在 PostgreSQL中,建立安全的数据库连接是由用户标识和认证技术来共同实现,而建立连接后的安全访问保护则是基于角色的对象访问控制。
数据库里的每个对象所拥有的权限信息经常会发生变化,比如授予对象的部分操作权限给其他用户,或者删除用户在对象上的操作权限,亦或是对用户在对象上的操作权限进行更新等。以上操作在 SQL 中体现为 GRANT 和 REVOKE 语句,且都涉及对象权限信息的动态管理,即权限控制中的对象权限管理。
为了保护数据安全,当用户要对某个数据库对象进行操作之前,必须检查用户在对象上的操作权限,仅当用户对此对象拥有进行合法操作的权限时,才允许用户对此对象执行相应操作。上述操作检查的过程被称为对象权限检查。
ACL
访问控制列表(Access Control List,ACL)是对象权限管理和权限检查的基础,PostgreSQL 通过操作 ACL 实现对象的访问控制管理,在 PostgreSQL 中每个数据库对象都具有 ACL ,每个对象的 ACL 存储了此对象的所有授权信息。当用户访问对象时,只有它在对象的 ACL 中并且具有所需的权限时才能访问该对象。当用户要更新对象的权限时,只需要更新 ACL 上的权限信息即可。
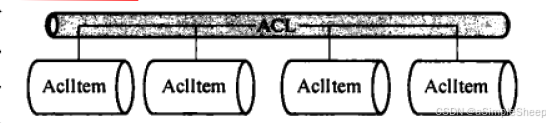
ACL 是存储控制项(Access Control Entruy,ACE)的集合,组织结构如图(取自《PostgreSQL 数据库内核分析》):
每个 ACL 实际是一个由多个 AclItem 构成的链表。每个 AclItem 对应一个 ACE 。 ACE 中记录着可访问对象的用户或者执行单元,此外还记录了可在对象上进行权限操作的用户或者执行单元。PostgreSQL 中,ACE 由受权者、授权者以及权限位三部分组成。
/*
* AclItem
*
* Note: must be same size on all platforms, because the size is hardcoded
* in the pg_type.h entry for aclitem.
*/
typedef struct AclItem
{
Oid ai_grantee; /* ID that this item grants privs to */
Oid ai_grantor; /* grantor of privs */
AclMode ai_privs; /* privilege bits */
} AclItem;
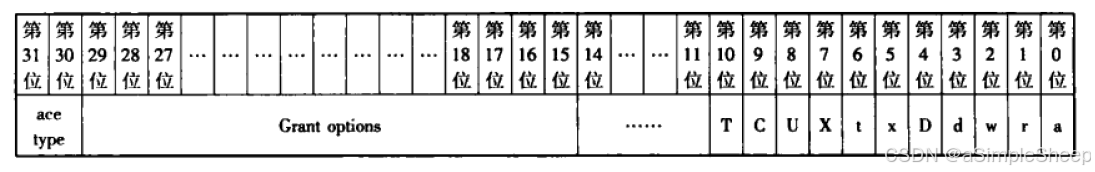
其中,字段 ai_privs 是 AclMode 类型。AclMode 是一个 32 位的比特位,其高 16 位为权限选项位,低 16 位为该 ACE 中的操作位权限。每个操作权限占 1 个比特位,当该比特位的取值为 1 时,表示 ACE 中的 ai_grabtee 对应的用户(受权者)具有此对象的相应操作权限,否则,表示用户没有相应权限。AclMode 结构如下所示(取自《PostgreSQL 数据库内核分析》):
ace type:记录了 ACE 的被授权者(受权者)类型,可以是用户、组或者 public。
Grant options:记录了各权限位对应的授出或者被转授选项。
低 16 位:分别记录了各个权限位的授予情况,从低到高依次为 INSERT、SELECT、UPDATE、DELETE、TRUNCATE 等等。若当授予语句使用 ALL 时,则表示包含所有权限。
ACL 检查
调用 src/backend/catalog/aclchk.c 下的函数 pg_class_aclcheck ,获取用户在该表上的权限集,比较该权限集与操作所需权限集,若前者大于后者,则检查通过。
首先获取到对应的元组,从 pg_class 系统表中:
/*
* Must get the relation's tuple from pg_class
*/
tuple = SearchSysCache1(RELOID, ObjectIdGetDatum(table_oid));
if (!HeapTupleIsValid(tuple))
{
if (is_missing != NULL)
{
/* return "no privileges" instead of throwing an error */
*is_missing = true;
return 0;
}
else
ereport(ERROR,
(errcode(ERRCODE_UNDEFINED_TABLE),
errmsg("relation with OID %u does not exist",
table_oid)));
}
classForm = (Form_pg_class) GETSTRUCT(tuple);
判断操作的表是否是系统表,如果是系统表则禁止操作。通过 IsSystemClass 函数判断其 relid 是否小于 FirstUnpinnedObjectId。
/*
* Deny anyone permission to update a system catalog unless
* pg_authid.rolsuper is set.
*
* As of 7.4 we have some updatable system views; those shouldn't be
* protected in this way. Assume the view rules can take care of
* themselves. ACL_USAGE is if we ever have system sequences.
*/
if ((mask & (ACL_INSERT | ACL_UPDATE | ACL_DELETE | ACL_TRUNCATE | ACL_USAGE)) &&
IsSystemClass(table_oid, classForm) &&
classForm->relkind != RELKIND_VIEW &&
!superuser_arg(roleid))
mask &= ~(ACL_INSERT | ACL_UPDATE | ACL_DELETE | ACL_TRUNCATE | ACL_USAGE);
从 pg_class 系统表中取出操作表的 ACL ,产生一个副本
/*
* Normal case: get the relation's ACL from pg_class
*/
ownerId = classForm->relowner;
aclDatum = SysCacheGetAttr(RELOID, tuple, Anum_pg_class_relacl,
&isNull);
if (isNull)
{
/* No ACL, so build default ACL */
switch (classForm->relkind)
{
case RELKIND_SEQUENCE:
acl = acldefault(OBJECT_SEQUENCE, ownerId);
break;
default:
acl = acldefault(OBJECT_TABLE, ownerId);
break;
}
aclDatum = (Datum) 0;
}
else
{
/* detoast rel's ACL if necessary */
acl = DatumGetAclP(aclDatum);
}
如果是NULL则设置默认ACL。
然后调用 aclmask 获取用户在该表的操作权限集。如果操作用户是该表的拥有者,则有该表的所有权限。若不是该表的拥有者,则检查用户被被授予的权限,以及表的公共权限。
result = aclmask(acl, roleid, ownerId, mask, how);
/*
* Check if ACL_SELECT is being checked and, if so, and not set already as
* part of the result, then check if the user is a member of the
* pg_read_all_data role, which allows read access to all relations.
*/
if (mask & ACL_SELECT && !(result & ACL_SELECT) &&
has_privs_of_role(roleid, ROLE_PG_READ_ALL_DATA))
result |= ACL_SELECT;
/*
* Check if ACL_INSERT, ACL_UPDATE, or ACL_DELETE is being checked and, if
* so, and not set already as part of the result, then check if the user
* is a member of the pg_write_all_data role, which allows
* INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE access to all relations (except system catalogs,
* which requires superuser, see above).
*/
if (mask & (ACL_INSERT | ACL_UPDATE | ACL_DELETE) &&
!(result & (ACL_INSERT | ACL_UPDATE | ACL_DELETE)) &&
has_privs_of_role(roleid, ROLE_PG_WRITE_ALL_DATA))
result |= (mask & (ACL_INSERT | ACL_UPDATE | ACL_DELETE));
ACL 更新
对某个对象进行权限授予/回收,实际上就是在 ACL 上进行添加或删除指定的权限,同时更新 ACL 。将对应的权限标志位置 0 或 1 即可。
在该过程中需要注意的一点是,会调用 src/backend/utils/adt/acl.c 中的函数 check_circularity(const Acl *old_acl, const AclItem *mod_aip, Oid ownerId),通过递归删除所有被授予者拥有的可再授予权限,检查权限授予是否会有环形成。
通过 old_acl 去 copy 一个副本 acl 调用 aclupdate 进行递归删除操作。
/* Zap all grant options of target grantee, plus what depends on 'em */
cc_restart:
num = ACL_NUM(acl);
aip = ACL_DAT(acl);
for (i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
if (aip[i].ai_grantee == mod_aip->ai_grantee &&
ACLITEM_GET_GOPTIONS(aip[i]) != ACL_NO_RIGHTS)
{
Acl *new_acl;
/* We'll actually zap ordinary privs too, but no matter */
new_acl = aclupdate(acl, &aip[i], ACL_MODECHG_DEL,
ownerId, DROP_CASCADE);
pfree(acl);
acl = new_acl;
goto cc_restart;
}
}
删除完成后,检查授予者是否还有可在授予权限,如果没有,则授予者不能进行授权。
对象权限管理
对象的权限管理主要是通过使用 SQL 命令 GRANT 和 REVOKE 授予或回收一个或多个角色在对象上的权限。
Grant 语法:
GRANT { { SELECT | INSERT | UPDATE | DELETE | TRUNCATE | REFERENCES | TRIGGER }
[, ...] | ALL [ PRIVILEGES ] }
ON { [ TABLE ] table_name [, ...]
| ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA schema_name [, ...] }
TO role_specification [, ...] [ WITH GRANT OPTION ]
[ GRANTED BY role_specification ]
Revoke 语法:
REVOKE [ GRANT OPTION FOR ]
{ { SELECT | INSERT | UPDATE | DELETE | TRUNCATE | REFERENCES | TRIGGER }
[, ...] | ALL [ PRIVILEGES ] }
ON { [ TABLE ] table_name [, ...]
| ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA schema_name [, ...] }
FROM role_specification [, ...]
[ GRANTED BY role_specification ]
[ CASCADE | RESTRICT ]
上述只是展示了其中的一种用法,详细语法规则感兴趣的小伙伴可以查看官方文档:
http://postgres.cn/docs/15/sql-grant.html
http://postgres.cn/docs/15/sql-revoke.html
GRANT/REVOKE 命令都是由函数 ExecuteGrantStmt 实现,该函数只有一个类型为 GrantStmt 的参数。
但函数首先会将 GrantStmt 的参数分别转换为 InternalGrant 结构,将命令的权限列表转化成内部的 AclMode 表示。两个结构如下:
typedef struct GrantStmt
{
NodeTag type;
bool is_grant; /* true = GRANT, false = REVOKE */
GrantTargetType targtype; /* type of the grant target */
ObjectType objtype; /* kind of object being operated on */
List *objects; /* list of RangeVar nodes, ObjectWithArgs
* nodes, or plain names (as String values) */
List *privileges; /* list of AccessPriv nodes */
/* privileges == NIL denotes ALL PRIVILEGES */
List *grantees; /* list of RoleSpec nodes */
bool grant_option; /* grant or revoke grant option */
RoleSpec *grantor;
DropBehavior behavior; /* drop behavior (for REVOKE) */
} GrantStmt;
/*
* The information about one Grant/Revoke statement, in internal format: object
* and grantees names have been turned into Oids, the privilege list is an
* AclMode bitmask. If 'privileges' is ACL_NO_RIGHTS (the 0 value) and
* all_privs is true, 'privileges' will be internally set to the right kind of
* ACL_ALL_RIGHTS_*, depending on the object type (NB - this will modify the
* InternalGrant struct!)
*
* Note: 'all_privs' and 'privileges' represent object-level privileges only.
* There might also be column-level privilege specifications, which are
* represented in col_privs (this is a list of untransformed AccessPriv nodes).
* Column privileges are only valid for objtype OBJECT_TABLE.
*/
typedef struct
{
bool is_grant;
ObjectType objtype;
List *objects;
bool all_privs;
AclMode privileges;
List *col_privs;
List *grantees;
bool grant_option;
DropBehavior behavior;
} InternalGrant;
当 privileges 取值为 NIL 时,表示授予或回收所有的权限,此时 InternalGrant 的 all_privs 字段为true,且 InternalGrant 的 privileges 字段被设置为 ACL_NO_RIGHTS 也表示 ACL_ALL_RIGHTS。
InternalGrant 中的 all_privs 和 privileges 只表示对象级的权限集合。列级的权限集合是用 col_privs 表示的,它的值通过 GrantStmt 中的 privileges 给出。
GrantStmt 中的 grantees 链表为 PrivGrantee 结构,而 InternalStmt 中为 OID 结构,在此也会进行转换,若 PrivGrantee 结构中 rolename 为空,则会将 ACL_ID_PUBLIC 加入到 OID 链表中。
转换完成之后,通过函数 ExecGrantStmt_oids(&istmt) 判断操作对象的类型,并调用相应的授予或回收权限函数。
以对象是表为例:
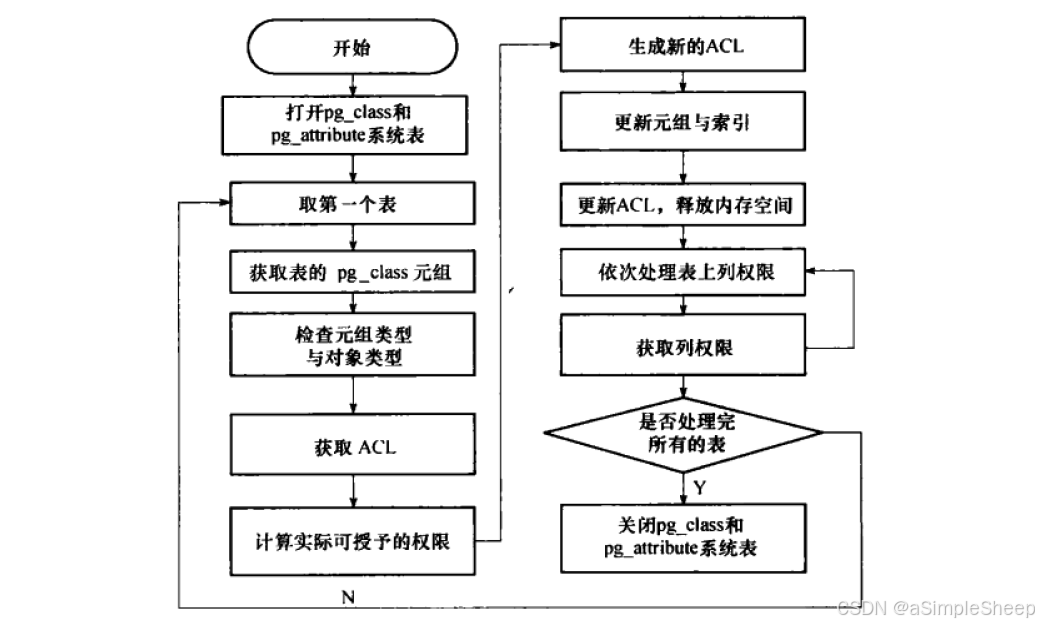
表的权限管理函数为 ExecGrant_Relation(istmt)。基本流程图如下(取自《PostgreSQL 数据库内核分析》):
先打开 pg_class 和 pg_attribute 系统表
relation = table_open(RelationRelationId, RowExclusiveLock);
attRelation = table_open(AttributeRelationId, RowExclusiveLock);
接着,获取第一个对象表的 pg_class 元组,
tuple = SearchSysCache1(RELOID, ObjectIdGetDatum(relOid));
if (!HeapTupleIsValid(tuple))
elog(ERROR, "cache lookup failed for relation %u", relOid);
pg_class_tuple = (Form_pg_class) GETSTRUCT(tuple);
通过 pg_class_tuple->kind 和 istmt->objtype 检查元组类型和对象类型
从 pg_class_tuple 中获取对象表的 ownerId 和 ACL ,若不存在 ACL ,就新建一个 ACL ,并将默认的权限信息赋给该 ACL(根据对象的不同,默认权限也会不同)。若存在,则直接将旧的 ACL 存储为一个副本。
生成新的 ACL 时,如果是授予权限,则将命令中给出的权限添加到就的 ACL 中;如果是撤销权限,则将命令中的给出的要回收的权限从旧的 ACL 删除。
通过函数 merge_acl_with_grant 来获取新的 ACL ,其中调用 aclupdate ,在 ACL 中搜索该受权者和授予者的现有条目。如果存在,只需就地修改条目;否则,在末尾插入新条目。
for (dst = 0; dst < num; ++dst)
{
if (aclitem_match(mod_aip, old_aip + dst))
{
/* found a match, so modify existing item */
new_acl = allocacl(num);
new_aip = ACL_DAT(new_acl);
memcpy(new_acl, old_acl, ACL_SIZE(old_acl));
break;
}
}
if (dst == num)
{
/* need to append a new item */
new_acl = allocacl(num + 1);
new_aip = ACL_DAT(new_acl);
memcpy(new_aip, old_aip, num * sizeof(AclItem));
/* initialize the new entry with no permissions */
new_aip[dst].ai_grantee = mod_aip->ai_grantee;
new_aip[dst].ai_grantor = mod_aip->ai_grantor;
ACLITEM_SET_PRIVS_GOPTIONS(new_aip[dst],
ACL_NO_RIGHTS, ACL_NO_RIGHTS);
num++; /* set num to the size of new_acl */
}
根据修改模式进行相应条目的权限修改
/* apply the specified permissions change */
switch (modechg)
{
case ACL_MODECHG_ADD:
ACLITEM_SET_RIGHTS(new_aip[dst],
old_rights | ACLITEM_GET_RIGHTS(*mod_aip));
break;
case ACL_MODECHG_DEL:
ACLITEM_SET_RIGHTS(new_aip[dst],
old_rights & ~ACLITEM_GET_RIGHTS(*mod_aip));
break;
case ACL_MODECHG_EQL:
ACLITEM_SET_RIGHTS(new_aip[dst],
ACLITEM_GET_RIGHTS(*mod_aip));
break;
}
新的 ACL 生成之后,将其插入元组中,更新到 pg_class 中相应元组,
接下来就是依次处理列权限,调用函数 expand_col_privileges 将列权限列表转换成数组形式表示。依次判断每一列的权限,调用函数 ExecGrant_Attribute 计算每一列实际可以授予或回收的权限,然后更新 ACL。
每一列的 ACL 存放在该列对应的 pg_attribute 元组中,ExecGrant_Attribute 的处理过程与 ExecGrant_Relation 类似。但不同的是,目前只有表中才会有列级权限,所以 ExecGrant_Attribute 只能从 ExecGrant_Relation 处调用,而不能直接被 ExecGrandStmt 调用。
如果只有一个表对象则结束;如果有多个,则获取第二个表对象,继续处理。
对象权限检查
在对数据库对象操作时,必须要对该对象上的权限进行检查,只有拥有该操作权限时,才可以执行该操作。
例如,用户要查询表 table_test ,可以执行命令:SELECT * FROM table_test;。如果该用户在 table_test 上不具有查询权限,则不可以查询。通常数据库对象的拥有者具有该对象的一切操作权限,超级用户也拥有对所有对象的全部操作权限,而非属主用户在对数据库对象操作之前需要进行权限检查。
以表的检查权限为例。表上的权限检查由函数 ExecCheckRTEPerms 实现,该函数参数为 RangeTblEntry 。
typedef struct RangeTblEntry
{
NodeTag type;
RTEKind rtekind; /* 对象类型 */
······
AclMode requiredPerms; /* 需要的访问权限( AclMode 类型) */
Oid checkAsUser; /* 角色 ID */
Bitmapset *selectedCols; /* columns needing SELECT permission */
Bitmapset *insertedCols; /* columns needing INSERT permission */
Bitmapset *updatedCols; /* columns needing UPDATE permission */
Bitmapset *extraUpdatedCols; /* generated columns being updated */
List *securityQuals; /* security barrier quals to apply, if any */
} RangeTblEntry;
其中,字段 requiredPerms 表示需要访问的权限信息。 selectedCols 表示在表的操作中需要有 SELECT 权限的列的集合, insertedCols 则表示需要INSERT权限的列集合, 其他同理。
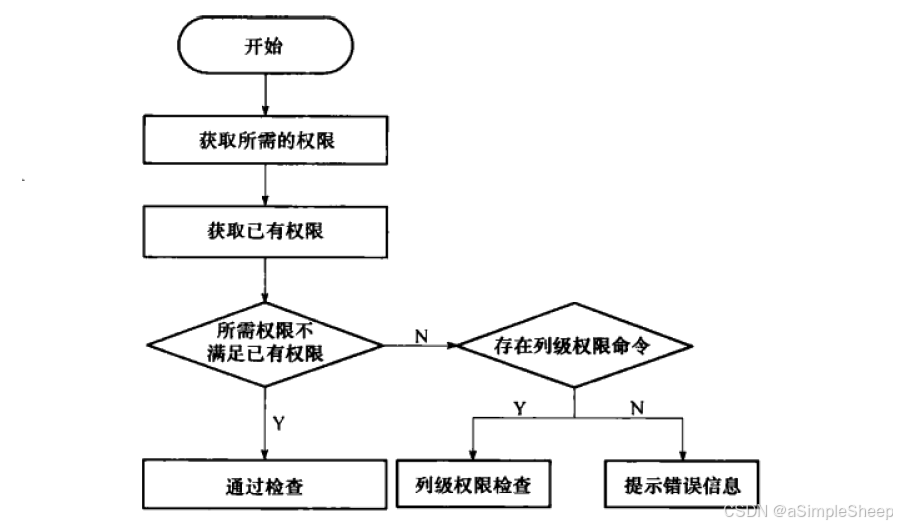
函数 ExecCheckRTEPerms 的基本流程如下(取自《PostgreSQL 数据库内核分析》):
首先获取需要的权限,通过传入的参数获取。
/*
* No work if requiredPerms is empty.
*/
requiredPerms = rte->requiredPerms;
if (requiredPerms == 0)
return true;
调用 aclmask 获取已有权限,原理是获取目标的 acl 中 AclItem 链表的个数和节点,依次去遍历链表,判断 AclItem 结构中当前用户直接被授予的权限。
num = ACL_NUM(acl);
aidat = ACL_DAT(acl);
/*
* Check privileges granted directly to roleid or to public
*/
for (i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
AclItem *aidata = &aidat[i];
if (aidata->ai_grantee == ACL_ID_PUBLIC ||
aidata->ai_grantee == roleid)
{
result |= aidata->ai_privs & mask;
if ((how == ACLMASK_ALL) ? (result == mask) : (result != 0))
return result;
}
}
调用 pg_class_aclmask 的进行判断,relPerms 是操作用户拥有的权限与请求权限 & 的结果:
/*
* We must have *all* the requiredPerms bits, but some of the bits can be
* satisfied from column-level rather than relation-level permissions.
* First, remove any bits that are satisfied by relation permissions.
*/
relPerms = pg_class_aclmask(relOid, userid, requiredPerms, ACLMASK_ALL);
remainingPerms = requiredPerms & ~relPerms;
if (remainingPerms != 0)
requiredPerms 和 ~relPerms 按位相与,若结果 remainingPerms 等于 0,则表示已有权限满足所需权限,检查结束,若不等于 0,进一步检查列级权限。
/*
* If we lack any permissions that exist only as relation permissions,
* we can fail straight away.
*/
if (remainingPerms & ~(ACL_SELECT | ACL_INSERT | ACL_UPDATE))
return false;
首先判断列级权限中有无 SELECT/UPDATE/INSERT,若没有返回 false,若有则进一步通过 requiredPerms 和SELECT/UPDATE/INSERT 依次相与,检查具体是那一个或那几个权限,并调用函数 pg_attribute_aclcheck 进行列级权限检查。
添加一个新的权限位
暂时没有,后面进行补充