参考
- (三)Kubernetes 源码剖析之学习Informer机制
- 如何高效掌控K8s资源变化?K8s Informer实现机制浅析
- 25 | 深入解析声明式API(二):编写自定义控制器
- k8s client-go informer中的processorlistener数据消费,缓存的分析
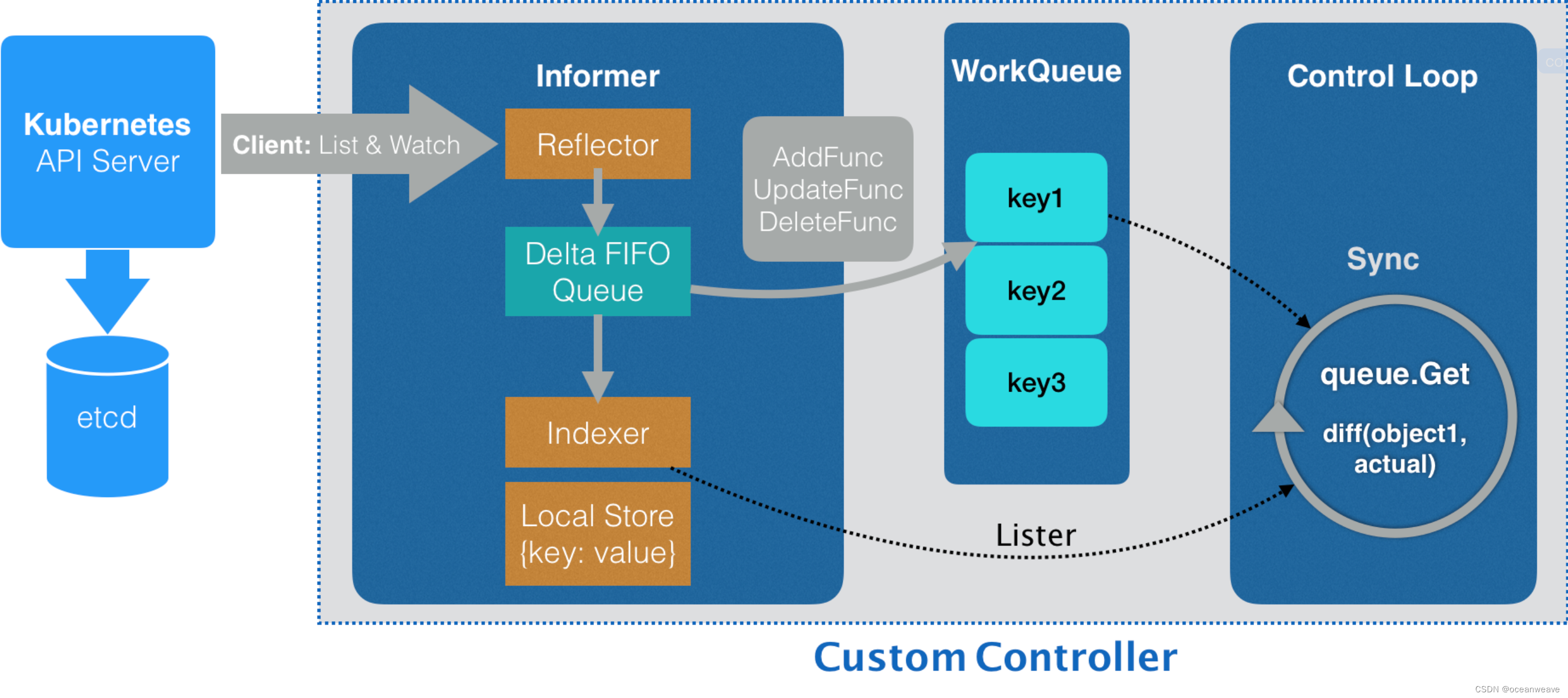
架构
Informer 和 Controller
- 便于理解的架构图
- 这里 Indexer「索引」 和 Local Store 「缓存」 是分开表示的
- 在源码级别,基本上是一起实现的,一个结构体内涵盖
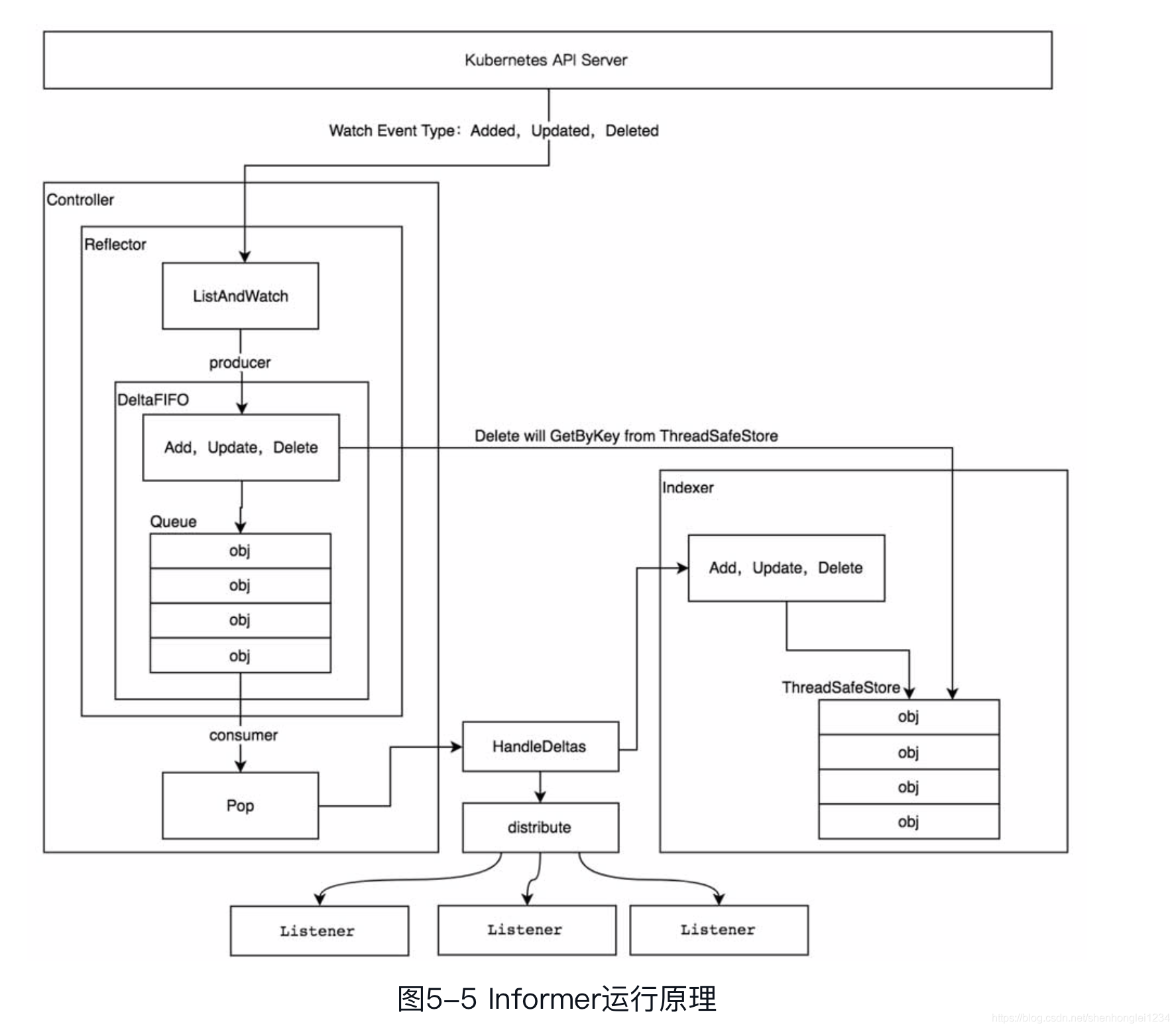
Informer 简要架构
- 源码级简要理解
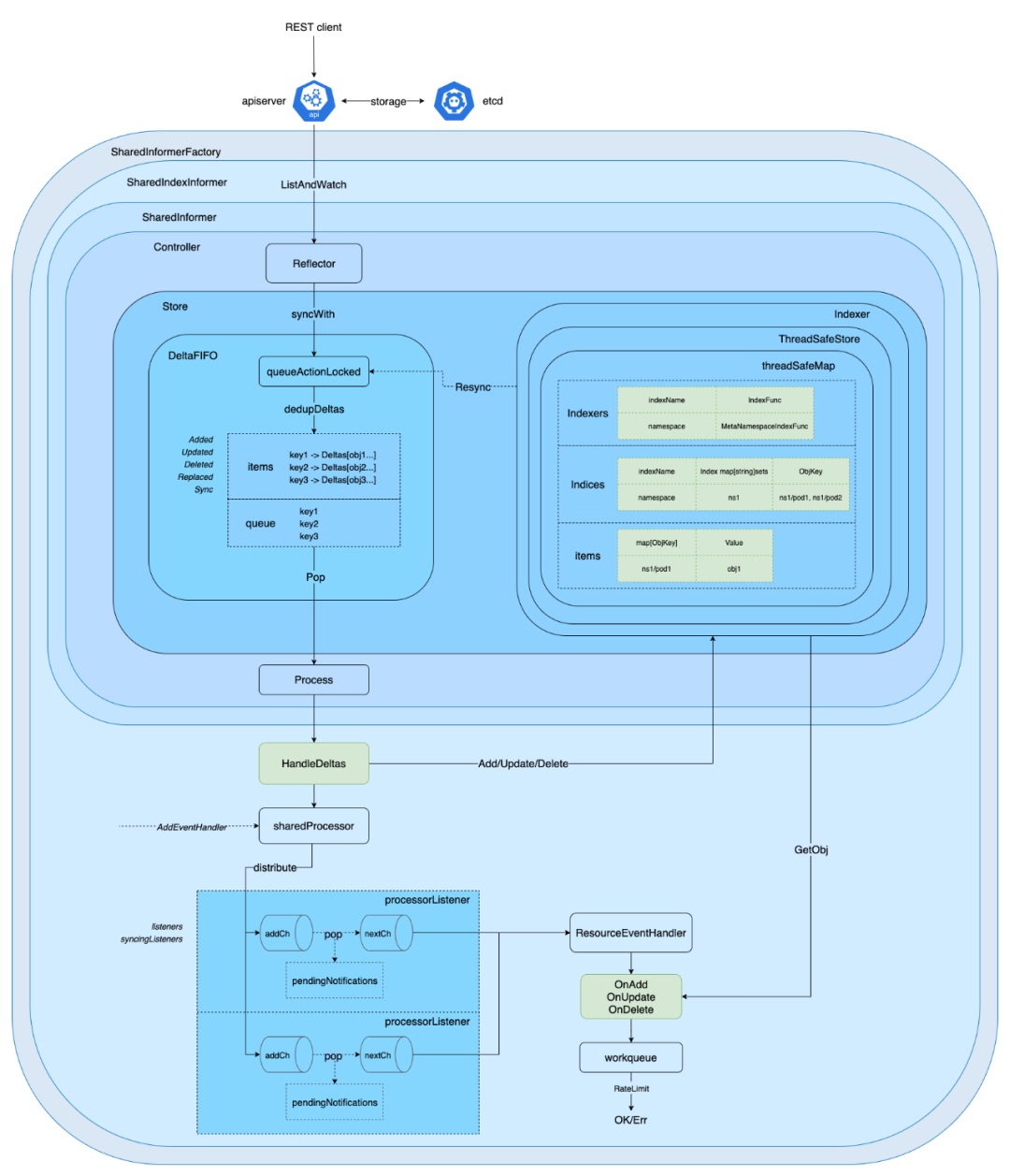
Informer 详细架构
- 源码级详细理解
代码解析
SharedInformer
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/shared_informer.go
type SharedIndexInformer interface {
SharedInformer
// AddIndexers add indexers to the informer before it starts.
AddIndexers(indexers Indexers) error
GetIndexer() Indexer
}
type sharedIndexInformer struct {
// 索引和 缓存 store
indexer Indexer
controller Controller
// 处理函数,将是重点
processor *sharedProcessor
// 检测 cache 是否有变化,一把用作调试,默认是关闭的
cacheMutationDetector MutationDetector
// 构造 Reflector 需要
listerWatcher ListerWatcher
// 目标类型,给 Reflector 判断资源类型
objectType runtime.Object
// Reflector 进行重新同步周期
resyncCheckPeriod time.Duration
// 如果使用者没有添加 Resync 时间,则使用这个默认的重新同步周期
defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod time.Duration
clock clock.Clock
// 两个 bool 表达了三个状态:controller 启动前、已启动、已停止
started, stopped bool
startedLock sync.Mutex
// 当 Pop 正在消费队列,此时新增的 listener 需要加锁,防止消费混乱
blockDeltas sync.Mutex
// Watch 返回 err 的回调函数
watchErrorHandler WatchErrorHandler
}
type sharedProcessor struct {
listenersStarted bool
listenersLock sync.RWMutex
listeners []*processorListener
syncingListeners []*processorListener // 需要 sync 的 listeners
clock clock.Clock
wg wait.Group
}
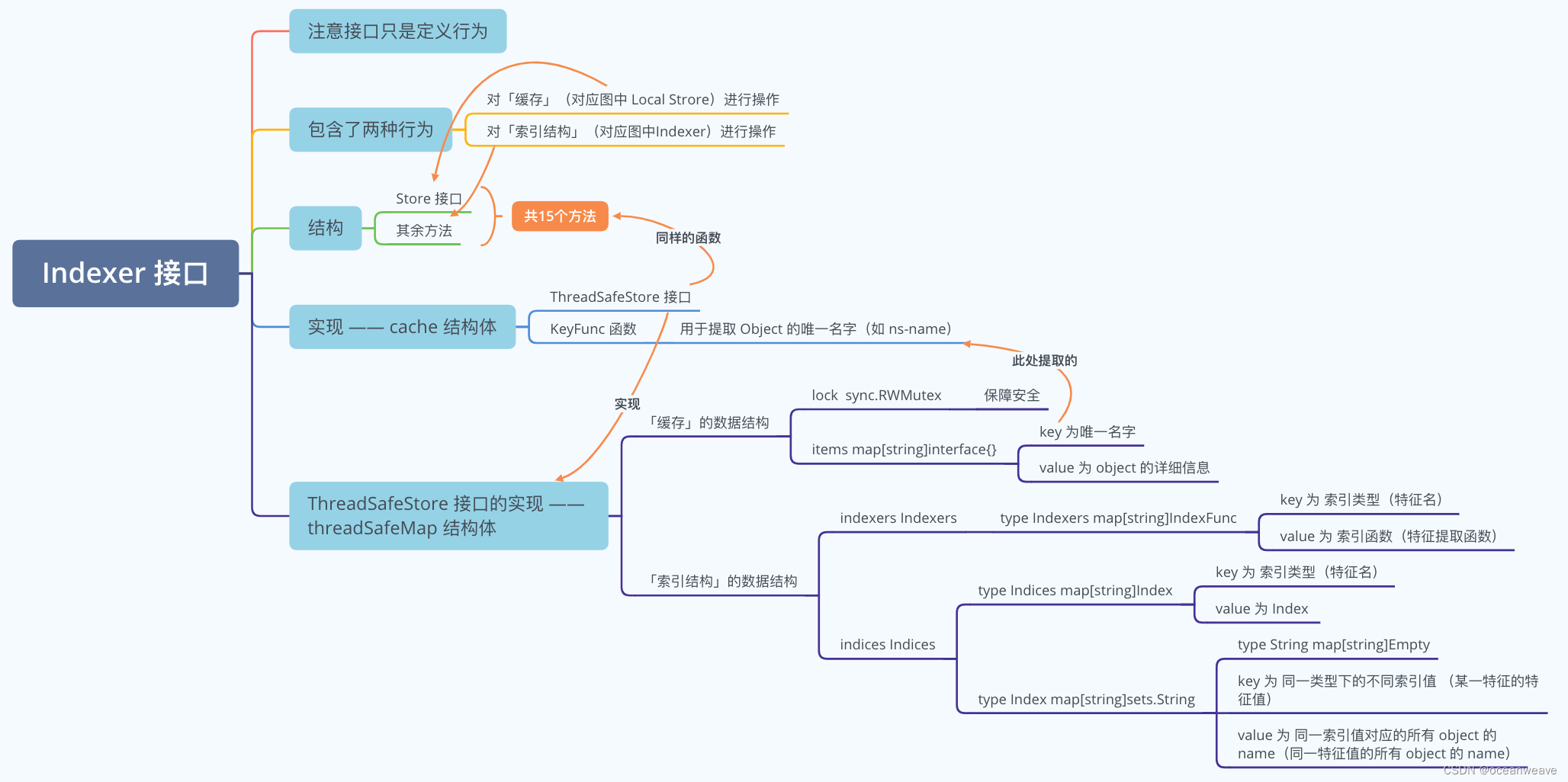
1. Indexer 结构讲解 —— 实现缓存和索引
Indexer 接口 —— 缓存和索引的高级抽象
可以看出 Indexer 封装了 Store 接口,那么就可以实现两部分行为
- 通过 Store 接口,实现对缓存(也就是图中 Local Store)的操作
- 通过本身的其他方法,构建便于查找数据的索引结构
// k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/index.go
// Indexer 封装了 Store 的接口(相当于可以对缓存进行操作)
// 同时 Indexer 本身定义了多种方法,对索引进行操作(构建索引等)
// Store 的作用是:对实际的数据操作,存储、更新等,构建简单的 key —— object 之间的映射
// Indexer 的作用是:构建便于搜索的结构,如 获取某个 namespace 下所有 pod,那可能构建这样索引结构, namespace-key —— (在此namespace 下的 pod1 key,pod2 key ...)
// 通过 pod key 可以在 Store 获取对应的 存储对象(就是 Pod 的具体信息)
type Indexer interface {
// 封装了 缓存 Local Store
Store
// 下面方法 为对 索引结构的操作
// Index returns the stored objects whose set of indexed values
// intersects the set of indexed values of the given object, for
// the named index
Index(indexName string, obj interface{}) ([]interface{}, error)
// IndexKeys returns the storage keys of the stored objects whose
// set of indexed values for the named index includes the given
// indexed value
IndexKeys(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]string, error)
// ListIndexFuncValues returns all the indexed values of the given index
ListIndexFuncValues(indexName string) []string
// ByIndex returns the stored objects whose set of indexed values
// for the named index includes the given indexed value
ByIndex(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]interface{}, error)
// GetIndexer return the indexers
GetIndexers() Indexers
// AddIndexers adds more indexers to this store. If you call this after you already have data
// in the store, the results are undefined.
AddIndexers(newIndexers Indexers) error
}
缓存 Local Store 的抽象定义 —— Store 接口
可以看出 Store 接口主要定义 对缓存(Local Store)的操作
// k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/store.go
// Store 接口定义了 对缓存的操作 (如删除、更新、获取等)
type Store interface {
Add(obj interface{}) error
Update(obj interface{}) error
Delete(obj interface{}) error
List() []interface{}
ListKeys() []string
Get(obj interface{}) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error)
GetByKey(key string) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error)
// Replace will delete the contents of the store, using instead the
// given list. Store takes ownership of the list, you should not reference
// it after calling this function.
Replace([]interface{}, string) error
Resync() error
}
Indexer 的实现 —— cache 结构体
查看代码可以发现,cache 结构体实现了 Indexer 中的所有方法(包含Store部分的方法)
因此可以说 cache 就是 Indexer 接口的实现
- 其中 ThreadSafeStore 接口中的方法涵盖了 Indexer 接口的所有方法,因此若实现了 ThreadSafeStore 接口 就相当于实现了 Indexer 接口
- KeyFunc 定义函数,用于计算 Object 的 key
// Store 的实际实现 cache
// k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/store.go
// cache responsibilities are limited to:
// 1. Computing keys for objects via keyFunc
// 2. Invoking methods of a ThreadSafeStorage interface
type cache struct {
// cacheStorage bears the burden of thread safety for the cache
// 这是个接口其实 就涵盖了 Indexer 接口 的所有方法
// 因此实现了 ThreadSafeStore 该接口,就相当于实现了 Indexer 接口
cacheStorage ThreadSafeStore
// keyFunc is used to make the key for objects stored in and retrieved from items, and
// should be deterministic.
// 用于计算 Object 的 key
keyFunc KeyFunc
}
ThreadSafeStore 接口 —— 实现 Indexer 接口的准备
可以数一数
Indexer 接口(包含Store接口)一共定义了 15 个方法
ThreadSafeStore 也定义了 15 个方法
同时他们的函数名称及函数定义一致
因此 实现了 ThreadSafeStore 接口 等同于 实现了 Indexer 接口
// k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
// ThreadSafeStore 接口
// 表示可以对缓存的操作
type ThreadSafeStore interface {
Add(key string, obj interface{})
Update(key string, obj interface{})
Delete(key string)
Get(key string) (item interface{}, exists bool)
List() []interface{}
ListKeys() []string
Replace(map[string]interface{}, string)
Index(indexName string, obj interface{}) ([]interface{}, error)
IndexKeys(indexName, indexKey string) ([]string, error)
ListIndexFuncValues(name string) []string
ByIndex(indexName, indexKey string) ([]interface{}, error)
GetIndexers() Indexers
// AddIndexers adds more indexers to this store. If you call this after you already have data
// in the store, the results are undefined.
AddIndexers(newIndexers Indexers) error
Resync() error
}
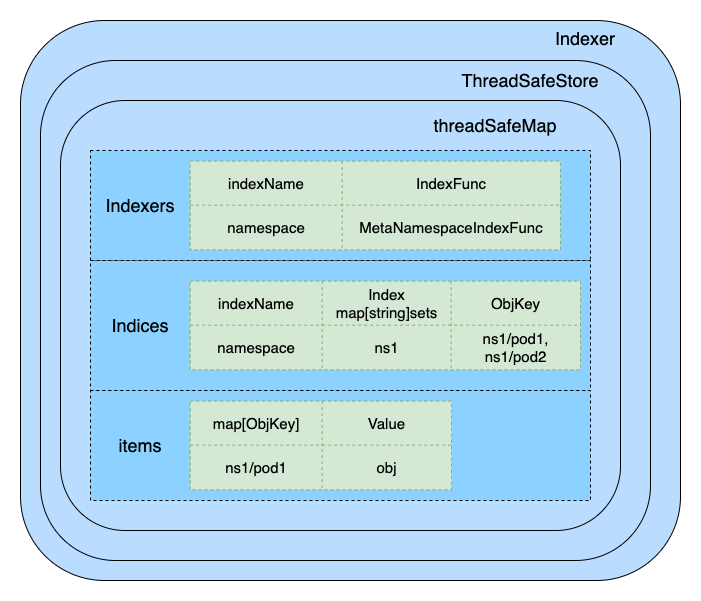
ThreadSafeStore 接口的实现 —— threadSafeMap 结构体
threadSafeMap 结构体 可以称之为 缓存(Local Store)的实际数据存储结构(通过map + Lock 进行存储)
- 数据的实际存储 —— items map[string]interface{}
- 索引的构建 —— indexers Indexers
- 索引的存储 —— indices Indices
// k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
// threadSafeMap implements ThreadSafeStore
type threadSafeMap struct {
// 相当于缓存的本质,存储着 key-object
lock sync.RWMutex
items map[string]interface{}
// Indexers Indices 也是map 结构
// 相当于 索引的 结构、下面详细介绍
// indexers maps a name to an IndexFunc
indexers Indexers
// indices maps a name to an Index
indices Indices
}
真正索引的结构 —— Indexers、Indices、Index
// map 索引类型 => 索引函数
type Indexers map[string]IndexFuncIndexers 可以理解为:key —— 特征名称(如 namespace 特征),value —— 特征提取函数的名称(该函数可提取 object 的 namespace 名称)
// map 索引类型 => 索引值 map
type Indices map[string]IndexIndices 可以理解为: key —— 特征名称(如 namespace 特征),value —— 不同特征值所对应的 object 列表(如存在 2 个 ns,每个 ns 中有多个 pod,不同的 ns 会计算出不同的 特征值,然后指向的 object 列表为其对应 ns 下的 所有 pod 名称)
// 索引值 map: 由索引函数计算所得索引值(indexedValue) => [objKey1, objKey2…]
type Index map[string]sets.StringIndex 可以理解为: key —— 特征值(每个 ns 的特征值都会不一致),value —— 特征值相同的所有 object(同一个ns 下的所有 pod 的特征值ns相同,因此该 object 列表记录着该 ns 下的所有 pod 名称)
// k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/index.go
// Index maps the indexed value to a set of keys in the store that match on that value
// 索引值 map: 由索引函数计算所得索引值(indexedValue) => [objKey1, objKey2...]
type Index map[string]sets.String
// Indexers maps a name to a IndexFunc
// map 索引类型 => 索引函数
type Indexers map[string]IndexFunc
// Indices maps a name to an Index
// map 索引类型 => 索引值 map
type Indices map[string]Index
// k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/util/sets/string.go
// sets.String 可以理解为 没有重复元素的数组,不过在 go 语言里面是采用 map 形式构建,因为 map 的 key 不能重复
// sets.String is a set of strings, implemented via map[string]struct{} for minimal memory consumption.
type String map[string]Empty
为了便于理解我举个例子
// map 索引类型 => 索引函数
type Indexers map[string]IndexFunc
// --------- 场景
// 目前 Indexers 中有这样的数据{"namespace":NsHashFunc,"labels":LabelsHashFunc}
// 同时此时有 3 个 pod
// default namespace 下有俩个 pod : pod1 pod2
// test namespace 下有一个 pod: pod3
// 且这三个 pod 的 label 都不相同
// --------- 构建索引
// namespace 接下来将构建 Indices 和 Index
// 1. 计算所有 pod 的索引值,将 pod 逐个通过 Indexers 中的所有函数进行计算
// pod1 —— NsHashFunc 计算结果为 100,LabelsHashFunc 计算结果为 2000
// pod2 —— NsHashFunc 计算结果为 100,LabelsHashFunc 计算结果为 3000
// pod3 —— NsHashFunc 计算结果为 200,LabelsHashFunc 计算结果为 4000
// 2. 构建索引 Indices map[string]Index
// 由 Indexers 有两种类型 namespace 和 labels,因此逐个构建 {"namespace":Index, "labels": Index}
// Index map[string]sets.String 的 key 为索引值,值为 objectKey( 就是通过 cache 结构体中 KeyFunc 计算得到的,namspace/name 的组合)
// 遍历 namespace 类型的索引值,构建了如下 Index 结构:
{
"100":{"default/pod1","default/pod2"},
"200":{"default/pod3"}
}
// 遍历 lables 类型的索引值,构建了如下 Index 结构:
{
"2000":{"default/pod1"},
"3000":{"default/pod2"},
"4000":{"default/pod3"}
}
// 所以最后成的 Indices 为
{
"nameapces":{
"100":{"default/pod1","default/pod2"},
"200":{"default/pod3"}
},
"labels":{
"2000":{"default/pod1"},
"3000":{"default/pod2"},
"4000":{"default/pod3"}
}
}