SpringBoot整合RabbitMQ
SpringBoot整合
1、生产者工程
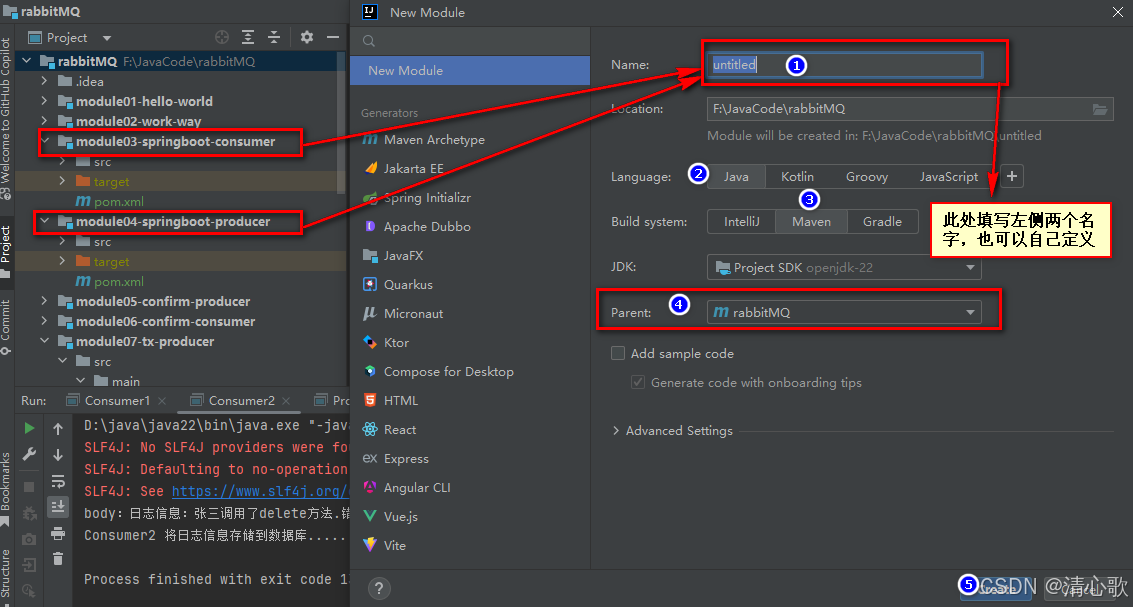
①创建module
②配置POM
添加如下依赖:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
③YAML
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.xxx.xxx
port: 5672
username: guest
password: 123456
virtual-host: /
④主启动类
package com.xxx.mq;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* @ClassName: RabbitMQProducerMainType
* @Package: com.xxx.mq
* @Author:
* @CreateDate:
* @Version: V1.0.0
* @Description:
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class RabbitMQProducerMainType {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RabbitMQProducerMainType.class, args);
}
}
⑤测试程序
在src目录下的test目录内新建测试类:
package com.xxx.mq.test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
/**
* @ClassName: RabbitMQTest
* @Package: com.xxx.mq.test
* @Author:
* @CreateDate:
* @Version: V1.0.0
* @Description:
*/
@SpringBootTest
public class RabbitMQTest {
public static final String EXCHANGE_DIRECT = "exchange.direct.order";
public static final String ROUTING_KEY = "order";
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Test
public void test01SendMessage() {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(EXCHANGE_DIRECT, ROUTING_KEY, "Hello Rabbit!SpringBoot!");
}
}
2、消费者工程
①创建module
②配置POM
添加如下依赖:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
③YAML
增加日志打印的配置:
新建名为application的yml文件。
文件内配置:
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.xxx.xxx
port: 5672
username: guest
password: 123456
virtual-host: /
logging:
level:
com.xxx.mq.listener.MyMessageListener: info
将host修改为自己的地址。
④主启动类
package com.xxx.mq;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* @ClassName: RabbitMQConsumerMainType
* @Package: com.xxx.mq
* @Author:
* @CreateDate:
* @Version: V1.0.0
* @Description:
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class RabbitMQConsumerMainType {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RabbitMQConsumerMainType.class, args);
}
}
⑤监听器
新建子包listener,并编写监听类:
package com.xxx.mq.listener;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Exchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.QueueBinding;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @ClassName: MyMessageListener
* @Package: com.xxx.mq.listener
* @Author:
* @CreateDate:
* @Version: V1.0.0
* @Description:
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class MyMessageListener {
public static final String EXCHANGE_DIRECT = "exchange.direct.order";
public static final String ROUTING_KEY = "order";
public static final String QUEUE_NAME = "queue.order";
// 写法一:监听 + 在 RabbitMQ 服务器上创建交换机、队列
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(value = QUEUE_NAME, durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(value = EXCHANGE_DIRECT),
key = {ROUTING_KEY}
)
)
// 写法二:监听
// @RabbitListener(queues = {QUEUE_NAME})
public void processMessage(String dataString, Message message, Channel channel) {
log.info("消费端接收到了消息:" + dataString);
}
}
3、@RabbitListener注解属性对比
①bindings属性
- 表面作用:
- 指定交换机和队列之间的绑定关系
- 指定当前方法要监听的队列
- 隐藏效果:如果RabbitMQ服务器上没有这里指定的交换机和队列,那么框架底层的代码会创建它们
②queues属性
@RabbitListener(queues = {QUEUE_TEST})
- 作用:指定当前方法要监听的队列
- 注意:此时框架不会创建相关交换机和队列,必须提前创建好
先启动生产者端代码,此时会立即执行完成。然后执行消费者端代码,等待消息。
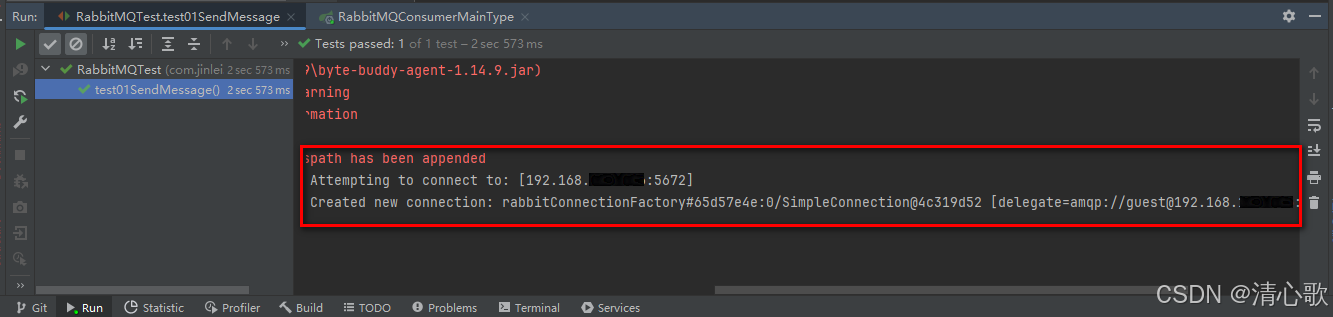
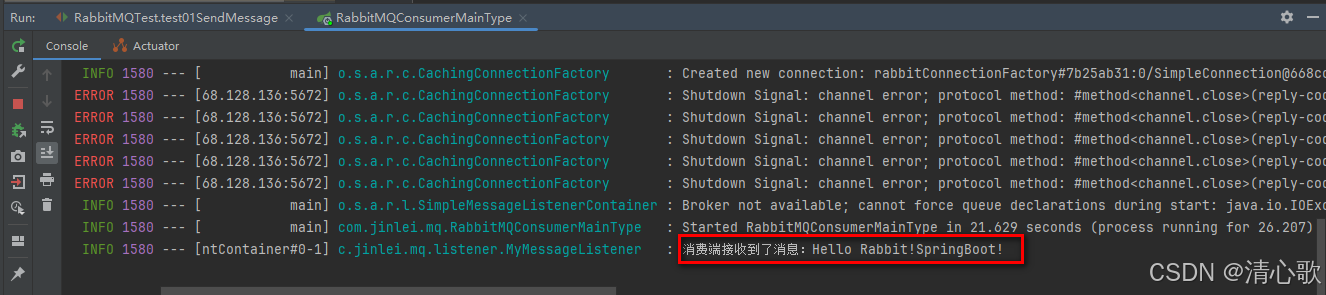
在生产者端module下的test内有创建好的测试代码,执行test01SendMessage测试方法,结果如图所示:
可以看到收到了生产者测试代码中的消息。前面的报错是因为我先启动了消费者端代码,此时找不到对应的交换机以及消息队列,当启动生产者端代码后就不会报错了,可以正确的接收到消息。