LangChain是一个用于大语言模型(LLM)应用开发的框架,它简化了LLM应用的开发难度,帮助开发者快速构建复杂的LLM应用。
一、LangChain 库简介
LangChain 包的主要价值主张是:
- 组件:用于处理语言模型的可组合工具和集成。无论你是否使用 LangChain 框架的其余部分,组件都是模块化的,易于使用
- 现成的链:用于完成高级任务的组件的内置组合
现成的链使得开始变得容易。组件使得定制现有链和构建新链变得容易。
LangChain 库本身由几个不同的包组成。
langchain-core:基础抽象和 LangChain 表达式语言。langchain-community:第三方集成。langchain:构成应用程序认知架构的链、代理和检索策略。
二、LangChain的核心组件
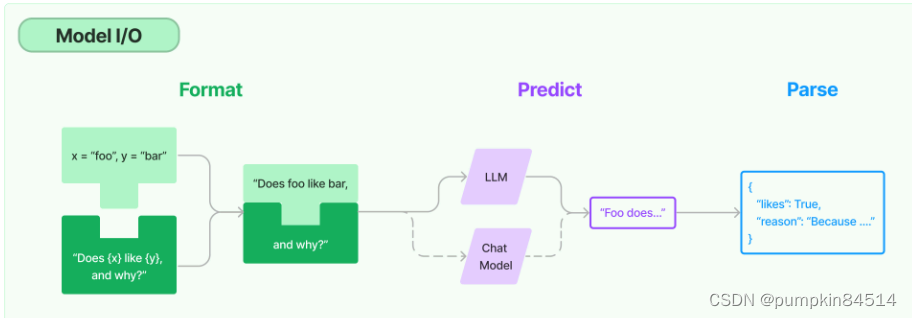
1、模型输入输出(Model I/O)
这是与各种大语言模型进行交互的基本组件。它允许开发者管理提示(prompt),通过通用接口调用语言模型,并从模型输出中提取信息。简单来说,这个组件负责与大语言模型“对话”,将我们的请求传递给模型,并接收模型的回复。
- 提示 prompts : 将模型输入模板化、动态选择和管理
- PromptTemplate 可以在模板中自定义变量
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
template = PromptTemplate.from_template("给我讲个关于{subject}的故事")
print(template.format(subject='星座'))- ChatPromptTemplate 用模板表示的对话上下文
from langchain.prompts import (
ChatPromptTemplate,
HumanMessagePromptTemplate,
SystemMessagePromptTemplate,
)
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
SystemMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(
"你是{product}的客服助手。你的名字叫{name}"),
HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("{query}"),
]
)
llm = ChatOpenAI()
prompt = template.format_messages(
product="手机客服",
name="小花",
query="你是谁"
)
ret = llm.invoke(prompt)
print(ret.content)- MessagesPlaceholder 把多轮对话变成模板
from langchain.prompts import (
ChatPromptTemplate,
HumanMessagePromptTemplate,
MessagesPlaceholder,
)
from langchain_core.messages import AIMessage, HumanMessage
human_prompt = "Translate your answer to {language}."
human_message_template = HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(human_prompt)
chat_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="conversation"), human_message_template]
)
human_message = HumanMessage(content="Who is Elon Musk?")
ai_message = AIMessage(
content="Elon Musk is a billionaire entrepreneur, inventor, and industrial designer"
)
messages = chat_prompt.format_prompt(
# 对 "conversation" 和 "language" 赋值
conversation=[human_message, ai_message], language="中文"
)
result = llm.invoke(messages)
print(result.content)- 语言模型 models : 通过常见接口调用语言模型
- LLMs: 输入一个文本字符串并返回一个文本字符串的模型
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo") # 默认是gpt-3.5-turbo
response = llm.invoke("你是谁")
print(response.content)- 聊天模型: 由语言模型支持的模型,接受一个聊天消息列表作为输入并返回一个聊天消息
from langchain.schema import (
AIMessage,
HumanMessage,
SystemMessage
)
messages = [
HumanMessage(content="今天天气怎么样?"),
AIMessage(content="已收到您的问题,正在查询..."),
SystemMessage(content="今天天气晴朗,气温适宜。")
]
ret = llm.invoke(messages)
print(ret)Class hierarchy:
BaseLanguageModel --> BaseLLM --> LLM --> Examples: AI21, HuggingFaceHub, OpenAI
--> BaseChatModel --> Examples: ChatOpenAI, ChatGooglePalm
- 输出解析器 output_parsers : 从模型输出中提取信息
LangChain 内置的 OutputParser 包括:
- ListParser
- DatetimeParser
- EnumParser
- JsonOutputParser
- PydanticParser
- XMLParser
等等
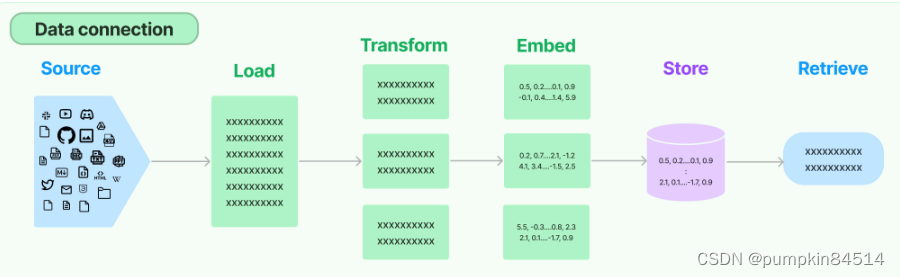
2、数据连接(Data Connection)
大语言模型的知识来源于其训练数据集,但并不包含用户信息或最新时事。数据连接模块提供了加载、转换、存储和查询数据的组件,使得大语言模型能够在训练数据集的基础上,利用自有数据中的信息来回答问题。这样,模型就能给出更有用的答案。
- Document Loaders:各种格式文件的加载器
- Document Transformers:对文档的常用操作,如:split, filter, translate, extract metadata, etc
- Text Embedding Models:文本向量化表示,用于检索等操作(啥意思?别急,后面详细讲)
- Verctorstores: (面向检索的)向量的存储
- Retrievers: 向量的检索
3、链(Chains)
对于复杂的需求,可能需要将多个大语言模型或其他组件进行链式组合。链允许将多个组件组合在一起,创建一个连贯的应用程序。例如,可以创建一个链,接受用户输入,对其进行格式化,然后将格式化后的提示词传递给大语言模型。
- 内置 Chain,比如LLMChain(基本的链类型)、SequentialChain(处理单个输入且单个输出的情况)、Router Chain(同一输入router到不同的输出)
简单的LLMChain形式:
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0.9)
prompt = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["product"],
template="What is a good name for a company that makes {product}?",
)
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt)
# Run the chain only specifying the input variable.
print(chain.run("colorful socks"))
LLMChain 中使用聊天模型
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.prompts.chat import (
ChatPromptTemplate,
HumanMessagePromptTemplate,
)
human_message_prompt = HumanMessagePromptTemplate(
prompt=PromptTemplate(
template="What is a good name for a company that makes {product}?",
input_variables=["product"],
)
)
chat_prompt_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([human_message_prompt])
chat = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.9)
chain = LLMChain(llm=chat, prompt=chat_prompt_template)
print(chain.run("colorful socks"))
LCEL可以实现:
1)配置运行时变量:Configure runtime chain internals | 🦜️🔗 Langchain
2)故障回退:Fallbacks | 🦜️🔗 Langchain
3)并行调用:Parallel: Format data | 🦜️🔗 Langchain
4)逻辑分支:Route logic based on input | 🦜️🔗 Langchain
5)调用自定义流式函数:Lambda: Run custom functions | 🦜️🔗 Langchain
6)链接外部 Memory:Add message history (memory) | 🦜️🔗 Langchain
更多例子:https://python.langchain.com/docs/expression_language/cookbook/
LCEL亮点如下:
1)流支持:使用 LCEL 构建 Chain 时,你可以获得最佳的首个令牌时间(即从输出开始到首批输出生成的时间)。对于某些 Chain,这意味着可以直接从 LLM 流式传输令牌到流输出解析器,从而以与 LLM 提供商输出原始令牌相同的速率获得解析后的、增量的输出。
2)异步支持:任何使用 LCEL 构建的链条都可以通过同步 API(例如,在 Jupyter 笔记本中进行原型设计时)和异步 API(例如,在 LangServe 服务器中)调用。这使得相同的代码可用于原型设计和生产环境,具有出色的性能,并能够在同一服务器中处理多个并发请求。
3)优化的并行执行:当你的 LCEL 链条有可以并行执行的步骤时(例如,从多个检索器中获取文档),我们会自动执行,无论是在同步还是异步接口中,以实现最小的延迟。
重试和回退:为 LCEL 链的任何部分配置重试和回退。这是使链在规模上更可靠的绝佳方式。目前我们正在添加重试/回退的流媒体支持,因此你可以在不增加任何延迟成本的情况下获得增加的可靠性。
4)访问中间结果:对于更复杂的链条,访问在最终输出产生之前的中间步骤的结果通常非常有用。这可以用于让最终用户知道正在发生一些事情,甚至仅用于调试链条。你可以流式传输中间结果,并且在每个 LangServe 服务器上都可用。
5)输入和输出模式:输入和输出模式为每个 LCEL 链提供了从链的结构推断出的 Pydantic 和 JSONSchema 模式。这可以用于输入和输出的验证,是 LangServe 的一个组成部分。
6)无缝 LangSmith 跟踪集成:随着链条变得越来越复杂,理解每一步发生了什么变得越来越重要。通过 LCEL,所有步骤都自动记录到 LangSmith,以实现最大的可观察性和可调试性。
7)无缝 LangServe 部署集成:任何使用 LCEL 创建的链都可以轻松地使用 LangServe 进行部署。
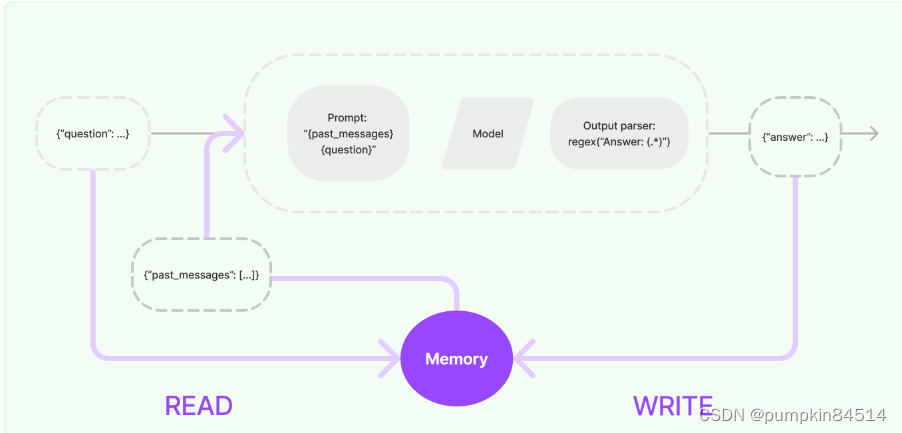
4、记忆(Memory)
由于大语言模型本身不具备上下文记忆,因此需要记忆组件来保存和模型交互时的上下文状态。这样,在与模型交互时,我们能够传递聊天内容的上下文,使对话更加连贯和有意义。
- 对话上下文:ConversationBufferMemor
- 只保留一个窗口的上下文:ConversationBufferWindowMemory
- 通过 Token 数控制上下文长度:ConversationTokenBufferMemory
- 更多类型
- ConversationSummaryMemory: 对上下文做摘要https://python.langchain.com/docs/modules/memory/types/summary
- ConversationSummaryBufferMemory: 保存 Token 数限制内的上下文,对更早的做摘要https://python.langchain.com/docs/modules/memory/types/summary_buffer
- VectorStoreRetrieverMemory: 将 Memory 存储在向量数据库中,根据用户输入检索回最相关的部分https://python.langchain.com/docs/modules/memory/types/vectorstore_retriever_memory
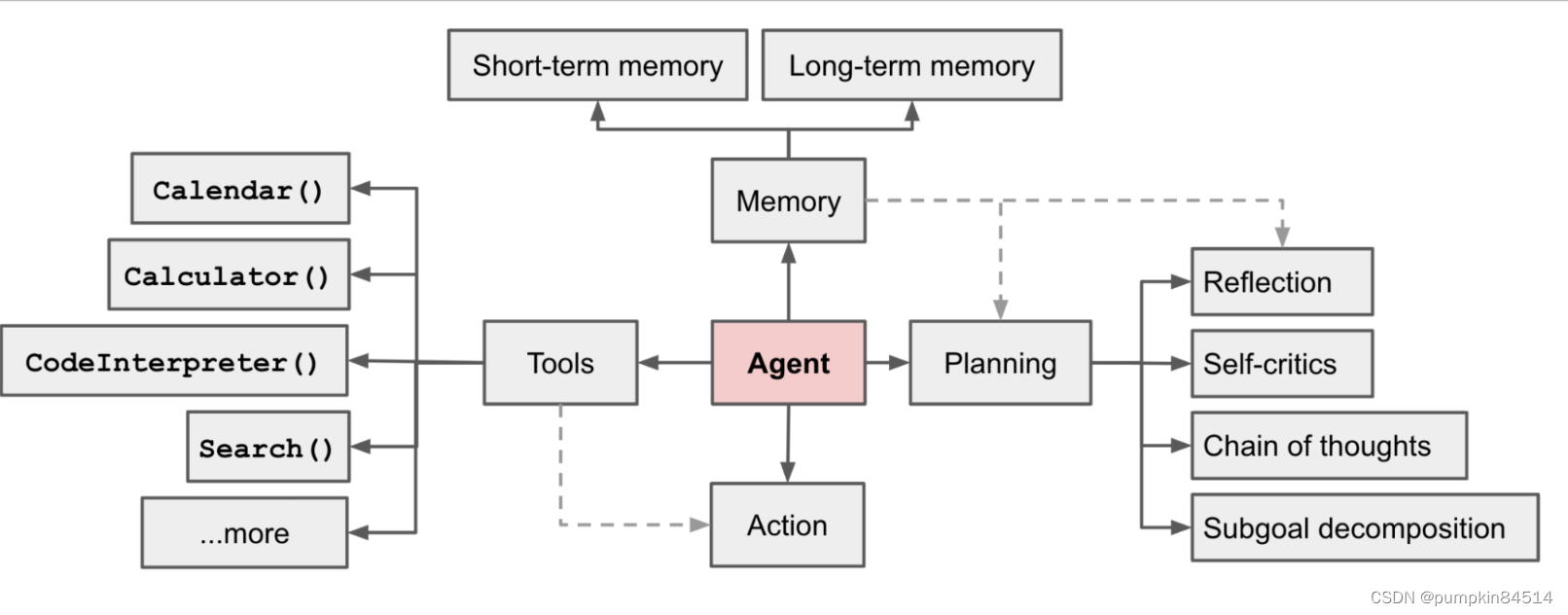
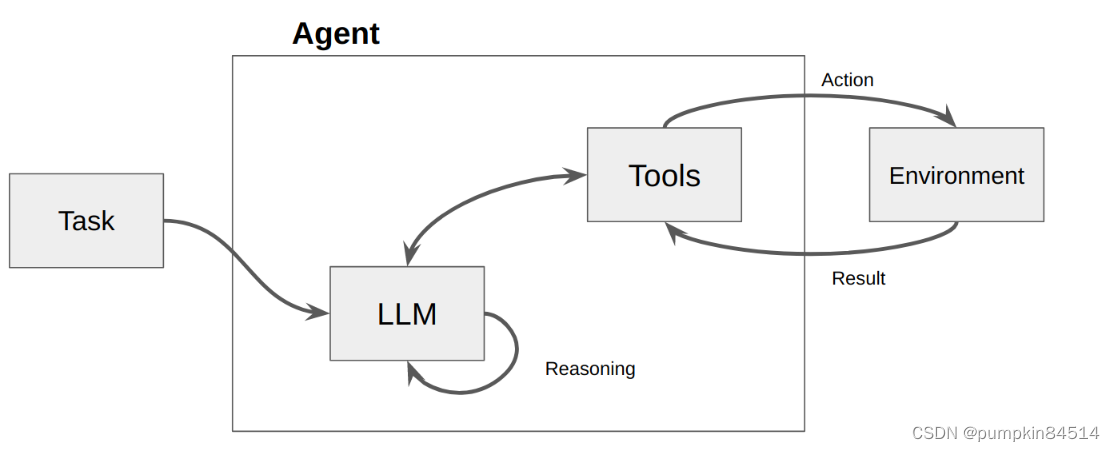
5、代理(Agents)
代理决定了模型应该采取哪些行动。通过代理,我们可以让语言模型具有主动性和智能性,动态地选择和调用链或已有的工具,以适应多种应用场景。
- 先定义一些工具:Tools
- 可以是一个函数或三方 API
- 也可以把一个 Chain 或者 Agent 的 run()作为一个 Tool
from langchain_community.utilities import SerpAPIWrapper
from langchain.tools import Tool, tool
search = SerpAPIWrapper()
tools = [
Tool.from_function(
func=search.run,
name="Search",
description="useful for when you need to answer questions about current events"
),
]import calendar
import dateutil.parser as parser
from datetime import date
# 自定义工具
@tool("weekday")
def weekday(date_str: str) -> str:
"""Convert date to weekday name"""
d = parser.parse(date_str)
return calendar.day_name[d.weekday()]
tools += [weekday]- 智能体类型:ReAct
!pip install google-search-results
!pip install --upgrade langchainhub
from langchain import hub
import json
# 下载一个现有的 Prompt 模板
prompt = hub.pull("hwchase17/react")
print(prompt.template)Answer the following questions as best you can. You have access to the following tools:
{tools}
Use the following format:
Question: the input question you must answer
Thought: you should always think about what to do
Action: the action to take, should be one of [{tool_names}]
Action Input: the input to the action
Observation: the result of the action
... (this Thought/Action/Action Input/Observation can repeat N times)
Thought: I now know the final answer
Final Answer: the final answer to the original input question
Begin!
Question: {input}
Thought:{agent_scratchpad}
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.agents import AgentExecutor, create_react_agent
llm = ChatOpenAI(model_name='gpt-3.5-turbo', temperature=0)
# 定义一个 agent: 需要大模型、工具集、和 Prompt 模板
agent = create_react_agent(llm, tools, prompt)
# 定义一个执行器:需要 agent 对象 和 工具集
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(agent=agent, tools=tools, verbose=True)
# 执行
agent_executor.invoke({"input": "**********"})- 智能体类型:SelfAskWithSearch
# 下载一个模板
prompt = hub.pull("hwchase17/self-ask-with-search")
print(prompt.template)Question: Who lived longer, Muhammad Ali or Alan Turing?
Are follow up questions needed here: Yes.
Follow up: How old was Muhammad Ali when he died?
Intermediate answer: Muhammad Ali was 74 years old when he died.
Follow up: How old was Alan Turing when he died?
Intermediate answer: Alan Turing was 41 years old when he died.
So the final answer is: Muhammad Ali
Question: When was the founder of craigslist born?
Are follow up questions needed here: Yes.
Follow up: Who was the founder of craigslist?
Intermediate answer: Craigslist was founded by Craig Newmark.
Follow up: When was Craig Newmark born?
Intermediate answer: Craig Newmark was born on December 6, 1952.
So the final answer is: December 6, 1952
Question: Who was the maternal grandfather of George Washington?
Are follow up questions needed here: Yes.
Follow up: Who was the mother of George Washington?
Intermediate answer: The mother of George Washington was Mary Ball Washington.
Follow up: Who was the father of Mary Ball Washington?
Intermediate answer: The father of Mary Ball Washington was Joseph Ball.
So the final answer is: Joseph Ball
Question: Are both the directors of Jaws and Casino Royale from the same country?
Are follow up questions needed here: Yes.
Follow up: Who is the director of Jaws?
Intermediate answer: The director of Jaws is Steven Spielberg.
Follow up: Where is Steven Spielberg from?
Intermediate answer: The United States.
Follow up: Who is the director of Casino Royale?
Intermediate answer: The director of Casino Royale is Martin Campbell.
Follow up: Where is Martin Campbell from?
Intermediate answer: New Zealand.
So the final answer is: No
Question: {input}
Are followup questions needed here:{agent_scratchpad}
from langchain.agents import create_self_ask_with_search_agent
tools = [
Tool(
name="Intermediate Answer",
func=search.run,
description="useful for when you need to ask with search.",
)
]
# self_ask_with_search_agent 只能传一个名为 'Intermediate Answer' 的 tool
agent = create_self_ask_with_search_agent(llm, tools, prompt)
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(agent=agent, tools=tools, verbose=True)
agent_executor.invoke({"input": "*********"})6、回调(Callbacks)
回调是用于在链中插入自定义逻辑的组件。它允许开发者在链中的任何位置执行自定义的函数或代码,从而对语言模型的行为进行控制和调整。
这些核心组件共同构成了LangChain框架的基础,使得开发者能够灵活地构建和定制大语言模型应用。
Callback 模块的具体实现包括两个主要功能:
- CallbackHandler :记录每个应用场景(如 Agent、LLchain 或 Tool )的日志,它是单个日志处理器,主要记录单个场景的完整日志信息。
- CallbackManager:封装和管理所有的 CallbackHandler ,包括单个场景的处理器,也包括整个运行时链路的处理器。"