置
成员变量mPrivateFlags的MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET位设置为0;
1.2 在onMeasure(w,h)执行完成后,判断if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) != PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET)决定是否抛出IllegalStateException异常;
二,实际测量方法onMeasure(w,h),
进入该方法查看源码:
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this);
if (opt