C++数据结构与算法
1.顺序表代码模版
C++顺序表模版
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 可以根据需要灵活变更类型
#define EleType int
struct SeqList
{
EleType* elements;
int size;
int capacity;
};
// Init a SeqList
void InitList(SeqList* list, int capacity)
{
list->elements = new EleType[capacity]();
list->size = 0;
list->capacity = capacity;
}
// Destory a SqeList
void DestoryList(SeqList* list)
{
list->size = 0;
delete[] list->elements;
}
// Is Empty
bool IsEmpty(SeqList* list)
{
return list->size == 0;
}
// Inser a value into SeqList at position
void Insert(SeqList* list, int index, EleType element)
{
// Check conditions
if (index < 0 || index > list->size)
{
throw std::invalid_argument("Invalid index when insert a value into SeqList");
}
// Enlarge the capacity, normally enlarge 1 times
if (list->size == list->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = list->capacity * 2;
EleType* newElements = new EleType[newCapacity]();
for (int i = 0; i < list->size; i++)
{
newElements[i] = list->elements[i];
}
delete[] list->elements;
list->elements = newElements;
list->capacity = newCapacity;
}
// Insert the data
for (int i = list->size; i > index; --i)
{
list->elements[i] = list->elements[i-1];
}
list->elements[index] = element;
list->size++;
}
// Delet the value at index
void DeleteElement(SeqList* list, int index)
{
if (index < 0 || index >= list->size)
{
throw std::invalid_argument("Invalid index of the elements which needed delete");
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < list->size - 1; i++)
{
list->elements[i] = list->elements[i + 1];
}
list->size--;
}
// Find element in list, return the index
int FindElement(SeqList* list, EleType element)
{
for (int i = 0; i < list->size; i++)
{
if (list->elements[i] == element)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// Get element at index in the list
EleType GetElement(SeqList* list, int index)
{
if(index < 0 || index >= list->size)
{
throw std::invalid_argument("Invalid index to get the element in list");
}
return list->elements[index];
}
// Update the value at index in list
void UpdateElement(SeqList* list, int index, EleType value)
{
if (index < 0 || index >= list->size)
{
throw std::invalid_argument("Invalid index to Update the element in list");
}
list->elements[index] = value;
}
// Show
void Show(SeqList* list)
{
if (list != NULL)
{
std::cout << "list size: " << list->size << std::endl;
std::cout << "List capacity:" << list->capacity << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < list->size; i++)
{
std::cout << "value[" << i << "] = " << list->elements[i] << " " << std::ends;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout << "The list is null" << std::endl;
}
}
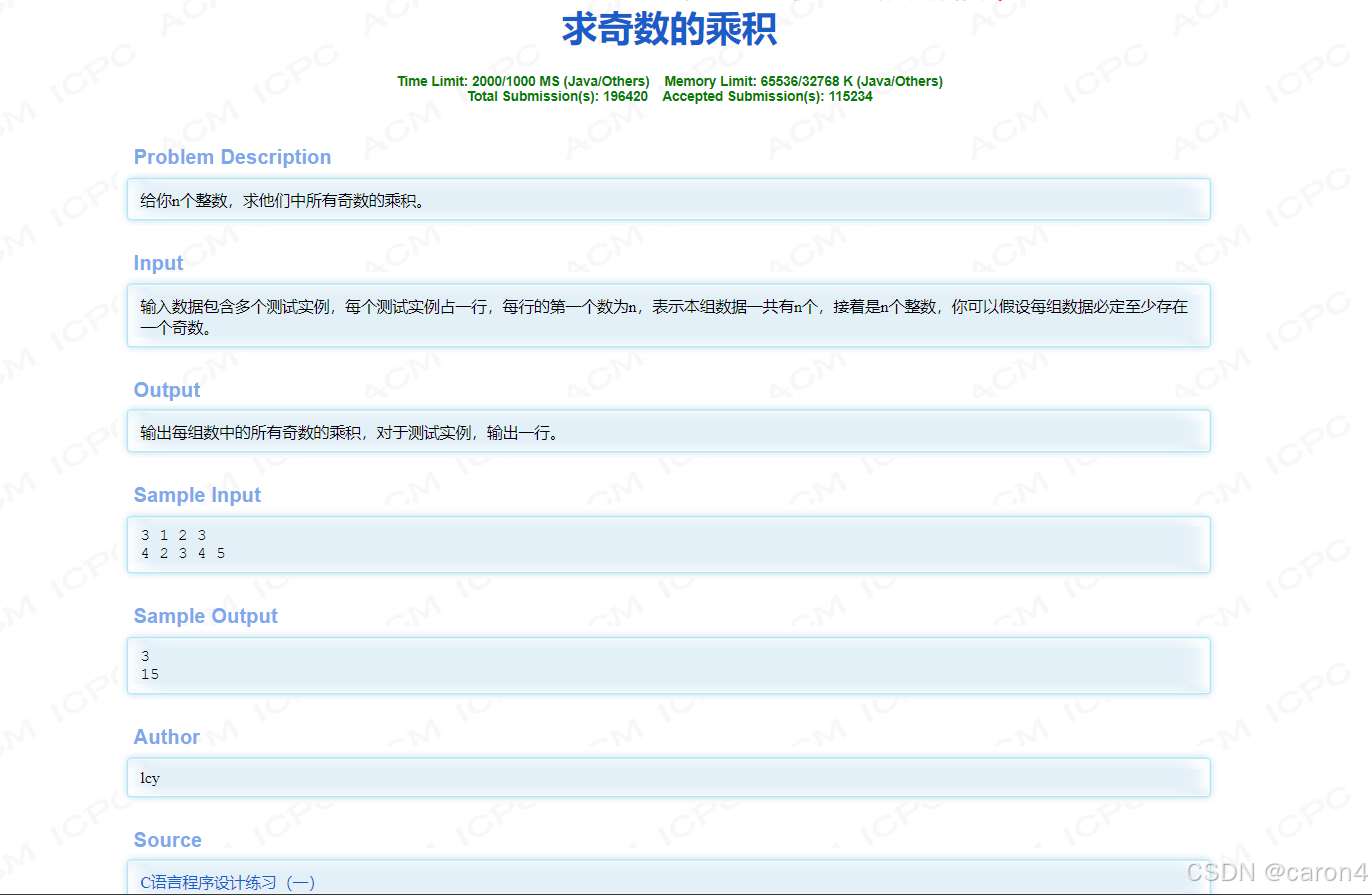
2.杭电算法2006-求奇数的乘积
1.题目–如图
2.使用顺序表解题代码
// 调用使用代码模版
int numbers[10000];
int main()
{
int n;
// 循环用例
while(cin >> n)
{
SeqList list;
InitList(&list, 1);
int prod = 1;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
Insert(&list, i, x);
EleType tmp = GetElement(&list, i);
if(tmp % 2 == 1)
{
prod = prod * tmp;
}
}
cout << prod <<endl;
}
return 0;
}
3.使用数组解题
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
while(cin >> n)
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
numbwers[i] = x;
}
int prod = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
int tmp = numbwers[i];
if(tmp % 2 == 1)
{
prod = prod * tmp;
}
}
cout << prod << endl;
}
return 0;
}
输入:
3 1 2 3
4 2 3 4 5
输出
3
15
3.顺序表模版更新
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 可以根据需要灵活变更类型
#define EleType int
struct SeqList
{
EleType* elements;
int size;
int capacity;
};
// Init a SeqList
void InitList(SeqList* list, int capacity)
{
list->elements = new EleType[capacity]();
list->size = 0;
list->capacity = capacity;
}
// Destory a SqeList
void DestoryList(SeqList* list)
{
list->size = 0;
delete[] list->elements;
}
// Is Empty
bool IsEmpty(SeqList* list)
{
return list->size == 0;
}
// Inser a value into SeqList at position
void Insert(SeqList* list, int index, EleType element)
{
// Check conditions
if (index < 0 || index > list->size)
{
throw std::invalid_argument("Invalid index when insert a value into SeqList");
}
// Enlarge the capacity, normally enlarge 1 times
if (list->size == list->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = list->capacity * 2;
EleType* newElements = new EleType[newCapacity]();
for (int i = 0; i < list->size; i++)
{
newElements[i] = list->elements[i];
}
delete[] list->elements;
list->elements = newElements;
list->capacity = newCapacity;
}
// Insert the data
for (int i = list->size; i > index; --i)
{
list->elements[i] = list->elements[i-1];
}
list->elements[index] = element;
list->size++;
}
// Delet the value at index
void DeleteElement(SeqList* list, int index)
{
if (index < 0 || index >= list->size)
{
throw std::invalid_argument("Invalid index of the elements which needed delete");
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < list->size - 1; i++)
{
list->elements[i] = list->elements[i + 1];
}
list->size--;
}
// Find element in list, return the index
int FindElement(SeqList* list, EleType element)
{
for (int i = 0; i < list->size; i++)
{
if (list->elements[i] == element)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// Get element at index in the list
EleType GetElement(SeqList* list, int index)
{
if(index < 0 || index >= list->size)
{
throw std::invalid_argument("Invalid index to get the element in list");
}
return list->elements[index];
}
// Update the value at index in list
void UpdateElement(SeqList* list, int index, EleType value)
{
if (index < 0 || index >= list->size)
{
throw std::invalid_argument("Invalid index to Update the element in list");
}
list->elements[index] = value;
}
// Show
void Show(SeqList* list)
{
if (list != NULL)
{
std::cout << "list size: " << list->size << std::endl;
std::cout << "List capacity:" << list->capacity << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < list->size; i++)
{
std::cout << "value[" << i << "] = " << list->elements[i] << " " << std::ends;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout << "The list is null" << std::endl;
}
}
4.杭电算法2008-数值统计
1.题目–如图
2.使用顺序表解题
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 使用模版
// EleType 为double类型
int main()
{
int n;
while(cin >> n && n)
{
// 创建初始化顺序表
SeqListlist;
InitList(&list, 1);
// 输出数据
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
eleType x;
cin >> x;
Insert(&list, i, x);
}
// 判断判断数据大小
EleType tmp;
int negative = 0;
int positive = 0;
int equalZero = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < GetSize(&list); ++i)
{
tmp = GetElement(&list, i);
if(tmp > 1e-8)
{
++positive;
}else if(tmp < -1e-8)
{
++negative;
}else
{
++equalZero;
}
}
cout << negative <<" "<< equalZero <<" " << positive << endl;
}
return 0;
}
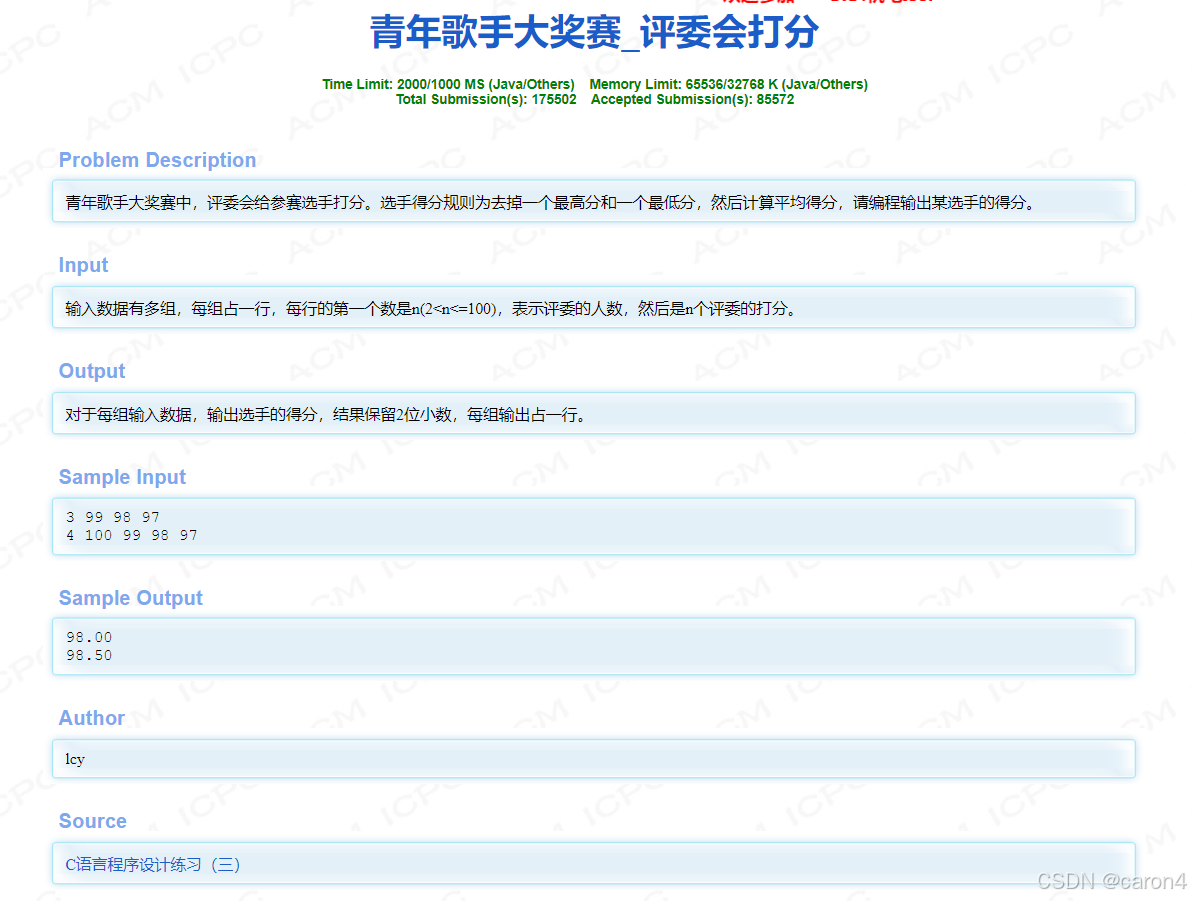
5.杭电算法2014-青年歌手大奖赛_评委会打分
1.题目–如图
2.顺序表解题
void Solution2014()
{
int n;
while (cin >> n)
{
SeqList list;
InitList(&list, 1);
EleType x;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> x;
Insert(&list, i, x);
}
EleType max = -1000000;
EleType min = 1000000;
EleType sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < list.size; i++)
{
if (max < list.elements[i])
{
max = list.elements[i];
}
if (min > list.elements[i])
{
min = list.elements[i];
}
sum += list.elements[i];
}
sum -= max;
sum -= min;
printf("%.2f\n", sum/(n-2));
}
}
int main()
{
Solution2014();
return 0;
}
3.使用数组解题
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
while(cin >> n)
{
doubel numbers[n];
// 输入数据
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
double x;
cin >> x;
numbers[i] = x
}
double eleMax = -10000000;
double eleMin = 10000000;
double sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
double ele = numbers[i];
if(ele > eleMax)
{
eleMax = ele;
}
if(ele < eleMin)
{
eleMin = ele;
}
sum += ele;
}
sum -= eleMax;
sum -= eleMin;
sum /= (n -2);
printf("%.2f\n", sum);
}
return 0;
}
6.LeetCode-LCP 01 猜数字
1.题目–如图
链接: LCP 01. 猜数字 - 力扣(LeetCode)
2.解题
class Solution {
public:
int game(vector<int>& guess, vector<int>& answer) {
int ret = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
if(guess[i] == answer[i])
ret++;
}
return ret;
}
};
7.LeetCode-LCP 06 拿硬币
1.题目–如图
2.解题:
class Solution {
public:
int minCount(vector<int>& coins) {
int count = 0;
for(int i= 0; i < coins.size(); i++)
{
count += coins[i] / 2;
if(coins[i]%2 == 1)
{
count+=1;
}
}
return count;
}
};
3.减少内存的做法
class Solution {
public:
int minCount(vector<int>& coins) {
int ret = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < coins.size(); ++i)
{
// 加上1 后再 整除2得到结果, cpu做加法快,分支慢
// 代替分支+/ + %的做法
ret += (coins[i] + 1) / 2;
}
return ret;
}
};
8.LeetCode-LCP 2057 值相等的最小索引
1.题目–如图
1.解题:
class Solution {
public:
int smallestEqual(vector<int>& nums) {
int ret = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i)
{
if(i % 10 == nums[i])
{
return i;
}
}
return ret;
}
};
9.LeetCode-LCP 485 最大连续的个数
1.题目–如题
2.解题
class Solution {
public:
int findMaxConsecutiveOnes(vector<int>& nums) {
// 00 111 01 0 1111 0000 11111111
int ret = 0; // 最终结果
int pre = 0; // 到当前数字最大连续1的个数(局部)
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i){
if(nums[i] == 1){
pre += 1;
// 局部与整体比较
if(pre > ret){
ret = pre;
}
}else{
pre = 0;
}
}
return ret;
}
};
3.减少内存的做法
原理: 将每一个数提取出来, 并作为if的条件判断 , 最终的落脚点是在当前的值和上一个的值的比较。
class Solution {
public:
int findMaxConsecutiveOnes(vector<int>& nums) {
int l = 0, r = 0;
int maxlen = 0;
int curlen = 0;
while(r < nums.size())
{
int in = nums[r];
r++;
if(in)
{
curlen++;
}
else
{
maxlen = max(maxlen, curlen);
curlen = 0;
l = r;
}
}
maxlen = max(maxlen, curlen);
return maxlen;
}
};
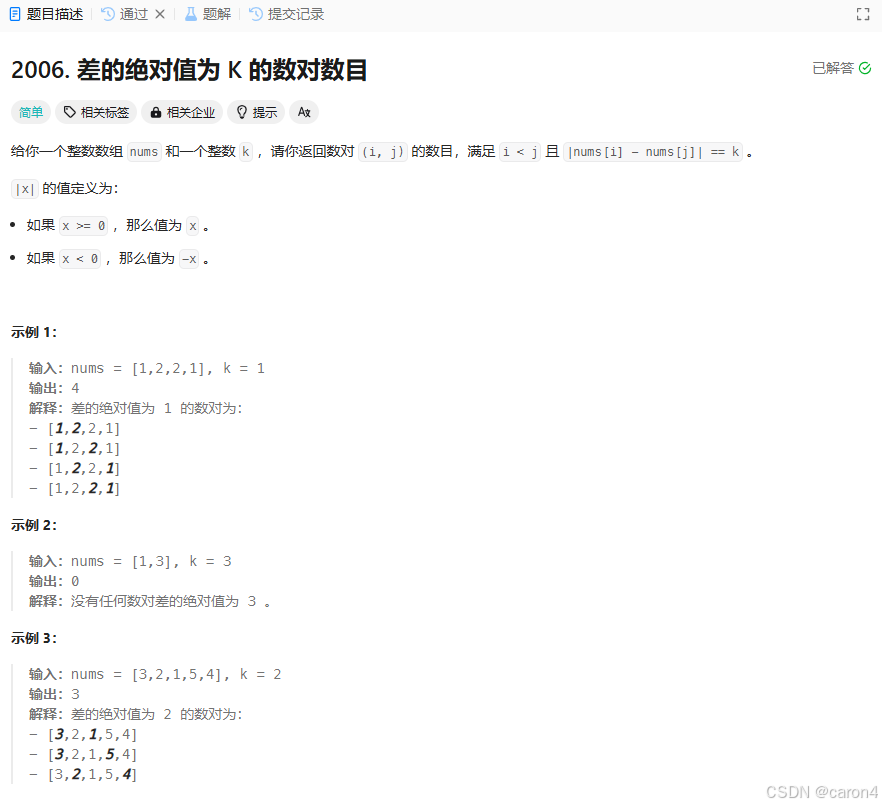
10.LeetCode-LCP 2006. 差的绝对值为 K 的数对数目
1.题目–如图
2.解题
class Solution {
public:
int countKDifference(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
int ret = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++)
{
for(int j = i+1; j < nums.size(); j++)
{
if(abs(nums[i] - nums[j]) == k)
{
ret++;
}
}
}
return ret;
}
};
11.LeetCode-LCP 1464. 数组中两元素的最大乘积
1.题目–如图
2.解题:
暴力破解
class Solution {
public:
int maxProduct(vector<int>& nums) {
int ret = 0;
int pre = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < nums.size(); j++)
{
if(i != j)
{
ret = (nums[i] - 1) * (nums[j] - 1);
if(pre < ret)
{
pre = ret;
}
}
}
}
return max(ret, pre);
}
};
减少时间复杂度的做法
找到最大值的下标和次最大值的下标即可
class Solution {
public:
int maxProduct(vector<int>& nums) {
int maxIndex = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i ++)
{
if(nums[i] > nums[maxIndex])
{
maxIndex = i;
}
}
int subMaxIndex = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i ++)
{
if(i != maxIndex)
{
if(nums[i] > nums[subMaxIndex])
{
subMaxIndex = i;
}
}
}
return (num(maxIndex)-1) * (num(subMaxIndex) - 1);
}
};
12.LeetCode-2535. 数组元素和与数字和的绝对差
1.题目–如图
2.解题
思路: 元素累加到x。 每一个元素的数字和累加到y, 得到x y差值的绝对值
class Solution {
public:
int differenceOfSum(vector<int>& nums) {
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++)
{
x += nums[i];
while(nums[i])
{
y += nums[i]%10;
nums[i] /= 10;
}
}
return abs(x-y);
}
};