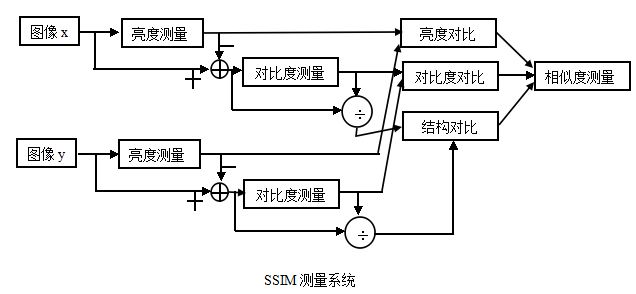
一、结构相似性(structural similarity)
自然图像具有极高的结构性,表现在图像的像素间存在着很强的相关性,尤其是在空间相似的情况下。这些相关性在视觉场景中携带着关于物体结构的重要信息。我们假设人类视觉系统(HSV)主要从可视区域内获取结构信息。所以通过探测结构信息是否改变来感知图像失真的近似信息。
大多数的基于误差敏感度(error sensitivity)的质量评估方法(如MSE,PSNR)使用线性变换来分解图像信号,这不会涉及到相关性。我们要讨论的SSIM就是要找到更加直接的方法来比较失真图像和参考图像的结构。
二、SSIM指数
物体表面的亮度信息与照度和反射系数有关,且场景中的物体的结构与照度是独立的,反射系数与物体有关。我们可以通过分离照度对物体的影响来探索一张图像中的结构信息。这里,把与物体结构相关的亮度和对比度作为图像中结构信息的定义。因为一个场景中的亮度和对比度总是在变化的,所以我们可以通过分别对局部的处理来得到更精确的结果。
由SSIM测量系统可得相似度的测量可由三种对比模块组成,分别为:亮度,对比度,结构。接下来我们将会对这三模块函数进行定义。
首先,对于离散信号,我们以平均灰度来作为亮度测量的估计:
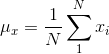
亮度对比函数l(x,y)是关于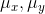
然后,由测量系统知道要把平均灰度值从信号中去除,对于离散信号,可使用标准差来做对比度估量值。
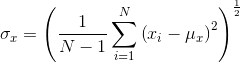
对比度对比函数c(x,y)就是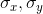
接下来,信号被自己的标准差相除,结构对比函数就被定义成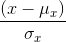
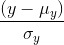
最后,三个对比模块组合成一个完整的相似测量函数:
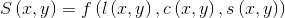
(注:上面公式(9)中

三、SSIM指数应用于图像质量评估
四、matlab附加代码实现
function [mssim, ssim_map] = ssim(img1, img2, K, window, L)
% ========================================================================
% SSIM Index with automatic downsampling, Version 1.0
% Copyright(c) 2009 Zhou Wang
% All Rights Reserved.
%
% ----------------------------------------------------------------------
% Permission to use, copy, or modify this software and its documentation
% for educational and research purposes only and without fee is hereby
% granted, provided that this copyright notice and the original authors'
% names appear on all copies and supporting documentation. This program
% shall not be used, rewritten, or adapted as the basis of a commercial
% software or hardware product without first obtaining permission of the
% authors. The authors make no representations about the suitability of
% this software for any purpose. It is provided "as is" without express
% or implied warranty.
%----------------------------------------------------------------------
%
% This is an implementation of the algorithm for calculating the
% Structural SIMilarity (SSIM) index between two images
%
% Please refer to the following paper and the website with suggested usage
%
% Z. Wang, A. C. Bovik, H. R. Sheikh, and E. P. Simoncelli, "Image
% quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity,"
% IEEE Transactios on Image Processing, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 600-612,
% Apr. 2004.
%
% http://www.ece.uwaterloo.ca/~z70wang/research/ssim/
%
% Note: This program is different from ssim_index.m, where no automatic
% downsampling is performed. (downsampling was done in the above paper
% and was described as suggested usage in the above website.)
%
% Kindly report any suggestions or corrections to [email protected]
%
%----------------------------------------------------------------------
%
%Input : (1) img1: the first image being compared
% (2) img2: the second image being compared
% (3) K: constants in the SSIM index formula (see the above
% reference). defualt value: K = [0.01 0.03]
% (4) window: local window for statistics (see the above
% reference). default widnow is Gaussian given by
% window = fspecial('gaussian', 11, 1.5);
% (5) L: dynamic range of the images. default: L = 255
%
%Output: (1) mssim: the mean SSIM index value between 2 images.
% If one of the images being compared is regarded as
% perfect quality, then mssim can be considered as the
% quality measure of the other image.
% If img1 = img2, then mssim = 1.
% (2) ssim_map: the SSIM index map of the test image. The map
% has a smaller size than the input images. The actual size
% depends on the window size and the downsampling factor.
%
%Basic Usage:
% Given 2 test images img1 and img2, whose dynamic range is 0-255
%
% [mssim, ssim_map] = ssim(img1, img2);
%
%Advanced Usage:
% User defined parameters. For example
%
% K = [0.05 0.05];
% window = ones(8);
% L = 100;
% [mssim, ssim_map] = ssim(img1, img2, K, window, L);
%
%Visualize the results:
%
% mssim %Gives the mssim value
% imshow(max(0, ssim_map).^4) %Shows the SSIM index map
%========================================================================
if (nargin < 2 || nargin > 5) %参数个数小于2个或者大于5个,则退出
mssim = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
if (size(img1) ~= size(img2)) %对比的两幅图大小要一致,否则退出
mssim = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
[M, N] = size(img1); %将图1的大小赋值给M N
if (nargin == 2) %参数为2时
if ((M < 11) || (N < 11)) %图像长宽都不能小于11,否则退出
mssim = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return
end
window = fspecial('gaussian', 11, 1.5); %建立预定义的滤波算子。
%为高斯低通滤波,有两个参数,hsize表示模板尺寸,默认值为[3 3],sigma为滤波器的标准值,单位为像素,默认值为0.5.
K(1) = 0.01; % default settings
K(2) = 0.03; %K L参数设置为最佳默认值
L = 255; %设置L的默认值
end
if (nargin == 3) %参数为3个时,第3个参数为K
if ((M < 11) || (N < 11))
mssim = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return
end
window = fspecial('gaussian', 11, 1.5); %获取滤波算子,类型为gaussian,11为窗口尺寸,1.5为标准差
L = 255;
if (length(K) == 2) %参数K为2个元素的数组,且都大于0
if (K(1) < 0 || K(2) < 0)
mssim = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
else
mssim = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
end
if (nargin == 4) %参数3为K,参数4为窗口大小
[H, W] = size(window); %window参数类似ones(8)
if ((H*W) < 4 || (H > M) || (W > N)) %窗口大小要求大于4或者长宽不小于图像的长宽
mssim = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return
end
L = 255;
if (length(K) == 2) %判断K数组的大小
if (K(1) < 0 || K(2) < 0)
mssim = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
else
mssim = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
end
if (nargin == 5) %当后3个参数都设置时,其中L参数执行传入的参数
[H, W] = size(window);
if ((H*W) < 4 || (H > M) || (W > N))
mssim = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return
end
if (length(K) == 2)
if (K(1) < 0 || K(2) < 0)
mssim = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
else
mssim = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
end
img1 = double(img1);
img2 = double(img2);
% automatic downsampling
f = max(1,round(min(M,N)/256)); %先选择行列两者中的最小值取整,再选择其中的最大值
%downsampling by f
%use a simple low-pass filter
if(f>1)
lpf = ones(f,f); %初始化一个单位矩阵,用于归一化
lpf = lpf/sum(lpf(:)); %归一化,除以单位矩阵的个数
img1 = imfilter(img1,lpf,'symmetric','same'); %使用滤波函数对img1进行处理,lpf是归一化的滤波模板,
%边界使用symmetric镜像反射填充边界
img2 = imfilter(img2,lpf,'symmetric','same');
%%% 以上两个相当于均值滤波,imfilter不将输入转换为double,输出只与输入同类型,有灵活的边界补充选项
img1 = img1(1:f:end,1:f:end); %向下隔点取样
img2 = img2(1:f:end,1:f:end);
end
C1 = (K(1)*L)^2; %求取论文中C1的值
C2 = (K(2)*L)^2; %求取论文中C2的值
window = window/sum(sum(window)); %滤波器归一化操作。缺省的sum(x)就是竖向相加,求每列的和,结果是行向量
mu1 = filter2(window, img1, 'valid'); %使用设定好的高斯低通滤波器window对img1进行滤波,结果保存在mu1中
%mu1相当于论文中的Ux,即图像img1的均值
mu2 = filter2(window, img2, 'valid'); %mu2相当于论文中的Uy,即图像img2的均值,点乘模板相加,因为window归一化了,所以是均值
mu1_sq = mu1.*mu1; %矩阵运算,相当于img1均值的矩阵乘法平方
mu2_sq = mu2.*mu2;
mu1_mu2 = mu1.*mu2; %img1和img2均值的矩阵乘法平方
sigma1_sq = filter2(window, img1.*img1, 'valid') - mu1_sq; %协方差期望公式:sigma_x=E(X^2)-(EX)^2
sigma2_sq = filter2(window, img2.*img2, 'valid') - mu2_sq; %协方差期望公式:sigma_y=E(Y^2)-(EY)^2
sigma12 = filter2(window, img1.*img2, 'valid') - mu1_mu2; %协方差期望公式:sigma_xy=E(XY)-(EX)*(EY)
if (C1 > 0 && C2 > 0)
ssim_map = ((2*mu1_mu2 + C1).*(2*sigma12 + C2))./((mu1_sq + mu2_sq + C1).*(sigma1_sq + sigma2_sq + C2));
else
numerator1 = 2*mu1_mu2 + C1;
numerator2 = 2*sigma12 + C2;
denominator1 = mu1_sq + mu2_sq + C1;
denominator2 = sigma1_sq + sigma2_sq + C2;
ssim_map = ones(size(mu1));
index = (denominator1.*denominator2 > 0);
ssim_map(index) = (numerator1(index).*numerator2(index))./(denominator1(index).*denominator2(index));
index = (denominator1 ~= 0) & (denominator2 == 0);
ssim_map(index) = numerator1(index)./denominator1(index);
end
mssim = mean2(ssim_map);
return