1. 基本概念
模拟鸟类觅食行为
个体最优:每一只鸟飞过的最优解
全局最优:全部鸟飞过的最优解
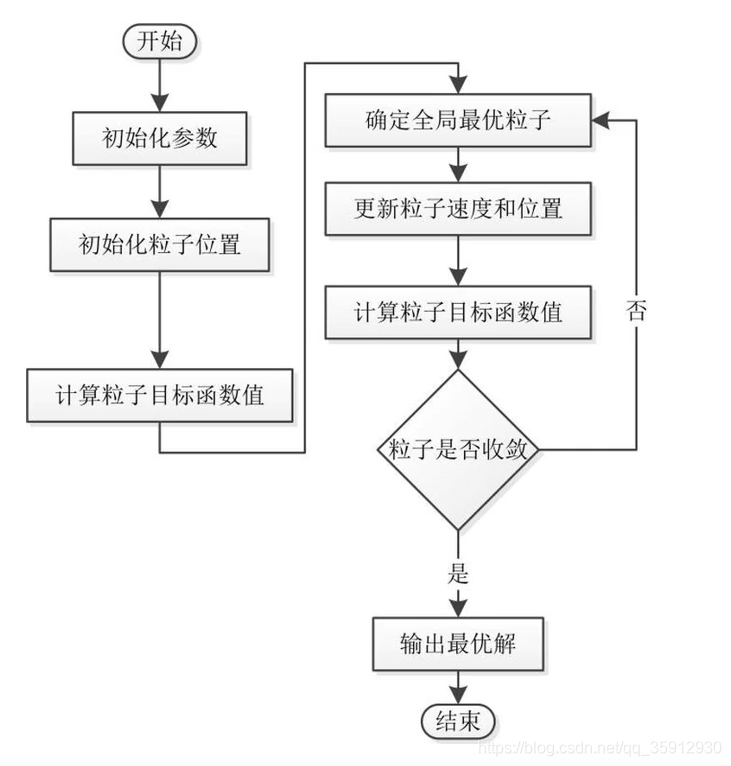
2. 算法流程图
3. 迭代方程
V i t + 1 = ω V i t + c 1 r 1 ( P i b e s t t − X i t ) + c 2 r 2 ( G b e s t t − X i t ) V_i^{t+1} = \omega V_i^t + c_1r_1(P_{ibest}^t-X_i^t) + c_2r_2(G_{best}^t - X_i^t) Vit+1=ωVit+c1r1(Pibestt−Xit)+c2r2(Gbestt−Xit)
- ω V i t \omega V_i^t ωVit:惯性
- c 1 r 1 ( P i b e s t t − X i t ) c_1r_1(P_{ibest}^t-X_i^t) c1r1(Pibestt−Xit):个体最优
- c 2 r 2 ( G b e s t t − X i t ) c_2r_2(G_{best}^t - X_i^t) c2r2(Gbestt−Xit):全局最优
X i t + 1 = X i t + V i t + 1 X_i^{t+1} = X_i^t + V_i^{t+1} Xit+1=Xit+Vit+1
- X i t + 1 X_i^{t+1} Xit+1:下一时刻位置
- X i t X_i^t Xit:当前位置
- V i t + 1 V_i^{t+1} Vit+1:下一时刻速度
图示
4. 代码示例
%目标函数
%能找目标函数的最小值
%如果找最大值,前加负号
function y = fun(x)
y = sum(x.^2);
clc
clear
c1 = 1.5;
c2 = 1.5;
w=1;
gen = 200; %迭代次数
size_pop = 50; %种群大小
pop_max = 100; %搜索范围
pop_min = -100;
nVar = 2;
V_max = 5; %速度最值
V_min = -5; %不能跨度太大,搜索精度不够,跨度太小,迭代次数过大
%初始种群
for i = 1 : size_pop
pop(i,:) = (pop_max - pop_min) * rands(1,nVar) ; %初始种群的位置
V(i,:) = (V_max - V_min) * rands(1,nVar); %初始种群的速度
fitness(i) = fun(pop(i,:)); %初始种群的目标函数
end
%初始化
[best_fitness,best_index] = max(fitness); %
g_best = pop(best_index,:);
p_best = pop;
fitness_p_best = fitness; %个人最优解
fitness_g_best = best_fitness; %全局最优解
for i = 1:gen
for j = 1:size_pop
%更新速度
V( j,: ) = V(j,:) + c1 * rand *(p_best(j,:) - pop(j,:)) + c2 * rand* (g_best(1,:) - pop(j,:));
V( j, find(V(j,:) > V_max )) = V_max;
V( j ,find(V(j,:) < V_min )) = V_min;
%更新位置
pop(j,:) = pop(j,:) + V(j,:);
pop( j, find(pop(j,:) > pop_max )) = pop_max;
pop( j ,find(pop(j,:) < pop_min )) = pop_min;
%
fitness(j) = fun(pop(j,:));
end
for j = 1:size_pop
%更新个人最优
if fitness(j) < fitness_p_best(j)
p_best(j,:) = pop(j,:);
fitness_p_best(j) = fitness(j);
end
%更新全局最优
if fitness(j) < fitness_g_best
g_best = pop(j,:);
fitness_g_best = fitness(j)
end
end
yy(i) = fitness_g_best;
end
plot(yy)
title('最优个体适应度','fontsize',12);
xlabel('迭代次数','fontsize',12);
ylabel('适应度','fontsize',12);
disp('函数值 变量')
disp([fitness_g_best,g_best]);
5. 特点
(1) 优点
- 理解简单
(2) 缺点
-
如果初始点选择不均匀,易出现收敛到局部最优解。
-
无法处理约束条件
6. 改良
(1) 惩罚函数
将有约束的目标函数转换为无约束的目标函数
降低分值,使其淘汰
%增加约束条件后的目标函数
function y = fun(x)
y = sum(x.^2);
if x(1) + x(2) > 2 %满足约束的正常
y=y;
else %不满足约束的淘汰
y = y + 1000;
end
(2) 增加变异操作
避免陷入局部最优解