cJSON,github仓库 cJSON repo
用C语言解析json转换为cJSON对象的开源库。
JSON全称: JavaScript Object Notation。
json:key-value类型。
json中有6种数据类型:数字(number,整数或浮点数)、字符串(string,在双引号中)、逻辑值(bool,true 或 false)、数组 (array,在方括号中)、对象 (object,在花括号中)、null。
cJSON
为什么使用cJSON
- 代码轻量级
- 使用广泛
- 可移植性高
2016-9-9用benchmark测试各个json解析库的性能
详细对比文档:https://github.com/miloyip/nativejson-benchmark
cJSON解析
在进行json解析的时候,通过type判断当前json的类型是哪一种,进行具体的解析。
/* cJSON Types: */
#define cJSON_Invalid (0)
#define cJSON_False (1 << 0)
#define cJSON_True (1 << 1)
#define cJSON_NULL (1 << 2)
#define cJSON_Number (1 << 3)
#define cJSON_String (1 << 4)
#define cJSON_Array (1 << 5)
#define cJSON_Object (1 << 6)
#define cJSON_Raw (1 << 7) /* raw json */
cJSON核心数据结构
/* The cJSON structure: */
typedef struct cJSON
{
struct cJSON *next; //后置节点指针
struct cJSON *prev; //前置节点指针
struct cJSON *child; //子节点指针
int type; //value 的类型
char *valuestring; //字符串数据
int valueint; //整型数据
double valuedouble; //浮点型数据
char *string; //key 的名称
} cJSON;
具体的解析流程是把一个json字符串递归解析成cJSON对象的树结构。cJSON对象也可以转换成字符串。
字符串 --> cJSON树:cJSON_Parse函数,可以递归解析json,成为一个cJSON对象。
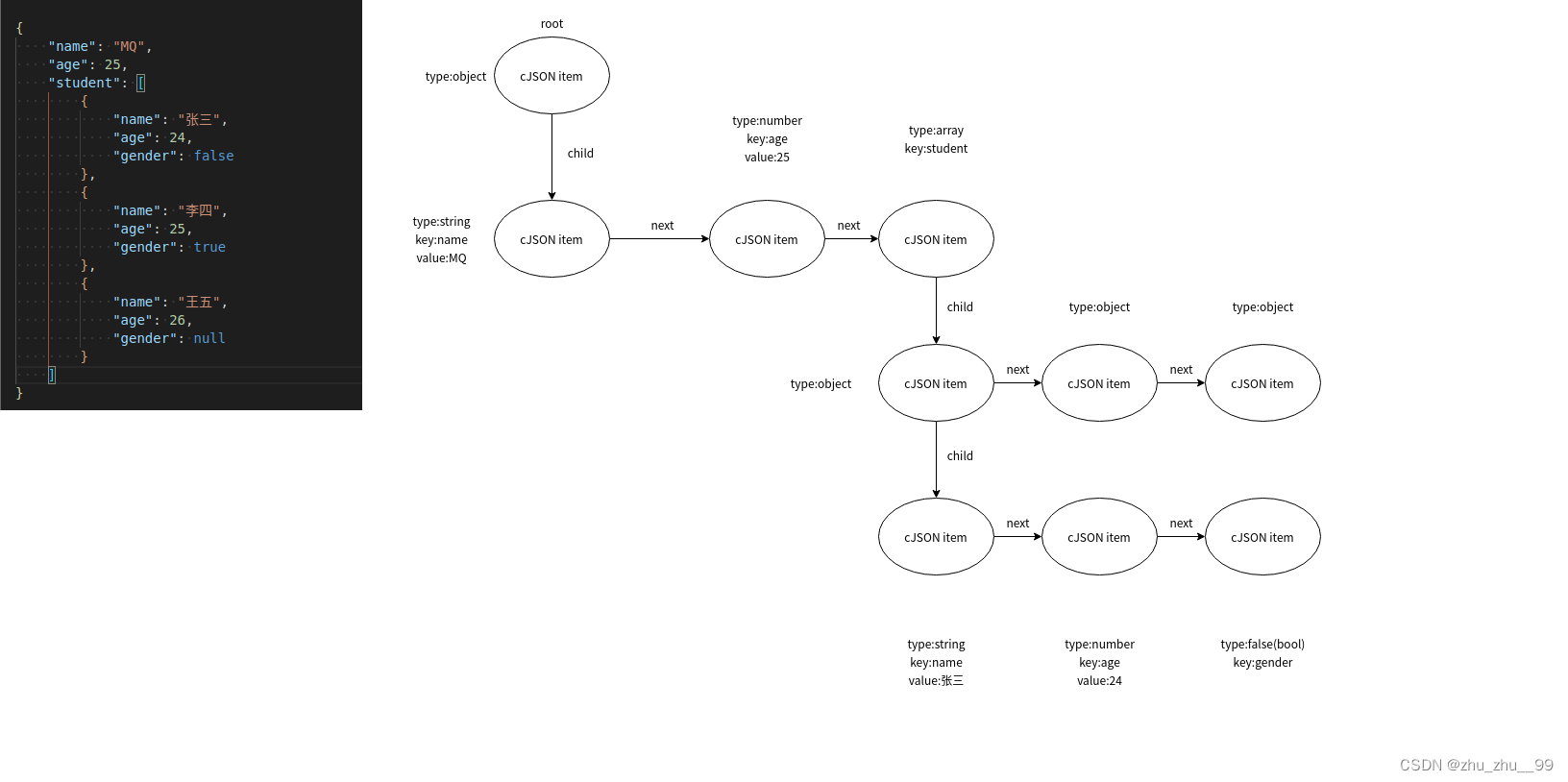
cJSON的Node中的type具体的值。具体来看一个例子:
左边是一个json,右边是cJSON解析时构建的结构。
cJSON中需要频繁的创建和释放内存,cJSON支持自定义内存函数。可以自定义malloc和free函数,数据结构如下,
typedef struct cJSON_Hooks
{
void *(CJSON_CDECL *malloc_fn)(size_t sz);
void (CJSON_CDECL *free_fn)(void *ptr);
} cJSON_Hooks;
具体的使用方法是这样的,使用者实现一个my_mem_alloc和my_mem_free,通过cJSON_Hooks结构体传给cJSON,让cJSON创建新的item时使用使用者的内存管理函数。有一个全局的global_hooks,保存内存分配的函数。
void set_cJSON_mem_hooks(){
cJSON_Hooks hooks = {
.malloc_fn = my_mem_alloc,
.free_fn = (void(CJSON_CDECL*)(void* ptr))my_mem_free,
};
cJSON_InitHooks(&hooks);
}
CJSON_PUBLIC(void) cJSON_InitHooks(cJSON_Hooks* hooks) {
if (hooks == NULL) {
/* Reset hooks */
global_hooks.allocate = malloc;
global_hooks.deallocate = free;
global_hooks.reallocate = realloc;
return;
}
global_hooks.allocate = malloc;
if (hooks->malloc_fn != NULL) {
global_hooks.allocate = hooks->malloc_fn;
}
global_hooks.deallocate = free;
if (hooks->free_fn != NULL) {
global_hooks.deallocate = hooks->free_fn;
}
...
}
创建一个节点时,例如调用cJSON_CreateNumber()函数,调用cJSON_New_Item创建cJSON节点,其中使用全局的global_hooks中的allocate进行内存分配。
CJSON_PUBLIC(cJSON*) cJSON_CreateNumber(double num) {
cJSON* item = cJSON_New_Item(&global_hooks);
if (item) {
item->type = cJSON_Number;
item->valuedouble = num;
/* use saturation in case of overflow */
if (num >= INT_MAX) {
item->valueint = INT_MAX;
} else if (num <= (double)INT_MIN) {
item->valueint = INT_MIN;
} else {
item->valueint = (int)num;
}
}
return item;
}
static cJSON* cJSON_New_Item(const internal_hooks* const hooks) {
cJSON* node = (cJSON*)hooks->allocate(sizeof(cJSON));
if (node) {
memset(node, '\0', sizeof(cJSON));
}
return node;
}
注意事项(小坑)
- cJSON_Print()这个函数的返回值是一个字符串,可供打印。::std::cout << cJSON_Print(root) << ::std::endl;
- cJSON_Print() 返回的字符串需要手动释放。cJSON_free();
- cJSON_Parse()、cJSON_CreateXXX 返回的cJSON对象需要手动释放。cJSON_Delete();