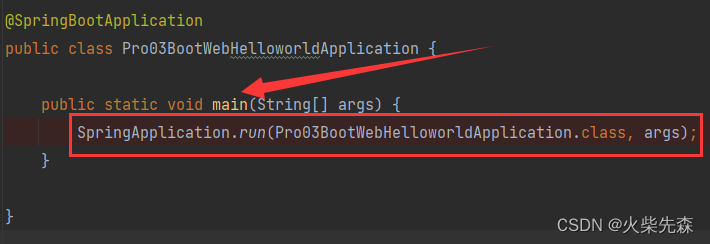
SpringBoot的主程序类
SpringApplication的静态方法run() 会做两件事情:
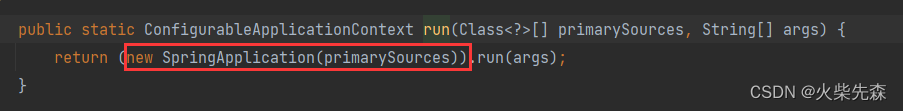
- 通过构造方法创建SpringApplication对象 ,并在构造方法中完成初始化
//先调用这个构造方法
public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources) {
this((ResourceLoader)null, primarySources);
}
//再加上资源加载器,间接调用这个构造方法(初始化操作!)
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.sources = new LinkedHashSet();
this.bannerMode = Mode.CONSOLE;
this.logStartupInfo = true;
this.addCommandLineProperties = true;
this.addConversionService = true;
this.headless = true;
this.registerShutdownHook = true;
this.additionalProfiles = Collections.emptySet();
this.isCustomEnvironment = false;
this.lazyInitialization = false;
this.applicationContextFactory = ApplicationContextFactory.DEFAULT;
this.applicationStartup = ApplicationStartup.DEFAULT;
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
// 在primarySources不为空时(这里是指主程序类的类对象),保存这个主程序类的类对象(是个配置类)
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
// 判断web应用的类型(这里是Servlet)
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
//获取BootstrapRegistryInitializer类实例,用于初始化各种BootstrapRegistry
//从"META-INF/spring.factories"中读取key为BootstrapRegistryInitializer类型的扩展点,
//并实例化出对应扩展点对象
//BootstrapRegistry对象的作用:
//可以用来注册一些对象,这些对象可以用在从SpringBoot启动到Spring容器初始化完成的过程中
//可以这样理解:没有Spring容器之前就利用BootstrapRegistry来共享一些对象,
//有了Spring容器之后就利用Spring容器来共享一些对象
this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers = new ArrayList(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(BootstrapRegistryInitializer.class));
// 获取并保存"容器初始化类",通常在web应用容器初始化使用
// 利用loadFactoryNames方法从路径MEAT-INF/spring.factories中找到所有的ApplicationContextInitializer(容器初始化类)
this.setInitializers(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// 获取并保存监听器
// 利用loadFactoryNames方法从路径MEAT-INF/spring.factories中找到所有的ApplicationListener
this.setListeners(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
// 从堆栈信息获取包含main方法的主配置类
this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
这样就成功创建了一个SpringApplication对象,并且完成了初始化!
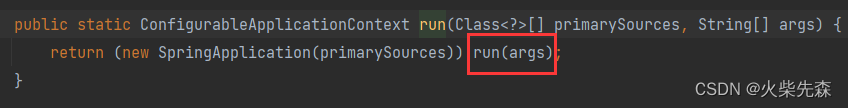
- 利用创建好的SpringApplication对象调用更底层的run方法:
准备spring的上下文,完成容器的初始化,创建,加载等。会在不同的时机触发监听器的不同事件。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
shutdownHook.enableShutdowHookAddition();
}
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = this.createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
// 配置属性
this.configureHeadlessProperty();
// 获取监听器
// 利用loadFactoryNames方法从路径MEAT-INF/spring.factories中找到所有的SpringApplicationRunListener
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this.getRunListeners(args);
// 启动监听
// 调用每个SpringApplicationRunListener的starting方法
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
// 将参数封装到ApplicationArguments对象中
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 准备环境
// 触发监听事件——调用每个SpringApplicationRunListener的environmentPrepared方法
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
// 从环境中取出Banner并打印
Banner printedBanner = this.printBanner(environment);
// ⭐依据是否为web环境创建web容器或者普通的IOC容器
context = this.createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
// 准备上下文
// 1.将environment保存到容器中
// 2.触发监听事件——调用每个SpringApplicationRunListeners的contextPrepared方法
// 3.调用ConfigurableListableBeanFactory的registerSingleton方法向容器中注入applicationArguments与printedBanner
// 4.触发监听事件——调用每个SpringApplicationRunListeners的contextLoaded方法
this.prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// 刷新容器,完成组件的扫描,创建,加载等
this.refreshContext(context);
this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
Duration timeTakenToStartup = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
(new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), timeTakenToStartup);
}
listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup);
this.callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
} catch (Throwable var12) {
if (var12 instanceof AbandonedRunException) {
throw var12;
}
this.handleRunFailure(context, var12, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(var12);
}
try {
if (context.isRunning()) {
Duration timeTakenToReady = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
listeners.ready(context, timeTakenToReady);
}
// ⭐返回容器
return context;
} catch (Throwable var11) {
if (var11 instanceof AbandonedRunException) {
throw var11;
} else {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var11, (SpringApplicationRunListeners)null);
throw new IllegalStateException(var11);
}
}
}
总结:
SpringApplication.run一共做了两件事
- 创建SpringApplication对象;在对象初始化时保存事件监听器,容器初始化类以及判断是否为web应用,保存包含main方法的主配置类。
- 调用run方法;准备spring的上下文,完成容器的初始化,创建,加载等。会在不同的时机触发监听器的不同事件。