💡🚀🚀🚀本博客 改进源代码改进 适用于 YOLO11 按步骤操作运行改进后的代码即可
YOLO11改进:注意力机制|YOLO11+SKAttention改进内容🚀🚀🚀
文章目录
1. SKAttention 论文
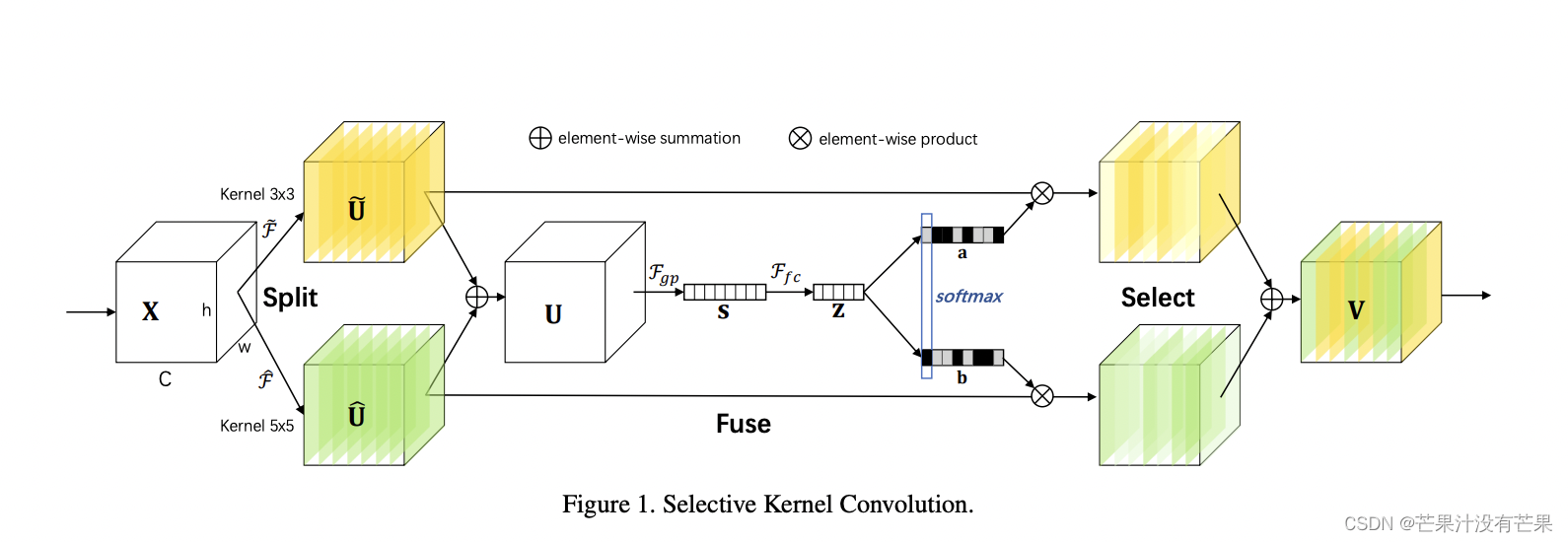
在标准卷积神经网络(CNN)中,每层人工神经元的感受野被设计为共享相同的大小。神经科学界众所周知,视觉皮层神经元的感受野大小是受刺激调节的,但在构建 CNN 时很少考虑这一点。我们在 CNN 中提出了一种动态选择机制,允许每个神经元根据输入信息的多个尺度自适应地调整其感受野大小。设计了一个称为选择性内核(SK)单元的构建块,其中使用由这些分支中的信息引导的 softmax 注意力来融合具有不同内核大小的多个分支。对这些分支的不同关注会产生融合层神经元有效感受野的不同大小。多个 SK 单元堆叠成一个称为选择性内核网络 (SKNet) 的深度网络。在 ImageNet 和 CIFAR 基准上,我们凭经验证明 SKNet 的性能优于现有最先进的架构,且模型复杂度较低。详细分析表明,SKNet中的神经元可以捕获不同尺度的目标物体,验证了神经元根据输入自适应调整其感受野大小的能力
具体细节可以去看原论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1903.06586.pdf
2. YOLO11 核心代码改进部分
2.1 核心代码
修改步骤:第一步
首先在ultralytics/nn/modules文件夹下,创建一个 sk.py文件,新增以下代码
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import init
from collections import OrderedDict
class SKAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel=512,out_channel=512,kernels=[1,3,5,7],reduction=16,group=1,L=32):
super().__init__()
self.d=max(L,channel//reduction)
self.convs=nn.ModuleList([])
for k in kernels:
self.convs.append(
nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
('conv',nn.Conv2d(channel,channel,kernel_size=k,padding=k//2,groups=group)),
('bn',nn.BatchNorm2d(channel)),
('relu',nn.ReLU())
]))
)
self.fc=nn.Linear(channel,self.d)
self.fcs=nn.ModuleList([])
for i in range(len(kernels)):
self.fcs.append(nn.Linear(self.d,channel))
self.softmax=nn.Softmax(dim=0)
def forward(self, x):
bs, c, _, _ = x.size()
conv_outs=[]
### split
for conv in self.convs:
conv_outs.append(conv(x))
feats=torch.stack(conv_outs,0)#k,bs,channel,h,w
### fuse
U=sum(conv_outs) #bs,c,h,w
### reduction channel
S=U.mean(-1).mean(-1) #bs,c
Z=self.fc(S) #bs,d
### calculate attention weight
weights=[]
for fc in self.fcs:
weight=fc(Z)
weights.append(weight.view(bs,c,1,1)) #bs,channel
attention_weughts=torch.stack(weights,0)#k,bs,channel,1,1
attention_weughts=self.softmax(attention_weughts)#k,bs,channel,1,1
### fuse
V=(attention_weughts*feats).sum(0)
return V
修改步骤:第二步
在ultralytics/nn/modules/init.py中导入 定义在 sk.py 里面的模块
from .sk import SKAttention
'SKAttention' 加到 __all__ = [...] 里面
修改步骤:第三步
在ultralytics/nn/tasks.py文件中,新增
from ultralytics.nn.modules import SKAttention
然后在 在tasks.py中配置
找到
elif m is nn.BatchNorm2d:
args = [ch[f]]
在这句上面加一个
elif m is SKAttention:
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != nc: # if c2 not equal to number of classes (i.e. for Classify() output)
c2 = make_divisible(min(c2, max_channels) * width, 8)
args = [c1, c2, *args[1:]]
修改步骤:第四步
2.3 YOLO11-SK 网络配置文件
新增YOLO11-SK.yaml
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLO11 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolo11n.yaml' will call yolo11.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.50, 0.25, 1024] # summary: 319 layers, 2624080 parameters, 2624064 gradients, 6.6 GFLOPs
s: [0.50, 0.50, 1024] # summary: 319 layers, 9458752 parameters, 9458736 gradients, 21.7 GFLOPs
m: [0.50, 1.00, 512] # summary: 409 layers, 20114688 parameters, 20114672 gradients, 68.5 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # summary: 631 layers, 25372160 parameters, 25372144 gradients, 87.6 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.50, 512] # summary: 631 layers, 56966176 parameters, 56966160 gradients, 196.0 GFLOPs
# YOLO11n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [256, False, 0.25]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False, 0.25]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
- [-1, 1, SKAttention, [1024]]
- [-1, 2, C2PSA, [1024]] # 10
# YOLO11n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False]] # 13
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [256, False]] # 16 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False]] # 19 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 11], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [1024, True]] # 22 (P5/32-large)
- [[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
2.4 运行代码
直接替换YOLO11-SK.yaml 进行训练即可
python train_v11.py --cfg YOLO11-SK.yaml
到这里就完成了这篇的改进。
改进说明
🥇🥇🥇
添加博主联系方式:
友好的读者可以添加博主QQ: 2434798737, 有空可以回答一些答疑和问题
🚀🚀🚀
参考
https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics