一、本文介绍
本文记录的是基于MobileOne的YOLOv9骨干网络改进方法研究。MobileOne的基础模块通过重参数化,降低了模型在推理过程中的参数量和计算量,降低推理延迟,提高内存访问效率。在将其替换YOLOv9的骨干网络后,实现模型轻量化。
| 模型 | 参数量 | 计算量 | 推理速度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv9-c | 50.69M | 236.6GFLOPs | 32.1ms |
| Improved | 42.93M | 196.36GFLOPs | 28.3ms |
文章目录
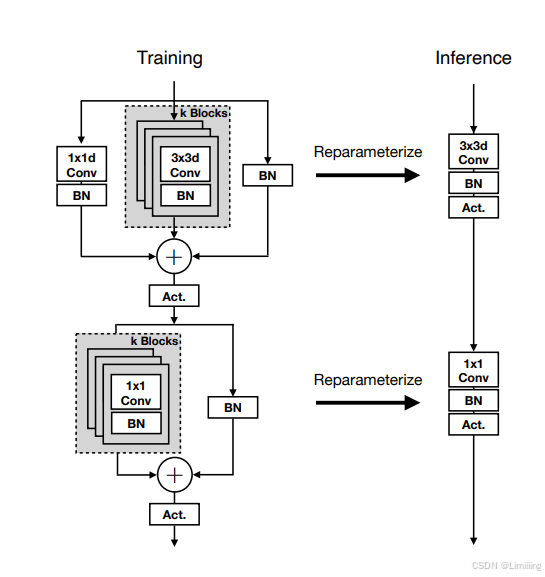
MobileOne Block是MobileOne架构中的基本模块。
二、MobileOne Block原理
2.1. 结构原理
基于MobileNetV1:以MobileNetV1的块(3x3深度卷积后跟1x1点卷积)为基础。
引入可重参数化跳过连接和分支:引入了可重参数化的跳跃连接以及复制该结构的分支,同时还引入了多个的过参数化分支。
根据文档内容,MobileOne Block的结构在训练时和推理时有所不同,具体步骤如下:
2.2 MobileOne Block训练步骤
- 输入特征图首先经过一个基于MobileNet - V1的基本块,包括3x3深度卷积和1x1点卷积。
- 然后,引入可重参数化跳跃连接(reparameterizable skip connection),该连接带有批归一化(batchnorm)。
- 同时,引入分支来复制上述结构,这些分支具有不同的超参数k(trivial over - parameterization factor),k的取值范围为1到5,通过实验来调整以获得最佳性能。
- 此时,模块具有分支结构。
2.3 MobileOne Block推理步骤
- 通过重参数化过程移除训练时的分支。
- 卷积和批归一化操作被折叠到一个单一的卷积层中,具体来说,对于卷积层,其权重W和偏置b通过对各分支相应参数进行求和计算得到;对于跳过连接的批归一化,被折叠到一个具有1x1恒等核的卷积层中,并通过填充K - 1个零来实现。
- 此时,模型具有简单的前馈结构,没有任何分支或跳跃连接,从而降低了内存访问成本。
综上所述,特征图在经过MobileOne Block时,经历了训练时的分支处理和推理时的重参数化以简化结构的步骤,以在保证性能的同时降低延迟和内存消耗。
2.4 优势
- 提高准确性:通过引入可重参数化分支和琐碎的过参数化分支,提高性能,优化损失。
- 降低内存访问成本:在推理时,
MobileOne模型没有任何分支,这是通过重参数化过程实现的,从而降低了内存访问成本。 - 有利于模型扩展:模型的这种结构和参数化方式使其能够更好地扩展模型参数,与其他多分支架构(如MobileNetV2、EfficientNets等)相比,能够在不产生显著延迟成本的情况下增加参数数量,从而使模型能够更好地泛化到其他计算机视觉任务。
论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.04040
源码:https://github.com/apple/ml-mobileone
三、MobileOne的实现代码
MobileOne的实现代码如下:
import copy as copy2
class SEBlock(nn.Module):
""" Squeeze and Excite module.
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1709.01507.pdf
"""
def __init__(self, in_channels: int, rd_ratio: float = 0.0625) -> None:
""" Construct a Squeeze and Excite Module.
:param in_channels: Number of input channels.
:param rd_ratio: Input channel reduction ratio.
"""
super(SEBlock, self).__init__()
self.reduce = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels,out_channels=int(in_channels * rd_ratio), kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=True)
self.expand = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=int(in_channels * rd_ratio),out_channels=in_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=True)
def forward(self, inputs: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
""" Apply forward pass. """
b, c, h, w = inputs.size()
x = F.avg_pool2d(inputs, kernel_size=[h, w])
x = self.reduce(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = self.expand(x)
x = torch.sigmoid(x)
x = x.view(-1, c, 1, 1)
return inputs * x
class MobileOneBlock(nn.Module):
""" MobileOne building block. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2206.04040.pdf
"""
def __init__(self, in_channels: int, out_channels: int, kernel_size: int, stride: int = 1,
padding: int = 0, dilation: int = 1, groups: int = 1, use_se: bool = False, num_conv_branches: int = 1, inference_mode: bool = False) -> None:
""" Construct a MobileOneBlock module.
:param in_channels: Number of channels in the input.
:param out_channels: Number of channels produced by the block.
:param kernel_size: Size of the convolution kernel.
:param stride: Stride size.
:param padding: Zero-padding size.
:param dilation: Kernel dilation factor.
:param groups: Group number.
:param inference_mode: If True, instantiates model in inference mode.
:param use_se: Whether to use SE-ReLU activations.
:param num_conv_branches: Number of linear conv branches.
"""
super(MobileOneBlock, self).__init__()
self.inference_mode = inference_mode
self.groups = groups
self.stride = stride
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.num_conv_branches = num_conv_branches # 4
# Check if SE-ReLU is requested
if use_se:
self.se = SEBlock(out_channels)
else:
self.se = nn.Identity()
self.activation = nn.ReLU()
if inference_mode:
self.reparam_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size,stride=stride, padding=padding, dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=True)
else:
# Re-parameterizable skip connection
self.rbr_skip = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=in_channels) if out_channels == in_channels and stride == 1 else None # BN skip
# Re-parameterizable conv branches
rbr_conv = list()
for _ in range(self.num_conv_branches):
rbr_conv.append(self._conv_bn(kernel_size=kernel_size, padding=padding))
self.rbr_conv = nn.ModuleList(rbr_conv)
# Re-parameterizable scale branch
self.rbr_scale = None
if kernel_size > 1:
self.rbr_scale = self._conv_bn(kernel_size=1, padding=0)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
""" Apply forward pass. """
# Inference mode forward pass.
if self.inference_mode:
return self.activation(self.se(self.reparam_conv(x)))
# Multi-branched train-time forward pass.
# Skip branch output
identity_out = 0
if self.rbr_skip is not None:
identity_out = self.rbr_skip(x)
# Scale branch output
scale_out = 0
if self.rbr_scale is not None:
scale_out = self.rbr_scale(x)
# Other branches
out = scale_out + identity_out
for ix in range(self.num_conv_branches):
out += self.rbr_conv[ix](x)
return self.activation(self.se(out))
def reparameterize(self):
""" Following works like `RepVGG: Making VGG-style ConvNets Great Again` -
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2101.03697.pdf. We re-parameterize multi-branched
architecture used at training time to obtain a plain CNN-like structure
for inference.
"""
if self.inference_mode:
return
kernel, bias = self._get_kernel_bias()
self.reparam_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.rbr_conv[0].conv.in_channels,
out_channels=self.rbr_conv[0].conv.out_channels,
kernel_size=self.rbr_conv[0].conv.kernel_size,
stride=self.rbr_conv[0].conv.stride,
padding=self.rbr_conv[0].conv.padding,
dilation=self.rbr_conv[0].conv.dilation,
groups=self.rbr_conv[0].conv.groups,
bias=True)
self.reparam_conv.weight.data = kernel
self.reparam_conv.bias.data = bias
# Delete un-used branches
for para in self.parameters():
para.detach_()
self.__delattr__('rbr_conv')
self.__delattr__('rbr_scale')
if hasattr(self, 'rbr_skip'):
self.__delattr__('rbr_skip')
self.inference_mode = True
def _get_kernel_bias(self) -> tuple([torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]):
""" Method to obtain re-parameterized kernel and bias.
Reference: https://github.com/DingXiaoH/RepVGG/blob/main/repvgg.py#L83
:return: Tuple of (kernel, bias) after fusing branches.
"""
# get weights and bias of scale branch
kernel_scale = 0
bias_scale = 0
if self.rbr_scale is not None:
kernel_scale, bias_scale = self._fuse_bn_tensor(self.rbr_scale)
# Pad scale branch kernel to match conv branch kernel size.
pad = self.kernel_size // 2
kernel_scale = torch.nn.functional.pad(kernel_scale, [pad, pad, pad, pad])
# get weights and bias of skip branch
kernel_identity = 0
bias_identity = 0
if self.rbr_skip is not None:
kernel_identity, bias_identity = self._fuse_bn_tensor(self.rbr_skip)
# get weights and bias of conv branches
kernel_conv = 0
bias_conv = 0
for ix in range(self.num_conv_branches):
_kernel, _bias = self._fuse_bn_tensor(self.rbr_conv[ix])
kernel_conv += _kernel
bias_conv += _bias
kernel_final = kernel_conv + kernel_scale + kernel_identity
bias_final = bias_conv + bias_scale + bias_identity
return kernel_final, bias_final
def _fuse_bn_tensor(self, branch) -> tuple([torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]):
""" Method to fuse batchnorm layer with preceeding conv layer.
Reference: https://github.com/DingXiaoH/RepVGG/blob/main/repvgg.py#L95
:param branch:
:return: Tuple of (kernel, bias) after fusing batchnorm.
"""
if isinstance(branch, nn.Sequential):
kernel = branch.conv.weight
running_mean = branch.bn.running_mean
running_var = branch.bn.running_var
gamma = branch.bn.weight
beta = branch.bn.bias
eps = branch.bn.eps
else:
assert isinstance(branch, nn.BatchNorm2d)
if not hasattr(self, 'id_tensor'):
input_dim = self.in_channels // self.groups
kernel_value = torch.zeros((self.in_channels, input_dim, self.kernel_size, self.kernel_size),
dtype=branch.weight.dtype, device=branch.weight.device)
for i in range(self.in_channels):
kernel_value[i, i % input_dim,self.kernel_size // 2, self.kernel_size // 2] = 1
self.id_tensor = kernel_value
kernel = self.id_tensor
running_mean = branch.running_mean
running_var = branch.running_var
gamma = branch.weight
beta = branch.bias
eps = branch.eps
std = (running_var + eps).sqrt()
t = (gamma / std).reshape(-1, 1, 1, 1)
return kernel * t, beta - running_mean * gamma / std
def _conv_bn(self, kernel_size: int, padding: int) -> nn.Sequential:
""" Helper method to construct conv-batchnorm layers.
:param kernel_size: Size of the convolution kernel.
:param padding: Zero-padding size.
:return: Conv-BN module.
"""
mod_list = nn.Sequential()
mod_list.add_module('conv', nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.in_channels,out_channels=self.out_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=self.stride, padding=padding, groups=self.groups, bias=False))
mod_list.add_module('bn', nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=self.out_channels))
return mod_list
class MobileOne(nn.Module):
""" MobileOne Model https://arxiv.org/pdf/2206.04040.pdf """
def __init__(self,
in_channels, out_channels,
num_blocks_per_stage = 2, num_conv_branches: int = 1,
use_se: bool = False, num_se: int = 0,
inference_mode: bool = False, ) -> None:
""" Construct MobileOne model.
:param num_blocks_per_stage: List of number of blocks per stage.
:param num_classes: Number of classes in the dataset.
:param width_multipliers: List of width multiplier for blocks in a stage.
:param inference_mode: If True, instantiates model in inference mode.
:param use_se: Whether to use SE-ReLU activations.
:param num_conv_branches: Number of linear conv branches.
"""
super().__init__()
self.inference_mode = inference_mode
self.use_se = use_se
self.num_conv_branches = num_conv_branches
self.stage = self._make_stage(in_channels, out_channels, num_blocks_per_stage, num_se_blocks= num_se if use_se else 0)
# planes指输出通道
def _make_stage(self, in_channels, out_channels, num_blocks: int, num_se_blocks: int) -> nn.Sequential:
""" Build a stage of MobileOne model.
:param planes: Number of output channels.
:param num_blocks: Number of blocks in this stage.
:param num_se_blocks: Number of SE blocks in this stage.
:return: A stage of MobileOne model.
"""
# Get strides for all layers
strides = [2] + [1]*(num_blocks-1)
blocks = []
for ix, stride in enumerate(strides): # 用于训练几个blocks
use_se = False
if num_se_blocks > num_blocks:
raise ValueError("Number of SE blocks cannot " "exceed number of layers.")
if ix >= (num_blocks - num_se_blocks):
use_se = True
# Depthwise conv
blocks.append(MobileOneBlock(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=in_channels,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, groups=in_channels,
inference_mode=self.inference_mode, use_se=use_se, num_conv_branches=self.num_conv_branches))
# Pointwise conv
blocks.append(MobileOneBlock(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, groups=1,
inference_mode=self.inference_mode, use_se=use_se, num_conv_branches=self.num_conv_branches))
in_channels = out_channels
return nn.Sequential(*blocks)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
""" Apply forward pass. """
x = self.stage(x)
return x
def reparameterize_model(model: torch.nn.Module) -> nn.Module:
""" Method returns a model where a multi-branched structure
used in training is re-parameterized into a single branch
for inference.
:param model: MobileOne model in train mode.
:return: MobileOne model in inference mode.
"""
# Avoid editing original graph
model = copy2.deepcopy(model)
for module in model.modules():
if hasattr(module, 'reparameterize'):
module.reparameterize()
return model
四、添加步骤
4.1 修改common.py
此处需要修改的文件是models/common.py
common.py中定义了网络结构的通用模块,我们想要加入新的模块就只需要将模块代码放到这个文件内即可。
此时需要将上方实现的代码添加到common.py中。
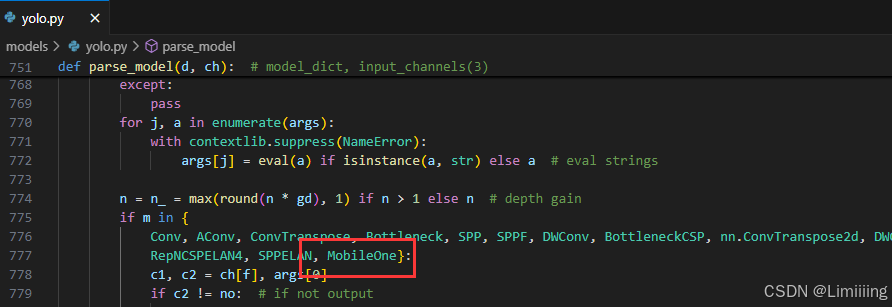
注意❗:在4.2小节中的yolo.py文件中需要声明的模块名称为:MobileOne。
4.2 修改yolo.py
此处需要修改的文件是models/yolo.py
1️⃣yolo.py用于函数调用,我们需要将common.py中定义的新的模块名添加到parse_model函数下即可。
MobileOne添加后如下:
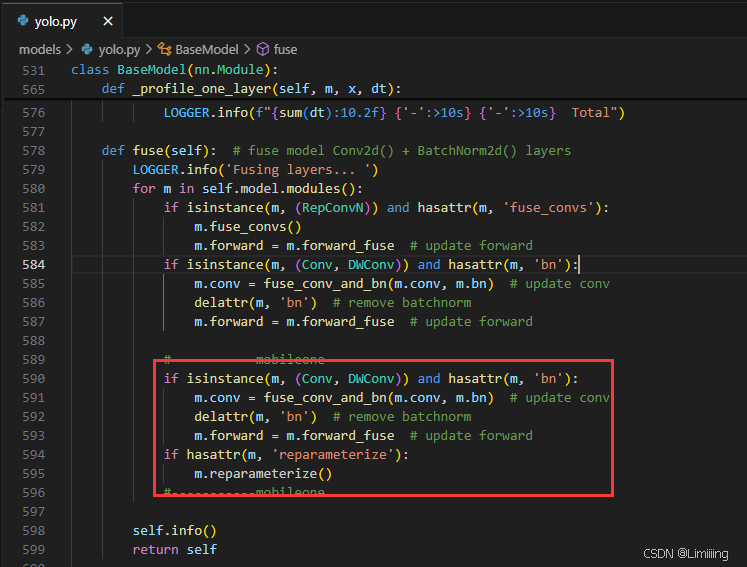
2️⃣在yolo.py的BaseModel类的fuse函数下添加如下代码,以在推理时去除分支结构。
if isinstance(m, (Conv, DWConv)) and hasattr(m, 'bn'):
m.conv = fuse_conv_and_bn(m.conv, m.bn) # update conv
delattr(m, 'bn') # remove batchnorm
m.forward = m.forward_fuse # update forward
if hasattr(m, 'reparameterize'):
m.reparameterize()
五、yaml模型文件
5.1 模型改进⭐
在代码配置完成后,配置模型的YAML文件。
此处以models/detect/yolov9-c.yaml为例,在同目录下创建一个用于自己数据集训练的模型文件yolov9-c-mobileone.yaml。
将yolov9-c.yaml中的内容复制到yolov9-c-mobileone.yaml文件下,修改nc数量等于自己数据中目标的数量。
📌 模型的修改方法是将骨干网络中的所有RepNCSPELAN4模块替换成mobileone模块。
结构如下:
# YOLOv9
# parameters
nc: 1 # number of classes
depth_multiple: 1.0 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 1.0 # layer channel multiple
#activation: nn.LeakyReLU(0.1)
#activation: nn.ReLU()
# anchors
anchors: 3
# YOLOv9 backbone
backbone:
[
[-1, 1, Silence, []],
# conv down
[-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]], # 1-P1/2
# conv down
[-1, 1, MobileOne, [64, 2, 4, False, 0]], # 2-P2/4
# avg-conv down
[-1, 1, MobileOne, [128, 8, 4, False, 0]], # 4-P3/8 3
# avg-conv down
[-1, 1, MobileOne, [256, 10, 4, True, 1]], # 6-P4/16 5
# avg-conv down
[-1, 1, MobileOne, [512, 1, 4, True, 1]], # 8-P5/32 7
]
# YOLOv9 head
head:
[
# elan-spp block
[-1, 1, SPPELAN, [512, 256]], # 10
# up-concat merge
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
# elan-2 block
[-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 1]], # 13
# up-concat merge
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 3], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
# elan-2 block
[-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [256, 256, 128, 1]], # 16 (P3/8-small)
# avg-conv-down merge
[-1, 1, ADown, [256]],
[[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4
# elan-2 block
[-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 1]], # 19 (P4/16-medium)
# avg-conv-down merge
[-1, 1, ADown, [512]],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
# elan-2 block
[-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 1]], # 22 (P5/32-large)
# multi-level reversible auxiliary branch
# routing
[3, 1, CBLinear, [[256]]], # 23
[4, 1, CBLinear, [[256, 512]]], # 24
[5, 1, CBLinear, [[256, 512, 512]]], # 25
# conv down
[0, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]], # 26-P1/2
# conv down
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 27-P2/4
# elan-1 block
[-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [256, 128, 64, 1]], # 28
# avg-conv down fuse
[-1, 1, ADown, [256]], # 29-P3/8
[[19, 20, 21, -1], 1, CBFuse, [[0, 0, 0]]], # 30
# elan-2 block
[-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 256, 128, 1]], # 31
# avg-conv down fuse
[-1, 1, ADown, [512]], # 32-P4/16
[[20, 21, -1], 1, CBFuse, [[1, 1]]], # 33
# elan-2 block
[-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 1]], # 34
# avg-conv down fuse
[-1, 1, ADown, [512]], # 35-P5/32
[[21, -1], 1, CBFuse, [[2]]], # 36
# elan-2 block
[-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 1]], # 37
# detection head
# detect
[[27, 30, 33, 12, 15, 18], 1, DualDDetect, [nc]], # DualDDetect(A3, A4, A5, P3, P4, P5)
]
六、成功运行结果
分别打印网络模型可以看到mobileone模块已经加入到模型中,并可以进行训练了。
yolov9-c-mobileone:
from n params module arguments
0 -1 1 0 models.common.Silence []
1 -1 1 1856 models.common.Conv [3, 64, 3, 2]
2 -1 1 40192 models.common.MobileOne [64, 64, 2, 4, False, 0]
3 -1 1 548416 models.common.MobileOne [64, 128, 8, 4, False, 0]
4 -1 1 2651296 models.common.MobileOne [128, 256, 10, 4, True, 1]
5 -1 1 582192 models.common.MobileOne [256, 512, 1, 4, True, 1]
6 -1 1 656896 models.common.SPPELAN [512, 512, 256]
7 -1 1 0 torch.nn.modules.upsampling.Upsample [None, 2, 'nearest']
8 [-1, 4] 1 0 models.common.Concat [1]
9 -1 1 2988544 models.common.RepNCSPELAN4 [768, 512, 512, 256, 1]
10 -1 1 0 torch.nn.modules.upsampling.Upsample [None, 2, 'nearest']
11 [-1, 3] 1 0 models.common.Concat [1]
12 -1 1 814336 models.common.RepNCSPELAN4 [640, 256, 256, 128, 1]
13 -1 1 164352 models.common.ADown [256, 256]
14 [-1, 9] 1 0 models.common.Concat [1]
15 -1 1 2988544 models.common.RepNCSPELAN4 [768, 512, 512, 256, 1]
16 -1 1 656384 models.common.ADown [512, 512]
17 [-1, 6] 1 0 models.common.Concat [1]
18 -1 1 3119616 models.common.RepNCSPELAN4 [1024, 512, 512, 256, 1]
19 3 1 33024 models.common.CBLinear [128, [256]]
20 4 1 197376 models.common.CBLinear [256, [256, 512]]
21 5 1 656640 models.common.CBLinear [512, [256, 512, 512]]
22 0 1 1856 models.common.Conv [3, 64, 3, 2]
23 -1 1 73984 models.common.Conv [64, 128, 3, 2]
24 -1 1 212864 models.common.RepNCSPELAN4 [128, 256, 128, 64, 1]
25 -1 1 164352 models.common.ADown [256, 256]
26 [19, 20, 21, -1] 1 0 models.common.CBFuse [[0, 0, 0]]
27 -1 1 847616 models.common.RepNCSPELAN4 [256, 512, 256, 128, 1]
28 -1 1 656384 models.common.ADown [512, 512]
29 [20, 21, -1] 1 0 models.common.CBFuse [[1, 1]]
30 -1 1 2857472 models.common.RepNCSPELAN4 [512, 512, 512, 256, 1]
31 -1 1 656384 models.common.ADown [512, 512]
32 [21, -1] 1 0 models.common.CBFuse [[2]]
33 -1 1 2857472 models.common.RepNCSPELAN4 [512, 512, 512, 256, 1]
34[27, 30, 33, 12, 15, 18] 1 21542822 DualDDetect [1, [512, 512, 512, 256, 512, 512]]