一、项目概述
随着人们生活节奏的加快,生活质量的普遍提高,足不出户享受美食的需求日益增长。在此背景下,订餐系统应运而生,即方便了商家,也方便了用户。本项目应用Google界面设计语言Material Design来设计UI,也就是按照Android5.0之后所有内置应用的界面风格来进行设计。
用户打开应用后会进入欢迎界面,然后进行注册登录,主界面有3个底部导航栏:首页、购物车和我的。首先展示所有美食列表,点进去是美食详情页,然后是可折叠式标题栏,可以进行添加购物车,多次点击会增加数量。然后购物车显示添加的商品列表,长按删除商品,点击提交订单后下拉刷新即可。我的里面可以侧滑菜单查看个人信息,可以查看订单信息,并长按删除订单,还可以通过其他应用分享软件。
二、使用技术
除了必备的SQLite数据库和基础的布局控件外,着重介绍Material Design的UI设计,它是由谷歌的设计工程师们基于传统优秀的设计原则,结合丰富的创意和科学技术所发明的一套全新的界面设计语言,包含了视觉、运动、互动效果等特性。Material Design的出现,使得Android首次在UI方面超越了iOS。这个库已经在2015年时就推出了,我们应该对这些控件非常熟悉了。
三、开发环境
四、详细设计
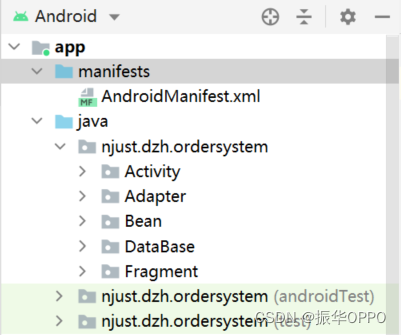
4.1 工程结构
- Activity包中是所有的Activity,包含欢迎、注册和登录等活动。
- Adapter包中是Food、Cart和Order三个实体类的适配器,将数据源按照我们设置的子项布局来显示到列表中。
- Bean包中是User、Food、Cart和Order四个实体类,包含成员属性、成员函数和构造函数。
- Database包中是数据库访问类,DataBaseHelper包含建库和建表语句,其他的类都是每张表的CURD操作的封装。
- Fragment包就是三个页面的碎片,首页、购物车和我的。
4.2 数据库设计
DataBaseHelper类就是我们的数据库,定义了数据库名称为ordersystem.db,版本号为1,然后定义了建表语句,分别是用户表User,购物车表Cart,订单表MyOrder。在onCreate中执行这些建表语句,就可以插入这三张表了。 最后onUpgrade,是在表进行变化时执行重新插入,只需改变版本号即可。DataBaseHelper完整代码如下:
// 数据库访问类
public class DataBaseHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
// 数据库名称
public static final String DATABASE = "ordersystem.db";
// 数据库版本号
public static final int VERSION = 1;
// 创建用户表User
public static final String CREATE_USER = "create table User ("
+ "account text primary key,"
+ "password text)";
// 创建购物车表Cart
public static final String CREATE_CART = "create table Cart ("
+ "name text primary key,"
+ "imageId integer,"
+ "price text,"
+ "num integer)";
// 创建订单表MyOrder
public static final String CREATE_ORDER = "create table MyOrder ("
+ "id integer primary key,"
+ "time text,"
+ "price text,"
+ "content text)";
// 创建DB对象时的构造函数
public DataBaseHelper(Context context) {
super(context, DATABASE, null, VERSION);
}
// 创建数据库
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
db.execSQL(CREATE_USER);
db.execSQL(CREATE_CART);
db.execSQL(CREATE_ORDER);
}
// 升级数据库
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
db.execSQL("drop table if exists User");
db.execSQL("drop table if exists Cart");
db.execSQL("drop table if exists MyOrder");
onCreate(db);
}
}
4.3 首页
首页的layout设计很简单,最外层是加强版FrameLayout,只包含一个SwipeRefreshLayout下拉刷新布局,然后嵌套一个RecyclerView滚动控件,大功告成。代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.coordinatorlayout.widget.CoordinatorLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto">
<androidx.swiperefreshlayout.widget.SwipeRefreshLayout
android:id="@+id/swipe_refresh"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
app:layout_behavior="@string/appbar_scrolling_view_behavior">
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/recycler_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
</androidx.swiperefreshlayout.widget.SwipeRefreshLayout>
</androidx.coordinatorlayout.widget.CoordinatorLayout>
java文件其实就是展示列表:1、创建数据源 2、创建适配器,同时加载数据源 3、设置适配器。
然后给下拉刷新布局设置个监听器,然后通知适配器更新数据源。
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_home, container, false);
// 创建数据源
initFoods();
RecyclerView recyclerView = view.findViewById(R.id.recycler_view);
GridLayoutManager gridLayoutManager = new GridLayoutManager(getContext(),2);
recyclerView.setLayoutManager(gridLayoutManager);
// 创建适配器,同时加载数据源
foodAdapter = new FoodAdapter(foodList);
// 设置适配器
recyclerView.setAdapter(foodAdapter);
swipeRefresh = view.findViewById(R.id.swipe_refresh);
swipeRefresh.setColorSchemeResources(R.color.design_default_color_primary);
swipeRefresh.setOnRefreshListener(new SwipeRefreshLayout.OnRefreshListener() {
@Override
public void onRefresh() {
refreshFoods();
}
});
return view;
}
4.4 购物车
购物车的layout也非常简单,需要注意每个布局/控件的layout_width和layout_height属性。
最外层CoordinatorLayout ,真的太好用了,强烈推荐!和首页布局唯一不同的就是里面还包了一个FloatingActionButton悬浮按钮。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.coordinatorlayout.widget.CoordinatorLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<com.google.android.material.floatingactionbutton.FloatingActionButton
android:id="@+id/fab"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="bottom|end"
android:layout_marginBottom="80dp"
android:layout_marginRight="30dp"
android:src="@mipmap/nav_task"
app:maxImageSize="50dp"
android:backgroundTint="@color/Azure"
android:elevation="8dp"/>
<androidx.swiperefreshlayout.widget.SwipeRefreshLayout
android:id="@+id/swipe_refresh"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
app:layout_behavior="@string/appbar_scrolling_view_behavior">
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/recycler_view"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</androidx.swiperefreshlayout.widget.SwipeRefreshLayout>
</androidx.coordinatorlayout.widget.CoordinatorLayout>
java文件其实就是获取控件实例,然后设置监听器,这里我们就展示悬浮按钮的监听器吧,复习下AlertDialog的标准用法,作为模板。
// 订单提交
fab.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
AlertDialog alertDialog = new AlertDialog.Builder(view.getContext())
.setTitle("提示")
.setIcon(R.drawable.ic_order)
.setMessage("您确定要提交订单吗?")
.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialogInterface, int i) {
cartDao.openDB();
cartDao.commitOrder();
cartDao.clearCart();
cartDao.closeDB();
Toast.makeText(getContext(), "下单成功!请下拉刷新页面~", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
})
.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialogInterface, int i) {
Toast.makeText(getContext(), "订单已取消", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
})
.show();
}
});
4.5 我的
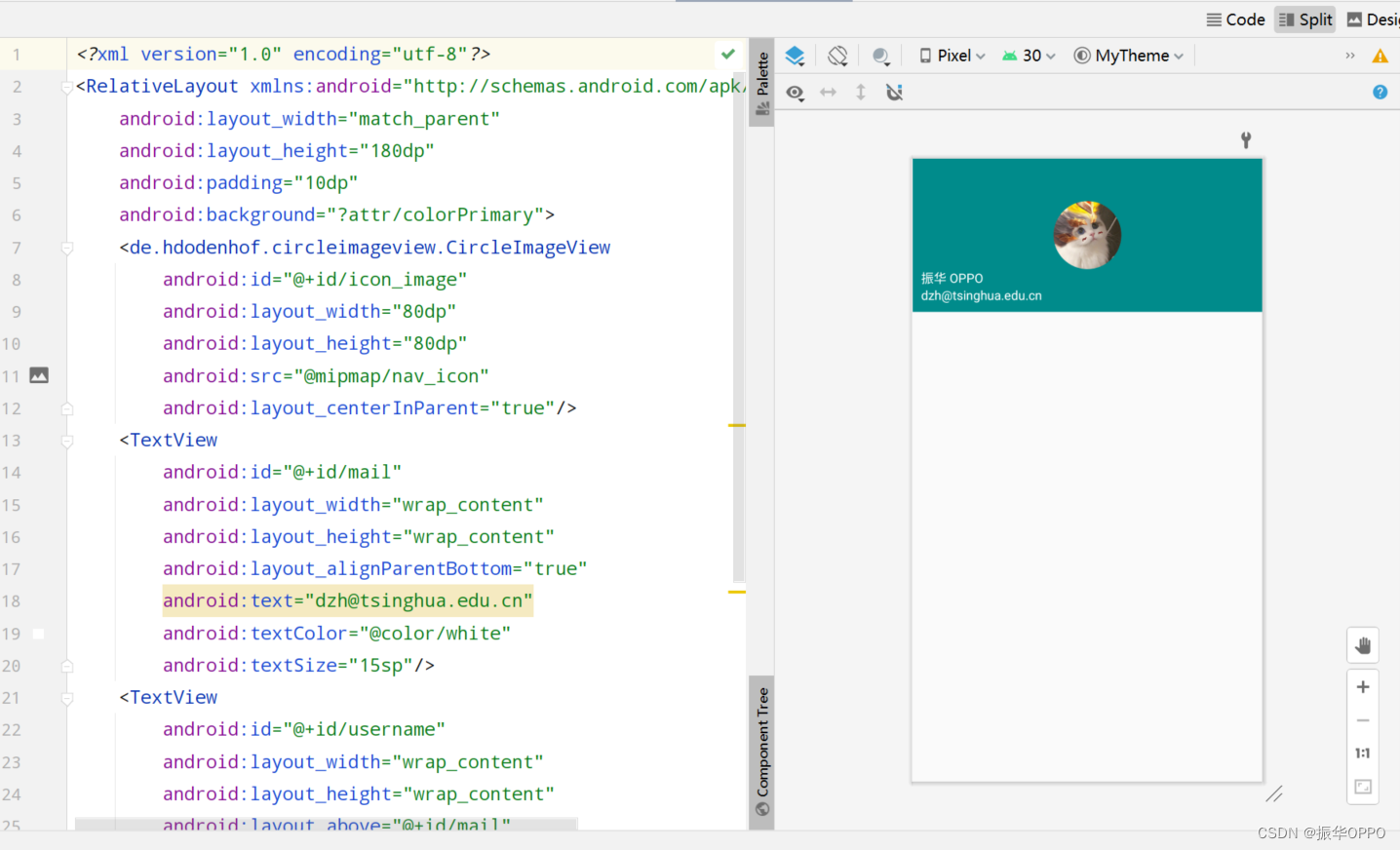
布局就很中规中矩了,最常见的布局和控件,不再赘述了,只要花时间都能设计好的布局。
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@color/Azure"
android:orientation="vertical">
<de.hdodenhof.circleimageview.CircleImageView
android:id="@+id/circle_image"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
app:civ_border_width="2dp"
android:src="@mipmap/nav_icon"
app:civ_border_color="@color/CadetBlue"
android:layout_marginBottom="20dp"/>
<ImageView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:background="@drawable/ic_chihuo"/>
<View
style="@style/PersonLineStyle"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:background="@color/white"/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@color/LightCyan">
<ImageView
style="@style/PersonImageStyle"
android:src="@drawable/ic_person"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/person"
style="@style/PersonTvStyle"
android:text="@string/person" />
</LinearLayout>
<View
style="@style/PersonLineStyle"
android:background="@color/white"/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@color/LightCyan">
<ImageView
style="@style/PersonImageStyle"
android:src="@drawable/ic_order"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/order"
style="@style/PersonTvStyle"
android:text="@string/order" />
</LinearLayout>
<View
style="@style/PersonLineStyle"
android:background="@color/white"/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@color/LightCyan">
<ImageView
style="@style/PersonImageStyle"
android:src="@drawable/ic_share"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/share"
style="@style/PersonTvStyle"
android:text="@string/share" />
</LinearLayout>
<View
style="@style/PersonLineStyle"
android:background="@color/white"/>
<androidx.cardview.widget.CardView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:cardCornerRadius="6dp"
android:elevation="5dp">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/ic_more"/>
</androidx.cardview.widget.CardView>
</LinearLayout>
java代码就是获取控件实例,然后绑定监听器,最后展示下滑动菜单栏选中事件的监听器,也就是关闭侧滑菜单。
// 菜单项选中事件的监听器
navigationView.setNavigationItemSelectedListener(new NavigationView.OnNavigationItemSelectedListener() {
@Override
public boolean onNavigationItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
drawerLayout.closeDrawers();
return true;
}
});
4.6 滑动菜单
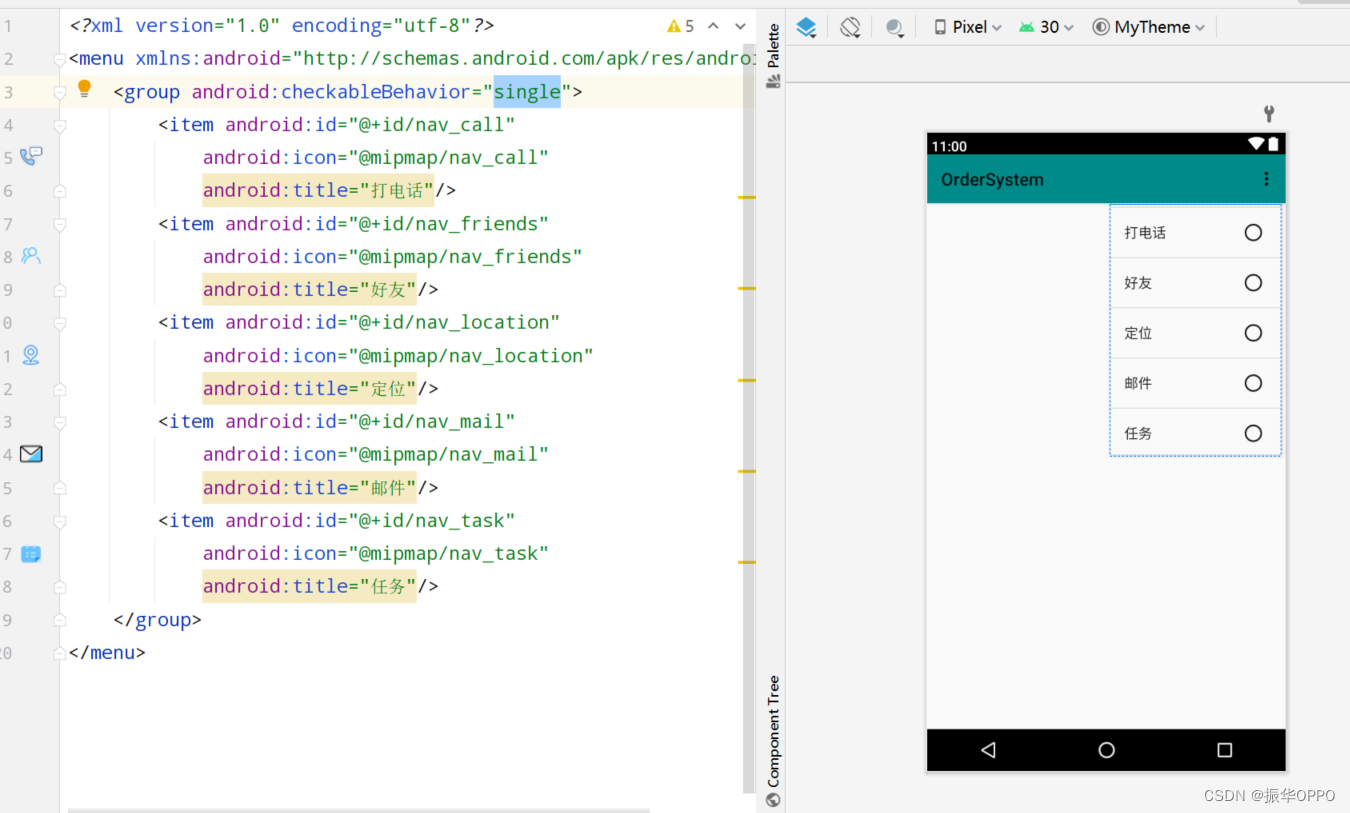
NavigationView是Design Support中提供的一个控件,使得滑动菜单界面的实现变得非常简单。NavigationView使用之前,还需要准备两个东西:menu和headerLayout,menu是用来在NavigationView中显示具体菜单项的,headerLayout则是用来在NavigationView中显示头部布局的。
res/menu/nav_menu.xml 就是具体的菜单项,< menu >标签中嵌套一个< group >标签,group表示一个组,checkableBehavior指定为single表示组中所有菜单项只能单选。然后定义五个< item >,使用id属性指定菜单项的id,icon指定菜单项的图标,title指定菜单项显示的文字,就是这么简单。
layout/nav_header 中就是头部布局,我们这里简单起见,只放置了头像、用户名和邮箱地址这三项内容,这里就用到了CircleImageView对头像进行圆形化。
五、运行演示
用AS打开项目,进行构建,Build成功后,打开AVD运行项目,因为本项目包含动画效果,所以通过视频展示效果最佳。
Android Studio实现订餐系统
六、项目总结
本次订餐系统,不同于以往任何项目,历史性地使用了Material Design来设计UI,drawable图标多达三十个,colors颜色使用了数十种,themes中定义了系统的主题,styles中定义了基础控件的属性。有九个功能页面,每一处点击都与数据库进行交互,可以说代码的健壮性已经经过多次测试,很鲁棒。每一处细节也尽量做到位,耗时25h打造。希望大家能从中学到Material Design的UI设计的风格。
七、源码获取
| ♻️下面两种方式都可以获取源代码 |
|---|
| 1️⃣ 点击直接下载 Android Studio 订餐系统 |
| 2️⃣关注公众号《 萌新加油站 》,后台回复: 订餐 |
| 🚀这有你错过的精彩内容 |
|---|
| Android Studio实现饮食搭配系统 |
| Android Studio实现考试管理系统 |
| Android Studio实现天气预报系统 |
| Android Studio实现图书馆订座系统 |
| Android Studio实现前后台分离的选课系统 |
古之立大事者,不惟有超世之才,亦必有坚忍不拔之志。——苏轼