Redis分布式缓存的实现
-
什么是缓存:
定义:就是计算机内存中一段数据
-
内存中数据特点:
- 读写快
- 断电立即丢失
-
缓存解决了什么问题?
- 提高了网站吞吐量提高网站运行效率
- 核心解决问题:缓存的存在是用来减轻数据库访问压力
-
既然缓存能提高效率,那项目中所有数据加入缓存,岂不是更好?
注意:使用缓存时一定是数据库中数据极少发生修改,更多用于查询这种情况
-
本地缓存和分布式缓存区别?
本地缓存:存在应用服务器内存中数据称之为本地缓存(local cache)
分布式缓存:存储在当前应用服务器内存之外数据称之为分布式缓存(distribute cache)
集群:将同一种服务的多个节点放在一起共同对系统提供服务过程称之为集群。
分布式:由多个不同服务器集群功能对系统提供服务,这个系统称之为分布式系统(distribute system)
利用mybatis自身本地缓存结合redis实现分布式缓存
a. mybatis中的应用级缓存(二级缓存) SQL session Factory级别缓存 所有会话共享
b. 如何开启(二级缓存)
mapper.xml加入<cache/>–本地缓存
但是本地缓存会占用本机的资源,而且随着本机的关闭,本地缓存也会消失。
c.mybatis底层默认是通过org.apache.ibatis.cache.impl.PerpetualCache实现的二级缓存。
d.自定义RedisCache实现
-
通过
PerpetualCache默认源码的知 可以使用自定义Cache类 implements Cache接口,并对里面方法进行实现 -
使用RedisCache实现
<cache type="xxx.RedisCache"/>Invalid base cache implementation (class com.liu.cache.RedisCache). Base cache implementations must have a constructor that takes a String id as a parameter.
当切换cache实现时,由于RedisCache类没有完成,它会提示上面的报错:必须实现一个带有String类型的id的构造方法。
代码实现Redis分布式缓存
- 安装redis
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41936090/article/details/112723876 - redis开启远程连接
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41936090/article/details/112758629 - redis配置文件启动
https://editor.csdn.net/md/?articleId=112724487 - 先搭建好springboot 的crud的环境
- 创建数据库和表
--建数据库
create database vue;
-- 建表
CREATE TABLE `employee` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int DEFAULT NULL,
`sex` varchar(3) DEFAULT NULL,
`birthday` date DEFAULT NULL,
`address` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL,
`phone` varchar(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=16070 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
- pom.xml加入此依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
-
application.yaml
spring: redis: host: 192.168.73.128 port: 7000 database: 0 datasource: username: root password: root url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/vue?characterEnocoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource mybatis: mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml type-aliases-package: com.liu.entity # 查看sql logging: level: com.liu: debug -
Employee.java
//必须要序列化,才能把数据放入redisTemplate缓存中,stringRedisTemplate不需要。 public class Employee implements Serializable { private Integer id; private String name; private Integer age; private String sex; private Date birthday; private String address; public Employee() { } public Employee(String name, Integer age, String sex, Date birthday, String address) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.sex = sex; this.birthday = birthday; this.address = address; } //getset略 -
EmployeeDao.java
@Component public interface EmployeeDao { //查询 List<Employee> findAll(); //添加 void add(Employee employee); //删除 void del(int id); //修改 void update(Employee employee); } -
EmployeeService.java
public interface EmployeeService {
List<Employee> findAll();
//添加
void add(Employee employee);
//删除
void del(int id);
//修改
void update(Employee employee);
}
- EmployeeServiceImpl.java
@Service
@Transactional
public class EmployeeServiceImpl implements EmployeeService {
@Autowired
EmployeeDao employeeDao;
@Override
public List<Employee> findAll() {
return employeeDao.findAll();
}
@Override
public void add(Employee employee) {
employeeDao.add(employee);
}
@Override
public void del(int id) {
employeeDao.del(id);
}
@Override
public void update(Employee employee) {
employeeDao.update(employee);
}
}
- SpringbootRedisApplication.java(启动类)
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.liu.dao")//Mapper扫描
public class SpringbootRedisApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootRedisApplication.class, args);
}
}
-
EmployeeDao.xml
cache标签本是用于指定实现二级缓存,下面的type,被我指定了自定义实现缓存的方式。
<cache type="com.liu.cache.RedisCache" />
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC
"-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.liu.dao.EmployeeDao">
<!--开启mybatis二级缓存-->
<cache type="com.liu.cache.RedisCache" />
<select id="findAll" resultType="Employee" >
select id,name,age,sex,birthday,address from Employee
</select>
<insert id="add" parameterType="Employee">
insert into employee (name,age,sex,birthday,address) VALUES
(#{name},#{age},#{sex},#{birthday},#{address})
</insert>
<delete id="del" parameterType="int">
delete from employee where id = #{id}
</delete>
<update id="update" parameterType="Employee">
update Employee set name = #{name} , age = #{age}, sex =#{age},birthday=#{birthday} where id =#{id}
</update>
</mapper>
-
testUserService.java(测试类)
为了方便测试,所以使用Junit测试,至此,已经可以完成简单的crud了
@SpringBootTest(classes = SpringbootRedisApplication.class)
public class testUserService {
@Autowired
EmployeeService employeeService;
Cache cache;
@Test
public void test(){
List<Employee> all = employeeService.findAll();
all.forEach(key-> System.out.println(key));
List<Employee> alls = employeeService.findAll();
alls.forEach(key-> System.out.println(key));
}
@Test
public void testdel(){
employeeService.del(1);
}
@Test
public void testadd(){
Employee employee = new Employee("张三",21,"男",new Date(),"北京");
employeeService.add(employee);
}
@Test
public void testupdate(){
Employee employee = new Employee("李四",22,"男",new Date(),"北京");
employeeService.update(employee);
}
}
-
接下来,实现分布式缓存
-
ApplicationContextUtils.java
需要获取redisTemplate来操作redis,如果一个类是由spring工厂管理,那么我们可以通过注入RedisTemplate来获取redisTemplate这个对象;
但是我们通过实现Cache类实现自定义缓存的类不是由spring工厂管理的,是由mybatis实例化的,通过上面所说的方法注入RedisTemplate来获取redisTemplate这个对象。
所以,我们可以去工厂启动的时候去拿,这就需要拿到springboot创建好的工厂,再去获取redisTemplate对象。
//用来获取springboot创建好的工厂 @Component public class ApplicationContextUtils implements ApplicationContextAware { //保存下来工厂 private static ApplicationContext applicationContext; //将创建好的工厂以参数的形式传递给这个类 @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { this.applicationContext = applicationContext; } //提供在工厂中获取对象的方法 public static Object getBean(String beanName){ return applicationContext.getBean(beanName); } } -
-
RedisCache.java
这个类首先做的是实现Cache接口的方法,用于完成Redis缓存的实现。
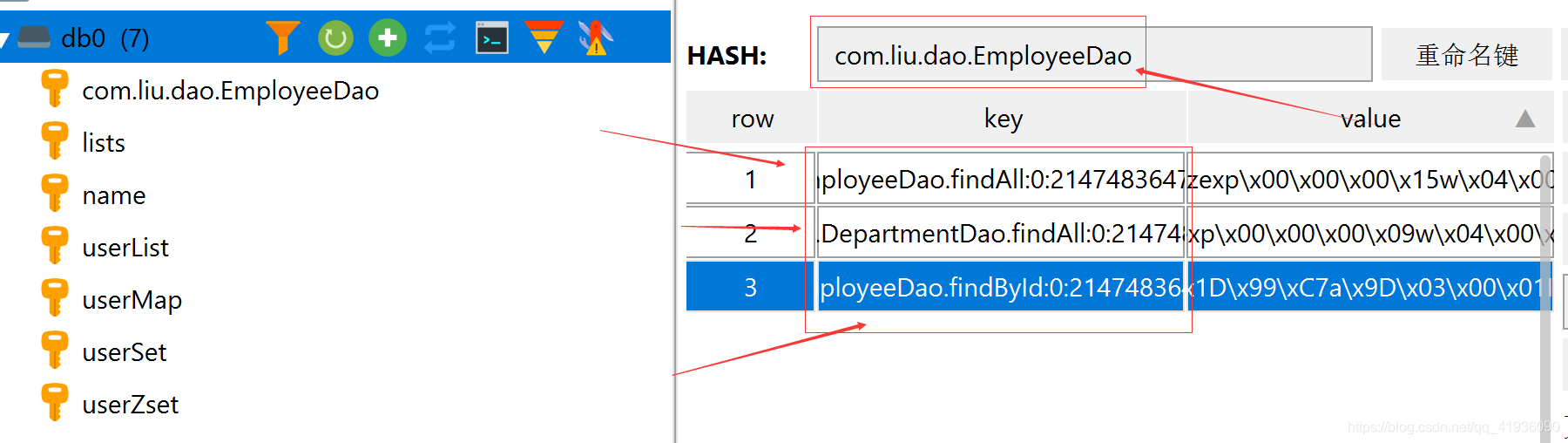
定义一个id,这个id是redis的key,也是mapper.xml的namespace,换而言之,mapper.xml的命名空间被用于作为redis,Hash的数据类型。
而我们需要给这个类获取redisTemplate对象,用于完成此类中方法对redis的操作。
// 自定义Redis缓存实现
public class RedisCache implements Cache {
//当前放入缓存的mapper的namespace
private final String id;
//默认必须存在的方法,参数是mapper.xml文件中的namespace,也是缓存中作为hash的key
public RedisCache(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
//返回cache唯一表示
@Override
public String getId() {
return this.id;
}
//获取redisTemplate对象
private RedisTemplate getRedisTemplate(){
//通过application工具类获取redisTemplate
RedisTemplate redisTemplate = (RedisTemplate) ApplicationContextUtils.getBean("redisTemplate");
//设置key和hash的序列化方式。
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
return redisTemplate;
}
// 缓存中放入数据
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) {
//使用redisHash类型作为缓存存储模型 key hashkey value
getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().put(id,key.toString(),value);
}
//缓存中获取数据
@Override
public Object getObject(Object o) {
//根据key从redis的hash类型中获取数据
return getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().get(id.toString(),o.toString());
}
//这个方法为mybatis方法,默认没有实现
@Override
public Object removeObject(Object o) {
//根据指定key删除缓存
return null;
}
//增删改走的都是这个方法,删除
@Override
public void clear() {
//清空缓存
getRedisTemplate().delete(id);
}
//用来计算缓存数量
@Override
public int getSize() {
return getRedisTemplate().opsForHash().size(id.toString()).intValue();
}
}
- 在mapper.xml文件中,将
<cache/>改为<cache type="com.liu.cache.RedisCache" />,实现我们自定义的缓存。
到此为止,我们的分布式缓存已经实现了。
-
经过一段测试,可以得出以下结论:
-
每次查询都会将此次查询的数据放入redis缓存中,之后再此查询,直接从缓存中获取(useCache=true)。
-
增删改默认会清空redis缓存(flushCache=true)。
-
当然flushCache,useCache可以控制是否将数据放入缓存以及清空缓存
(1)当为select语句时:
flushCache默认为false,表示任何时候语句被调用,都不会去清空本地缓存和二级缓存。
useCache默认为true,表示会将本条语句的结果进行二级缓存。
(2)当为insert、update、delete语句时:
flushCache默认为true,表示任何时候语句被调用,都会导致本地缓存和二级缓存被清空。
useCache属性在该情况下没有。
关于分布式缓存
-
缓存在项目中应用
a.如果项目中表查询之间没有任何关联查询使用现在的这种缓存方式没有任何问题
b.现有缓存方式在表连接查询过程中一定存在问题
-
在mybatis的缓存中如何要解决关联关系时更新缓存信息的问题?
<cache-ref/>//用来将多个具有关联关系的例如:
我在DepartmentDao.xml里面做了一个查询
<cache-ref namespace="com.liu.dao.EmployeeDao"/><!--引用别的命名空间作为键--> <select id="findAll" resultMap="DeptAndEmp"> select e.id,e.name,e.age,e.sex,e.birthday,e.address,e.deptid,d.id,d.name from Employee e, department d where e.deptid = d.id </select>
当系统进行查询时,会将缓存放入被引用的namespace,同时存在一个hash为com.liu.dao.EmployeeDao的键里,同时,当某一个命名空间的键做了修改,就会清除存在同一个键的缓存,起到数据一更新就不读取缓存数据,而是读取数据库最新数据的作用。
面试相关概念
- 什么是缓存穿透(缓存击穿)?
定义:客户端查询了数据库中没有的数据记录,导致缓存在这种情况下无法利用。
mybatis解决了缓存穿透,将数据库中没有查询到的结果进行缓存。
2)什么是缓存雪崩?
定义:在系统运行的某一时刻,突然系统中缓存全部失效,恰好这一刻涌来大量客户端请求,导致所有模块缓存无法利用,大量请求涌向数据库导致极端情况下,数据库阻塞或挂起。
缓存存储时:业务系统非常大 模块大 业务数据不同 不同模块在放入缓存时,都会设置一个缓存超时时间。
解决方案:①永久存储( 不推荐)②针对于不同业务数据一定要设置不同超时时间
3)项目有没有遇到?如何解决?