Redis分布式锁
一、前言
对于项目中使用Redis分布式锁,思考了个问题:Redis锁过期怎么办?如何续期?Redis锁超时,任务没完怎么办?
对这些问题做一下系统化、体系化的梳理。
二、Redis分布式锁过期处理
两大核心方案:
方案一:模拟CAS乐观锁方式,增加版本号
方案二:watch dog自动延期机制
三、Redis分布式实现
分布式锁特点:
互斥性:同一时刻只能有一个线程持有锁
可重入性:同一节点上的同一个线程如果获取了锁之后能够再次获取锁
锁超时:和J.U.C中的锁一样支持锁超时,防止死锁
高性能和高可用:加锁和解锁需要高效,同时也需要保证高可用,防止分布式锁失效
具备阻塞和非阻塞性:能够及时从阻塞状态中被唤醒
Redis分布式锁实现有两个维度:
(1)基于Jedis手工造轮子分布式锁
(2)Redission分布式锁的使用和原理。
3.1 基于Jedis 的API实现分布式锁
首先记录 Jedis 普通分布式锁实现,纯手工的模式,从最为基础的Redis命令开始。
充分了解与分布式锁相关的普通Redis命令,才能更好的了解高级的Redis分布式锁的实现,因为高级的分布式锁的实现完全基于普通Redis命令。
Redis几种常见部署架构:
单机模式; 主从模式; 哨兵模式; 集群模式;
原理都是类同的,主从模式、哨兵模式、集群模式的更加的高可用、或者更加高并发。
3.1.1 基础命令
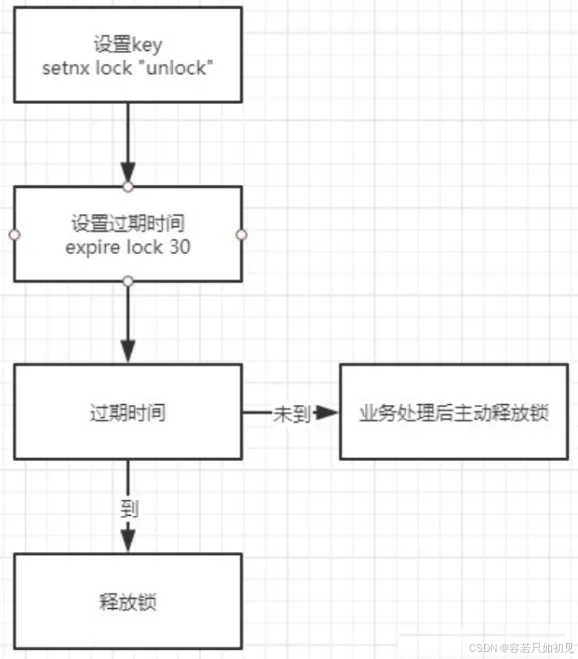
Redis分布式锁机制,主要借助setnx和expire两个命令完成。
setnx命令:SETNX 是SET if Not eXists的简写。
将 key 的值设为 value,当且仅当 key 不存在;若给定的 key 已经存在,则 SETNX 不做任何动作。
例如:
127.0.0.1:6379> set lock "unlock"
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> setnx lock "unlock"
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> setnx lock "lock"
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379>
expire命令:expire命令为 key 设置生存时间,当 key 过期时(生存时间为 0 ),它会被自动删除.expire 格式为:
EXPIRE key seconds
例如:
127.0.0.1:6379> expire lock 10
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> ttl lock
8
3.1.2 基于Jedis API的分布式锁
总体流程:
通过Redis的setnx、expire命令可以实现简单的锁机制:
(1)key不存在时创建,并设置value和过期时间,返回值为1;成功获取到锁;
(2)如key存在时直接返回0,抢锁失败;
(3)持有锁的线程释放锁时,手动删除key;或者过期时间到,key自动删除,锁释放。
线程调用setnx方法成功返回1认为加锁成功,其他线程要等到当前线程业务操作完成释放锁后,才能再次调用setnx加锁成功。
此时有个问题:
如果setnx是成功的,但是expire设置失败,一旦出现了释放锁失败,或者没有手工释放,那么这个锁永远被占用,其他线程永远也抢不到锁。
所以,需要保障setnx和expire两个操作的原子性,即:
要么 setnx和expire 全部执行,
要么 setnx和expire 全部不执行,
setnx和expire 二者不能分开。
解决方案:
(1)使用set的命令时,同时设置过期时间,不再单独使用 expire命令
(2)使用lua脚本,将加锁的命令放在lua脚本中原子性的执行
1.使用set的命令时,同时设置过期时间的示例如下:
127.0.0.1:6379> set unlock "234" EX 100 NX
(nil)
127.0.0.1:6379>
127.0.0.1:6379> set test "111" EX 100 NX
OK
这样就可解决分布式锁的原子性;set 命令的完整格式:
set key value [EX seconds] [PX milliseconds] [NX|XX]
EX seconds:设置失效时长,单位秒
PX milliseconds:设置失效时长,单位毫秒
NX:key不存在时设置value,成功返回OK,失败返回(nil)
XX:key存在时设置value,成功返回OK,失败返回(nil)
使用set命令实现加锁操作,加锁的简单代码实现:
package com.test.lock;
@Slf4j
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class JedisCommandLock {
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
private static final String LOCK_SUCCESS = "OK";
private static final String SET_IF_NOT_EXIST = "NX";
private static final String SET_WITH_EXPIRE_TIME = "PX";
/**
* 尝试获取分布式锁
* @param jedis Redis客户端
* @param lockKey 锁
* @param requestId 请求标识
* @param expireTime 超期时间
* @return 是否获取成功
*/
public static boolean tryGetDistributedLock(Jedis jedis, String lockKey, String requestId, int expireTime) {
String result = jedis.set(lockKey, requestId, SET_IF_NOT_EXIST, SET_WITH_EXPIRE_TIME, expireTime);
if (LOCK_SUCCESS.equals(result)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
加锁用Jedis的set Api:
jedis.set(String key, String value, String nxxx, String expx, int time)
五个形参:
第一个为key,使用key来当锁,因为key是唯一的。
第二个为value,传的是requestId,
此参数保证可靠性,通过给value赋值为requestId,就绑定此请求加的锁,解锁时就有依据。requestId可以使用UUID.randomUUID().toString()方法生成。
第三个为nxxx,这个参数填的是NX,意思是SET IF NOT EXIST,即当key不存在时,进行set操作;若key已经存在,则不做任何操作;
第四个为expx,这个参数传的是PX,意思是要给这个key加一个过期的设置,具体时间由第五个参数决定。
第五个为time,与第四个参数相呼应,代表key的过期时间。
只考虑Redis单机部署的场景,容错性暂不考虑。
2.基于Jedis 的API实现简单解锁
package com.test.lock;
@Slf4j
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class JedisCommandLock {
private static final Long RELEASE_SUCCESS = 1L;
/**
* 释放分布式锁
* @param jedis Redis客户端
* @param lockKey 锁
* @param requestId 请求标识
* @return 是否释放成功
*/
public static boolean releaseDistributedLock(Jedis jedis, String lockKey, String requestId) {
String script = "if redis.call('get', KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] then return redis.call('del', KEYS[1]) else return 0 end";
Object result = jedis.eval(script, Collections.singletonList(lockKey), Collections.singletonList(requestId));
if (RELEASE_SUCCESS.equals(result)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
Lua代码的功能:首先获取锁对应的value值,检查是否与requestId相等,如果相等则删除锁(解锁)。
使用Lua语言的原因:由于Redis的特性,执行eval()方法可以确保原子性,即在eval命令执行Lua代码的时候,Lua代码将被当成一个命令去执行,并且直到eval命令执行完成,Redis才会执行其他命令。
解锁会出现的问题:
示例一:直接使用 jedis.del() 方法删除锁
这种不先判断锁的拥有者而直接解锁的方式,会导致任何客户端都可以随时进行解锁,即使这把锁不是它的。
public static void wrongReleaseLock1(Jedis jedis, String lockKey) {
jedis.del(lockKey);
}
示例二:分成两条命令执行
这种解锁代码乍一看是没问题,甚至之前差点这样实现,与正确方式差不多,唯一区别的是分成两条命令去执行,代码如下:
public static void wrongReleaseLock2(Jedis jedis, String lockKey, String requestId) {
// 判断加锁与解锁是不是同一个客户端
if (requestId.equals(jedis.get(lockKey))) {
// 若在此时,这把锁突然不是这个客户端的,则会误解锁
jedis.del(lockKey);
}
}
3.1.3 基于Lua脚本实现分布式锁
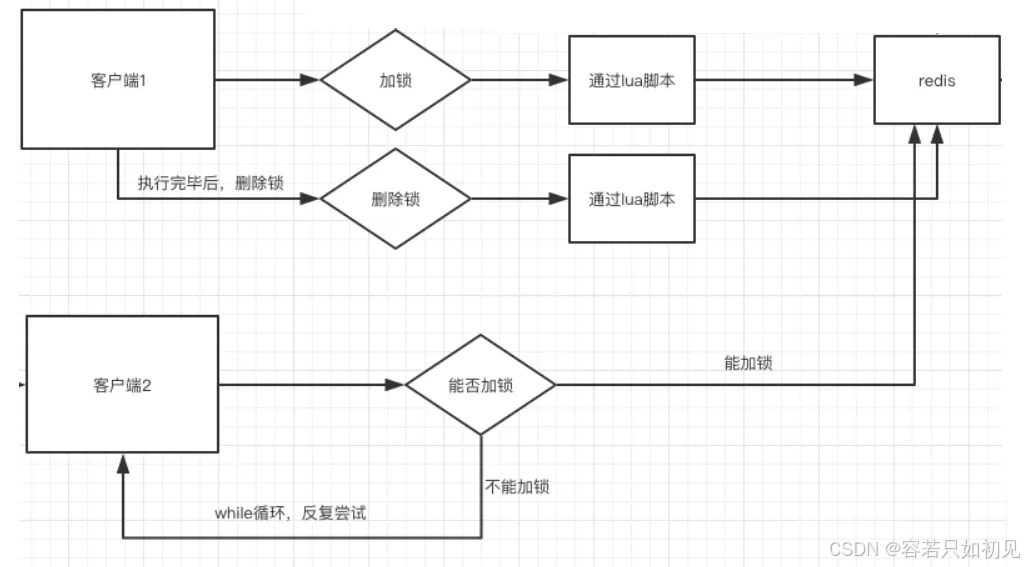
前面提到在redis中执行lua脚本有确保原子性的优势,且是是高并发、高性能的必备脚本语言,大部分的开源框架(如 redission)中的分布式锁组件,都是用纯lua脚本实现的。
那就阔以把加锁和删除锁的操作,使用纯lua进行封装,保障其执行时候的原子性。执行流程,大致如下:
加锁的Lua脚本:lock.lua
--- -1 failed
--- 1 success
---
local key = KEYS[1]
local requestId = KEYS[2]
local ttl = tonumber(KEYS[3])
local result = redis.call('setnx', key, requestId)
if result == 1 then
--PEXPIRE:以毫秒的形式指定过期时间
redis.call('pexpire', key, ttl)
else
result = -1;
-- 如果value相同,则认为是同一个线程的请求,则认为重入锁
local value = redis.call('get', key)
if (value == requestId) then
result = 1;
redis.call('pexpire', key, ttl)
end
end
-- 如果获取锁成功,则返回 1
return result
解锁的Lua脚本:unlock.lua:
--- -1 failed
--- 1 success
-- unlock key
local key = KEYS[1]
local requestId = KEYS[2]
local value = redis.call('get', key)
if value == requestId then
redis.call('del', key);
return 1;
end
return -1
把两个文件,放在资源文件夹下备用:
在Java中调用lua脚本,完成加锁操作:
package com.test.lock;
import com.crazymaker.springcloud.common.exception.BusinessException;
import com.crazymaker.springcloud.common.util.IOUtil;
import com.crazymaker.springcloud.standard.context.SpringContextUtil;
import com.crazymaker.springcloud.standard.lua.ScriptHolder;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisCallback;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.DefaultRedisScript;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.RedisScript;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Slf4j
public class InnerLock {
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
public static final Long LOCKED = Long.valueOf(1);
public static final Long UNLOCKED = Long.valueOf(1);
public static final int EXPIRE = 2000;
String key;
String requestId; // lockValue 锁的value ,代表线程的uuid
/**
* 默认为2000ms
*/
long expire = 2000L;
private volatile boolean isLocked = false;
private RedisScript lockScript;
private RedisScript unLockScript;
public InnerLock(String lockKey, String requestId) {
this.key = lockKey;
this.requestId = requestId;
lockScript = ScriptHolder.getLockScript();
unLockScript = ScriptHolder.getUnlockScript();
}
/**
* 抢夺锁
*/
public void lock() {
if (null == key) {
return;
}
try {
List<String> redisKeys = new ArrayList<>();
redisKeys.add(key);
redisKeys.add(requestId);
redisKeys.add(String.valueOf(expire));
Long res = (Long) getRedisTemplate().execute(lockScript, redisKeys);
isLocked = false;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw BusinessException.builder().errMsg("抢锁失败").build();
}
}
/**
* 有返回值的抢夺锁
*
* @param millisToWait
*/
public boolean lock(Long millisToWait) {
if (null == key) {
return false;
}
try {
List<String> redisKeys = new ArrayList<>();
redisKeys.add(key);
redisKeys.add(requestId);
redisKeys.add(String.valueOf(millisToWait));
Long res = (Long) getRedisTemplate().execute(lockScript, redisKeys);
return res != null && res.equals(LOCKED);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw BusinessException.builder().errMsg("抢锁失败").build();
}
}
//释放锁
public void unlock() {
if (key == null || requestId == null) {
return;
}
try {
List<String> redisKeys = new ArrayList<>();
redisKeys.add(key);
redisKeys.add(requestId);
Long res = (Long) getRedisTemplate().execute(unLockScript, redisKeys);
// boolean unlocked = res != null && res.equals(UNLOCKED);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw BusinessException.builder().errMsg("释放锁失败").build();
}
}
private RedisTemplate getRedisTemplate() {
if(null==redisTemplate)
{
redisTemplate= (RedisTemplate) SpringContextUtil.getBean("stringRedisTemplate");
}
return redisTemplate;
}
}
在Java中调用lua脚本,完成加锁操作,实现Lock接口, 完成JedisLock的分布式锁:
package com.test.lock;
import com.crazymaker.springcloud.common.exception.BusinessException;
import com.crazymaker.springcloud.common.util.ThreadUtil;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.RedisScript;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
@Slf4j
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class JedisLock implements Lock {
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
RedisScript<Long> lockScript = null;
RedisScript<Long> unLockScript = null;
public static final int DEFAULT_TIMEOUT = 2000;
public static final Long LOCKED = Long.valueOf(1);
public static final Long UNLOCKED = Long.valueOf(1);
public static final Long WAIT_GAT = Long.valueOf(200);
public static final int EXPIRE = 2000;
String key;
String lockValue; // lockValue 锁的value ,代表线程的uuid
/**
* 默认为2000ms
*/
long expire = 2000L;
public JedisLock(String lockKey, String lockValue) {
this.key = lockKey;
this.lockValue = lockValue;
}
private volatile boolean isLocked = false;
private Thread thread;
/**
* 获取一个分布式锁 , 超时则返回失败
*
* @return 获锁成功 - true | 获锁失败 - false
*/
@Override
public boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
//本地可重入
if (isLocked && thread == Thread.currentThread()) {
return true;
}
expire = unit != null ? unit.toMillis(time) : DEFAULT_TIMEOUT;
long startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
Long millisToWait = expire;
boolean localLocked = false;
int turn = 1;
while (!localLocked) {
localLocked = this.lockInner(expire);
if (!localLocked) {
millisToWait = millisToWait - (System.currentTimeMillis() - startMillis);
startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (millisToWait > 0L) {
/**
* 还没有超时
*/
ThreadUtil.sleepMilliSeconds(WAIT_GAT);
log.info("睡眠一下,重新开始,turn:{},剩余时间:{}", turn++, millisToWait);
} else {
log.info("抢锁超时");
return false;
}
} else {
isLocked = true;
localLocked = true;
}
}
return isLocked;
}
/**
* 有返回值的抢夺锁
*
* @param millisToWait
*/
public boolean lockInner(Long millisToWait) {
if (null == key) {
return false;
}
try {
List<String> redisKeys = new ArrayList<>();
redisKeys.add(key);
redisKeys.add(lockValue);
redisKeys.add(String.valueOf(millisToWait));
Long res = (Long) redisTemplate.execute(lockScript, redisKeys);
return res != null && res.equals(LOCKED);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw BusinessException.builder().errMsg("抢锁失败").build();
}
}
}
通过实现JUC的显示锁Lock接口,调用unlock.lua脚本完成,实现简单的分布式锁:
package com.test.lock;
import com.crazymaker.springcloud.common.exception.BusinessException;
import com.crazymaker.springcloud.common.util.ThreadUtil;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.RedisScript;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
@Slf4j
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class JedisLock implements Lock {
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
RedisScript<Long> lockScript = null;
RedisScript<Long> unLockScript = null;
//释放锁
@Override
public void unlock() {
if (key == null || requestId == null) {
return;
}
try {
List<String> redisKeys = new ArrayList<>();
redisKeys.add(key);
redisKeys.add(requestId);
Long res = (Long) redisTemplate.execute(unLockScript, redisKeys);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw BusinessException.builder().errMsg("释放锁失败").build();
}
}
}
编写RedisLockService分布式锁服务,用于加载lua脚本,管理JedisLock,创建 分布式锁:
package com.test.lock;
import com.crazymaker.springcloud.common.util.IOUtil;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.DefaultRedisScript;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.RedisScript;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
@Slf4j
@Data
public class RedisLockService
{
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
static String lockLua = "script/lock.lua";
static String unLockLua = "script/unlock.lua";
static RedisScript<Long> lockScript = null;
static RedisScript<Long> unLockScript = null;
{
String script = IOUtil.loadJarFile(RedisLockService.class.getClassLoader(),lockLua);
// String script = FileUtil.readString(lockLua, Charset.forName("UTF-8" ));
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(script))
{
log.error("lua load failed:"+lockLua);
}
lockScript = new DefaultRedisScript<>(script, Long.class);
// script = FileUtil.readString(unLockLua, Charset.forName("UTF-8" ));
script = IOUtil.loadJarFile(RedisLockService.class.getClassLoader(),unLockLua);
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(script))
{
log.error("lua load failed:"+unLockLua);
}
unLockScript = new DefaultRedisScript<>(script, Long.class);
}
public RedisLockService(RedisTemplate redisTemplate)
{
this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate;
}
public Lock getLock(String lockKey, String lockValue) {
JedisLock lock=new JedisLock(lockKey,lockValue);
lock.setRedisTemplate(redisTemplate);
lock.setLockScript(lockScript);
lock.setUnLockScript(unLockScript);
return lock;
}
}
测试用例:
package com.test.lock;
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = {DemoCloudApplication.class})
// 指定启动类
public class RedisLockTest {
@Resource
RedisLockService redisLockService;
private ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
@Test
public void testLock() {
int threads = 10;
final int[] count = {0};
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(threads);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < threads; i++) {
pool.submit(() ->
{
String lockValue = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
try {
Lock lock = redisLockService.getLock("test:lock:1", lockValue);
boolean locked = lock.tryLock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (locked) {
for (int j = 0; j < 1000; j++) {
count[0]++;
}
log.info("count = " + count[0]);
lock.unlock();
} else {
System.out.println("抢锁失败");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
try {
countDownLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("10个线程每个累加1000为:= " + count[0]);
//输出统计结果
float time = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.println("运行的时长为(ms):" + time);
System.out.println("每一次执行的时长为(ms):" + time / count[0]);
}
}
结果如下:
2024-09-13 10:02:11.900 INFO 22120 --- [pool-1-thread-7] c.c.springcloud.lock.RedisLockTest LN:50 count = 6000
2024-09-13 10:02:11.901 INFO 22120 --- [pool-1-thread-1] c.c.springcloud.standard.lock.JedisLock LN:81 睡眠一下,重新开始,turn:3,剩余时间:9585
2024-09-13 10:02:11.902 INFO 22120 --- [pool-1-thread-1] c.c.springcloud.lock.RedisLockTest LN:50 count = 7000
2024-09-13 10:02:12.100 INFO 22120 --- [pool-1-thread-4] c.c.springcloud.standard.lock.JedisLock LN:81 睡眠一下,重新开始,turn:3,剩余时间:9586
2024-09-13 10:02:12.101 INFO 22120 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.c.springcloud.standard.lock.JedisLock LN:81 睡眠一下,重新开始,turn:3,剩余时间:9585
2024-09-13 10:02:12.101 INFO 22120 --- [pool-1-thread-8] c.c.springcloud.standard.lock.JedisLock LN:81 睡眠一下,重新开始,turn:3,剩余时间:9585
2024-09-13 10:02:12.101 INFO 22120 --- [pool-1-thread-4] c.c.springcloud.lock.RedisLockTest LN:50 count = 8000
2024-09-13 10:02:12.102 INFO 22120 --- [pool-1-thread-8] c.c.springcloud.lock.RedisLockTest LN:50 count = 9000
2024-09-13 10:02:12.304 INFO 22120 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.c.springcloud.standard.lock.JedisLock LN:81 睡眠一下,重新开始,turn:4,剩余时间:9383
2024-09-13 10:02:12.307 INFO 22120 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.c.springcloud.lock.RedisLockTest LN:50 count = 10000
10个线程每个累加1000为:= 10000
运行的时长为(ms):827.0
每一次执行的时长为(ms):0.0827
STW导致的锁过期问题:
如果在写文件过程中,发生 fullGC,并且其时间跨度较长, 超过了10秒,由于锁的有效期就是 10s,这时候任务没有执行完成,分布式锁就自动过期。
//写数据到文件
function writeData(filename, data) {
boolean locked = lock.tryLock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (!locked) {
throw 'Failed to acquire lock';
}
try {
//将数据写到文件
var file = storage.readFile(filename);
var updated = updateContents(file, data);
storage.writeFile(filename, updated);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
即STW导致的锁过期问题:在过程中,b抢到锁,在写文件,而a的fullGC完成后,也继续写文件,此时a的并没有占用锁,此时写入会导致文件数据错乱,发生线程安全问题。
锁过期问题 的解决方案:
1:模拟CAS乐观锁的方式,增加版本号
- 在每次写操作时加入一个 token。token 可以是一个递增的数字(lock service 可以做到),每次有 client 申请锁就递增一次。
2:watch dog自动延期机制
- a加锁的锁key默认生存时间30秒,如果超过30秒,a还想一直持有这把锁,就会启动一个watch dog看门狗,它是一个后台线程,会每隔10秒检查一下,如果a还持有锁key,那么就会不断的延长锁key的生存时间。即在锁没有过期之前,不断的延长锁的有效期。
推荐使用Redission采用的就是watch dog机制,此方案不会入侵业务代码,基于Netty实现,更高性能的Redis第三方库。
四、Redisson的使用
•Maven
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.11.4</version>
</dependency>
•Gradle
compile group: 'org.redisson', name: 'redisson', version: '3.11.4'
RedissonClient有多种模式,主要的模式有:
单节点模式;哨兵模式;主从模式;集群模式
单节点模式的程序化配置方法,大致如下:
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://myredisserver:6379");
RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config);
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://myredisserver:6379");
RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config);// connects to 127.0.0.1:6379 by defaultRedisson
Client redisson = Redisson.create();
SingleServerConfig singleConfig = config.useSingleServer();
SpringBoot整合Redisson:
配置文件:
spring:
redis:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 6379
database: 0
timeout: 5000
配置类 RedissonConfig.java:
import org.redisson.Redisson;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.redisson.config.Config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class RedissonConfig {
@Autowired
private RedisProperties redisProperties;
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient() {
Config config = new Config();
String redisUrl = String.format("redis://%s:%s", redisProperties.getHost() + "", redisProperties.getPort() + "");
config.useSingleServer().setAddress(redisUrl).setPassword(redisProperties.getPassword());
config.useSingleServer().setDatabase(3);
return Redisson.create(config);
}
}
自定义starter:由于redission可以有多种模式,处于学习的目的,将多种模式封装成一个start,可以学习一下starter的制作。
封装一个RedissonManager,通过策略模式,根据不同的配置类型,创建 RedissionConfig实例,然后创建RedissionClient对象。
使用 RLock 可重入锁机制实现 Redis 分布式锁:
public class RedissionTest {
@Resource
RedissonManager redissonManager;
@Test
public void testLockExamples() {
// 默认连接上 127.0.0.1:6379
RedissonClient redisson = redissonManager.getRedisson();
// RLock 继承了 java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock 接口
RLock lock = redisson.getLock("redission:test:lock:1");
final int[] count = {0};
int threads = 10;
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(threads);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < threads; i++) {
pool.submit(() ->
{
for (int j = 0; j < 1000; j++) {
lock.lock();
count[0]++;
lock.unlock();
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
try {
countDownLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("10个线程每个累加1000为:= " + count[0]);
//输出统计结果
float time = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.println("运行的时长为:" + time);
System.out.println("每一次执行的时长为:" + time/count[0]);
}
}
输出:
10个线程每个累加1000为:= 10000
运行的时长为:14172.0
每一次执行的时长为:1.4172
五、Redision锁 核心源码分析
单机模式下,简单Redision锁的使用如下:
// 构造redisson实现分布式锁必要的Config
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://172.29.1.180:5379").setPassword("a123456").setDatabase(0);
// 构造RedissonClient
RedissonClient redissonClient = Redisson.create(config);
// 设置锁定资源名称
RLock disLock = redissonClient.getLock("DISLOCK");
//尝试获取分布式锁
boolean isLock= disLock.tryLock(500, 15000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (isLock) {
try {
//TODO if get lock success, do something;
Thread.sleep(15000);
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
// 无论如何, 最后都要解锁
disLock.unlock();
}
}
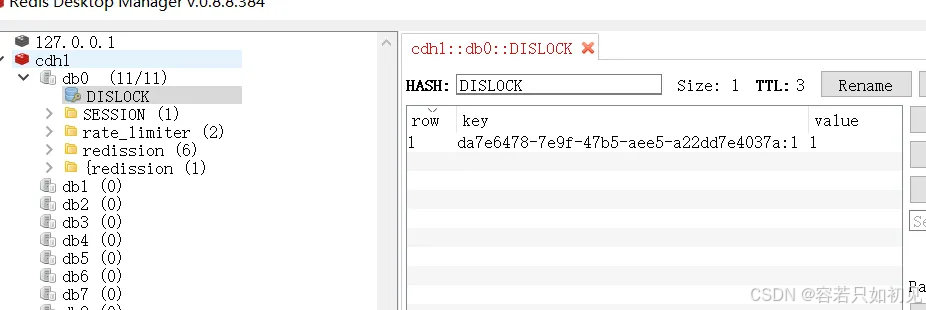
Redis中存储:
hash结构的key就是UUID+threadId;
hash结构的value就是重入值,在分布式锁时,这个值为1
172.29.1.180:5379> hgetall DISLOCK
1) "01a6d806-d282-4715-9bec-f51b9aa98110:1"
2) "1"
Redisson还可以实现重入锁,那么这个值就取决于重入次数
getLock()方法:
//name:锁的名称
public RLock getLock(String name) {
//默认创建的同步执行器, (存在异步执行器, 因为锁的获取和释放是有强一致性要求, 默认同步)
return new RedissonLock(this.connectionManager.getCommandExecutor(), name);
}
击 RedissonLock 进去,发现这是一个 RedissonLock 构造方法,主要初始化一些属性。
public RedissonLock(CommandAsyncExecutor commandExecutor, String name) {
super(commandExecutor, name);
this.commandExecutor = commandExecutor;
//唯一ID
this.id = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getId();
//等待获取锁时间
this.internalLockLeaseTime = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout();
//ID + 锁名称
this.entryName = this.id + ":" + name;
//发布订阅
this.pubSub = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getSubscribeService().getLockPubSub();
}
点击 getLockWatchdogTimeout() 进去:
`public` `class` `Config {`` ` ` ``private` `long` `lockWatchdogTimeout = ``30` `* ``1000``;`` ` ` ``public` `long` `getLockWatchdogTimeout() {`` ``return` `lockWatchdogTimeout;`` ``}`` ` ` ``//省略``}`
internalLockLeaseTime 分布式锁的超时时间,默认是 30 秒。
tryLock方法源码:
@Override
public boolean tryLock(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
long time = unit.toMillis(waitTime);
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
Long ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// lock acquired
if (ttl == null) {
return true;
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(threadId);
return false;
}
current = System.currentTimeMillis();
RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> subscribeFuture = subscribe(threadId);
if (!subscribeFuture.await(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
if (!subscribeFuture.cancel(false)) {
subscribeFuture.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId);
}
});
}
acquireFailed(threadId);
return false;
}
try {
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(threadId);
return false;
}
while (true) {
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// lock acquired
if (ttl == null) {
return true;
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(threadId);
return false;
}
// waiting for message
currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (ttl >= 0 && ttl < time) {
getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(threadId);
return false;
}
}
} finally {
unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId);
}
// return get(tryLockAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit));
}
tryAcquire()方法:
tryLockInnerAsync:
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
if (leaseTime != -1L) {
//进行异步获取锁
return this.tryLockInnerAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
} else {
//尝试异步获取锁, 获取锁成功返回空, 否则返回锁剩余过期时间
RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture = this.tryLockInnerAsync(this.commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
//ttlRemainingFuture 执行完成后触发此操作
ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
//ttlRemaining == null 代表获取了锁
//获取到锁后执行续时操作
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
this.scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
});
return ttlRemainingFuture;
}
}
由于leaseTime == -1,于是走tryLockInnerAsync()方法,这个方法才是关键:
evalWriteAsync方法的定义:
<T, R> RFuture<R> evalWriteAsync(String key, Codec codec, RedisCommand<T> evalCommandType, String script, List<Object> keys, Object ... params);
注意,其最后两个参数分别是keys和params
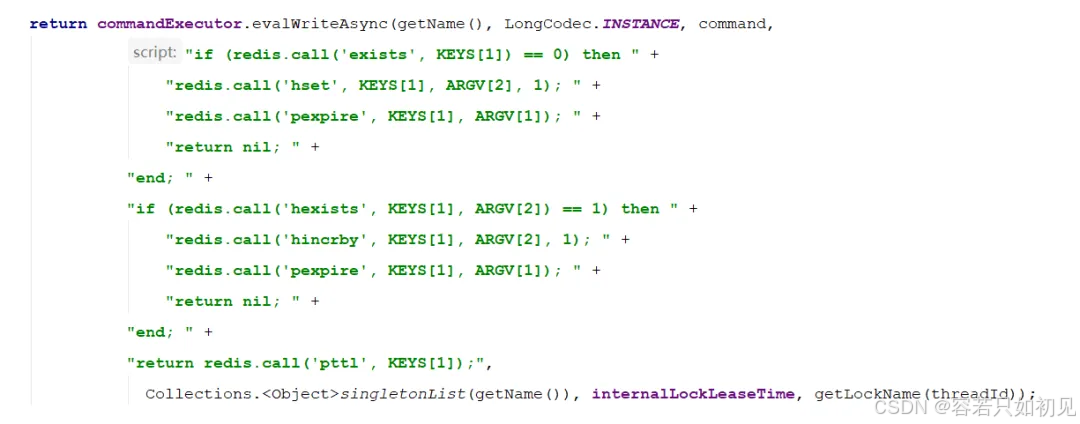
实际调用:
commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
"redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
这里KEYS[1]就是getName(),ARGV[2]是getLockName(threadId)
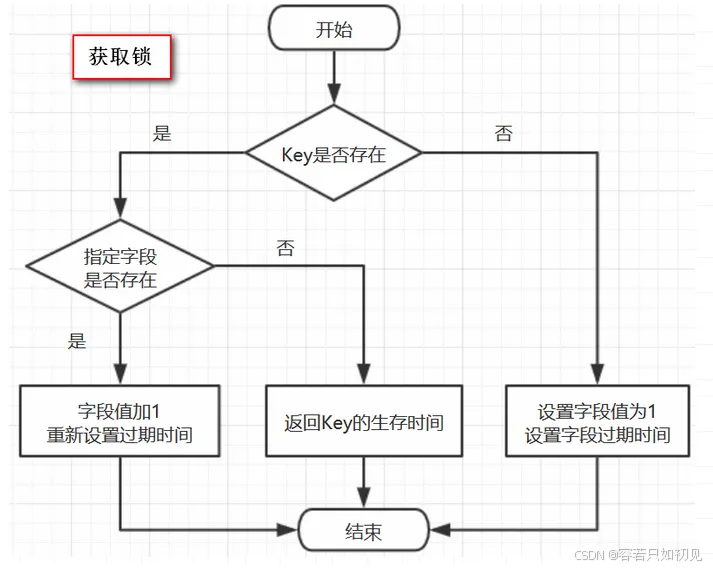
原理:加锁机制
用的数据结构是hash,hash的结构是:key 字段1 值1 字段2 值2 … … …
用在锁这个场景下,key就表示锁的名称,也可以理解为临界资源,字段就表示当前获得锁的线程所有竞争这把锁的线程都要判断在这个key下有没有自己线程的字段,如果没有则不能获得锁,如果有,则相当于重入,字段值加1(次数)
通过封装在lua脚本中发送给redis,保证这段复杂业务逻辑执行的原子性:
lua脚本的参数解释:
KEYS[1]代表的是你加锁的那个key,比如说:RLock lock = redisson.getLock("DISLOCK");这里自定义设置加锁的那个锁key就是“DISLOCK”。
ARGV[1]代表的就是锁key的默认生存时间调用的时候,传递的参数为 internalLockLeaseTime ,该值默认30秒。
ARGV[2]代表的是加锁的客户端的ID,lua脚本的第一段if判断语句,就是用“exists DISLOCK”命令判断一下,如果要加锁的那个锁key不存在的话,就进行加锁。redis命令:hset DISLOCK cid:1 1
通过这个命令设置一个hash数据结构,这行命令执行后,会出现一个类似下面的数据结构:
DISLOCK:
{
cid:1 1
}
接着会执行“pexpire DISLOCK 30000”命令,设置DISLOCK这个锁key的生存时间是30秒(默认)
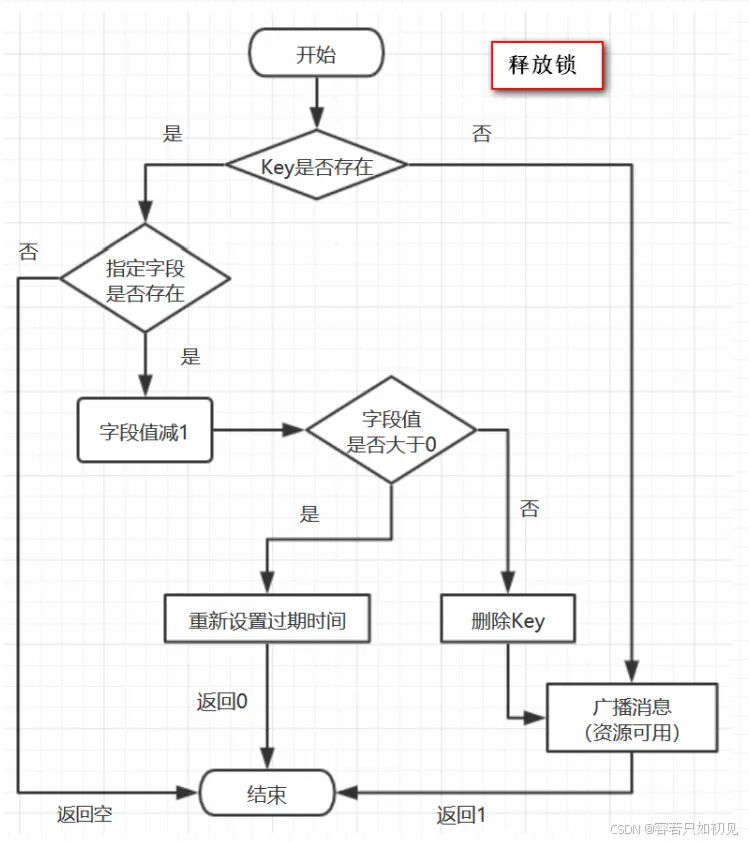
Redision 解锁机制:
protected RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId) {
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then " +
"return nil;" +
"end; " +
"local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); " +
"if (counter > 0) then " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); " +
"return 0; " +
"else " +
"redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); " +
"redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; "+
"end; " +
"return nil;",
Arrays.<Object>asList(getName(), getChannelName()), LockPubSub.UNLOCK_MESSAGE, internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}
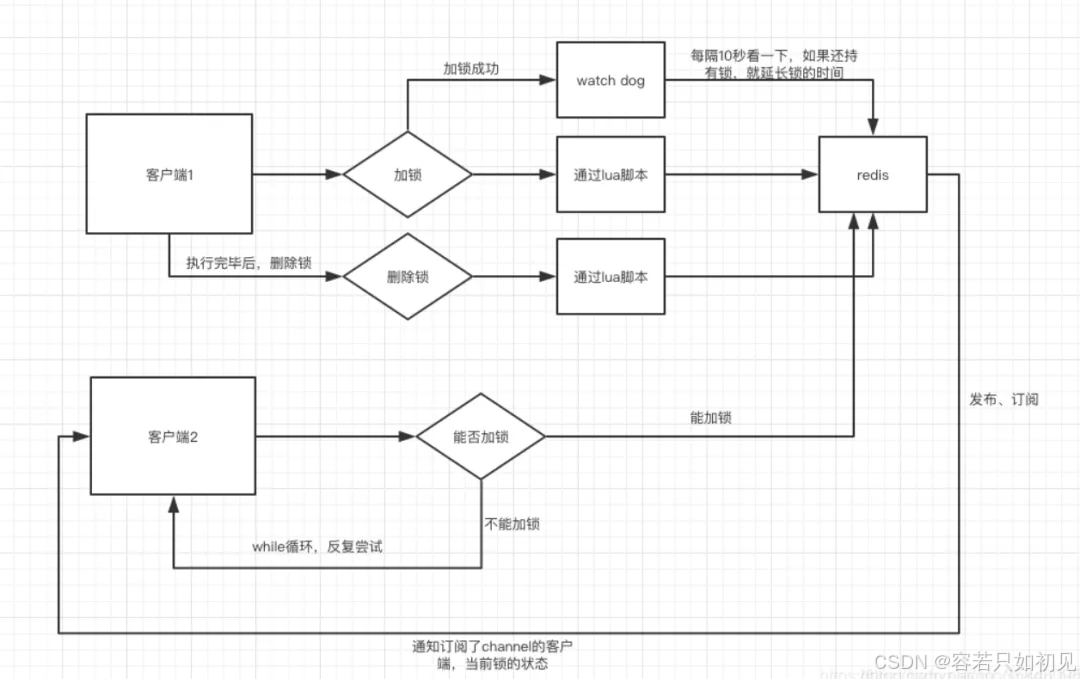
redisson watchdog 使用和原理
redisson加锁的基本流程图:
watchdog的具体思路是 加锁时,默认加锁 30秒,每10秒钟检查一次,如果存在就重新设置 过期时间为30秒。然后设置默认加锁时间的参数是 lockWatchdogTimeout(监控锁的看门狗超时,单位:毫秒)
注意:
1.watchDog 只有在未显示指定加锁时间时才会生效。(这点很重要)
2.lockWatchdogTimeout设定的时间不要太小 ,比如之前设置的是 100毫秒,由于网络直接导致加锁完后,watchdog去延期时,这个key在redis中已经被删除。
在调用lock方法时,会最终调用到tryAcquireAsync:
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
//如果指定了加锁时间,会直接去加锁
if (leaseTime != -1) {
return tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
}
//没有指定加锁时间 会先进行加锁,并且默认时间就是 LockWatchdogTimeout的时间
//这个是异步操作 返回RFuture 类似netty中的future
RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime,
commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(),
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
//这里也是类似netty Future 的addListener,在future内容执行完成后执行
ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
return;
}
// lock acquired
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
//这里是定时执行 当前锁自动延期的动作
scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
});
return ttlRemainingFuture;
}
scheduleExpirationRenewal():
private void scheduleExpirationRenewal(long threadId) {
RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry entry = new RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry();
RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry oldEntry = (RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry)EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.putIfAbsent(this.getEntryName(), entry);
if (oldEntry != null) {
oldEntry.addThreadId(threadId);
} else {
entry.addThreadId(threadId);
this.renewExpiration();
}
}
renewExpiration() 启用一个timeout定时,去执行延期动作:
private void renewExpiration() {
//从容器中去获取要被续期的锁
RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry ee = (RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry)EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(this.getEntryName());
//容器中没有要续期的锁,直接返回null
if (ee != null) {
//创建定时任务
//并且执行的时间为 30000/3 毫秒,也就是 10 秒后
Timeout task = this.commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
//从容器中取出线程
RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry ent = (RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry)RedissonLock.EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(RedissonLock.this.getEntryName());
if (ent != null) {
Long threadId = ent.getFirstThreadId();
if (threadId != null) {
//Redis进行锁续期
//这个方法的作用其实底层也是去执行LUA脚本
RFuture<Boolean> future = RedissonLock.this.renewExpirationAsync(threadId);
//同理去处理Redis续命结果
future.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
RedissonLock.log.error("Can't update lock " + RedissonLock.this.getName() + " expiration", e);
} else {
//如果成功续期,递归继续创建下一个 10S 后的任务
if (res) {
//递归继续创建下一个10S后的任务
RedissonLock.this.renewExpiration();
}
}
});
}
}
}
}, this.internalLockLeaseTime / 3L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
ee.setTimeout(task);
}
}
watchDog总结:
1.要使 watchDog机制生效 ,lock时 不要设置 过期时间
2.watchDog的延时时间 可以由 lockWatchdogTimeout指定默认延时时间,但是不要设置太小。如100
3.watchdog 会每 lockWatchdogTimeout/3时间,去延时。
4.watchdog 通过 类似netty的 Future功能来实现异步延时
5.watchdog 最终还是通过 lua脚本来进行延时
六、总结
Redis分布式锁过期两种方案:
(1)模拟CAS乐观锁的方式,增加版本号
(2)watch dog自动延期机制
第一种方案是入侵性比较强,在代码里边需要进行版本的检查。
第一种方案是入侵性比较弱,建议使用第二种。
如果使用第二种方案,就是设计一个watch dog 看门狗后台线程, 最好是能够定时调度的线程。
只要客户端一旦加锁成功,watch dog 看门狗后台线程添加一个定时任务,会每隔 10 秒检查一下,如果客户端还持有锁 key,那么就会不断的延长锁 key 的过期时间。
并且再一次创建一个续期的定时任务,为下一次续期做准备。
默认情况下,加锁的时间是 30 秒,.如果加锁的业务没有执行完,就会进行一次续期,把锁重置成 30 秒,万一业务的机器宕机了,那就续期不了,30 秒之后锁就解开了。