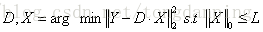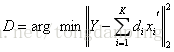稀疏表示(二)——KSVD算法详解(结合代码和算法思路)
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1sVMl3s-c7U1aaI9jzr3DTw 提取码: 55wx
——————————————————————我是分割线————————————————————————————
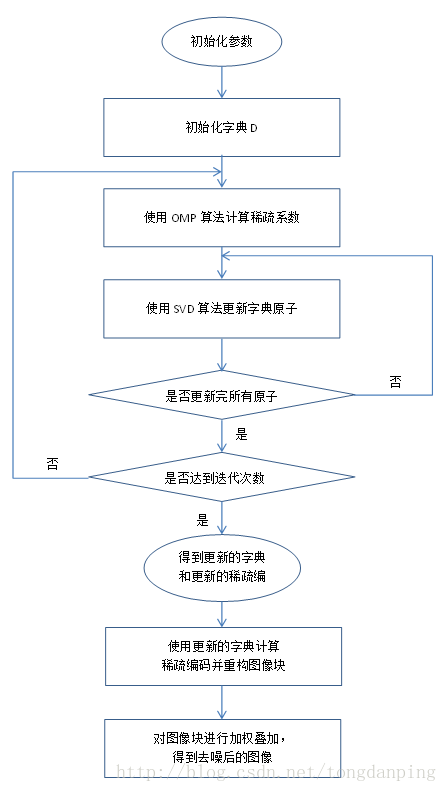
KSVD是一种稀疏表示中字典学习的算法,其名字的由来是该算法要经过K此迭代,且每一次迭代都要使用SVD分解。
在KSVD去噪算法中,稀疏编码可以使用OMP或者任意其它的稀疏编码算法,KSVD是用于字典更新的算法,KSVD在字典更新的过程中,每次只更新一个原子和对应的稀疏编码向量,在更新该原子时,其它原子是不变的,每次更新完字典的所有原子就同时更新了系数编码系数,这叫作一次迭代,在KSVD算法中,可以选择稀疏表示的第2种模型或者第3种模型见我的上一篇文章 ,在程序中可以通过参数 errorFlag来设置,如果errorFlag 为0,表示是用第2种模型,如果errorFlag 为1,表示是用第3种模型。在程序中的参数说明如下:
% errorFlag... if =0, a fix number of coefficients is
% used for representation of each signal. If so, param.L must be
% specified as the number of representing atom. if =1, arbitrary number
% of atoms represent each signal, until a specific representation error
% is reached. If so, param.errorGoal must be specified as the allowed
% error.在这里,我们使用第2种模式,也就是令errorFlag 为0。
整个KSVD的算法流程如下:
字典的初始化可以选取原始数据中的K个原子,或者使用一个固定的字典,比如DCT字典。
稀疏表示的两个主要阶段如下:
第一阶段:稀疏编码
对于模型:
此时的字典是已知的,利用OMP算法,计算得到稀疏编码矩阵X,在得到X后,进入第二阶段。
第二阶段:字典学习
在第一阶段中已经计算好了X,因此模型可以简化为:
在这里把矩阵用向量表示:
那么,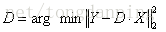
即把一个秩为K的矩阵分解为K个秩为1 的矩阵相加,现在假设我们要跟新第k列的原子,那么其他原子固定,即
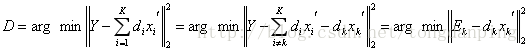
这里看出,当更新第k个原子的时候,只考虑第k个原子和稀疏向量带来的表示误差,这里问题就转化为求解一个最接近
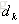
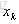
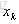
在这里,我们只保留上一次迭代中使用到了第k个原子的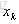
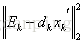
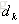
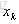
接下来,我们将结合KSVD去噪的程序来说明KSVD算法的流程。KSVD去噪算法可以在pudn上下载,去噪的程序denoiseImageKSVD.m 和 KSVD算法的程序 KSVD.m 都在文章末尾。接下来我们将把程序的每个部分提出来分析其功能。
KSVD的核心程序如下:
在程序中使用了I_findDistanseBetweenDictionaries()函数来更新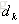
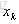
rPerm = randperm(size(Dictionary,2));%size(Dictionary,2)=256 ,该函数产生1到256的随机的整数
for j = rPerm %j的值为从1到256的随机整数值(没有重复的)
[betterDictionaryElement,CoefMatrix,addedNewVector] = I_findBetterDictionaryElement(Data,...
[FixedDictionaryElement,Dictionary],j+size(FixedDictionaryElement,2),...
CoefMatrix,param.L);
Dictionary(:,j) = betterDictionaryElement;
replacedVectorCounter = replacedVectorCounter+addedNewVector;
end这个函数是随机的更新字典中的每个向量,其中I_findDistanseBetweenDictionaries()函数是这样的:
function [betterDictionaryElement,CoefMatrix,NewVectorAdded] = I_findBetterDictionaryElement(Data,Dictionary,j,CoefMatrix,numCoefUsed)
relevantDataIndices = find(CoefMatrix(j,:));
% 查找出系数矩阵中每一行中非0元素的序号,即使用了第j个原子的的序号
if (length(relevantDataIndices)<1) %(length(relevantDataIndices)==0) %如果系数矩阵为空,则进行如下的语句 。 如果relevantDataIndices为0,说明没有patch表达需要用到第j个原子,则执行以下语句,称为语句块1
ErrorMat = Data-Dictionary*CoefMatrix;
ErrorNormVec = sum(ErrorMat.^2);
[d,i] = max(ErrorNormVec);
betterDictionaryElement = Data(:,i);
betterDictionaryElement = betterDictionaryElement./sqrt(betterDictionaryElement'*betterDictionaryElement);%归一化
betterDictionaryElement = betterDictionaryElement.*sign(betterDictionaryElement(1));
CoefMatrix(j,:) = 0;
NewVectorAdded = 1%%%%%实验证明(针对w.jpg图像),值累加了一次
% liuzhe=1 没进行此句,说明稀疏矩阵的每一行都有非零的元素
return;
end
%如果length(relevantDataIndices)不为0,也就是说有patch的表达使用到了第j个原子,则执行以下语句,称为语句块2
NewVectorAdded = 0;
tmpCoefMatrix = CoefMatrix(:,relevantDataIndices); %将稀疏矩阵中使用了第j个原子的系数向量取出来,tmpCoefMatrix尺寸为:256*length(relevantDataIndices)
tmpCoefMatrix(j,:) = 0;% the coeffitients of the element we now improve are not relevant.
errors =(Data(:,relevantDataIndices) - Dictionary*tmpCoefMatrix); % vector of errors that we want to minimize with the new element D:64*256 tmpCoefMatrix尺寸为:256*length(relevantDataIndices) Data(:,relevantDataIndices):64*relevantDataIndices
%%在这里使用SVD就可以达到|| errors - beta*element ||_F^2误差最小的效果
[betterDictionaryElement,singularValue,betaVector] = svds(errors,1);%%%%%%%仅仅取出了第一主分量,betterDictionaryElement*singularValue*betaVector'近似的可以表示errors
CoefMatrix(j,relevantDataIndices) = singularValue*betaVector';%这里把SVD向量的左奇异矩阵的第一主向量作为更新的字典原子dk,把奇异值和右奇异向量的第一主向量的乘积作为更新的稀疏向量xk
对I_findDistanseBetweenDictionaries()函数进行分析:
如果上一次迭代中没有任何图像块的系数表示使用过第j个原子,则if语句条件成立,那么利用上一次的稀疏矩阵计算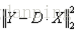
如果上一次迭代中使用过第j个原子,也就是if条件不成立,那么就执行语句块2,在语句块2中,把上一次迭代中使用了第j个原子的xk提取出来,并且计算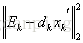
以下是有详细注释的程序
denoiseImageKSVD.m
-
function [IOut,output] = denoiseImageKSVD(Image,sigma,K,varargin)
-
%==========================================================================
-
% P E R F O R M D E N O I S I N G U S I N G A D I C T I O N A R Y
-
% T R A I N E D O N N O I S Y I M A G E
-
%==========================================================================
-
% function IOut = denoiseImageKSVD(Image,sigma,K,varargin)
-
% denoise an image by sparsely representing each block
with the
-
% already overcomplete trained Dictionary,
and averaging the represented parts.
-
% Detailed description can be found
in
"Image Denoising Via Sparse and Redundant
-
% representations over Learned Dictionaries", (appeared
in the
-
% IEEE Trans. on Image Processing, Vol.
15, no.
12, December
2006).
-
% This function may take some time to process. Possible factor that effect
-
% the processing time are:
-
%
1. number of KSVD iterations - the default number of iterations
is
10.
-
% However, fewer iterations may,
in most cases, result an acceleration
in
-
% the process, without effecting the result too much. Therefore, when
-
% required, this parameter may be re-set.
-
%
2. maxBlocksToConsider - The maximal number of blocks to train on. If this
-
% number
is larger the number of blocks
in the image, random blocks
-
%
from the image will be selected
for training.
-
% ===================================================================
-
% INPUT ARGUMENTS : Image - the noisy image (gray-level scale)
-
% sigma - the s.d. of the noise (assume to be white Gaussian).
-
% K - the number of atoms
in the trained dictionary.
-
% Optional arguments:
-
%
'blockSize' - the size of the blocks the algorithm
-
% works. All blocks are squares, therefore the given
-
% parameter should be one number (width
or height).
-
% Default value:
8.
-
%
'errorFactor' - a factor that multiplies sigma
in order
-
% to set the allowed representation error. In the
-
% experiments presented
in the paper, it was set to
1.15
-
% (which
is also the default value here).
-
%
'maxBlocksToConsider' - maximal number of blocks that
-
% can be processed. This number
is dependent on the memory
-
% capabilities of the machine,
and performances?
-
% considerations. If the number of available blocks
in the
-
% image
is larger than
'maxBlocksToConsider', the sliding
-
% distance between the blocks increases. The default value
-
%
is:
250000.
-
%
'slidingFactor' - the sliding distance between processed
-
% blocks. Default value
is
1. However,
if the image
is
-
% large, this number increases automatically (because of
-
% memory requirements). Larger values result faster
-
% performances (because of fewer processed blocks).
-
%
'numKSVDIters' - the number of KSVD iterations processed
-
% blocks
from the noisy image. If the number of
-
% blocks
in the image
is larger than this number,
-
% random blocks
from all available blocks will be
-
% selected. The default value
for this parameter
is:
-
%
10
if sigma >
5,
and
5 otherwise.
-
%
'maxNumBlocksToTrainOn' - the maximal number of blocks
-
% to train on. The default value
for this parameter
is
-
%
65000. However, it might
not be enough
for very large
-
% images
-
%
'displayFlag' -
if this flag
is switched on,
-
% announcement after finishing each it