前言
关于Dubbo,本系列文章主要讲三方面内容。前两讲我们已经了解到Dubbo的基本特性,常用配置、自适应扩展点与服务发布,服务注册的过程。
- 解开Dubbo的神秘面纱
- Dubbo常用配置
- Dubbo源码分析(上篇)
- Dubbo源码分析(中篇)
- Dubbo源码分析(下篇)
本节我们讲3、4
- Dubbo Extension扩展点
- 服务发布过程
- 消费端初始化过程
- 服务端调用过程
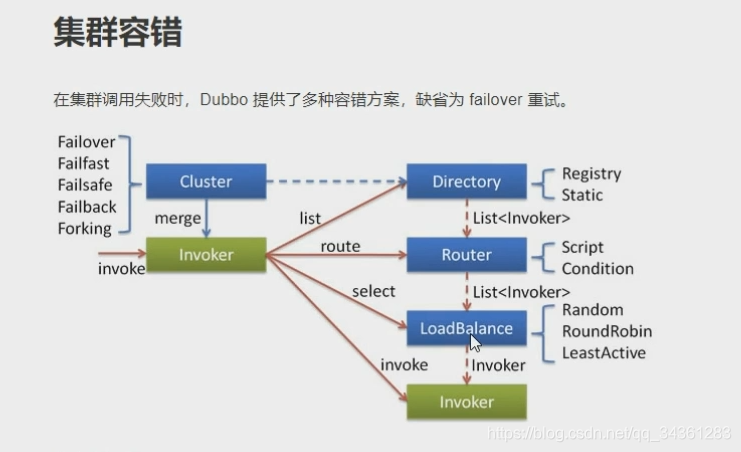
- Directory
- Cluster
- LoadBalance
Tips:本节文末有Dubbo中文注释版的源码哦~
消费端初始化过程
前面提到的的dubbo客户端配置文件,要指定消费的服务信息:
<dubbo:reference id="xxxService" interface="xxx.xxx.Service"/>
消费端的代码解析是从下面这段代码开始的
ReferenceBean(afterPropertiesSet) ->getObject() ->get()->init()->createProxy 最终会获得一个代理对象
public class ReferenceBean<T> extends ReferenceConfig<T> implements FactoryBean, ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {}
Tips:
我们之前提到过的ServiceBean也是通过实现InitializingBean接口,在Spring容器初始化时,就执行afterPropertiesSet方法,这里的ReferenceBean也是如此
ReferenceConfig.createProxy
然后我们顺着ReferenceBean(afterPropertiesSet) ->getObject() ->get()->init()->createProxy思路,就进入到ReferenceConfig.createProxy
前面很多代码都是初始化的动作,需要仔细分析的代码代码从createProxy开始
private T createProxy(Map<String, String> map) {
URL tmpUrl = new URL("temp", "localhost", 0, map);
final boolean isJvmRefer;
if (isInjvm() == null) {
if (url != null && url.length() > 0) { //指定URL的情况下,不做本地引用
isJvmRefer = false;
} else if (InjvmProtocol.getInjvmProtocol().isInjvmRefer(tmpUrl)) {
//默认情况下如果本地有服务暴露,则引用本地服务.
isJvmRefer = true;
} else {
isJvmRefer = false;
}
} else {
isJvmRefer = isInjvm().booleanValue();
}
if (isJvmRefer) {
URL url = new URL(Constants.LOCAL_PROTOCOL, NetUtils.LOCALHOST, 0, interfaceClass.getName()).addParameters(map);
invoker = refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, url);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Using injvm service " + interfaceClass.getName());
}
} else {
if (url != null && url.length() > 0) { // 用户指定URL,指定的URL可能是对点对直连地址,也可能是注册中心URL
String[] us = Constants.SEMICOLON_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(url);
if (us != null && us.length > 0) {
for (String u : us) {
URL url = URL.valueOf(u);
if (url.getPath() == null || url.getPath().length() == 0) {
url = url.setPath(interfaceName);
}
if (Constants.REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) {
urls.add(url.addParameterAndEncoded(Constants.REFER_KEY, StringUtils.toQueryString(map)));
} else {
urls.add(ClusterUtils.mergeUrl(url, map));
}
}
}
} else { // 通过注册中心配置拼装URL
List<URL> us = loadRegistries(false);
if (us != null && us.size() > 0) {
for (URL u : us) {
URL monitorUrl = loadMonitor(u);
if (monitorUrl != null) {
map.put(Constants.MONITOR_KEY, URL.encode(monitorUrl.toFullString()));
}
urls.add(u.addParameterAndEncoded(Constants.REFER_KEY, StringUtils.toQueryString(map)));
}
}
if (urls == null || urls.size() == 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No such any registry to reference " + interfaceName + " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ", please config <dubbo:registry address=\"...\" /> to your spring config.");
}
}
if (urls.size() == 1) {
invoker = refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, urls.get(0));
} else {
List<Invoker<?>> invokers = new ArrayList<Invoker<?>>();
URL registryURL = null;
for (URL url : urls) {
invokers.add(refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, url));
if (Constants.REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) {
registryURL = url; // 用了最后一个registry url
}
}
if (registryURL != null) { // 有 注册中心协议的URL
// 对有注册中心的Cluster 只用 AvailableCluster
URL u = registryURL.addParameter(Constants.CLUSTER_KEY, AvailableCluster.NAME);
invoker = cluster.join(new StaticDirectory(u, invokers));
} else { // 不是 注册中心的URL
invoker = cluster.join(new StaticDirectory(invokers));
}
}
}
//...
// 创建服务代理
return (T) proxyFactory.getProxy(invoker);
}
}
refprotocol.refer
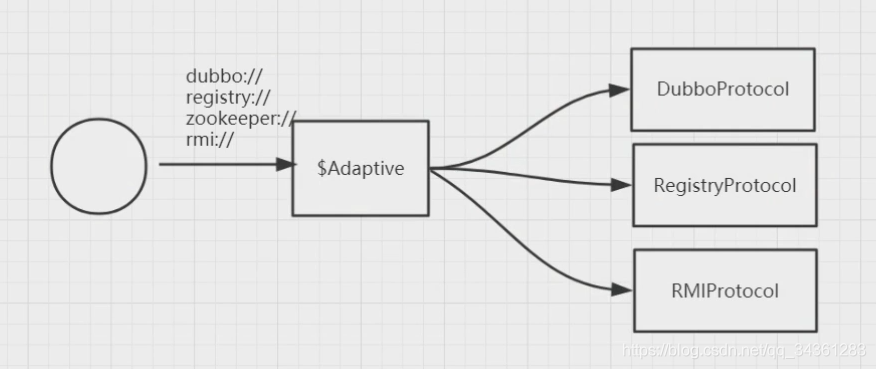
refprotocol这个对象,定义的代码如下,是一个自适应扩展点,得到的是Protocol$Adaptive。
Protocol refprotocol = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
直接找到Protocol$Adaptive代码中的refer代码块如下
这段代码中,根据当前的协议url,得到一个指定的扩展点,传递进来的参数中,协议地址为registry://,所以,我们可以直接定位到RegistryProtocol.refer代码
public com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker refer(java.lang.Class arg0, com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL arg1) throws com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcException {
if (arg1 == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL url = arg1;
String extName = (url.getProtocol() == null ? "dubbo" : url.getProtocol());
if (extName == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Fail to get extension(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol) name from url(" + url.toString() + ") use keys([protocol])");
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol extension = (com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol) ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.class).getExtension(extName);
return extension.refer(arg0, arg1);
}
RegistryProtocol.refer
这个方法里面的代码,基本上都能看懂
- 根据根据url获得注册中心,这个registry是zookeeperRegistry
- 调用doRefer,按方法,传递了几个参数, 其中有一个culster参数,这个需要注意下
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException {
url = url.setProtocol(url.getParameter(Constants.REGISTRY_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_REGISTRY)).removeParameter(Constants.REGISTRY_KEY);
Registry registry = registryFactory.getRegistry(url);
if (RegistryService.class.equals(type)) {
return proxyFactory.getInvoker((T) registry, type, url);
}
// group="a,b" or group="*"
Map<String, String> qs = StringUtils.parseQueryString(url.getParameterAndDecoded(Constants.REFER_KEY));
String group = qs.get(Constants.GROUP_KEY);
if (group != null && group.length() > 0 ) {
if ( ( Constants.COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN.split( group ) ).length > 1
|| "*".equals( group ) ) {
return doRefer( getMergeableCluster(), registry, type, url );
}
}
return doRefer(cluster, registry, type, url);
}
cluster
doRefer方法中有一个参数是cluster,我们找到它的定义代码如下,。又是一个自动注入的扩展点。
private Cluster cluster;
public void setCluster(Cluster cluster) {
this.cluster = cluster;
}
从下面的代码可以看出,这个不仅仅是一个扩展点,而且方法层面上,还有一个@Adaptive,表示会动态生成一个自适应适配器Cluster$Adaptive
@SPI(FailoverCluster.NAME)
public interface Cluster {
/**
* Merge the directory invokers to a virtual invoker.
*
* @param <T>
* @param directory
* @return cluster invoker
* @throws RpcException
*/
@Adaptive
<T> Invoker<T> join(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException;
}
Cluster$Adaptive
通过debug的方式,,获取到Cluster$Adaptive这个适配器,代码如下。我们知道cluster这个对象的实例以后,继续看doRefer方法;
注意:这里的Cluster$Adaptive也并不单纯,大家还记得在讲扩展点的时候有一个扩展点装饰器吗?如果这个扩展点存在一个构造函数,并且构造函数就是扩展接口本身,那么这个扩展点就会这个wrapper装饰,而Cluster被装饰的是:MockClusterWrapper
public class Cluster$Adaptive implements com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster {
public com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker join(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory arg0) throws com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcException {
if (arg0 == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory argument == null");
if (arg0.getUrl() == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory argument getUrl() == null");
com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL url = arg0.getUrl();
String extName = url.getParameter("cluster", "failover");
if (extName == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Fail to get extension(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster) name from url(" + url.toString() + ") use keys([cluster])");
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster extension = (com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster) ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster.class).getExtension(extName);
return extension.join(arg0);
}
}
RegistryProtocol.doRefer
这段代码中,有一个RegistryDirectory,可能看不懂,我们暂时先忽略,等会单独讲.(基于注册中心动态发现服务提供者)
- 将consumer://协议地址注册到注册中心
- 订阅zookeeper地址的变化
- 调用cluster.join()方法
private <T> Invoker<T> doRefer(Cluster cluster, Registry registry, Class<T> type, URL url) {
RegistryDirectory<T> directory = new RegistryDirectory<T>(type, url);
directory.setRegistry(registry);
directory.setProtocol(protocol);
URL subscribeUrl = new URL(Constants.CONSUMER_PROTOCOL, NetUtils.getLocalHost(), 0, type.getName(), directory.getUrl().getParameters());
if (! Constants.ANY_VALUE.equals(url.getServiceInterface())
&& url.getParameter(Constants.REGISTER_KEY, true)) {
registry.register(subscribeUrl.addParameters(Constants.CATEGORY_KEY, Constants.CONSUMERS_CATEGORY,
Constants.CHECK_KEY, String.valueOf(false)));
}
directory.subscribe(subscribeUrl.addParameter(Constants.CATEGORY_KEY,
Constants.PROVIDERS_CATEGORY
+ "," + Constants.CONFIGURATORS_CATEGORY
+ "," + Constants.ROUTERS_CATEGORY));
return cluster.join(directory);
}
cluster.join
由前面的Cluster$Adaptive这个类中的join方法的分析,得知cluster.join会调用MockClusterWrapper.join方法, 然后再调用FailoverCluster.join方法。
MockClusterWrapper.join
这个意思很明显了。也就是我们之前提到过的mock容错机制,如果出现异常情况,会调用MockClusterInvoker,否则,调用FailoverClusterInvoker.
public class MockClusterWrapper implements Cluster {
private Cluster cluster;
public MockClusterWrapper(Cluster cluster) {
this.cluster = cluster;
}
public <T> Invoker<T> join(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
return new MockClusterInvoker<T>(directory,
this.cluster.join(directory));
}
}
小结
回到最初的起点到ReferenceConfig:
if (urls.size() == 1) {
invoker = refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, urls.get(0));
}
通过前面的代码逻辑,我们知道:invoker 得到的就是MockClusterInvoker(FailoverClusterInvoker)。这里面一定还有疑问,我们先把主线走完,再回过头看看什么是cluster?什么是directory?
proxyFactory.getProxy(invoker);
再回到ReferenceConfig这个类,在createProxy方法的最后一行,调用proxyFactory.getProxy(invoker). 把前面生成的invoker对象作为参数,再通过proxyFactory工厂去获得一个代理对象。接下来我们分析下这段代码做了什么。
其实前面在分析服务发布的时候,基本分析过了,所以再看这段代码,应该会很熟悉
ProxyFactory, 会生成一个动态的自适应适配器。ProxyFactory$Adaptive,然后调用这个适配器中的getProxy方法,代码如下
public java.lang.Object getProxy(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker arg0) throws com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcException {
if (arg0 == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker argument == null");
if (arg0.getUrl() == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker argument getUrl() == null");com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL url = arg0.getUrl();
String extName = url.getParameter("proxy", "javassist");
if(extName == null) throw new IllegalStateException("Fail to get extension(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory) name from url(" + url.toString() + ") use keys([proxy])");
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory extension = (com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory.class).getExtension(extName);
return extension.getProxy(arg0);
}
很显然,又是通过javassist实现的一个动态代理,我们来看看JavassistProxyFactory.getProxy
JavassistProxyFactory.getProxy
通过javasssist动态字节码生成动态代理类,
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
return (T) Proxy.getProxy(interfaces).newInstance(new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker));
}
proxy.getProxy(interfaces)
在Proxy.getProxy这个类的如下代码中添加断点,在debug下可以看到动态字节码如下
public java.lang.String sayHello(java.lang.String arg0){
Object[] args = new Object[1];
args[0] = ($w)$1;
Object ret = handler.invoke(this, methods[0], args);
return (java.lang.String)ret;
}
上面的handler,就是在JavassistProxyFactory.getProxy中。传递的new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker)
最后回到主线ReferenceConfig.createProxy创建服务代理看到这里,我们不禁思考?什么时候和服务端建立连接呢?服务是怎么调用的?
什么时候和服务端建立连接
前面我们通过代码分析到了,消费端的初始化过程,但是似乎没有看到客户端和服务端建立NIO连接。实际上,建立连接的过程在消费端初始化的时候就建立好的,只是前面我们没有分析,代码在RegistryProtocol.doRefer方法内的directory.subscribe方法中。
private <T> Invoker<T> doRefer(Cluster cluster, Registry registry, Class<T> type, URL url) {
RegistryDirectory<T> directory = new RegistryDirectory<T>(type, url);
directory.setRegistry(registry);
directory.setProtocol(protocol);
URL subscribeUrl = new URL(Constants.CONSUMER_PROTOCOL, NetUtils.getLocalHost(), 0, type.getName(), directory.getUrl().getParameters());
if (! Constants.ANY_VALUE.equals(url.getServiceInterface())
&& url.getParameter(Constants.REGISTER_KEY, true)) {
registry.register(subscribeUrl.addParameters(Constants.CATEGORY_KEY, Constants.CONSUMERS_CATEGORY,
Constants.CHECK_KEY, String.valueOf(false)));
}
// build connection
directory.subscribe(subscribeUrl.addParameter(Constants.CATEGORY_KEY,
Constants.PROVIDERS_CATEGORY
+ "," + Constants.CONFIGURATORS_CATEGORY
+ "," + Constants.ROUTERS_CATEGORY));
return cluster.join(directory);
}
directory.subscribe
调用链为: RegistryDirectory.subscribe ->FailbackRegistry. subscribe->-AbstractRegistry.subscribe>zookeeperRegistry.doSubscribe
public void subscribe(URL url) {
setConsumerUrl(url);
registry.subscribe(url, this);
}
FailbackRegistry. subscribe
调用FailbackRegistry.subscribe 进行订阅,这里有一个特殊处理,如果订阅失败,则会添加到定时任务中进行重试
@Override
public void subscribe(URL url, NotifyListener listener) {
super.subscribe(url, listener);
removeFailedSubscribed(url, listener);
try {
// 向服务器端发送订阅请求
doSubscribe(url, listener);
} catch (Exception e) {
Throwable t = e;
List<URL> urls = getCacheUrls(url);
if (urls != null && urls.size() > 0) {
notify(url, listener, urls);
logger.error("Failed to subscribe " + url + ", Using cached list: " + urls + " from cache file: " + getUrl().getParameter(Constants.FILE_KEY, System.getProperty("user.home") + "/dubbo-registry-" + url.getHost() + ".cache") + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
} else {
// 如果开启了启动时检测,则直接抛出异常
boolean check = getUrl().getParameter(Constants.CHECK_KEY, true)
&& url.getParameter(Constants.CHECK_KEY, true);
boolean skipFailback = t instanceof SkipFailbackWrapperException;
if (check || skipFailback) {
if(skipFailback) {
t = t.getCause();
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to subscribe " + url + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
} else {
logger.error("Failed to subscribe " + url + ", waiting for retry, cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
}
// 将失败的订阅请求记录到失败列表,定时重试
addFailedSubscribed(url, listener);
}
}
zookeeperRegistry. doSubscribe
调用zookeeperRegistry执行真正的订阅操作,这里面主要做两个操作:
- 对providers/routers/configuration三个节点进行创建和监听
- 调用notify(url,listener,urls) 将已经可用的列表进行通知
protected void doSubscribe(final URL url, final NotifyListener listener) {
try {
if (Constants.ANY_VALUE.equals(url.getServiceInterface())) {
String root = toRootPath();
ConcurrentMap<NotifyListener, ChildListener> listeners = zkListeners.get(url);
if (listeners == null) {
zkListeners.putIfAbsent(url, new ConcurrentHashMap<NotifyListener, ChildListener>());
listeners = zkListeners.get(url);
}
ChildListener zkListener = listeners.get(listener);
if (zkListener == null) {
listeners.putIfAbsent(listener, new ChildListener() {
public void childChanged(String parentPath, List<String> currentChilds) {
for (String child : currentChilds) {
child = URL.decode(child);
if (! anyServices.contains(child)) {
anyServices.add(child);
subscribe(url.setPath(child).addParameters(Constants.INTERFACE_KEY, child,
Constants.CHECK_KEY, String.valueOf(false)), listener);
}
}
}
});
zkListener = listeners.get(listener);
}
zkClient.create(root, false);
List<String> services = zkClient.addChildListener(root, zkListener);
if (services != null && services.size() > 0) {
for (String service : services) {
service = URL.decode(service);
anyServices.add(service);
subscribe(url.setPath(service).addParameters(Constants.INTERFACE_KEY, service,
Constants.CHECK_KEY, String.valueOf(false)), listener);
}
}
} else {
List<URL> urls = new ArrayList<URL>();
for (String path : toCategoriesPath(url)) {
ConcurrentMap<NotifyListener, ChildListener> listeners = zkListeners.get(url);
if (listeners == null) {
zkListeners.putIfAbsent(url, new ConcurrentHashMap<NotifyListener, ChildListener>());
listeners = zkListeners.get(url);
}
ChildListener zkListener = listeners.get(listener);
if (zkListener == null) {
listeners.putIfAbsent(listener, new ChildListener() {
public void childChanged(String parentPath, List<String> currentChilds) {
ZookeeperRegistry.this.notify(url, listener, toUrlsWithEmpty(url, parentPath, currentChilds));
}
});
zkListener = listeners.get(listener);
}
zkClient.create(path, false);
List<String> children = zkClient.addChildListener(path, zkListener);
if (children != null) {
urls.addAll(toUrlsWithEmpty(url, path, children));
}
}
notify(url, listener, urls);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RpcException("Failed to subscribe " + url + " to zookeeper " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
此方法真正的调用zookeeper的api,操作zk的节点,这也是为什么我们在zk的客户端可以看到,通过dubbo路由的服务,会产生providers/routers/configuration这三个节点
AbstractRegistry.notify
这里注意notify方法调用层次:FailbackRegistry(notify)-> AbstractRegistry(notify)
protected void notify(URL url, NotifyListener listener, List<URL> urls) {
//
Map<String, List<URL>> result = new HashMap<String, List<URL>>();
for (URL u : urls) {
if (UrlUtils.isMatch(url, u)) {
String category = u.getParameter(Constants.CATEGORY_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_CATEGORY);
List<URL> categoryList = result.get(category);
if (categoryList == null) {
categoryList = new ArrayList<URL>();
result.put(category, categoryList);
}
categoryList.add(u);
}
}
if (result.size() == 0) {
return;
}
Map<String, List<URL>> categoryNotified = notified.get(url);
if (categoryNotified == null) {
notified.putIfAbsent(url, new ConcurrentHashMap<String, List<URL>>());
categoryNotified = notified.get(url);
}
//对providers/routers/configuration 路径下进行notify
//第一次调用
//后续的(watcher机制)notify(通知)
for (Map.Entry<String, List<URL>> entry : result.entrySet()) {
String category = entry.getKey();
List<URL> categoryList = entry.getValue();
categoryNotified.put(category, categoryList);
saveProperties(url);
listener.notify(categoryList);
}
}
listener.notify(categoryList);
这里调用RegistryDirectory.notify
public interface NotifyListener {
/**
* 当收到服务变更通知时触发。
*
* 通知需处理契约:<br>
* 1. 总是以服务接口和数据类型为维度全量通知,即不会通知一个服务的同类型的部分数据,用户不需要对比上一次通知结果。<br>
* 2. 订阅时的第一次通知,必须是一个服务的所有类型数据的全量通知。<br>
* 3. 中途变更时,允许不同类型的数据分开通知,比如:providers, consumers, routers, overrides,允许只通知其中一种类型,但该类型的数据必须是全量的,不是增量的。<br>
* 4. 如果一种类型的数据为空,需通知一个empty协议并带category参数的标识性URL数据。<br>
* 5. 通知者(即注册中心实现)需保证通知的顺序,比如:单线程推送,队列串行化,带版本对比。<br>
*
* @param urls 已注册信息列表,总不为空,含义同{@link com.alibaba.dubbo.registry.RegistryService#lookup(URL)}的返回值。
*/
void notify(List<URL> urls);
}
RegistryDirectory.notify
public synchronized void notify(List<URL> urls) {
List<URL> invokerUrls = new ArrayList<URL>();
List<URL> routerUrls = new ArrayList<URL>();
List<URL> configuratorUrls = new ArrayList<URL>();
for (URL url : urls) {
String protocol = url.getProtocol();
String category = url.getParameter(Constants.CATEGORY_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_CATEGORY);
if (Constants.ROUTERS_CATEGORY.equals(category)
|| Constants.ROUTE_PROTOCOL.equals(protocol)) {
routerUrls.add(url);
} else if (Constants.CONFIGURATORS_CATEGORY.equals(category)
|| Constants.OVERRIDE_PROTOCOL.equals(protocol)) {
configuratorUrls.add(url);
} else if (Constants.PROVIDERS_CATEGORY.equals(category)) {
invokerUrls.add(url);
} else {
logger.warn("Unsupported category " + category + " in notified url: " + url + " from registry " + getUrl().getAddress() + " to consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost());
}
}
// configurators
if (configuratorUrls != null && configuratorUrls.size() >0 ){
this.configurators = toConfigurators(configuratorUrls);
}
// routers
if (routerUrls != null && routerUrls.size() >0 ){
List<Router> routers = toRouters(routerUrls);
if(routers != null){ // null - do nothing
setRouters(routers);
}
}
List<Configurator> localConfigurators = this.configurators; // local reference
// 合并override参数
this.overrideDirectoryUrl = directoryUrl;
if (localConfigurators != null && localConfigurators.size() > 0) {
for (Configurator configurator : localConfigurators) {
this.overrideDirectoryUrl = configurator.configure(overrideDirectoryUrl);
}
}
// providers
refreshInvoker(invokerUrls);
}
refreshInvoker
/**
* 根据invokerURL列表转换为invoker列表。转换规则如下:
* 1.如果url已经被转换为invoker,则不在重新引用,直接从缓存中获取,注意如果url中任何一个参数变更也会重新引用
* 2.如果传入的invoker列表不为空,则表示最新的invoker列表
* 3.如果传入的invokerUrl列表是空,则表示只是下发的override规则或route规则,需要重新交叉对比,决定是否需要重新引用。
* @param invokerUrls 传入的参数不能为null
*/
private void refreshInvoker(List<URL> invokerUrls){
if (invokerUrls != null && invokerUrls.size() == 1 && invokerUrls.get(0) != null
&& Constants.EMPTY_PROTOCOL.equals(invokerUrls.get(0).getProtocol())) {
this.forbidden = true; // 禁止访问
this.methodInvokerMap = null; // 置空列表
destroyAllInvokers(); // 关闭所有Invoker
} else {
this.forbidden = false; // 允许访问
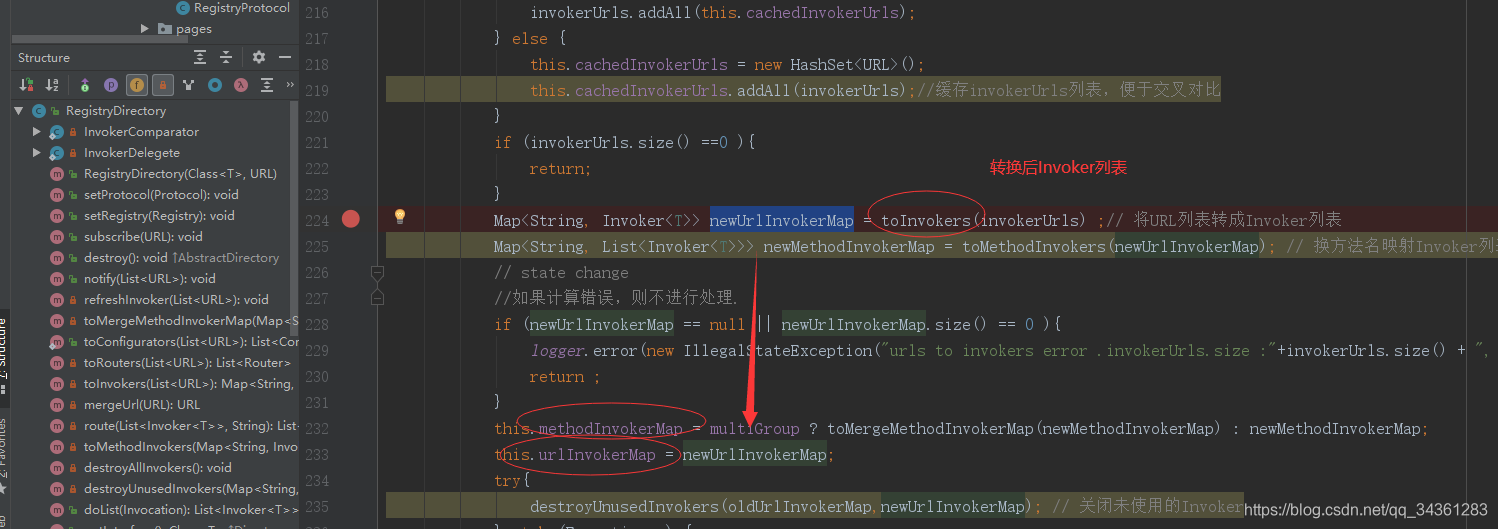
Map<String, Invoker<T>> oldUrlInvokerMap = this.urlInvokerMap; // local reference
if (invokerUrls.size() == 0 && this.cachedInvokerUrls != null){
invokerUrls.addAll(this.cachedInvokerUrls);
} else {
this.cachedInvokerUrls = new HashSet<URL>();
this.cachedInvokerUrls.addAll(invokerUrls);//缓存invokerUrls列表,便于交叉对比
}
if (invokerUrls.size() ==0 ){
return;
}
Map<String, Invoker<T>> newUrlInvokerMap = toInvokers(invokerUrls) ;// 将URL列表转成Invoker列表
Map<String, List<Invoker<T>>> newMethodInvokerMap = toMethodInvokers(newUrlInvokerMap); // 换方法名映射Invoker列表
// state change
//如果计算错误,则不进行处理.
if (newUrlInvokerMap == null || newUrlInvokerMap.size() == 0 ){
logger.error(new IllegalStateException("urls to invokers error .invokerUrls.size :"+invokerUrls.size() + ", invoker.size :0. urls :"+invokerUrls.toString()));
return ;
}
this.methodInvokerMap = multiGroup ? toMergeMethodInvokerMap(newMethodInvokerMap) : newMethodInvokerMap;
this.urlInvokerMap = newUrlInvokerMap;
try{
destroyUnusedInvokers(oldUrlInvokerMap,newUrlInvokerMap); // 关闭未使用的Invoker
}catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("destroyUnusedInvokers error. ", e);
}
}
}
Tips:
RegistryDirectory:
- 整合多个Invoker
- 监听注册中心的变化,刷新本地的
List<Invoke>,这里是为了路由和负载均衡
我们看这行:
Map<String, Invoker<T>> newUrlInvokerMap = toInvokers(invokerUrls) ;// 将URL列表转成Invoker列表
进入转换Invoke的方法( 将URL列表转成Invoker列表)
类似于传入的是 dubbo://192.168.1.1 转化成 DubboInvoker ->invoke
/**
* 将urls转成invokers,如果url已经被refer过,不再重新引用。
*/
private Map<String, Invoker<T>> toInvokers(List<URL> urls) {
Map<String, Invoker<T>> newUrlInvokerMap = new HashMap<String, Invoker<T>>();
if(urls == null || urls.size() == 0){
return newUrlInvokerMap;
}
Set<String> keys = new HashSet<String>();
String queryProtocols = this.queryMap.get(Constants.PROTOCOL_KEY);
for (URL providerUrl : urls) {
//如果reference端配置了protocol,则只选择匹配的protocol
if (queryProtocols != null && queryProtocols.length() >0) {
boolean accept = false;
String[] acceptProtocols = queryProtocols.split(",");
for (String acceptProtocol : acceptProtocols) {
if (providerUrl.getProtocol().equals(acceptProtocol)) {
accept = true;
break;
}
}
if (!accept) {
continue;
}
}
if (Constants.EMPTY_PROTOCOL.equals(providerUrl.getProtocol())) {
continue;
}
if (! ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).hasExtension(providerUrl.getProtocol())) {
logger.error(new IllegalStateException("Unsupported protocol " + providerUrl.getProtocol() + " in notified url: " + providerUrl + " from registry " + getUrl().getAddress() + " to consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost()
+ ", supported protocol: "+ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getSupportedExtensions()));
continue;
}
URL url = mergeUrl(providerUrl);
String key = url.toFullString(); // URL参数是排序的
if (keys.contains(key)) { // 重复URL
continue;
}
keys.add(key);
// 缓存key为没有合并消费端参数的URL,不管消费端如何合并参数,如果服务端URL发生变化,则重新refer
Map<String, Invoker<T>> localUrlInvokerMap = this.urlInvokerMap; // local reference
Invoker<T> invoker = localUrlInvokerMap == null ? null : localUrlInvokerMap.get(key);
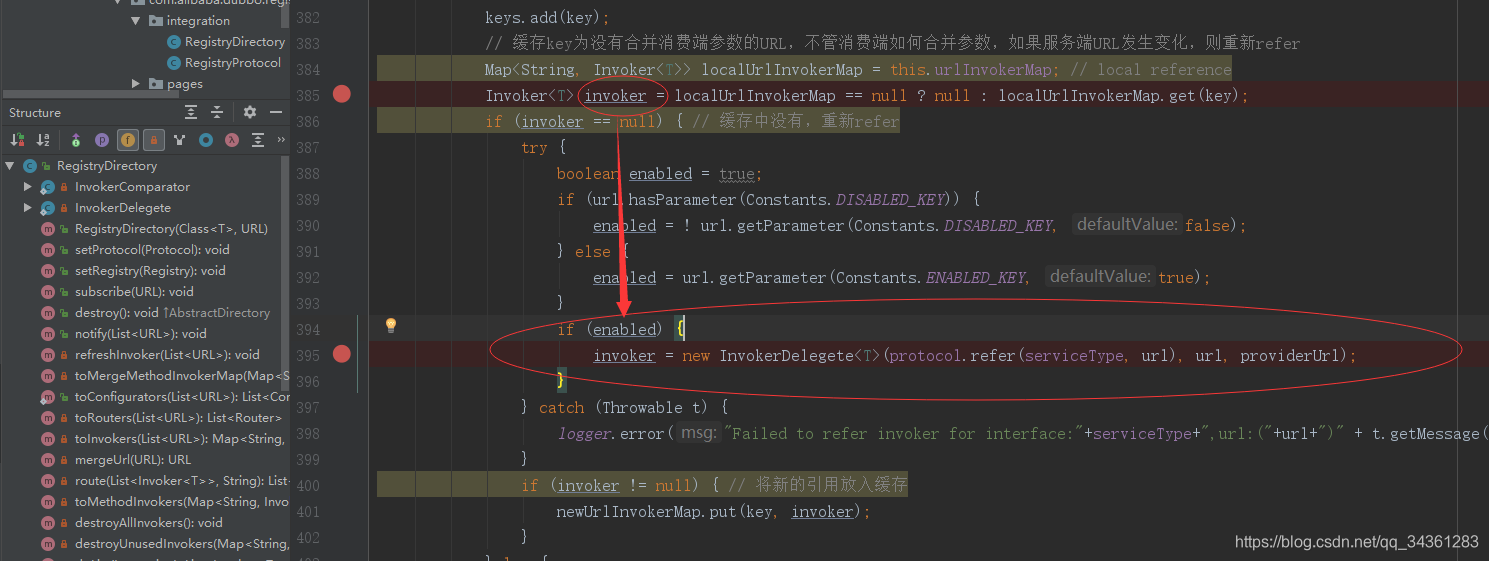
if (invoker == null) { // 缓存中没有,重新refer
try {
boolean enabled = true;
if (url.hasParameter(Constants.DISABLED_KEY)) {
enabled = ! url.getParameter(Constants.DISABLED_KEY, false);
} else {
enabled = url.getParameter(Constants.ENABLED_KEY, true);
}
if (enabled) {
invoker = new InvokerDelegete<T>(protocol.refer(serviceType, url), url, providerUrl);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Failed to refer invoker for interface:"+serviceType+",url:("+url+")" + t.getMessage(), t);
}
if (invoker != null) { // 将新的引用放入缓存
newUrlInvokerMap.put(key, invoker);
}
}else {
newUrlInvokerMap.put(key, invoker);
}
}
keys.clear();
return newUrlInvokerMap;
}
这里又出现了一个扩展点:
invoker = new InvokerDelegete<T>(protocol.refer(serviceType, url), url, providerUrl);
我们看protocol是RegistryDirectory注入初始化的Protocol类,所以应该是Protocol$Adaptive,在前面多次分析扩展点的问题,适配生成的getExtension这里就应该是根据名称dubbo来获取,那么dubbo对应的是filter(listener(DubboProtocol)),所以接着往下看DubboProtocol.refer
DubboProtocol.refer
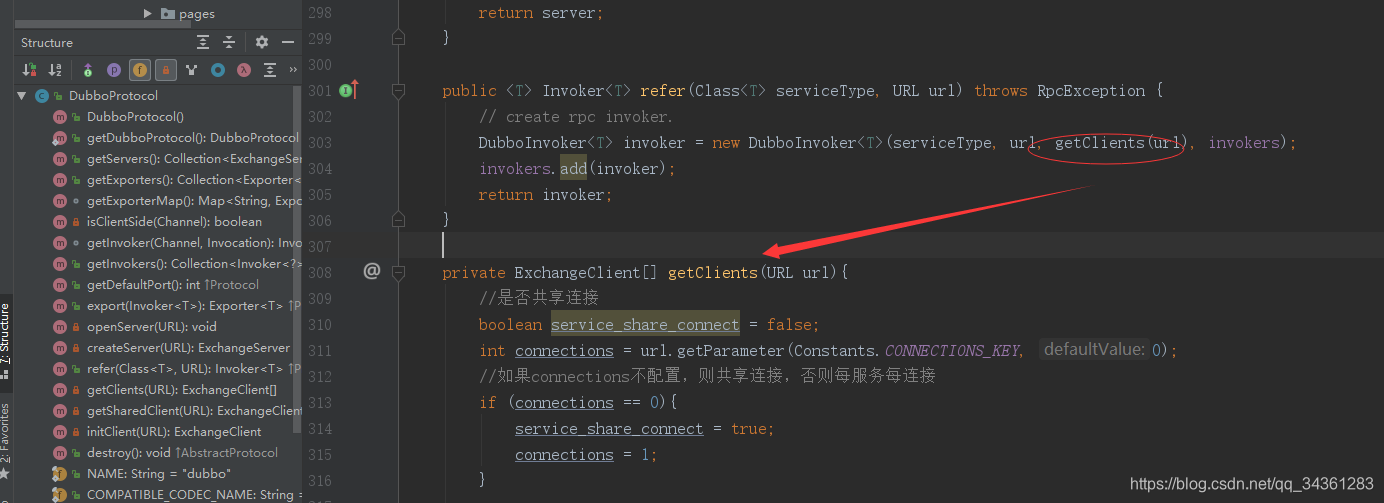
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> serviceType, URL url) throws RpcException {
// create rpc invoker.
DubboInvoker<T> invoker = new DubboInvoker<T>(serviceType, url, getClients(url), invokers);
invokers.add(invoker);
return invoker;
}
这里初始化DubboInvoker时根据url获取客户端,看看是怎么回事?
private ExchangeClient[] getClients(URL url){
//是否共享连接
boolean service_share_connect = false;
int connections = url.getParameter(Constants.CONNECTIONS_KEY, 0);
//如果connections不配置,则共享连接,否则每服务每连接
if (connections == 0){
service_share_connect = true;
connections = 1;
}
ExchangeClient[] clients = new ExchangeClient[connections];
for (int i = 0; i < clients.length; i++) {
if (service_share_connect){
clients[i] = getSharedClient(url);
} else {
clients[i] = initClient(url);
}
}
return clients;
}
继续调用getSharedClient:
/**
*获取共享连接
*/
private ExchangeClient getSharedClient(URL url){
String key = url.getAddress();
ReferenceCountExchangeClient client = referenceClientMap.get(key);
if ( client != null ){
if ( !client.isClosed()){
client.incrementAndGetCount();
return client;
} else {
// logger.warn(new IllegalStateException("client is closed,but stay in clientmap .client :"+ client));
referenceClientMap.remove(key);
}
}
ExchangeClient exchagneclient = initClient(url);
client = new ReferenceCountExchangeClient(exchagneclient, ghostClientMap);
referenceClientMap.put(key, client);
ghostClientMap.remove(key);
return client;
}
继续调用initClient:
/**
* 创建新连接.
*/
private ExchangeClient initClient(URL url) {
// client type setting.
String str = url.getParameter(Constants.CLIENT_KEY, url.getParameter(Constants.SERVER_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_REMOTING_CLIENT));
String version = url.getParameter(Constants.DUBBO_VERSION_KEY);
boolean compatible = (version != null && version.startsWith("1.0."));
url = url.addParameter(Constants.CODEC_KEY, Version.isCompatibleVersion() && compatible ? COMPATIBLE_CODEC_NAME : DubboCodec.NAME);
//默认开启heartbeat
url = url.addParameterIfAbsent(Constants.HEARTBEAT_KEY, String.valueOf(Constants.DEFAULT_HEARTBEAT));
// BIO存在严重性能问题,暂时不允许使用
if (str != null && str.length() > 0 && ! ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Transporter.class).hasExtension(str)) {
throw new RpcException("Unsupported client type: " + str + "," +
" supported client type is " + StringUtils.join(ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Transporter.class).getSupportedExtensions(), " "));
}
ExchangeClient client ;
try {
//设置连接应该是lazy的
if (url.getParameter(Constants.LAZY_CONNECT_KEY, false)){
client = new LazyConnectExchangeClient(url ,requestHandler);
} else {
client = Exchangers.connect(url ,requestHandler);
}
} catch (RemotingException e) {
throw new RpcException("Fail to create remoting client for service(" + url
+ "): " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
return client;
}
继续调用Exchangers.connect:
public static ExchangeClient connect(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
if (url == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
}
if (handler == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("handler == null");
}
url = url.addParameterIfAbsent(Constants.CODEC_KEY, "exchange");
return getExchanger(url).connect(url, handler);
}
欢迎来到协议层,接着往下走,看connect方法:
public class HeaderExchanger implements Exchanger {
public static final String NAME = "header";
public ExchangeClient connect(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
return new HeaderExchangeClient(Transporters.connect(url, new DecodeHandler(new HeaderExchangeHandler(handler))));
}
public ExchangeServer bind(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
return new HeaderExchangeServer(Transporters.bind(url, new DecodeHandler(new HeaderExchangeHandler(handler))));
}
}
这里,先看connect方法:
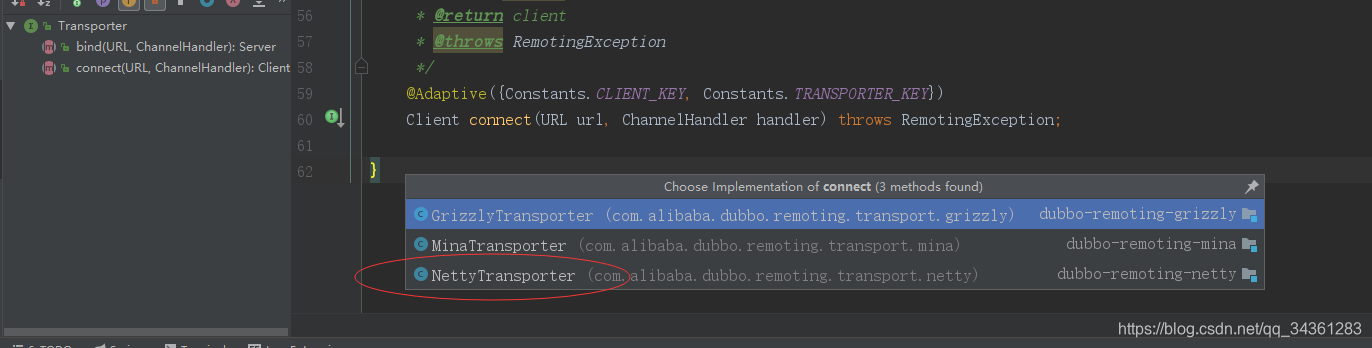
public static Client connect(URL url, ChannelHandler... handlers) throws RemotingException {
if (url == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
}
ChannelHandler handler;
if (handlers == null || handlers.length == 0) {
handler = new ChannelHandlerAdapter();
} else if (handlers.length == 1) {
handler = handlers[0];
} else {
handler = new ChannelHandlerDispatcher(handlers);
}
return getTransporter().connect(url, handler);
}
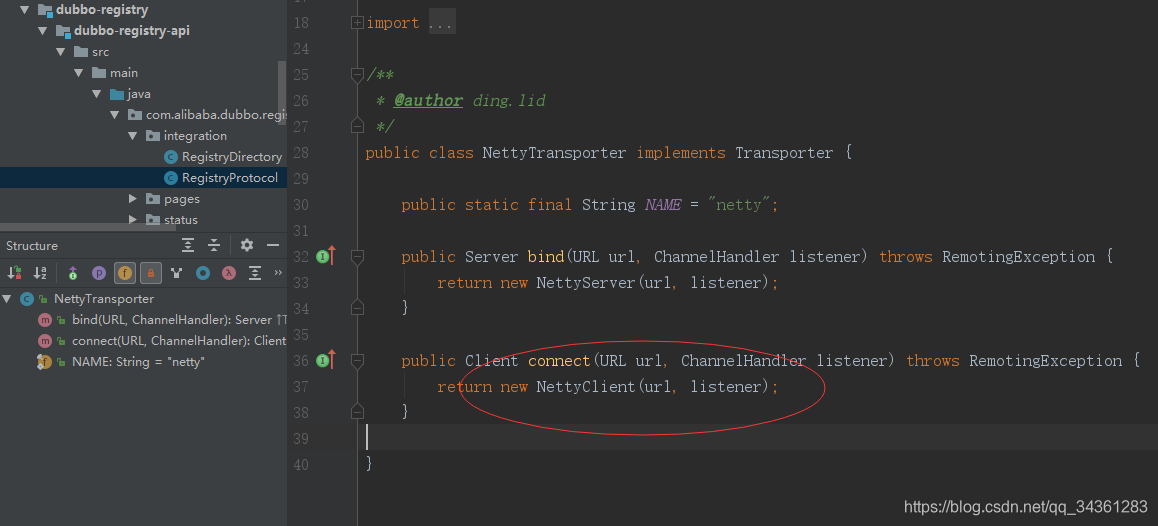
接着走connect方法,看Netty的实现类:
看到netty协议协议:
后续内容我们在netty专题单独讲,这里我们知道dubbo的client是通过netty通信就行,回到主线剧情:
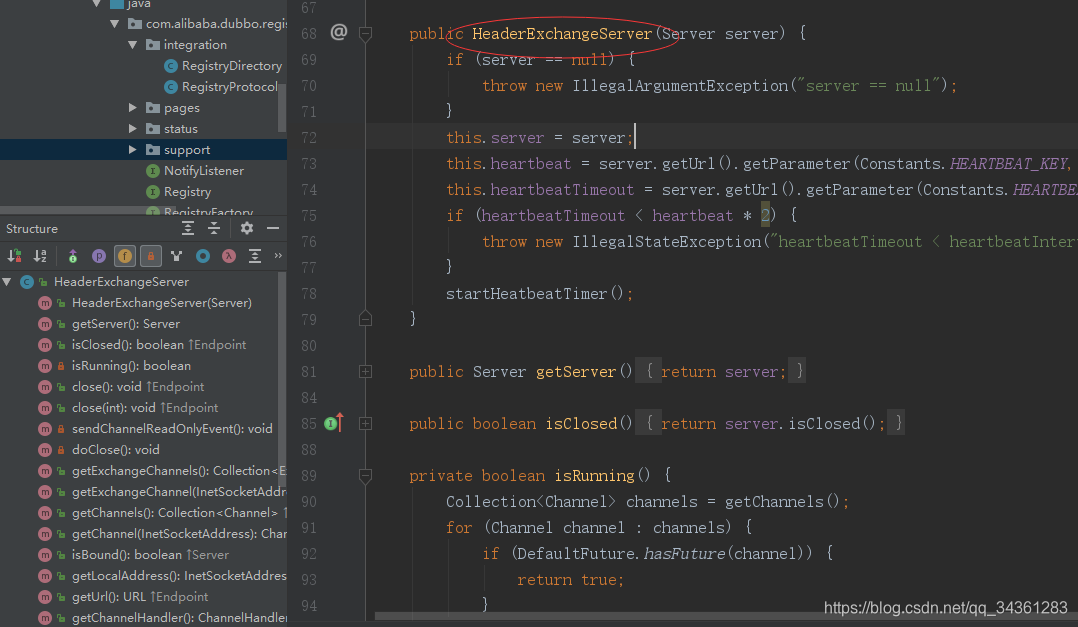
我们看创建HeaderExchangeServer时有一个心跳机制,新鲜吧,看看什么情况?
private void startHeatbeatTimer() {
stopHeartbeatTimer();
if (heartbeat > 0) {
heatbeatTimer = scheduled.scheduleWithFixedDelay(
new HeartBeatTask( new HeartBeatTask.ChannelProvider() {
public Collection<Channel> getChannels() {
return Collections.unmodifiableCollection(
HeaderExchangeServer.this.getChannels() );
}
}, heartbeat, heartbeatTimeout),
heartbeat, heartbeat,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
一定时间发送一个心跳包,其实底层也是基于netty~好的,知道这些,我们跳出初始化代码
刚才我们是从这里开始副本的,现在呢,再次退出此段,回到这里:
这里的invoke实际上就是DubboInvoke,并且invoke的client(属性)就是NettyClient
然后再跳出一层代码,看到这里获取的Invoker列表是放在局部变量,这里就是伏笔,以后用在别的地方用到,很关键好吧~
服务调用
前面源码分析内容,主要讲了服务发布,服务注册,消费端初始化,以及与客户端建立连接的过程,这里我们做一个小的梳理:
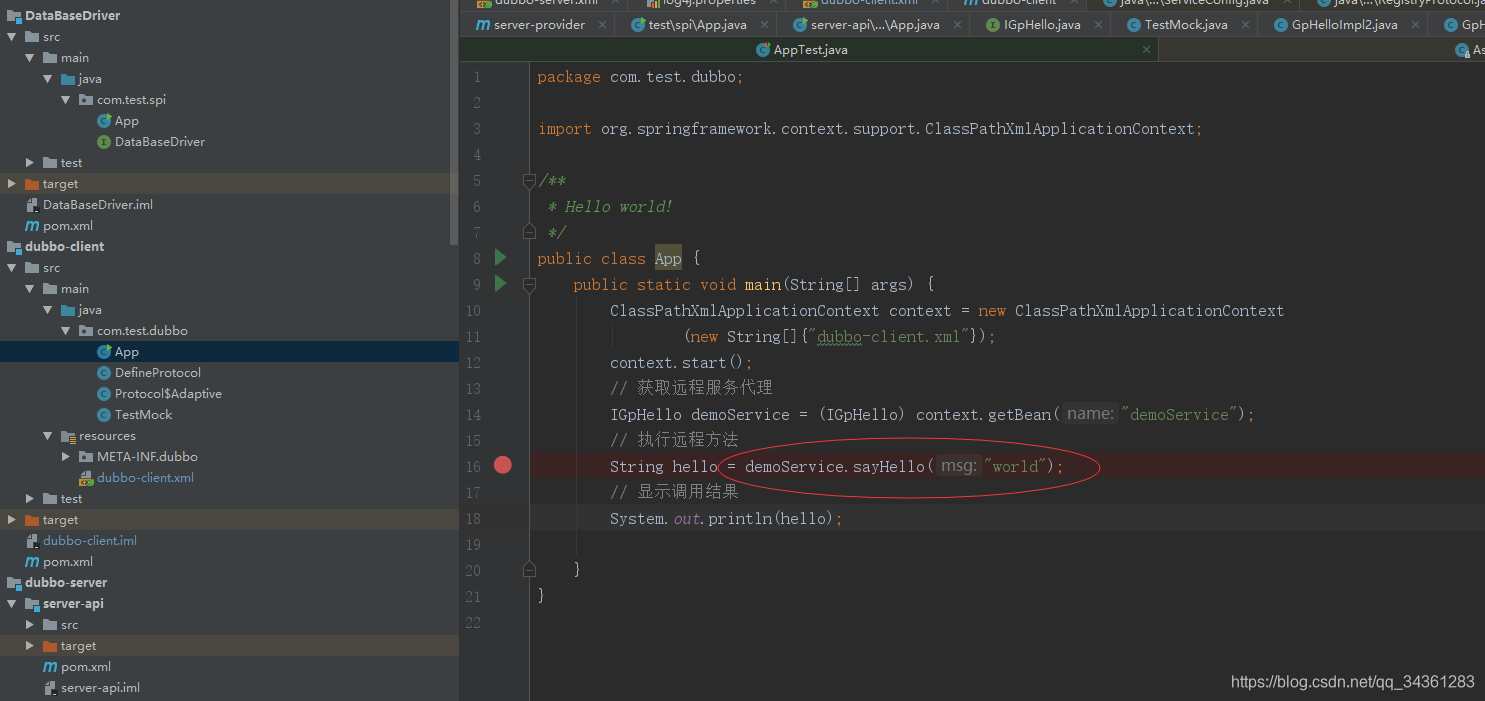
回到我们之前演示的客户端的demo:
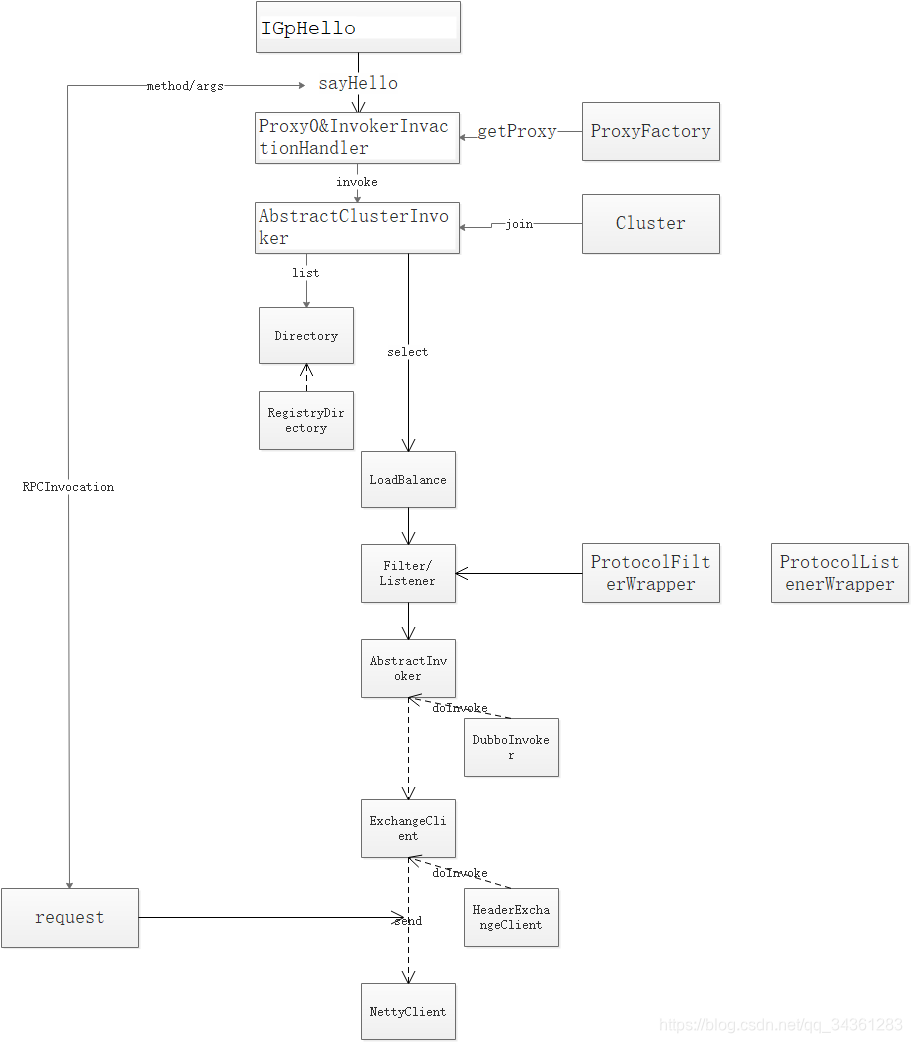
demoService实际上会调用什么呢?
通过前面的分析,答案显而易见,就是InvokerInvocationHandler的invoke
public class InvokerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private final Invoker<?> invoker;
public InvokerInvocationHandler(Invoker<?> handler){
this.invoker = handler;
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return method.invoke(invoker, args);
}
if ("toString".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 0) {
return invoker.toString();
}
if ("hashCode".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 0) {
return invoker.hashCode();
}
if ("equals".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 1) {
return invoker.equals(args[0]);
}
return invoker.invoke(new RpcInvocation(method, args)).recreate();
}
}
MockClusterInvoker.invoke
上面在源码注释有提到,这里应该调用MockClu sterInvoker的invoke
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
Result result = null;
String value = directory.getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.MOCK_KEY, Boolean.FALSE.toString()).trim();
if (value.length() == 0 || value.equalsIgnoreCase("false")){
//no mock
result = this.invoker.invoke(invocation);
} else if (value.startsWith("force")) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.info("force-mock: " + invocation.getMethodName() + " force-mock enabled , url : " + directory.getUrl());
}
//force:direct mock
result = doMockInvoke(invocation, null);
} else {
//fail-mock
try {
result = this.invoker.invoke(invocation);
}catch (RpcException e) {
if (e.isBiz()) {
throw e;
} else {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.info("fail-mock: " + invocation.getMethodName() + " fail-mock enabled , url : " + directory.getUrl(), e);
}
result = doMockInvoke(invocation, e);
}
}
}
return result;
}
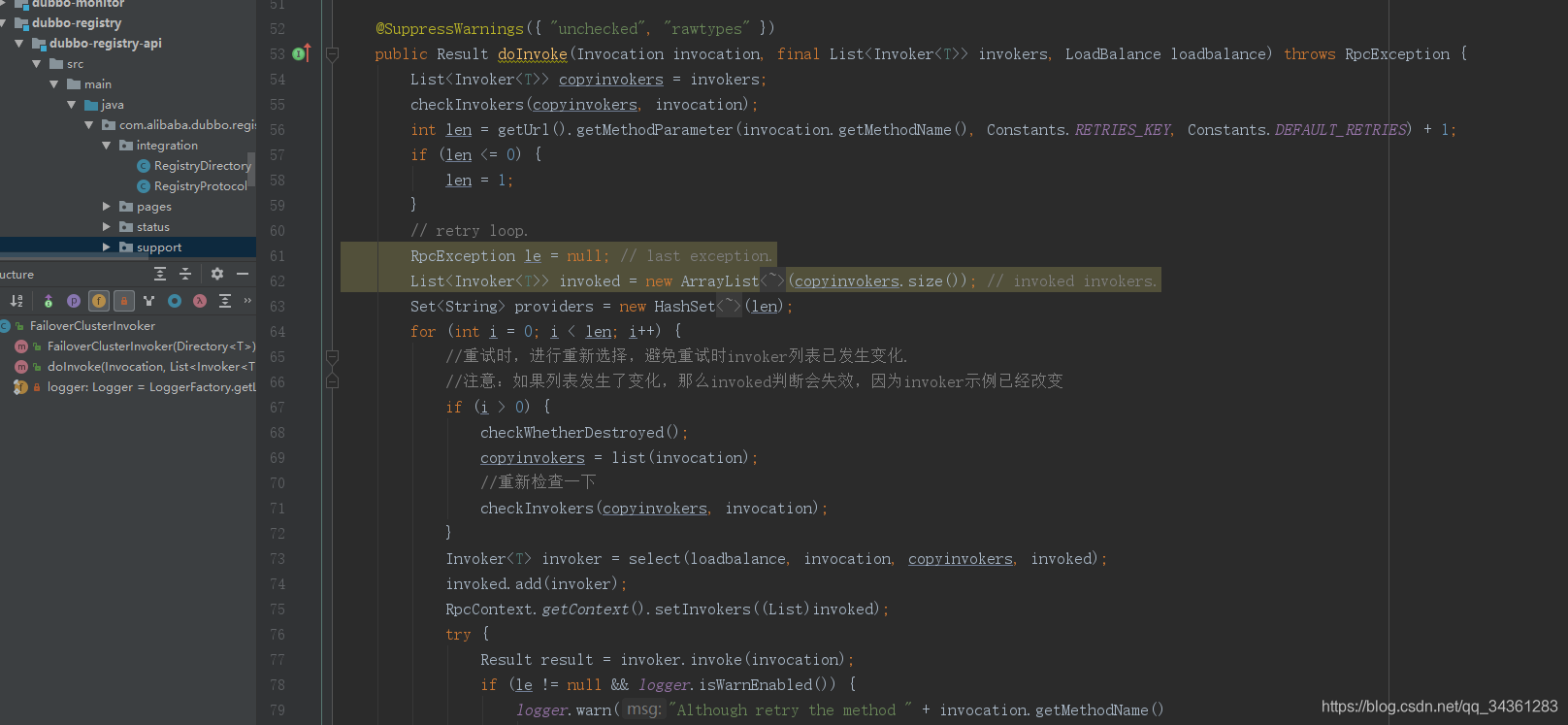
这里看result = this.invoker.invoke(invocation); 实际上会调动fileover,但是invoke的实现类里并没有fileover,通常这种情况就看fieover的父类,找到了AbstractClusterInvoker:
public Result invoke(final Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
checkWhetherDestroyed();
LoadBalance loadbalance;
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = list(invocation);
if (invokers != null && invokers.size() > 0) {
loadbalance = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(LoadBalance.class).getExtension(invokers.get(0).getUrl()
.getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(),Constants.LOADBALANCE_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_LOADBALANCE));
} else {
loadbalance = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(LoadBalance.class).getExtension(Constants.DEFAULT_LOADBALANCE);
}
RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(getUrl(), invocation);
return doInvoke(invocation, invokers, loadbalance);
}
看list方法:
protected List<Invoker<T>> list(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
//directory里获取Invoker的集合
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = directory.list(invocation);
return invokers;
}
这里是从directory里获取,directory接口我们后面还会提到:
接下来我们看directory的list方法,看一个有意思的地方:
public List<Invoker<T>> doList(Invocation invocation) {
if (forbidden) {
throw new RpcException(RpcException.FORBIDDEN_EXCEPTION, "Forbid consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " access service " + getInterface().getName() + " from registry " + getUrl().getAddress() + " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ", Please check registry access list (whitelist/blacklist).");
}
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = null;
Map<String, List<Invoker<T>>> localMethodInvokerMap = this.methodInvokerMap; // local reference
if (localMethodInvokerMap != null && localMethodInvokerMap.size() > 0) {
String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
Object[] args = RpcUtils.getArguments(invocation);
if(args != null && args.length > 0 && args[0] != null
&& (args[0] instanceof String || args[0].getClass().isEnum())) {
invokers = localMethodInvokerMap.get(methodName + "." + args[0]); // 可根据第一个参数枚举路由
}
if(invokers == null) {
invokers = localMethodInvokerMap.get(methodName);
}
if(invokers == null) {
invokers = localMethodInvokerMap.get(Constants.ANY_VALUE);
}
if(invokers == null) {
Iterator<List<Invoker<T>>> iterator = localMethodInvokerMap.values().iterator();
if (iterator.hasNext()) {
invokers = iterator.next();
}
}
}
return invokers == null ? new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(0) : invokers;
}
这里的methodInvokerMap不就是我们前面提到的用map存储的本地局部变量么,对于Invoker来说,前者是往里放·数据,而这里是从中获取数据,那么什么时候去刷新本地的Invoker的地址呢?
就是在当前类RegistryDirectory.notify:
public synchronized void notify(List<URL> urls) {
List<URL> invokerUrls = new ArrayList<URL>();
List<URL> routerUrls = new ArrayList<URL>();
List<URL> configuratorUrls = new ArrayList<URL>();
for (URL url : urls) {
String protocol = url.getProtocol();
String category = url.getParameter(Constants.CATEGORY_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_CATEGORY);
if (Constants.ROUTERS_CATEGORY.equals(category)
|| Constants.ROUTE_PROTOCOL.equals(protocol)) {
routerUrls.add(url);
} else if (Constants.CONFIGURATORS_CATEGORY.equals(category)
|| Constants.OVERRIDE_PROTOCOL.equals(protocol)) {
configuratorUrls.add(url);
} else if (Constants.PROVIDERS_CATEGORY.equals(category)) {
invokerUrls.add(url);
} else {
logger.warn("Unsupported category " + category + " in notified url: " + url + " from registry " + getUrl().getAddress() + " to consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost());
}
}
// configurators
if (configuratorUrls != null && configuratorUrls.size() >0 ){
this.configurators = toConfigurators(configuratorUrls);
}
// routers
if (routerUrls != null && routerUrls.size() >0 ){
List<Router> routers = toRouters(routerUrls);
if(routers != null){ // null - do nothing
setRouters(routers);
}
}
List<Configurator> localConfigurators = this.configurators; // local reference
// 合并override参数
this.overrideDirectoryUrl = directoryUrl;
if (localConfigurators != null && localConfigurators.size() > 0) {
for (Configurator configurator : localConfigurators) {
this.overrideDirectoryUrl = configurator.configure(overrideDirectoryUrl);
}
}
// providers
refreshInvoker(invokerUrls);
}
这里我们前面有提到过,notify什么时候被调用呢?
当服务端的地址发生变化时,就会调用notify刷新缓存里的地址
好的,回到主线AbstractClusterInvoker.invoke:
public Result invoke(final Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
checkWhetherDestroyed();
LoadBalance loadbalance;
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = list(invocation);
if (invokers != null && invokers.size() > 0) {
loadbalance = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(LoadBalance.class).getExtension(invokers.get(0).getUrl()
.getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(),Constants.LOADBALANCE_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_LOADBALANCE));
} else {
loadbalance = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(LoadBalance.class).getExtension(Constants.DEFAULT_LOADBALANCE);
}
RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(getUrl(), invocation);
return doInvoke(invocation, invokers, loadbalance);
}
看返回这里,是doInvoke也是模板方法
这里做了一个负载,我们接着看select方法:
/**
* 使用loadbalance选择invoker.</br>
* a)先lb选择,如果在selected列表中 或者 不可用且做检验时,进入下一步(重选),否则直接返回</br>
* b)重选验证规则:selected > available .保证重选出的结果尽量不在select中,并且是可用的
*
* @param availablecheck 如果设置true,在选择的时候先选invoker.available == true
* @param selected 已选过的invoker.注意:输入保证不重复
*
*/
protected Invoker<T> select(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, List<Invoker<T>> selected) throws RpcException {
if (invokers == null || invokers.size() == 0)
return null;
String methodName = invocation == null ? "" : invocation.getMethodName();
boolean sticky = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName,Constants.CLUSTER_STICKY_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_CLUSTER_STICKY) ;
{
//ignore overloaded method
if ( stickyInvoker != null && !invokers.contains(stickyInvoker) ){
stickyInvoker = null;
}
//ignore cucurrent problem
if (sticky && stickyInvoker != null && (selected == null || !selected.contains(stickyInvoker))){
if (availablecheck && stickyInvoker.isAvailable()){
return stickyInvoker;
}
}
}
Invoker<T> invoker = doselect(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected);
if (sticky){
stickyInvoker = invoker;
}
return invoker;
}
然后我们回到FailoverClusterInvoker.doInvoke方法,通过负载均衡算法过滤后将结果进行、
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
通过debug,这里的invoker对象是DubboInvoker,但是我们看invoke的实现类里并没有,所以就看DubboI女OK儿的父类为AbstractInvoker,所以方法走到这里就走AbstractInvoker.invoke(在dubbo源码里这个套路很常见,之前我们多次提到)
AbstractInvoker.invoke
public Result invoke(Invocation inv) throws RpcException {
if(destroyed) {
throw new RpcException("Rpc invoker for service " + this + " on consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost()
+ " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion()
+ " is DESTROYED, can not be invoked any more!");
}
RpcInvocation invocation = (RpcInvocation) inv;
invocation.setInvoker(this);
if (attachment != null && attachment.size() > 0) {
invocation.addAttachmentsIfAbsent(attachment);
}
Map<String, String> context = RpcContext.getContext().getAttachments();
if (context != null) {
invocation.addAttachmentsIfAbsent(context);
}
if (getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.ASYNC_KEY, false)){
invocation.setAttachment(Constants.ASYNC_KEY, Boolean.TRUE.toString());
}
RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(getUrl(), invocation);
try {
return doInvoke(invocation);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) { // biz exception
Throwable te = e.getTargetException();
if (te == null) {
return new RpcResult(e);
} else {
if (te instanceof RpcException) {
((RpcException) te).setCode(RpcException.BIZ_EXCEPTION);
}
return new RpcResult(te);
}
} catch (RpcException e) {
if (e.isBiz()) {
return new RpcResult(e);
} else {
throw e;
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
return new RpcResult(e);
}
}
这里返回的invoke实际上调用的是DubboInvoker.doInvoke方法:
@Override
protected Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
RpcInvocation inv = (RpcInvocation) invocation;
final String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
inv.setAttachment(Constants.PATH_KEY, getUrl().getPath());
inv.setAttachment(Constants.VERSION_KEY, version);
ExchangeClient currentClient;
if (clients.length == 1) {
currentClient = clients[0];
} else {
currentClient = clients[index.getAndIncrement() % clients.length];
}
try {
boolean isAsync = RpcUtils.isAsync(getUrl(), invocation);
boolean isOneway = RpcUtils.isOneway(getUrl(), invocation);
int timeout = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.TIMEOUT_KEY,Constants.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
//判断当前通信是单向通信
if (isOneway) {
boolean isSent = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.SENT_KEY, false);
currentClient.send(inv, isSent);
RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(null);
return new RpcResult();
//通信方式:异步
} else if (isAsync) {
ResponseFuture future = currentClient.request(inv, timeout) ;
RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(new FutureAdapter<Object>(future));
return new RpcResult();
} else {
RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(null);
//创建dubbo的客户端建立的连接(nettyClient)
return (Result) currentClient.request(inv, timeout).get();
}
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
throw new RpcException(RpcException.TIMEOUT_EXCEPTION, "Invoke remote method timeout. method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
} catch (RemotingException e) {
throw new RpcException(RpcException.NETWORK_EXCEPTION, "Failed to invoke remote method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
这里就是底层的网络通信,可以将当前的请求传到服务端,做一个处理
在currentClient.request这里,我们看这里实际上调用HeaderExchangeClient.request:
public ResponseFuture request(Object request, int timeout) throws RemotingException {
if (closed) {
throw new RemotingException(this.getLocalAddress(), null, "Failed to send request " + request + ", cause: The channel " + this + " is closed!");
}
// create request.
Request req = new Request();
req.setVersion("2.0.0");
req.setTwoWay(true);
req.setData(request);
DefaultFuture future = new DefaultFuture(channel, req, timeout);
try{
channel.send(req);
}catch (RemotingException e) {
future.cancel();
throw e;
}
return future;
}
再看如何发送数据?send方法实际调用HeaderExchangeChannel.send:
public void send(Object message) throws RemotingException {
send(message, getUrl().getParameter(Constants.SENT_KEY, false));
}
接着往里走:
public void send(Object message, boolean sent) throws RemotingException {
if (closed) {
throw new RemotingException(this.getLocalAddress(), null, "Failed to send message " + message + ", cause: The channel " + this + " is closed!");
}
if (message instanceof Request
|| message instanceof Response
|| message instanceof String) {
channel.send(message, sent);
} else {
Request request = new Request();
request.setVersion("2.0.0");
request.setTwoWay(false);
request.setData(message);
channel.send(request, sent);
}
}
这里的send实际上会走NettyChannel.send:
public void send(Object message, boolean sent) throws RemotingException {
super.send(message, sent);
boolean success = true;
int timeout = 0;
try {
ChannelFuture future = channel.write(message);
if (sent) {
timeout = getUrl().getPositiveParameter(Constants.TIMEOUT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
success = future.await(timeout);
}
Throwable cause = future.getCause();
if (cause != null) {
throw cause;
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RemotingException(this, "Failed to send message " + message + " to " + getRemoteAddress() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
if(! success) {
throw new RemotingException(this, "Failed to send message " + message + " to " + getRemoteAddress()
+ "in timeout(" + timeout + "ms) limit");
}
}
好的,走到这一步,过程就告一段落,我们画一个活动图总结一下:
回顾一下我们之前通过dubbo跟踪客户端的代码逻辑:
后记
关于Dubbo自适应扩展点
实际上,XX$Adeptive 适配器 是根据不同的协议,动态生成代码,来适配相应的Protocol的,这也是Dubbo里常见的技术手段~
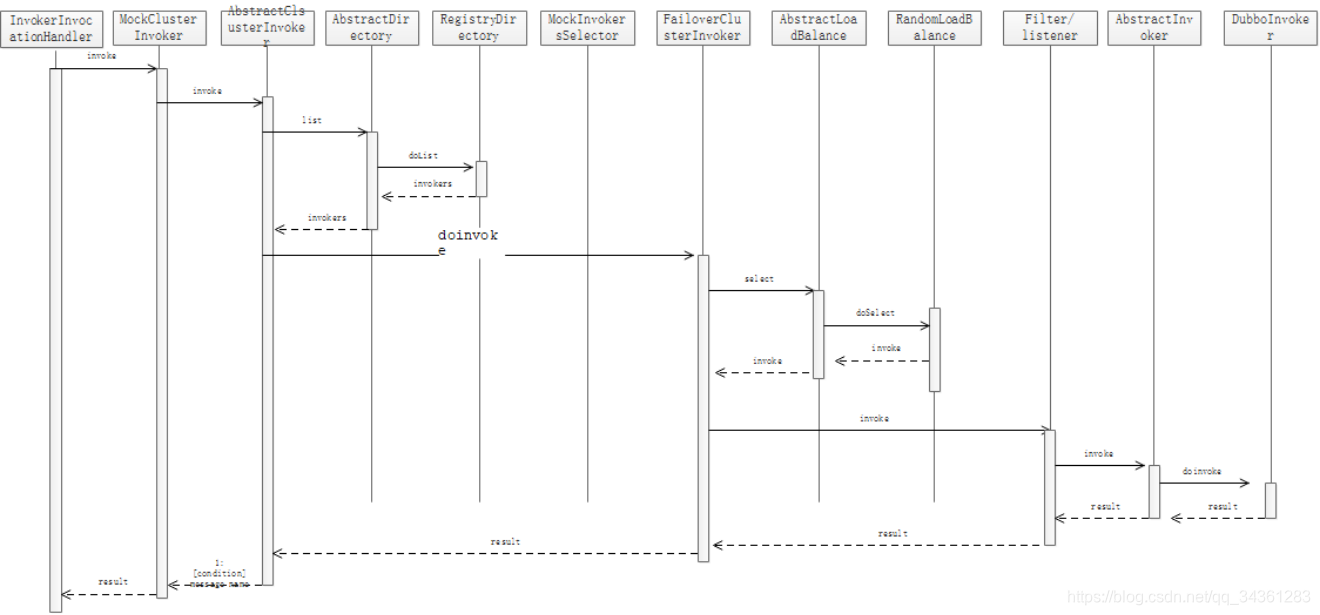
本节关于dubbo的消费端启动与服务端建立连接的时序图:
Dubbo中文注释版:DubboV2.5.4下载地址
更多架构知识,欢迎关注本套Java系列文章-地址导航:Java架构师成长之路