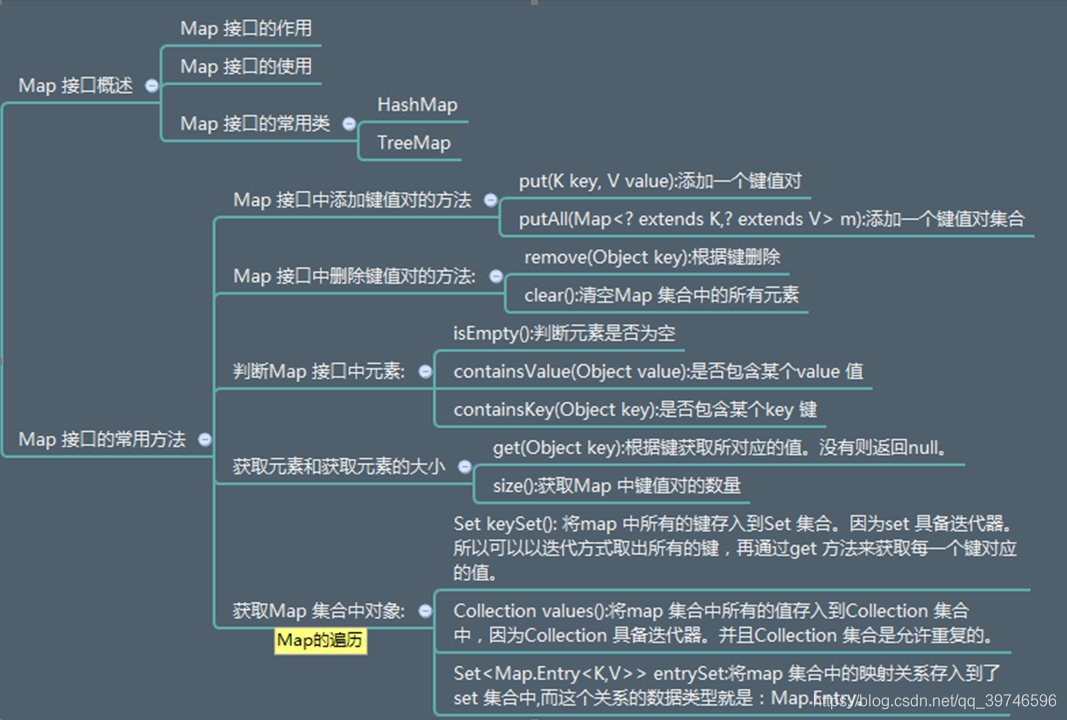
文章目录
Map家族
特点:键值对存储
(1),为什么需要使用map?前面源码分析中常见它的身影,在里面充当了一个什么作用?
Map存储的元素为键值对,通常称为key-value
而key是不允许重复的
Set唯一
(2),掌握Map的常用方法–整体有个印象,我们首先掌握的是HashMap
(3),一一掌握上述的每个方法的应用(采用String,Integer等JDK已提供的引用数据类型)
基本方法的使用
重点掌握数据的存储及遍历的方式(两种遍历方式都要掌握)
(4),深入掌握HashMap的关键技术点,如何区分是否重复?以自定义类型来作为key探究问题的关键
—Map<String,String>
—Mp<自定义类型,String>
看要怎么保证键的唯一性?自定义类型也需要根据业务需求来确定唯一性,(hashcode,equals)
(5),LinkedHashMap
上述的HashMap存储的数据是唯一但无序的,而如果采用LinkedHashMap则是有序且唯一的
(6),TreeMap
有排序的功能,先采用String类型或Integer类型来学习TreeMap的特点
—TreeMap<String,String>
—TreeMap<Integer,Integer>
再以自定义类型来作为key,这个时候又需要我们做什么来保证可排序性?
—TreeMap<自定义类型,String>
1. HashMap(实现类)
特点:key是唯一的
package com.dream.hashmap_class;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 使用HashMap的常用方法
*/
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
//添加元素
map.put("麻生希", 29);
map.put("椎名空", 24);
map.put("爱田奈奈", 36);
map.put("古川伊织", 28);
map.put("小峰由衣", 34);
map.put("北条麻衣", 34);
//替换 - 如果key存在,直接替换value值,并返回原来的value
Integer put = map.put("麻生希", 30);
System.out.println("获取被替换掉的原值:" + put);
//替换
map.replace("麻生希", 31);//通过key替换value
map.replace("麻生希", 31, 32);//通过key和value替换value
//如果key存在,返回值key对应的value
//如果key不存在,添加元素
Integer putIfAbsent = map.putIfAbsent("xxx", 1000);
System.out.println(putIfAbsent);
//添加整个集合
HashMap<String, Integer> newMap1 = new HashMap<>();
newMap1.put("古川伊织", 29);
newMap1.put("aaa", 28);
newMap1.put("bbb", 28);
newMap1.put("ccc", 28);
map.putAll(newMap1);
//删除
map.remove("爱田奈奈");//通过key删除映射关系
map.remove("椎名空", 100);//通过key和value删除映射关系
//通过Key获取Value
Integer v = map.get("古川伊织");
System.out.println("通过Key获取Value:" + v);
System.out.println("判断集合中是否有某个key:" + map.containsKey("椎名空"));
System.out.println("判断集合中是否有某个value:" + map.containsValue(34));
System.out.println("获取key对应的value值,如果key不存在,就返回默认值:" + map.getOrDefault("椎名空1", 100));
System.out.println("判断集合中是否没有元素:" + map.isEmpty());
System.out.println("获取集合中映射关系的个数:" + map.size());
//将Map集合中所有的value取出存入到Collection集合中
Collection<Integer> values = map.values();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(values.toArray()));
System.out.println("-------------------");
//遍历
//keySet():将map集合中所有的key取出,存入Set集合中,遍历Set集合,将Key依次取出,再取出对应的value
Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();
for (String key : keySet) {
Integer value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " -- " + value);
}
System.out.println("-------------------");
//entrySet():将map集合中所有的Entry取出,存入Set集合中,遍历Set集合,将Entry依次取出,再取出Entry里的key和value
Set<Entry<String, Integer>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Entry<String, Integer> entry : entrySet) {
String key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " -- " + value);
}
}
}
2. LinkedHashMap
package com.dream.linkedhashmap_class;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 使用LinkedHashMap的常用方法
*/
LinkedHashMap<String, Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
//添加元素
map.put("麻生希", 29);
map.put("椎名空", 24);
map.put("爱田奈奈", 36);
map.put("古川伊织", 28);
map.put("小峰由衣", 34);
map.put("北条麻衣", 34);
//替换 - 如果key存在,直接替换value值,并返回原来的value
Integer put = map.put("麻生希", 30);
System.out.println("获取被替换掉的原值:" + put);
//替换
map.replace("麻生希", 31);//通过key替换value
map.replace("麻生希", 31, 32);//通过key和value替换value
//如果key存在,返回值key对应的value
//如果key不存在,添加元素
Integer putIfAbsent = map.putIfAbsent("xxx", 1000);
System.out.println(putIfAbsent);
//添加整个集合
LinkedHashMap<String, Integer> newMap1 = new LinkedHashMap<>();
newMap1.put("古川伊织", 29);
newMap1.put("aaa", 28);
newMap1.put("bbb", 28);
newMap1.put("ccc", 28);
map.putAll(newMap1);
//删除
map.remove("爱田奈奈");//通过key删除映射关系
map.remove("椎名空", 100);//通过key和value删除映射关系
//通过Key获取Value
Integer v = map.get("古川伊织");
System.out.println("通过Key获取Value:" + v);
System.out.println("判断集合中是否有某个key:" + map.containsKey("椎名空"));
System.out.println("判断集合中是否有某个value:" + map.containsValue(34));
System.out.println("获取key对应的value值,如果key不存在,就返回默认值:" + map.getOrDefault("椎名空1", 100));
System.out.println("判断集合中是否没有元素:" + map.isEmpty());
System.out.println("获取集合中映射关系的个数:" + map.size());
//将Map集合中所有的value取出存入到Collection集合中
Collection<Integer> values = map.values();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(values.toArray()));
System.out.println("-------------------");
//遍历
//keySet():将map集合中所有的key取出,存入Set集合中,遍历Set集合,将Key依次取出,再取出对应的value
Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();
for (String key : keySet) {
Integer value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " -- " + value);
}
System.out.println("-------------------");
//entrySet():将map集合中所有的Entry取出,存入Set集合中,遍历Set集合,将Entry依次取出,再取出Entry里的key和value
Set<Entry<String, Integer>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Entry<String, Integer> entry : entrySet) {
String key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " -- " + value);
}
}
}
3. Hashtable
package com.dream.hashtable_class;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 使用Hashtable的常用方法
*/
Hashtable<String, Integer> map = new Hashtable<>();
//添加元素
map.put("麻生希", 29);
map.put("椎名空", 24);
map.put("爱田奈奈", 36);
map.put("古川伊织", 28);
map.put("小峰由衣", 34);
map.put("北条麻衣", 34);
//替换 - 如果key存在,直接替换value值,并返回原来的value
Integer put = map.put("麻生希", 30);
System.out.println("获取被替换掉的原值:" + put);
//替换
map.replace("麻生希", 31);//通过key替换value
map.replace("麻生希", 31, 32);//通过key和value替换value
//如果key存在,返回值key对应的value
//如果key不存在,添加元素
Integer putIfAbsent = map.putIfAbsent("xxx", 1000);
System.out.println(putIfAbsent);
//添加整个集合
Hashtable<String, Integer> newMap1 = new Hashtable<>();
newMap1.put("古川伊织", 29);
newMap1.put("aaa", 28);
newMap1.put("bbb", 28);
newMap1.put("ccc", 28);
map.putAll(newMap1);
//删除
map.remove("爱田奈奈");//通过key删除映射关系
map.remove("椎名空", 100);//通过key和value删除映射关系
//通过Key获取Value
Integer v = map.get("古川伊织");
System.out.println("通过Key获取Value:" + v);
System.out.println("判断集合中是否有某个key:" + map.containsKey("椎名空"));
System.out.println("判断集合中是否有某个value:" + map.containsValue(34));
System.out.println("获取key对应的value值,如果key不存在,就返回默认值:" + map.getOrDefault("椎名空1", 100));
System.out.println("判断集合中是否没有元素:" + map.isEmpty());
System.out.println("获取集合中映射关系的个数:" + map.size());
//将Map集合中所有的value取出存入到Collection集合中
Collection<Integer> values = map.values();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(values.toArray()));
System.out.println("-------------------");
//遍历
//keySet():将map集合中所有的key取出,存入Set集合中,遍历Set集合,将Key依次取出,再取出对应的value
Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();
for (String key : keySet) {
Integer value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " -- " + value);
}
System.out.println("-------------------");
//entrySet():将map集合中所有的Entry取出,存入Set集合中,遍历Set集合,将Entry依次取出,再取出Entry里的key和value
Set<Entry<String, Integer>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Entry<String, Integer> entry : entrySet) {
String key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " -- " + value);
}
}
}
4. ConcurrentHashMap
package com.dream.concurrenthashmap_class;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 使用ConcurrentHashMap的常用方法
*/
ConcurrentHashMap<String, Integer> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//添加元素
map.put("麻生希", 29);
map.put("椎名空", 24);
map.put("爱田奈奈", 36);
map.put("古川伊织", 28);
map.put("小峰由衣", 34);
map.put("北条麻衣", 34);
//替换 - 如果key存在,直接替换value值,并返回原来的value
Integer put = map.put("麻生希", 30);
System.out.println("获取被替换掉的原值:" + put);
//替换
map.replace("麻生希", 31);//通过key替换value
map.replace("麻生希", 31, 32);//通过key和value替换value
//如果key存在,返回值key对应的value
//如果key不存在,添加元素
Integer putIfAbsent = map.putIfAbsent("xxx", 1000);
System.out.println(putIfAbsent);
//添加整个集合
ConcurrentHashMap<String, Integer> newMap1 = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
newMap1.put("古川伊织", 29);
newMap1.put("aaa", 28);
newMap1.put("bbb", 28);
newMap1.put("ccc", 28);
map.putAll(newMap1);
//删除
map.remove("爱田奈奈");//通过key删除映射关系
map.remove("椎名空", 100);//通过key和value删除映射关系
//通过Key获取Value
Integer v = map.get("古川伊织");
System.out.println("通过Key获取Value:" + v);
System.out.println("判断集合中是否有某个key:" + map.containsKey("椎名空"));
System.out.println("判断集合中是否有某个value:" + map.containsValue(34));
System.out.println("获取key对应的value值,如果key不存在,就返回默认值:" + map.getOrDefault("椎名空1", 100));
System.out.println("判断集合中是否没有元素:" + map.isEmpty());
System.out.println("获取集合中映射关系的个数:" + map.size());
//将Map集合中所有的value取出存入到Collection集合中
Collection<Integer> values = map.values();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(values.toArray()));
System.out.println("-------------------");
//遍历
//keySet():将map集合中所有的key取出,存入Set集合中,遍历Set集合,将Key依次取出,再取出对应的value
Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();
for (String key : keySet) {
Integer value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " -- " + value);
}
System.out.println("-------------------");
//entrySet():将map集合中所有的Entry取出,存入Set集合中,遍历Set集合,将Entry依次取出,再取出Entry里的key和value
Set<Entry<String, Integer>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Entry<String, Integer> entry : entrySet) {
String key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " -- " + value);
}
}
}
package com.dream.concurrenthashmap_class;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* HashMap vs Hashtable vs ConcurrentHashMap
*
* HashMap 允许存储null键
* Hashtable 不允许存储null键
* ConcurrentHashMap 不允许存储null键
*/
// HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// map.put(null, "111");
Hashtable<Object,Object> map = new Hashtable<>();
map.put(null, "111");
// ConcurrentHashMap<Object,Object> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// map.put(null, "111");
}
}
5. TreeMap
package com.dream.treemap_class;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 做实验理解 TreeMap 的自然排序
*
* 注意:针对于Key排序
*/
TreeMap<String, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("b", 34);
map.put("d", 28);
map.put("a", 33);
map.put("e", 20);
map.put("c", 26);
Set<Entry<String,Integer>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Entry<String, Integer> entry : entrySet) {
String key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " -- " + value);
}
}
}
package com.dream.treemap_class;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 使用内置比较器
*/
TreeMap<Student, String> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put(new Student("麻生希", '女', 28, "2101", "001"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("椎名空", '女', 23, "2101", "002"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("北岛玲", '女', 27, "2101", "003"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("水野朝阳", '女', 31, "2101", "004"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("三上悠亚", '女', 26, "2101", "005"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("濑亚美莉", '女', 32, "2101", "006"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("爱田奈奈", '女', 36, "2102", "001"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("深田咏美", '女', 28, "2102", "002"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("小西满里惠", '女', 28, "2102", "003"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("桃谷绘里香", '女', 29, "2102", "004"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("明日花绮罗", '女', 29, "2102", "005"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("铃原爱蜜莉", '女', 29, "2102", "006"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("波多野结衣", '女', 34, "2102", "007"), "123456789");
Set<Entry<Student,String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Entry<Student, String> entry : entrySet) {
Student key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " -- " + value);
}
}
}
Student类
package com.dream.treemap_class;
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
private String name;
private int age;
private char sex;
private String classId;
private String id;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, char sex,int age, String classId, String id) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
this.classId = classId;
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public char getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(char sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getClassId() {
return classId;
}
public void setClassId(String classId) {
this.classId = classId;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", sex=" + sex + ", classId=" + classId + ", id=" + id + "]";
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(this == obj){
return true;
}
if(obj instanceof Student){
Student stu = (Student) obj;
if(this.classId.equals(stu.classId) && this.id.equals(stu.id)){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//排序方法
//排序规则:年龄排序
//返回值:负数-比比较对象小
//返回值:正数-比比较对象大
//返回值:0-和比较对象一致(不存储)
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
return this.age - o.age;
}
}
测试类
package com.dream.treemap_class;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 使用外置比较器
*/
//外置比较器
//比较规则:先判断两个学生是否相同,再按照姓名长度,再按照年龄
TreeMap<Student, String> map = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
if(o1.equals(o2)){
return 0;
}
if(o1.getName().length() != o2.getName().length()){
return o1.getName().length() - o2.getName().length();
}
if(o1.getAge() != o2.getAge()){
return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();
}
return 1;
}
});
map.put(new Student("麻生希", '女', 28, "2101", "001"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("椎名空", '女', 23, "2101", "002"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("北岛玲", '女', 27, "2101", "003"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("水野朝阳", '女', 31, "2101", "004"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("三上悠亚", '女', 26, "2101", "005"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("濑亚美莉", '女', 32, "2101", "006"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("爱田奈奈", '女', 36, "2102", "001"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("深田咏美", '女', 28, "2102", "002"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("小西满里惠", '女', 28, "2102", "003"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("桃谷绘里香", '女', 29, "2102", "004"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("明日花绮罗", '女', 29, "2102", "005"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("铃原爱蜜莉", '女', 29, "2102", "006"), "123456789");
map.put(new Student("波多野结衣", '女', 34, "2102", "007"), "123456789");
Set<Entry<Student,String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Entry<Student, String> entry : entrySet) {
Student key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " -- " + value);
}
}
}
6. Properties
package com.dream.properties_class;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/**
* 操作Properties
*/
//创建配置文件对象
Properties p = new Properties();
//把文件加载到对象中
p.load(Test01.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("DBConfig.properties"));
//获取配置文件中的数据
String username = p.getProperty("username");
String password = p.getProperty("password");
System.out.println(username + " -- " + password);
}
}
DBConfig.properties
username=hhy
password=123123
7. Collections工具类
package com.dream.collections_class;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 使用集合工具类操作集合
*/
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
//批量添加
Collections.addAll(list, 4,6,2,1,5,3);
//排序
Collections.sort(list);
// Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Integer>() {
// @Override
// public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
// // TODO Auto-generated method stub
// return o2-o1;
// }
// });
System.out.println("查询元素在集合中的下标:" + Collections.binarySearch(list, 3));
//拷贝
ArrayList<Integer> newList = new ArrayList<>();
newList.add(0);
newList.add(0);
newList.add(0);
newList.add(0);
newList.add(0);
newList.add(0);
Collections.copy(newList, list);
System.out.println("获取最大值:" + Collections.max(newList));
System.out.println("获取最小值:" + Collections.min(newList));
System.out.println(newList);
}
}
8. EnumSet工具类
Signal接口
package com.dream.enum_util_class;
public enum Signal {
RED, YELLOW, GREEN;
}
测试类
package com.dream.enum_util_class;
import java.util.EnumSet;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
*
* EnumSet工具类
*
* 将枚举类中对象放入Set集合中
*/
EnumSet<Signal> set = EnumSet.allOf(Signal.class);
for (Signal signal : set) {
System.out.println(signal);
}
}
}
测试类
package com.dream.enum_util_class;
import java.util.EnumMap;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
*
* EnumMap工具类
*
* 将枚举类中对象放入Map集合中
*/
EnumMap<Signal, String> map = new EnumMap<>(Signal.class);
map.put(Signal.RED, "红灯");
map.put(Signal.YELLOW, "黄灯");
map.put(Signal.GREEN, "绿灯");
Set<Entry<Signal,String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Entry<Signal, String> entry : entrySet) {
Signal key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " -- " + value);
}
}
}