一个CORS请求的流程
-
发送一个预检请求
都为Options请求,因为Options请求不会对服务器做出任何改动。且带有"contentType:"application/json"请求头的get或者post才会进行预检请求。
-
检查
- 服务器验证该请求的origin是否在Access-Control-Allow-Origin范围内
- 请求方法是否在Access-Control-Allow-Methods范围内
- 请求头是否都在Access-Control-Allow-Headers范围内
-
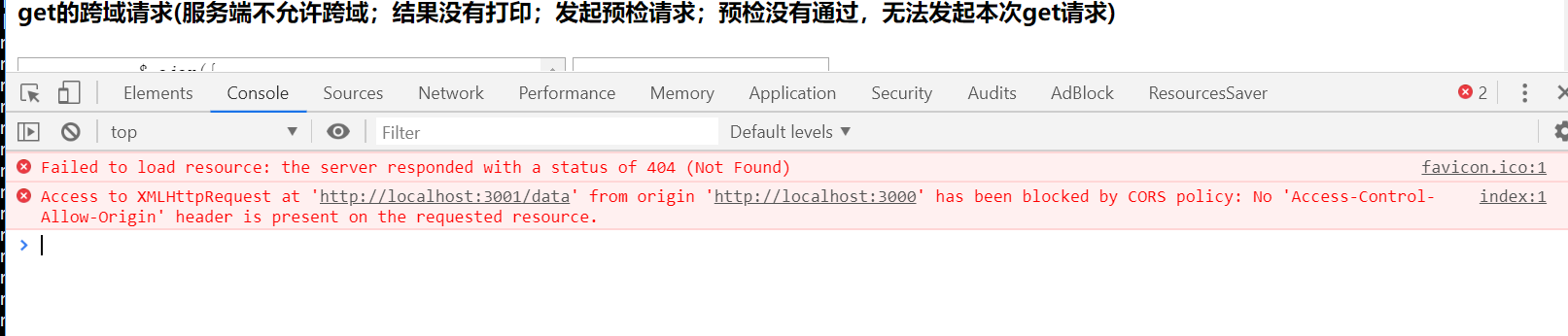
如果都符合了,浏览器将继续执行ajax请求,否则浏览器的控制台则打印以下信息:
img
如何开启并成功请求
-
只需要在服务端开启即可。客户端无需任何改动
-
NodeJs版:
var app = express(); app.use(bodyParser.json()); app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({extended: false})); app.use(function (req, res, next) { res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "http://localhost:3000"); res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "PUT, GET, POST, DELETE, OPTIONS"); res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "Origin, X-Requested-With, Content-Type, Accept, Authorization, Access-Control-Allow-Credentials"); res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Credentials", "true"); next(); }); -
java版(spring-boot)
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod; import org.springframework.web.cors.CorsConfiguration; import org.springframework.web.cors.UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource; import org.springframework.web.filter.CorsFilter; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.CorsRegistry; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter; @Configuration public class CorsConfig { private CorsConfiguration buildConfig() { CorsConfiguration corsConfiguration = new CorsConfiguration(); corsConfiguration.addAllowedOrigin("*"); corsConfiguration.addAllowedHeader("*"); corsConfiguration.setMaxAge(86400L); corsConfiguration.addAllowedMethod(HttpMethod.GET); corsConfiguration.addAllowedMethod(HttpMethod.POST); corsConfiguration.addAllowedMethod(HttpMethod.PUT); corsConfiguration.addAllowedMethod(HttpMethod.DELETE); return corsConfiguration; } @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean corsFilter() { UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource source = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource(); source.registerCorsConfiguration("/**", buildConfig()); FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean(new CorsFilter(source)); return bean; } } -
java-spring-mvc版
import org.springframework.web.filter.OncePerRequestFilter; import javax.servlet.FilterChain; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; /** * @author shihu */ public class CorsFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter { //可以自行设置允许跨域的域名。或者*,代表允许所有 private final static String[] allowOrigin = new String[]{"localhost:3000","localhost:3001"}; @Override public void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException { String currentOrigin = request.getHeader("Origin"); List<String> allowOriginList = Arrays .asList(allowOrigin); if (!allowOriginList.isEmpty()) { if (allowOriginList.contains("*") || allowOriginList.contains(currentOrigin)) { response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin",currentOrigin); } } response.setHeader("Access-Control-Max-Age", "86400");//设置再次发起预检请求的过期时间 response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, OPTIONS"); response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Credentials","true"); response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "*"); filterChain.doFilter(request, response); } @Override public void destroy() { } }
-
注意事项
-
有人想每次发起预检Options请求会觉得浪费资源。后端可以设置Access-Control-Max-Age,就允许在这个时间段内,客户端可以不用再次发起预检请求。
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Max-Age", "86400"); -
为什么能够发起请求,并且成功得到了响应,响应也有内容,但是浏览器不执行请求的响应的脚本。
如:发起一个get请求。得到了服务器的响应。
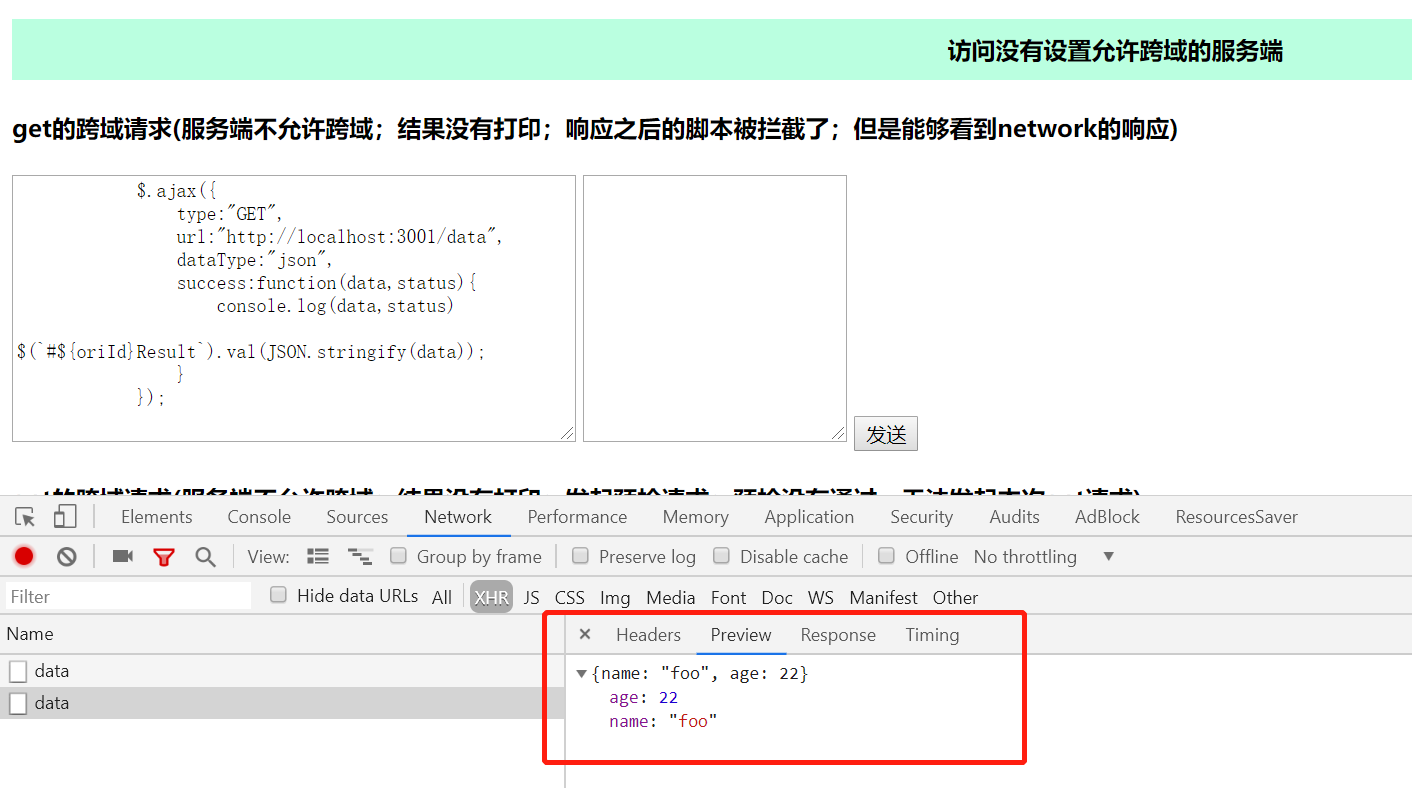
但是浏览器控制台没有继续执行。并报一下错误。因为没有带contentType:"application/json请求头的get请求不会发起预检请求。浏览器无法得知是否允许。但是当响应了,发起请求的域名没有在允许跨域的列表内,浏览器就会为了安全,不会继续执行请求之后的脚本
例子
我写了一个例子
https://github.com/shihua-guo/Java-Learn/tree/master/CORS-Test。
包含了很多种情况的跨域请求。大家能够非常直观的观察跨域请求是如何进行的:


总结
因为之前一直都是复制别人的代码来处理跨域的,自己没有去了解过。而且大部分都是通过代理解决跨域的。这次就写的详细一点,以后就不会忘记了
其实很简单,就是在服务端设置了允许跨域的域(Access-Control-Allow-Origin)、设置了允许跨域的方法(Access-Control-Allow-Methods)、设置了允许跨域的请求头(Access-Control-Allow-Headers)就可以解决跨域共享的问题了。