使用Runtime.getRuntime().exec执行LINUX shell命令没反应
在网上找了很多资料,都说的不是很清楚
正常在linux 环境下执行shell 命令的格式就是:sh xxxx.sh [自定义参数]
由于项目中执行的命令需要重定向输出日志到指定的日志文件。例如:
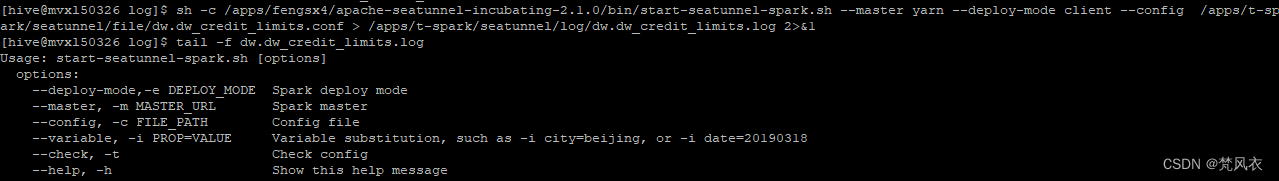
sh /apps/fengsx4/apache-seatunnel-incubating-2.1.0/bin/start-seatunnel-spark.sh --master yarn --deploy-mode client --config /apps/t-spark/seatunnel/file/dw.dw_credit_limits.conf > /apps/t-spark/seatunnel/log/dw.dw_credit_limits.log 2>&1
这样手动执行是可以生效的,在代码中的实现方式:
String executeCommands = String.format("%s --master yarn --deploy-mode client --config %s > %s 2>&1",
seatunnelEnvConf.getSeatunnelHomePath()+seatunnelEnvConf.getSeatunnelRunCommand(),filePath,logPath);
String[] cmd = {"sh", executeCommands };
log.info("执行命令:" + Arrays.toString(cmd));
Process process = run.exec(cmd);
这里在linux环境下执行命令是没有任何反应,也不报错。
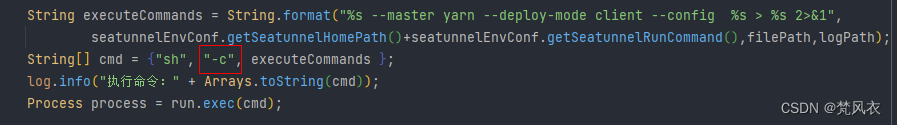
经过一番验证,正确的执行复杂shell 命令并且带重定向管道输出日志文件的实现方式:
String executeCommands = String.format("%s --master yarn --deploy-mode client --config %s > %s 2>&1",
seatunnelEnvConf.getSeatunnelHomePath()+seatunnelEnvConf.getSeatunnelRunCommand(),filePath,logPath);
String[] cmd = {"sh", "-c", executeCommands };
log.info("执行命令:" + Arrays.toString(cmd));
Process process = run.exec(cmd);
看到有啥不同了没有,对,你没看错,就是sh命令后带了 -c 标识
而手动执行是不支持-c 标识的,手动执行会报错:
至于为啥要带-c 标识,参考网上大神的解释:
传参为String类型时,命令不能带有空格或管道符,否则会被截断,这样就不能执行了;
想要执行复杂点的命令,使用重载的方法public Process exec(String [] cmdArray):
其中-c表示后面跟的executeCommands 是一条命令,从而不会被截断,至此运行成功
方法:
| 对象 | 方法说明 |
|---|---|
| Process | exec(String command) 在单独的进程中执行指定的字符串命令。 |
| Process | exec(String cmdarray[]) 在单独的进程中执行指定命令和变量。 |
| Process | exec(String[] cmdarray, String[] envp) 在指定环境的独立进程中执行指定命令和变量。 |
| Process | exec(String[] cmdarray, String[] envp, File dir) 在指定环境和工作目录的独立进程中执行指定的命令和变量。 |
| Process | exec(String command, String[] envp) 在指定环境的单独进程中执行指定的字符串命令。 |
| Process | exec(String command, String[] envp, File dir) 在有指定环境和工作目录的独立进程中执行指定的字符串命令。 |