1.SENet
SENet属于通道注意力机制。2017年提出,是imageNet最后的冠军
SENet采用的方法是对于特征层赋予权值。
重点在于如何赋权
1.将输入信息的所有通道平均池化。
2.平均池化后进行两次全连接,第一次全连接链接的神经元较少,第二次全连接神经元数和通道数一致
3.将Sigmoid的值固定为0-1之间
4.将权值和特征层相乘。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import math
class se_block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, ratio=16):
super(se_block, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(channel, channel // ratio, bias=False),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(channel // ratio, channel, bias=False),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, _, _ = x.size()
y = self.avg_pool(x).view(b, c)
y = self.fc(y).view(b, c, 1, 1)
return x * y
2.ECANet
细心的人会发现,全连接其实是一个非常耗费算力的东西,对于边缘设备的压力非常大,所以ECANet觉得SENet并不需要那么多的全连接,我们直接在GAP后做一维卷积,而后取sigmoid为0-1来获取权值即可。
ECANet认为SE的全通道信息捕获是多此一举,而卷积就有很好的跨通道信息获取能力。
class eca_block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, b=1, gamma=2):
super(eca_block, self).__init__()
kernel_size = int(abs((math.log(channel, 2) + b) / gamma))
kernel_size = kernel_size if kernel_size % 2 else kernel_size + 1
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.conv = nn.Conv1d(1, 1, kernel_size=kernel_size, padding=(kernel_size - 1) // 2, bias=False)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
y = self.avg_pool(x)
y = self.conv(y.squeeze(-1).transpose(-1, -2)).transpose(-1, -2).unsqueeze(-1)
y = self.sigmoid(y)
return x * y.expand_as(x)
4.GCNet
GCNet是我们项目的模型中使用的一种注意力机制
GCNet主要借鉴了SENet和NLNet的优点,主要基于NLNet,把NLNet的计算量削减了数倍
先看他是怎么用NLNet的
NLNet原公式
改进后的NLNet公式
改进的区别就是去掉了Wz系数。
Wz系数的削减主要是对图像中的观察得出的创意。
作者说,attention map在不同位置上计算的结果几乎一致,那么我们只需要计算一次然后共享attention map应该也可以获得很好的效果,并且计算量可以下降到1/(W*H)。
Simple NL Block和NL Block的结构对比如图所示,并且经过文章的实验表明,简化后的性能与原本的性能相当。
接着,作者基于S-NLNet和SENet的有点提出了GCNet
(1) 相比于SNL,SNL中的transform的1x1卷积在res5中是2048x1x1x2048,其计算量较大,所以借鉴SE的方法,加入压缩因子,为了更好的优化,还加入了layernorm。
(2)相比于SE,一方面是提取的全局信息更加充分(其实在后续的实验中说服力不是很强,单独avg pooling+add,只掉了0.3个点,但是更加简洁),另一方面则是加号和乘号的区别,而且在实验结果上,加号比乘号有显著的优势。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision
class GlobalContextBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
inplanes,
ratio,
pooling_type='att',
fusion_types=('channel_add', )):
super(GlobalContextBlock, self).__init__()
assert pooling_type in ['avg', 'att']
assert isinstance(fusion_types, (list, tuple))
valid_fusion_types = ['channel_add', 'channel_mul']
assert all([f in valid_fusion_types for f in fusion_types])
assert len(fusion_types) > 0, 'at least one fusion should be used'
self.inplanes = inplanes
self.ratio = ratio
self.planes = int(inplanes * ratio)
self.pooling_type = pooling_type
self.fusion_types = fusion_types
if pooling_type == 'att':
self.conv_mask = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, 1, kernel_size=1)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=2)
else:
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
if 'channel_add' in fusion_types:
self.channel_add_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, self.planes, kernel_size=1),
nn.LayerNorm([self.planes, 1, 1]),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True), # yapf: disable
nn.Conv2d(self.planes, self.inplanes, kernel_size=1))
else:
self.channel_add_conv = None
if 'channel_mul' in fusion_types:
self.channel_mul_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, self.planes, kernel_size=1),
nn.LayerNorm([self.planes, 1, 1]),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True), # yapf: disable
nn.Conv2d(self.planes, self.inplanes, kernel_size=1))
else:
self.channel_mul_conv = None
def spatial_pool(self, x):
batch, channel, height, width = x.size()
if self.pooling_type == 'att':
input_x = x
# [N, C, H * W]
input_x = input_x.view(batch, channel, height * width)
# [N, 1, C, H * W]
input_x = input_x.unsqueeze(1)
# [N, 1, H, W]
context_mask = self.conv_mask(x)
# [N, 1, H * W]
context_mask = context_mask.view(batch, 1, height * width)
# [N, 1, H * W]
context_mask = self.softmax(context_mask)
# [N, 1, H * W, 1]
context_mask = context_mask.unsqueeze(-1)
# [N, 1, C, 1]
context = torch.matmul(input_x, context_mask)
# [N, C, 1, 1]
context = context.view(batch, channel, 1, 1)
else:
# [N, C, 1, 1]
context = self.avg_pool(x)
return context
def forward(self, x):
# [N, C, 1, 1]
context = self.spatial_pool(x)
out = x
if self.channel_mul_conv is not None:
# [N, C, 1, 1]
channel_mul_term = torch.sigmoid(self.channel_mul_conv(context))
out = out * channel_mul_term
if self.channel_add_conv is not None:
# [N, C, 1, 1]
channel_add_term = self.channel_add_conv(context)
out = out + channel_add_term
return out
if __name__=='__main__':
model = GlobalContextBlock(inplanes=16, ratio=0.25)
print(model)
input = torch.randn(1, 16, 64, 64)
out = model(input)
print(out.shape)
4.CA注意力机制
CA机制也是和之前的GCNet一样对两个已有注意力(SENet和CBAM)进行了改进。
CA提出
1.SENet作为通道注意力机制,侧重通道之前的依赖关系,忽略了空间特征的作用。
2.CBAM可以一定程度弥补,但是CBAM对于长程依赖有待改进。
经过融合改进后,CA机制有以下优点
1、不仅考虑了通道信息,还考虑了方向相关的位置信息。
2、足够的灵活和轻量,能够简单的插入到轻量级网络的核心模块中。
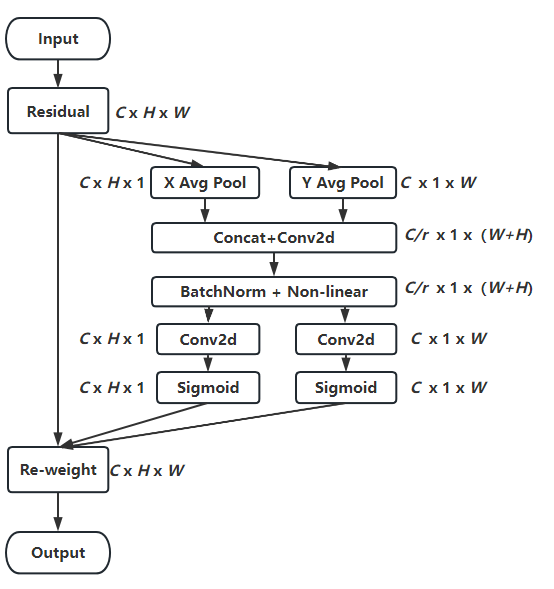
CA机制的算法流程图如下
1.CA机制为了避免将空间特征全都压缩到通道中,放弃了全局平均池化,转为分别对x和y方向进行
别生成尺寸为C ∗ H ∗ 1 和C ∗ 1 ∗ W 的attention map
2.将生成的两个attention map进行池化,然后concat,然后进行F1操作(利用1*1卷积核进行降维,如SE注意力中操作)和激活操作,生成特征图f
这图怎么这么大?
3.沿着空间维度,再将f进行split操作,分别得到h和w的特征图后再用1 × 1卷积进行升维度操作,结合sigmoid激活函数得到最后的注意力向量gh和gw
代码
class CoordAtt(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inp, oup, groups=32):
super(CoordAtt, self).__init__()
self.pool_h = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((None, 1))
self.pool_w = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, None))
mip = max(8, inp // groups)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inp, mip, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(mip)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(mip, oup, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(mip, oup, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.relu = h_swish()
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
n,c,h,w = x.size()
x_h = self.pool_h(x)
x_w = self.pool_w(x).permute(0, 1, 3, 2)
y = torch.cat([x_h, x_w], dim=2)
y = self.conv1(y)
y = self.bn1(y)
y = self.relu(y)
x_h, x_w = torch.split(y, [h, w], dim=2)
x_w = x_w.permute(0, 1, 3, 2)
x_h = self.conv2(x_h).sigmoid()
x_w = self.conv3(x_w).sigmoid()
x_h = x_h.expand(-1, -1, h, w)
x_w = x_w.expand(-1, -1, h, w)
y = identity * x_w * x_h
return y
明日:ODConv,数据结构复习,套磁老师