Spring boot集成Mybatis
文章目录
JPA方式在中国以外地区开发而言基本是标配,在国内MyBatis及其延伸框架较为主流
一:基础知识
1:什么是MyBatis
MyBatis是一款优秀的基于java的持久层框架,它内部封装了jdbc,使开发者只需要关注sql语句本身,而不需要花费精力去处理加载驱动、创建连接、创建statement等繁杂的过程。
MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持定制化 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。
- mybatis是一个优秀的基于java的持久层框架,它内部封装了jdbc,使开发者只需要关注sql语句本身,而不需要花费精力去处理加载驱动、创建连接、创建statement等繁杂的过程。
- mybatis通过xml或注解的方式将要执行的各种statement配置起来,并通过java对象和statement中sql的动态参数进行映射生成最终执行的sql语句,最后由mybatis框架执行sql并将结果映射为java对象并返回。
MyBatis的主要设计目的就是让我们对执行SQL语句时对输入输出的数据管理更加方便
所以方便地写出SQL和方便地获取SQL的执行结果才是MyBatis的核心竞争力。
Mybatis的功能架构分为三层:
2:为什么说MyBatis是半自动ORM
Mybatis 在查询关联对象或关联集合对象时,需要手动编写 sql 来完成,所以,称之为半自动ORM 映射工具。
正是由于MyBatis是半自动框架,基于MyBatis技术栈的框架开始考虑兼容MyBatis开发框架的基础上提供自动化的能力,比如MyBatis-plus等框架
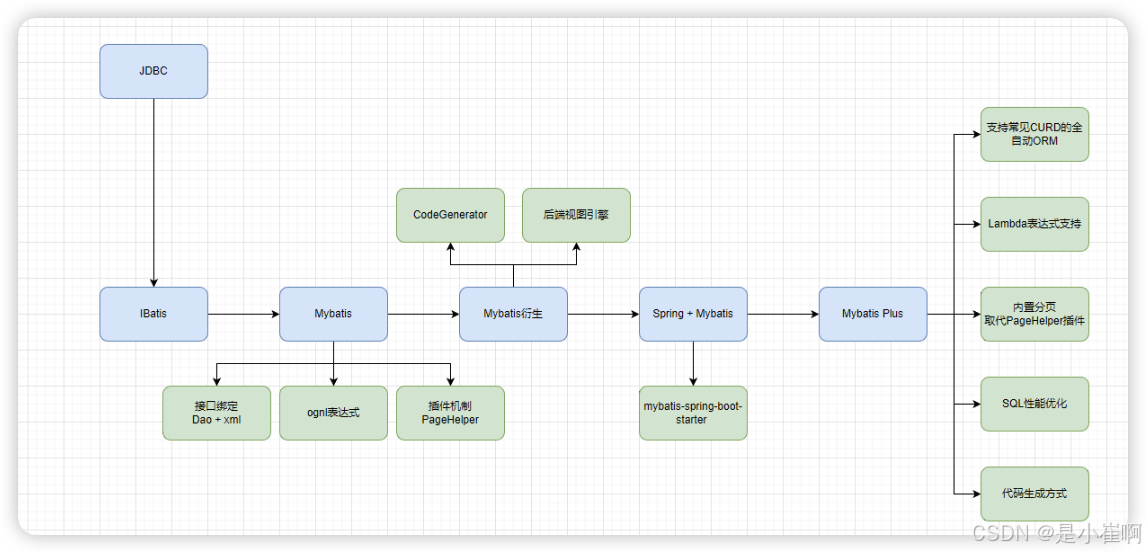
3:MyBatis栈技术演进
3.1:JDBC,自行封装JDBCUtil
底层具体实现看这个:https://blog.csdn.net/Fire_Cloud_1/article/details/130791820
Java5的时代,通常的开发中会自行封装JDBC的Util,比如创建 Connection,以及确保关闭 Connection等
- 依赖和配置文件
<!-- MYSQL驱动 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Boot JDBC -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
- 调用
@Service
public class DatabaseService {
private final JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
public DatabaseService(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
public void insertData(String data) {
jdbcTemplate.update("INSERT INTO your_table (column_name) VALUES (?)", data);
}
public void deleteData(String data) {
jdbcTemplate.update("DELETE FROM your_table WHERE column_name = ?", data);
}
// 更多数据库操作方法...
}
3.2:IBatis
MyBatis的前身,它封装了绝大多数的 JDBC 样板代码,使得开发者只需关注 SQL 本身
而不需要花费精力去处理例如注册驱动,创建 Connection,以及确保关闭 Connection 这样繁杂的代码
3.3:Mybatis
伴随着JDK5+ 泛型和注解特性开始流行,IBatis在3.0变更为MyBatis,对泛型和注解等特性开始全面支持,同时支持了很多新的特性,比如:
- mybatis实现了接口绑定,通过Dao接口 和xml映射文件的绑定,自动生成接口的具体实现
- mybatis支持 ognl表达式,比如
<if>, <else>使用ognl进行解析 - mybatis插件机制等,(PageHelper分页插件应用而生,解决了数据库层的分页封装问题)
3.4:Mybatis衍生
MyBatis提供了开发上的便捷,但是依然需要写大量的xml配置,并且很多都是CRUD级别的(这便有了很多重复性的工作)
所以为了减少重复编码,衍生出了MyBatis代码生成工具, 比如CodeGenerator等。
其它开发IDE也开始出现封装一些工具和插件来生成代码生成工具等。
由于后端视图解析引擎多样性(比如freemarker, volicty, thymeleaf等),以及前后端分离前端独立等,为了进一步减少重复代码的编写(包括视图层),自动生成的代码工具也开始演化为自动生成前端视图代码
3.5:spring+Mybatis基于注解的配置集成
与此同时,Spring 2.5 开始完全支持基于注解的配置并且也支持JSR250 注解。
在Spring后续的版本发展倾向于通过注解和Java配置结合使用。
基于Spring+MyBatis开发技术栈开始有xml配置方式往注解和java配置方式反向发展。
Spring Boot的出现便是要解决配置过多的问题,它实际上通过约定大于配置的方式大大简化了用户的配置,对于三方组件使用xx-starter统一的对Bean进行默认初始化,用户只需要很少的配置就可以进行开发了。
所以出现了mybatis-spring-boot-starter的封装等。
这个阶段,主要的开发技术栈是 Spring + mybatis-spring-boot-starter 自动化配置 + PageHelper,并且很多数据库实体mapper还是通过xml方式配置的(伴随着使用一些自动化生成工具)
3.6:Mybatis-plus
为了更高的效率,出现了MyBatis-Plus这类工具,对MyBatis进行增强。
-
考虑到MyBatis是半自动化ORM,MyBatis-Plus 启动即会自动注入基本 CURD,性能基本无损耗,直接面向对象操作; 并且内置通用 Mapper、通用 Service,仅仅通过少量配置即可实现单表大部分 CRUD 操作,更有强大的条件构造器,满足各类使用需求;总体上让其支持全自动化的使用方式(本质上借鉴了Hibernate思路)。
-
考虑到Java8 Lambda(函数式编程)开始流行,MyBatis-Plus支持 Lambda 表达式,方便的编写各类查询条件,无需再担心字段写错
-
考虑到MyBatis还需要独立引入PageHelper分页插件,MyBatis-Plus支持了内置分页插件,同PageHelper一样基于 MyBatis 物理分页,开发者无需关心具体操作,配置好插件之后,写分页等同于普通 List 查询
-
考虑到自动化代码生成方式,MyBatis-Plus也支持了内置代码生成器,采用代码或者 Maven 插件可快速生成 Mapper 、 Model 、 Service 、 Controller 层代码,支持模板引擎,更有超多自定义配置等您来使用
-
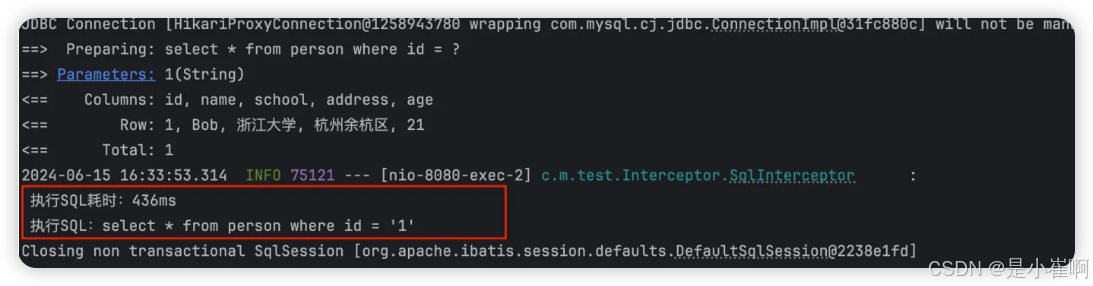
考虑到SQL性能优化等问题,MyBatis-Plus内置性能分析插件, 可输出 SQL 语句以及其执行时间,建议开发测试时启用该功能,能快速揪出慢查询
-
其它还有解决一些常见开发问题,比如支持主键自动生成,支持4 种主键策略(内含分布式唯一 ID 生成器 - Sequence),可自由配置,完美解决主键问题;以及内置全局拦截插件,提供全表 delete 、 update 操作智能分析阻断,也可自定义拦截规则,预防误操作
二:xml方式
1:准备DB和依赖配置
-- tb_user
create table tb_user
(
id int auto_increment
primary key,
user_name varchar(45) not null,
password varchar(45) not null,
email varchar(45) null,
phone_number int null,
description varchar(255) null,
create_time datetime null,
update_time datetime null
);
INSERT INTO `tb_user` VALUES (1,'pdai','dfasdf','[email protected]',1212121213,'afsdfsaf','2021-09-08 17:09:15','2021-09-08 17:09:15');
-- tb_role
create table tb_role
(
id int auto_increment
primary key,
name varchar(255) not null,
role_key varchar(255) not null,
description varchar(255) null,
create_time datetime null,
update_time datetime null
);
INSERT INTO `tb_role` VALUES (1,'admin','admin','admin','2021-09-08 17:09:15','2021-09-08 17:09:15');
-- tb_user_role
create table tb_user_role
(
user_id int not null,
role_id int not null
);
INSERT INTO `tb_user_role` VALUES (1,1);
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.4.7</version>
</dependency>
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: 314159
# mybatis
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml # mapper文件存储的位置
type-aliases-package: com.study.study_demo_of_spring-boot.entity # 对应的实体的位置
configuration:
cache-enabled: true # 开启二级缓存
use-generated-keys: true # 主键回填
# SimpleExecutor:简单执行器,每一次都会创建一个新的预处理器(prepareStatement)
# ReuseExecutor:可重用执行器,相同的SQL只进行一次预处理
# BatchExecutor:批处理提交修改,必须执行flushStatements才会生效
default-executor-type: reuse
use-actual-param-name: true # 默认为true,使用方法名作为参数名称
# log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl # 打印sql
# map-underscore-to-camel-case: true # 开启驼峰命名
2:entity
BaseEntity
import java.io.Serializable;
// 实体类都继承这个,实现序列化
public interface BaseEntity extends Serializable {
}
User
@Getter
@Setter
public class User implements BaseEntity {
private Long id;
private String userName;
// JSON序列化的时候忽略Password,安全性
@JsonIgnore
private String password;
private String email;
private long phoneNumber;
private String description;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
// 一个user,对应多个角色,一对多
private List<Role> roles;
}
Role
@Getter
@Setter
public class Role implements BaseEntity {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String roleKey;
private String description;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
}
RoleQueryBean
// findList方法会以这个为入参
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
public class RoleQueryBean {
private String name;
private String description;
private String roleKey;
}
UserQueryBean
// findList方法会以这个为入参
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
public class UserQueryBean {
private String userName;
private String description;
private String phoneNumber;
private String email;
}
ResponseResult
Data
@Builder
public class ResponseResult<T> {
private long timestamp;
private String status;
private String message;
private T data;
// success
public static <T> ResponseResult<T> success() {
return success(null);
}
public static <T> ResponseResult<T> success(T data) {
return ResponseResult.<T>builder().data(data)
.message(ResponseStatus.SUCCESS.getDescription())
.status(ResponseStatus.SUCCESS.getResponseCode())
.timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build();
}
// fail
public static <T extends Serializable> ResponseResult<T> fail(String message) {
return fail(null, message);
}
public static <T> ResponseResult<T> fail(T data, String message) {
return ResponseResult.<T>builder().data(data)
.message(message)
.status(ResponseStatus.FAIL.getResponseCode())
.timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build();
}
}
3:Dao接口 & Mapper文件
3.1:Dao接口
定义了要实现的接口
UserDao
@Mapper
public interface IUserDao {
List<User> findList(UserQueryBean userQueryBean);
User findById(Long id);
int deleteById(Long id);
int deleteByIds(Long[] ids);
int update(User user);
int save(User user);
int updatePassword(User user);
}
RoleDao
@Mapper
public interface IRoleDao {
List<Role> findList(RoleQueryBean roleQueryBean);
}
3.2:mapper文件
mapper文件定义在配置的路径中(classpath:mapper/*.xml)
UserMapper
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql57.mybatis.xml.dao.IUserDao">
<!-- 声明resultMap,type对应的实体类,id是为了后面语句调用用 -->
<resultMap type="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql57.mybatis.xml.entity.User" id="UserResult">
<!-- 下面就是type所指的实体类和数据的列的映射关系 -->
<!-- id是主键的特殊声明 -->
<!-- property指的是实体类对应的字段,column是数据库对应的列 -->
<id property="id" column="id" />
<result property="userName" column="user_name" />
<result property="password" column="password" />
<result property="email" column="email" />
<result property="phoneNumber" column="phone_number" />
<result property="description" column="description" />
<result property="createTime" column="create_time" />
<result property="updateTime" column="update_time" />
<!-- 一对多,对应的是List<Role>那个字段 -->
<!-- property指定的是字段的名称,ofType是指List中的单个对象的type类型是Role实体 -->
<collection property="roles" ofType="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql57.mybatis.xml.entity.Role">
<!-- 下面是role和数据库列的映射关系 -->
<result property="id" column="rid" />
<result property="name" column="rname" />
<result property="roleKey" column="role_key" />
<result property="description" column="rdescription" />
<result property="createTime" column="rcreate_time" />
<result property="updateTime" column="rupdate_time" />
</collection>
</resultMap>
<!-- sql片段:为了后面使用的通用性,尤其是select的部分 -->
<sql id="selectUserSql">
<!-- 这里的select结果就是对应上面的resultMap,这样如果返回的是resultMap的,都可以引用这个sql片段 -->
select
u.id,
u.password,
u.user_name,
u.email,
u.phone_number,
u.description,
u.create_time,
u.update_time,
r.id rid,
r.name rname,
r.role_key,
r.description rdescription,
r.create_time rcreate_time,
r.update_time rupdate_time
from
tb_user u
left join
tb_user_role ur on u.id=ur.user_id
inner join
tb_role r on ur.role_id=r.id <!-- 跨中间表的三表联查 -->
</sql>
<!-- findList的sql实现,注意如果param是一个实体类,注意全路径 -->
<select id="findList" parameterType="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql57.mybatis.xml.entity.query.UserQueryBean" resultMap="UserResult">
<!-- include引入sql片段,refid = 对应的sql片段的id -->
<include refid="selectUserSql"/>
<!-- 对应的查询条件,使用了ognl表达式 -->
where u.id != 0
<!-- test表示条件,userName等于输入的UserQueryBean中的userName -->
<if test="userName != null and userName != ''">
AND u.user_name like concat('%', #{user_name}, '%')
</if>
<if test="description != null and description != ''">
AND u.description like concat('%', #{description}, '%')
</if>
<if test="phoneNumber != null and phoneNumber != ''">
AND u.phone_number like concat('%', #{phoneNumber}, '%')
</if>
<if test="email != null and email != ''">
AND u.email like concat('%', #{email}, '%')
</if>
</select>
<!-- 如果入参是基本类型,直接就是Long, Integer等等 -->
<select id="findById" parameterType="Long" resultMap="UserResult">
<include refid="selectUserSql"/>
where u.id = #{id}
</select>
<delete id="deleteById" parameterType="Long">
delete from tb_user where id = #{id}
</delete>
<!-- 注意这里的foreach的使用, parameterType是List中单个的实体的类型 -->
<delete id="deleteByIds" parameterType="Long">
delete from tb_user where id in
<!--
collection:指定数组或者集合
item:代表数组或集合中的元素
separator:循环之间的分隔符
open:在标签先添加的符号
close:在标签后添加的符号
-->
<foreach collection="array" item="id" open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{id} <!-- (111, 222, 333, 444) -->
</foreach>
</delete>
<!-- update使用set -->
<update id="update" parameterType="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql57.mybatis.xml.entity.User">
update tb_user
<set>
<if test="userName != null and userName != ''">user_name = #{userName},</if>
<if test="email != null and email != ''">email = #{email},</if>
<if test="phoneNumber != null and phoneNumber != ''">phone_number = #{phoneNumber},</if>
<if test="description != null and description != ''">description = #{description},</if>
update_time = sysdate()
</set>
where id = #{id}
</update>
<update id="updatePassword" parameterType="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql57.mybatis.xml.entity.User">
update tb_user
<set>
password = #{password}, update_time = sysdate()
</set>
where id = #{id}
</update>
<!-- 注意insert的时候这两个的设置:useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id" -->
<insert id="save" parameterType="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql57.mybatis.xml.entity.User" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into tb_user(
<if test="userName != null and userName != ''">user_name,</if>
<if test="password != null and password != ''">password,</if>
<if test="email != null and email != ''">email,</if>
<if test="phoneNumber != null and phoneNumber != ''">phone_number,</if>
<if test="description != null and description != ''">description,</if>
create_time,
update_time
)values(
<if test="userName != null and userName != ''">#{userName},</if>
<if test="password != null and password != ''">#{password},</if>
<if test="email != null and email != ''">#{email},</if>
<if test="phoneNumber != null and phoneNumber != ''">#{phoneNumber},</if>
<if test="description != null and description != ''">#{description},</if>
sysdate(),
sysdate()
)
</insert>
</mapper>
RoleMapper
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql57.mybatis.xml.dao.IRoleDao">
<resultMap type="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql57.mybatis.xml.entity.Role" id="RoleResult">
<id property="id" column="id" />
<result property="name" column="name" />
<result property="roleKey" column="role_key" />
<result property="description" column="description" />
<result property="createTime" column="create_time" />
<result property="updateTime" column="update_time" />
</resultMap>
<sql id="selectRoleSql">
select r.id, r.name, r.role_key, r.description, r.create_time, r.update_time
from tb_role r
</sql>
<select id="findList" parameterType="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql57.mybatis.xml.entity.query.RoleQueryBean" resultMap="RoleResult">
<include refid="selectRoleSql"/>
where r.id != 0
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
AND r.name like concat('%', #{name}, '%')
</if>
<if test="roleKey != null and roleKey != ''">
AND r.role_key = #{roleKey}
</if>
<if test="description != null and description != ''">
AND r.description like concat('%', #{description}, '%')
</if>
</select>
</mapper>
3.3:resultType & resultMap
resultmap与resulttype的区别为:对象不同、描述不同、类型适用不同
对象不同
resultMap如果查询出来的列名和pojo的属性名不一致,通过定义一个resultMap对列名和pojo属性名之间作一个映射关系。
resultType使用resultType进行输出映射,只有查询出来的列名和pojo中的属性名一致,该列才可以映射成功。
描述不同
resultMap对于一对一表连接的处理方式通常为在主表的pojo中添加嵌套另一个表的pojo,然后在mapper.xml中采用association节点元素进行对另一个表的连接处理。
resultType无法查询结果映射到pojo对象的pojo属性中,根据对结构集查询遍历的需要选择使用resultType还是resultMap。
类型适用不同
mybatis中在查询进行select映射的时候,返回类型可以用resultType,也可以用resultMap。
resultType是直接表示返回类型的,而resultMap则是对外部ResultMap的引用,但是resultType跟resultMap不能同时存在。
如果你要用resulttype返回一个复杂对象的话,就必须返回这个对象的所有属性。
说白了就是resultMap和resultType都是作为sql的返回结果集,但是resultMap适用于pojo类和表字段不匹配以及复杂表的关联查询,不可以直接返回
resultMap的返回类型必须是外部自己定义的resultMap的引用但是resultType可以直接返回返回类型,但是实体类对应关系一定要名字完全对应。当然resultType也可以实现关联查询的只是这需要思考出方法来实现。
Mapper文件常用写法 -> from RUO_YI系统
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.ruoyi.system.mapper.SysDeptMapper">
<resultMap type="SysDept" id="SysDeptResult">
<id property="deptId" column="dept_id" />
<result property="parentId" column="parent_id" />
<result property="ancestors" column="ancestors" />
<result property="deptName" column="dept_name" />
<result property="orderNum" column="order_num" />
<result property="leader" column="leader" />
<result property="phone" column="phone" />
<result property="email" column="email" />
<result property="status" column="status" />
<result property="delFlag" column="del_flag" />
<result property="parentName" column="parent_name" />
<result property="createBy" column="create_by" />
<result property="createTime" column="create_time" />
<result property="updateBy" column="update_by" />
<result property="updateTime" column="update_time" />
</resultMap>
<sql id="selectDeptVo">
select d.dept_id, d.parent_id, d.ancestors, d.dept_name, d.order_num, d.leader, d.phone, d.email, d.status, d.del_flag, d.create_by, d.create_time
from sys_dept d
</sql>
<select id="selectDeptList" parameterType="SysDept" resultMap="SysDeptResult">
<include refid="selectDeptVo"/>
where d.del_flag = '0'
<if test="deptId != null and deptId != 0">
AND dept_id = #{deptId}
</if>
<if test="parentId != null and parentId != 0">
AND parent_id = #{parentId}
</if>
<if test="deptName != null and deptName != ''">
AND dept_name like concat('%', #{deptName}, '%')
</if>
<if test="status != null and status != ''">
AND status = #{status}
</if>
<!-- 数据范围过滤 -->
${params.dataScope}
order by d.parent_id, d.order_num
</select>
<select id="selectDeptListByRoleId" resultType="Long">
select d.dept_id
from sys_dept d
left join sys_role_dept rd on d.dept_id = rd.dept_id
where rd.role_id = #{roleId}
<if test="deptCheckStrictly">
and d.dept_id not in (select d.parent_id from sys_dept d inner join sys_role_dept rd on d.dept_id = rd.dept_id and rd.role_id = #{roleId})
</if>
order by d.parent_id, d.order_num
</select>
<select id="selectDeptById" parameterType="Long" resultMap="SysDeptResult">
select d.dept_id, d.parent_id, d.ancestors, d.dept_name, d.order_num, d.leader, d.phone, d.email, d.status,
(select dept_name from sys_dept where dept_id = d.parent_id) parent_name
from sys_dept d
where d.dept_id = #{deptId}
</select>
<select id="checkDeptExistUser" parameterType="Long" resultType="int">
select count(1) from sys_user where dept_id = #{deptId} and del_flag = '0'
</select>
<select id="hasChildByDeptId" parameterType="Long" resultType="int">
select count(1) from sys_dept
where del_flag = '0' and parent_id = #{deptId} limit 1
</select>
<select id="selectChildrenDeptById" parameterType="Long" resultMap="SysDeptResult">
select * from sys_dept where find_in_set(#{deptId}, ancestors)
</select>
<select id="selectNormalChildrenDeptById" parameterType="Long" resultType="int">
select count(*) from sys_dept where status = 0 and del_flag = '0' and find_in_set(#{deptId}, ancestors)
</select>
<select id="checkDeptNameUnique" resultMap="SysDeptResult">
<include refid="selectDeptVo"/>
where dept_name=#{deptName} and parent_id = #{parentId} and del_flag = '0' limit 1
</select>
<insert id="insertDept" parameterType="SysDept">
insert into sys_dept(
<if test="deptId != null and deptId != 0">dept_id,</if>
<if test="parentId != null and parentId != 0">parent_id,</if>
<if test="deptName != null and deptName != ''">dept_name,</if>
<if test="ancestors != null and ancestors != ''">ancestors,</if>
<if test="orderNum != null">order_num,</if>
<if test="leader != null and leader != ''">leader,</if>
<if test="phone != null and phone != ''">phone,</if>
<if test="email != null and email != ''">email,</if>
<if test="status != null">status,</if>
<if test="createBy != null and createBy != ''">create_by,</if>
create_time
)values(
<if test="deptId != null and deptId != 0">#{deptId},</if>
<if test="parentId != null and parentId != 0">#{parentId},</if>
<if test="deptName != null and deptName != ''">#{deptName},</if>
<if test="ancestors != null and ancestors != ''">#{ancestors},</if>
<if test="orderNum != null">#{orderNum},</if>
<if test="leader != null and leader != ''">#{leader},</if>
<if test="phone != null and phone != ''">#{phone},</if>
<if test="email != null and email != ''">#{email},</if>
<if test="status != null">#{status},</if>
<if test="createBy != null and createBy != ''">#{createBy},</if>
sysdate()
)
</insert>
<update id="updateDept" parameterType="SysDept">
update sys_dept
<set>
<if test="parentId != null and parentId != 0">parent_id = #{parentId},</if>
<if test="deptName != null and deptName != ''">dept_name = #{deptName},</if>
<if test="ancestors != null and ancestors != ''">ancestors = #{ancestors},</if>
<if test="orderNum != null">order_num = #{orderNum},</if>
<if test="leader != null">leader = #{leader},</if>
<if test="phone != null">phone = #{phone},</if>
<if test="email != null">email = #{email},</if>
<if test="status != null and status != ''">status = #{status},</if>
<if test="updateBy != null and updateBy != ''">update_by = #{updateBy},</if>
update_time = sysdate()
</set>
where dept_id = #{deptId}
</update>
<update id="updateDeptChildren" parameterType="java.util.List">
update sys_dept set ancestors =
<foreach collection="depts" item="item" index="index"
separator=" " open="case dept_id" close="end">
when #{item.deptId} then #{item.ancestors}
</foreach>
where dept_id in
<foreach collection="depts" item="item" index="index"
separator="," open="(" close=")">
#{item.deptId}
</foreach>
</update>
<update id="updateDeptStatusNormal" parameterType="Long">
update sys_dept set status = '0' where dept_id in
<foreach collection="array" item="deptId" open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{deptId}
</foreach>
</update>
<delete id="deleteDeptById" parameterType="Long">
update sys_dept set del_flag = '2' where dept_id = #{deptId}
</delete>
</mapper>
三:注解方式说明
1:基本的增删改查
1.1:查询操作
@Results和@Result注解
对于xml配置查询时定义的ResultMap, 在注解中如何定义呢?
<resultMap type="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql57.mybatis.xml.entity.User" id="UserResult1">
<id property="id" column="id" />
<result property="userName" column="user_name" />
<result property="password" column="password" />
<result property="email" column="email" />
<result property="phoneNumber" column="phone_number" />
<result property="description" column="description" />
<result property="createTime" column="create_time" />
<result property="updateTime" column="update_time" />
</resultMap>
@Results(
id = "UserResult1",
value = {
@Result(id = true, property = "id", column = "id"),
@Result(property = "userName", column = "user_name"),
@Result(property = "password", column = "password"),
@Result(property = "email", column = "email"),
@Result(property = "phoneNumber", column = "phone_number"),
@Result(property = "description", column = "description"),
@Result(property = "createTime", column = "create_time"),
@Result(property = "updateTime", column = "update_time")
}
)
@Select和@Param注解
对于查询,用@Select注解;对于参数, 使用@Param注解
@Results(
id = "UserResult1",
value = {
@Result(id = true, property = "id", column = "id"),
@Result(property = "userName", column = "user_name"),
@Result(property = "password", column = "password"),
@Result(property = "email", column = "email"),
@Result(property = "phoneNumber", column = "phone_number"),
@Result(property = "description", column = "description"),
@Result(property = "createTime", column = "create_time"),
@Result(property = "updateTime", column = "update_time")
}
)
@Select("select u.id, u.password, u.user_name, u.email, u.phone_number, u.description, u.create_time, u.update_time from tb_user u where id = #{id}")
User findById1(@Param("id") Long id);
@ResultMap注解
xml配置查询时定义的ResultMap是可以复用的,那么我们上面通过@Results定义在某个方法上的,如何复用呢?
比如查询所有用户返回用户实体@Results是和查询单个用户一致的,那么我们可以通过@ResultMap指定返回值对应关系
@ResultMap("UserResult1")
@Select("select u.id, u.password, u.user_name, u.email, u.phone_number, u.description, u.create_time, u.update_time from tb_user u")
User findAll1();
由此你可以猜到,@ResultMap定义在哪个方法上并没有什么关系,因为它会被优先通过注解解析为数据库字段与Java字段的映射关系。
1.2:表关联查询
用户和角色存在着一对多的关系,上面的查询只是查询了用户的基本信息,如何关联查询(查询用户同时返回角色信息)呢?
<resultMap type="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql57.mybatis.xml.entity.User" id="UserResult">
<id property="id" column="id" />
<result property="userName" column="user_name" />
<result property="password" column="password" />
<result property="email" column="email" />
<result property="phoneNumber" column="phone_number" />
<result property="description" column="description" />
<result property="createTime" column="create_time" />
<result property="updateTime" column="update_time" />
<collection property="roles" ofType="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql57.mybatis.xml.entity.Role">
<result property="id" column="id" />
<result property="name" column="name" />
<result property="roleKey" column="role_key" />
<result property="description" column="description" />
<result property="createTime" column="create_time" />
<result property="updateTime" column="update_time" />
</collection>
</resultMap>
上面是在xml方式下的resultMap实现方式,那么对于注解方式,是使用@result + @Many进行实现的
@Results(
id = "UserResult",
value = {
@Result(id = true, property = "id", column = "id"),
@Result(property = "userName", column = "user_name"),
@Result(property = "password", column = "password"),
@Result(property = "email", column = "email"),
@Result(property = "phoneNumber", column = "phone_number"),
@Result(property = "description", column = "description"),
@Result(property = "createTime", column = "create_time"),
@Result(property = "updateTime", column = "update_time"),
// 注意这里
@Result(property = "roles", column = "id", many = @Many(select = "tech.pdai.springboot.mysql57.mybatis.anno.dao.IRoleDao.findRoleByUserId", fetchType = FetchType.EAGER))
}
)
其中findRoleByUserId是通过user表中的id查找Role, 具体方法如下
@Results(
id = "RoleResult",
value = {
@Result(id = true, property = "id", column = "id"),
@Result(property = "name", column = "name"),
@Result(property = "roleKey", column = "role_key"),
@Result(property = "description", column = "description"),
@Result(property = "createTime", column = "create_time"),
@Result(property = "updateTime", column = "update_time")
}
)
@Select("select r.id, r.name, r.role_key, r.description, r.create_time, r.update_time from tb_role r, tb_user_role ur where r.id = ur.user_id and ur.user_id = #{userId}")
List<Role> findRoleByUserId(Long userId);
🎉 对于一对一的可以使用@One注解
1.3:插入操作
涉及插入操作的主要注解有:@Insert, @SelectKey等。
@Insert
对于插入操作,在xml配置可以定义为:
<insert id="save" parameterType="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql57.mybatis.xml.entity.User" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into tb_user(
<if test="userName != null and userName != ''">user_name,</if>
<if test="password != null and password != ''">password,</if>
<if test="email != null and email != ''">email,</if>
<if test="phoneNumber != null and phoneNumber != ''">phone_number,</if>
<if test="description != null and description != ''">description,</if>
create_time,
update_time
)values(
<if test="userName != null and userName != ''">#{userName},</if>
<if test="password != null and password != ''">#{password},</if>
<if test="email != null and email != ''">#{email},</if>
<if test="phoneNumber != null and phoneNumber != ''">#{phoneNumber},</if>
<if test="description != null and description != ''">#{description},</if>
sysdate(),
sysdate()
)
</insert>
特别是,这里通过<if>判断条件更新的情况应该如何在注解中写呢? -> 可以通过@Insert + <script>
@Insert({"<script> ", "insert into tb_user(\n" +
" <if test=\"userName != null and userName != ''\">user_name,</if>\n" +
" <if test=\"password != null and password != ''\">password,</if>\n" +
" <if test=\"email != null and email != ''\">email,</if>\n" +
" <if test=\"phoneNumber != null and phoneNumber != ''\">phone_number,</if>\n" +
" <if test=\"description != null and description != ''\">description,</if>\n" +
" create_time,\n" +
" update_time\n" +
" )values(\n" +
" <if test=\"userName != null and userName != ''\">#{userName},</if>\n" +
" <if test=\"password != null and password != ''\">#{password},</if>\n" +
" <if test=\"email != null and email != ''\">#{email},</if>\n" +
" <if test=\"phoneNumber != null and phoneNumber != ''\">#{phoneNumber},</if>\n" +
" <if test=\"description != null and description != ''\">#{description},</if>\n" +
" sysdate(),\n" +
" sysdate()\n" +
" )", " </script>"})
@Options(useGeneratedKeys = true, keyProperty = "id") // 指定自动生成key,以及主键对应的属性名为id
int save(User user);
上述
@Options(useGeneratedKeys = true, keyProperty = "id")表示什么意思呢?
表示,如果数据库提供了自增列生成Key的方式(比如这里的id), 并且需要返回自增主键时,可以通过这种方式返回实体。
那么,如果id的自增不使用数据库自增主键时, 在xml中可以使用SelectKey:
<selectKey keyColumn="id" resultType="long" keyProperty="id" order="AFTER">
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()
</selectKey>
对应着注解:
@SelectKey(statement = "SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()", keyColumn = "id", keyProperty = "id", resultType = Long.class, before = false)
before = false, 相当于XML中的order=“AFTRE”,这是MySql数据库的配置。before = true, 相当于XML中的order=“BEFORE”,这是Oracle数据库的配置。
注意事项:不同的数据库statement的值会不同,上面中的值适用于MySql数据库,使用其他类型的数据库时要注意修改。
1.4:更新操作
涉及更新操作的主要注解有:@Update等。
<update id="update" parameterType="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql57.mybatis.xml.entity.User">
update tb_user
<set>
<if test="userName != null and userName != ''">user_name = #{userName},</if>
<if test="email != null and email != ''">email = #{email},</if>
<if test="phoneNumber != null and phoneNumber != ''">phone_number = #{phoneNumber},</if>
<if test="description != null and description != ''">description = #{description},</if>
update_time = sysdate()
</set>
where id = #{id}
</update>
<update id="updatePassword" parameterType="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql57.mybatis.xml.entity.User">
update tb_user
<set>
password = #{password}, update_time = sysdate()
</set>
where id = #{id}
</update>
对应的注解写法如下:
@Update({"update tb_user set password = #{password}, update_time = sysdate()", " where id = #{id}"})
int updatePassword(User user);
@Update({"<script> ", "update tb_user\n" +
" <set>\n" +
" <if test=\"userName != null and userName != ''\">user_name = #{userName},</if>\n" +
" <if test=\"email != null and email != ''\">email = #{email},</if>\n" +
" <if test=\"phoneNumber != null and phoneNumber != ''\">phone_number = #{phoneNumber},</if>\n" +
" <if test=\"description != null and description != ''\">description = #{description},</if>\n" +
" update_time = sysdate()\n" +
" </set>\n" +
" where id = #{id}", " </script>"})
int update(User user);
1.5:删除操作
涉及删除操作的主要注解有:@Delete等。
<delete id="deleteById" parameterType="Long">
delete from tb_user where id = #{id}
</delete>
<delete id="deleteByIds" parameterType="Long">
delete from tb_user where id in
<foreach collection="array" item="id" open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{id}
</foreach>
</delete>
对应的注解写法如下:
@Delete("delete from tb_user where id = #{id}")
int deleteById(Long id);
@Delete({"<script> ", "delete from tb_user where id in\n" +
"<foreach collection=\"array\" item=\"id\" open=\"(\" separator=\",\" close=\")\">\n" +
"#{id}\n" +
"</foreach>", " </script>"})
int deleteByIds(Long[] ids);
2:Provider注解加持
其实你可以发现通过注解方式,对于有一些需要通过动态构建查询条件的操作是非常不方便的。
MyBatis的作者们自然就想到了动态构建SQL,动态构建SQL的方式是配合@Provider注解来完成的。
MyBatis提供了4种Provider注解,分别是@SelectProvider、@InsertProvider、@UpdateProvider和@DeleteProvider。
这里以@SelectProvider为例来根据Id查询User
2.1:定义动态SQL类
public class UserDaoProvider {
public String findById(final Long id) {
SQL sql = new SQL();
sql.SELECT("u.id, u.password, u.user_name, u.email, u.phone_number, u.description, u.create_time, u.update_time");
sql.FROM("tb_user u");
sql.WHERE("id = " + id);
return sql.toString();
}
}
2.2:注解关联
// 通过@SelectProvider注解关联到定义的类和方法
@ResultMap("UserResult")
@SelectProvider(type = UserDaoProvider.class, method = "findById")
User findById2(Long id);
3:进一步理解注解
3.1:其它注解
- @CacheNamespace:为给定的命名空间 (比如类) 配置缓存。对应xml中的
<cache>。 - @CacheNamespaceRef:参照另外一个命名空间的缓存来使用。
- @ConstructorArgs:收集一组结果传递给一个劫夺对象的构造方法。
- @Arg:单独的构造方法参数, 是 ConstructorArgs 集合的一部分。
- @Case:独实例的值和它对应的映射。
- @TypeDiscriminator:一组实例值被用来决定结果映射的表现。
- @Flush:在MyBatis 3.3以上版本,可以通过此注解在Mapper接口中调用
SqlSession#flushStatements()。
3.2:xml方式和注解方式融合
xml方式和注解方式是可以融合写的, 我们可以将复杂的SQL写在xml中
比如将resultMap定义在xml中:
<resultMap type="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql57.mybatis.xml.entity.User" id="UserResult">
<id property="id" column="id" />
<result property="userName" column="user_name" />
<result property="password" column="password" />
<result property="email" column="email" />
<result property="phoneNumber" column="phone_number" />
<result property="description" column="description" />
<result property="createTime" column="create_time" />
<result property="updateTime" column="update_time" />
<collection property="roles" ofType="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql57.mybatis.xml.entity.Role">
<result property="id" column="id" />
<result property="name" column="name" />
<result property="roleKey" column="role_key" />
<result property="description" column="description" />
<result property="createTime" column="create_time" />
<result property="updateTime" column="update_time" />
</collection>
</resultMap>
然后在方法使用使用:
@ResultMap("UserResult")
@Select("select u.id, u.password, u.user_name, u.email, u.phone_number, u.description, u.create_time, u.update_time from tb_user u")
User findAll1();
3.3:为什么纯注解方式不是最佳选择
- 对于复杂的SQL,特别是按照条件动态生成方式极为不便,即便有
<script>, 代码的阅读体验和维护极为不佳; - 对于复杂的SQL,即便有@Provider方式,这种充其量是一个半成品
- 不是所见即所得的写法,需要再定义额外的类和方法
- 动态构建时不便利
- 函数式编程成为主流,lambda方式才是未来
- …
这也是mybatis-plus等工具改进的地方。
四:PageHelper分页插件
1:前置知识
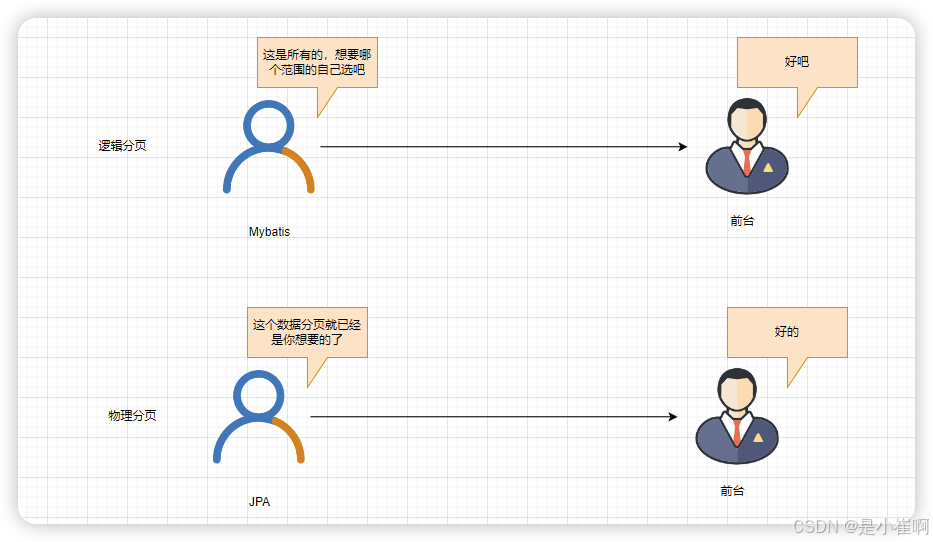
1.1:逻辑分页和物理分页的区别
- 逻辑分页:从数据库将所有记录查询出来,存储到内存中,展示当前页,然后数据再直接从内存中获取(前台分页)
- 物理分页:只从数据库中查询当前页的数据(后台分页)
由于MyBatis默认实现中采用的是逻辑分页,所以才诞生了PageHelper一类的物理分页框架。
hibernate不用是因为hibernate采用的就是物理分页。(JPA前身)
1.2:不同数据库的物理分页是如何实现的
MySQL 使用 LIMIT
SELECT username, password
FROM tb_user
WHERE id = 1
LIMIT 100,10
oracle
SELECT *
FROM (SELECT AA.*, ROWNUM RN
FROM (SELECT * FROM USERS ORDER BY ID DESC) AA
WHERE ROWNUM <= 10 )
WHERE RN > 0
SqlServer
SELECT top(50) LastName, FirstName, EmailAddress
FROM Employee
ORDER BY LastName, FirstName, EmailAddress
OFFSET 14000 ROWS
FETCH NEXT 50 ROWS ONLY;
1.3:PageHelper工作原理
MyBatis提供了一种插件(plugin)的功能,虽然叫做插件,但其实这是拦截器功能。
Mybatis采用责任链模式,通过动态代理组织多个拦截器(插件),通过这些拦截器可以改变Mybatis的默认行为
Mybatis的分页功能很弱,它是基于内存的分页(查出所有记录再按偏移量和limit取结果),在大数据量的情况下这样的分页基本上是没有用的
而PageHelper插件,通过拦截StatementHandler重写sql语句,实现数据库的物理分页
2:简单使用
2.1:RowBounds方式的调用
List<User> list = sqlSession.selectList("x.y.selectIf", null, new RowBounds(0, 10));
2.2:Mapper接口方式的调用startPage
PageHelper.startPage(1, 10);
List<User> list = userMapper.selectIf(1);
2.3:Mapper接口方式的调用offsetPage
PageHelper.offsetPage(1, 10);
List<User> list = userMapper.selectIf(1);
2.4:参数方法调用
//存在以下 Mapper 接口方法,你不需要在 xml 处理后两个参数
public interface CountryMapper {
List<User> selectByPageNumSize( @Param("user") User user, @Param("pageNum") int pageNum, @Param("pageSize") int pageSize);
}
//配置supportMethodsArguments=true
//在代码中直接调用:
List<User> list = userMapper.selectByPageNumSize(user, 1, 10);
2.5:参数对象
//如果 pageNum 和 pageSize 存在于 User 对象中,只要参数有值,也会被分页
//有如下 User 对象
public class User {
//其他fields
//下面两个参数名和 params 配置的名字一致
private Integer pageNum;
private Integer pageSize;
}
//存在以下 Mapper 接口方法,你不需要在 xml 处理后两个参数
public interface CountryMapper {
List<User> selectByPageNumSize(User user);
}
//当 user 中的 pageNum!= null && pageSize!= null 时,会自动分页
List<User> list = userMapper.selectByPageNumSize(user);
2.6:ISelect
Page<User> page = PageHelper.startPage(1, 10).doSelectPage(()-> userMapper.selectGroupBy());
// 也可以直接返回PageInfo
pageInfo = PageHelper.startPage(1, 10).doSelectPageInfo(new ISelect() {
@Override
public void doSelect() {
userMapper.selectGroupBy();
}
});
3:进一步理解
3.1:PageHelper是如何实现分页的
我们知道如何使用PageHelper后,我们发现使用
PageHelper.startPage(pageNum, pageSize, orderBy)方法后的第一个select是具备分页能力的,那它是如何做到的呢?
- 相对对于JDBC这种嵌入式的分页而言,PageHelper分页是独立的,能做到独立分页查询,那它必然是通过某个拦截点进行了拦截,这样它才能够进行解耦分离出分页。
- 我们通过
PageHelper.startPage(pageNum, pageSize, orderBy)方法后的第一个select是具备分页能力的,那它必然缓存了分页信息,同时结合线程知识,这里必然使用的是本地栈ThreadLocal,即每个线程有一个本地缓存。
所以结合这两点,可以看到PageHelper实现的关键就是两点(拦截,ThreadLocal):
/**
* Mybatis拦截器方法
*
* @param invocation 拦截器入参
* @return 返回执行结果
* @throws Throwable 抛出异常
*/
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
if (autoRuntimeDialect) {
SqlUtil sqlUtil = getSqlUtil(invocation);
return sqlUtil.processPage(invocation);
} else {
if (autoDialect) {
initSqlUtil(invocation);
}
return sqlUtil.processPage(invocation);
}
}
/**
*
* @param invocation 拦截器入参
* @return 返回执行结果
* @throws Throwable 抛出异常
*/
private Object _processPage(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
final Object[] args = invocation.getArgs();
Page page = null;
//支持方法参数时,会先尝试获取Page
if (supportMethodsArguments) {
// 从线程本地变量中获取Page信息,就是我们刚刚设置的
page = getPage(args);
}
//分页信息
RowBounds rowBounds = (RowBounds) args[2];
//支持方法参数时,如果page == null就说明没有分页条件,不需要分页查询
if ((supportMethodsArguments && page == null)
//当不支持分页参数时,判断LocalPage和RowBounds判断是否需要分页
|| (!supportMethodsArguments && SqlUtil.getLocalPage() == null && rowBounds == RowBounds.DEFAULT)) {
return invocation.proceed();
} else {
//不支持分页参数时,page==null,这里需要获取
if (!supportMethodsArguments && page == null) {
page = getPage(args);
}
// 进入查看
return doProcessPage(invocation, page, args);
}
}
所以startPage方法和这里的getPage(args);这方法里应该包含了ThreadLocal中设置和获取分页参数的
public static <E> Page<E> startPage(int pageNum, int pageSize, boolean count, Boolean reasonable, Boolean pageSizeZero) {
Page<E> page = new Page(pageNum, pageSize, count);
page.setReasonable(reasonable);
page.setPageSizeZero(pageSizeZero);
Page<E> oldPage = getLocalPage();
if (oldPage != null && oldPage.isOrderByOnly()) {
page.setOrderBy(oldPage.getOrderBy());
}
setLocalPage(page);
return page;
}
// ...
protected static final ThreadLocal<Page> LOCAL_PAGE = new ThreadLocal();
protected static void setLocalPage(Page page) {
LOCAL_PAGE.set(page); // 看这里
}
3.2:使用PageHelper有何注意点
- 只有紧跟在
PageHelper.startPage方法后的**第一个Mybatis的查询(Select)**方法会被分页。 - 不要配置多个分页插件
- 对于带有
for update的sql,PageHelper会抛出运行时异常,对于这样的sql建议手动分页,毕竟这样的sql需要重视。 - 分页插件不支持嵌套结果映射: 由于嵌套结果方式会导致结果集被折叠,因此分页查询的结果在折叠后总数会减少,所以无法保证分页结果数量正确。
五:Mybatis多数据源
1:什么场景会出现多个数据源
- 场景一:不同的业务涉及的表位于不同的数据库
- 随着业务的拓展,模块解耦,服务化的拆分等,不同的业务涉及的表会放在不同的数据库中。
- 场景二:主库和从库分离(读写分离)
- 场景三:数据库的分片
- 场景四:多租户隔离
- 所有数据库表结构一致,只是不同客户的数据放在不同数据库中,通过数据库名对不同客户的数据隔离。
2:常见的多数据源的实现思路
- 针对场景一:不同的业务涉及的表位于不同的数据库 -> 考虑不同的package去隔离,不同的数据源放在不同的包下的代码中
- 针对场景二:主库和从库分离(读写分离) -> 动态数据源,通常方式使用AOP方式拦截+ThreadLocal切换。
3:简单使用
3.1:分包方式实现
- 在application.properties中配置两个数据库:
## test1 database
spring.datasource.test1.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3307/multipledatasource1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
spring.datasource.test1.username=root
spring.datasource.test1.password=root
spring.datasource.test1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
## test2 database
spring.datasource.test2.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3307/multipledatasource2?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
spring.datasource.test2.username=root
spring.datasource.test2.password=root
spring.datasource.test2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
- 建立两个数据源的配置文件:
第一个配置类
//表示这个类为一个配置类
@Configuration
// 配置mybatis的接口类放的地方
@MapperScan(
basePackages = "com.mzd.multipledatasources.mapper.test01",
sqlSessionFactoryRef = "test1SqlSessionFactory")
public class DataSourceConfig1 {
@Bean(name = "test1DataSource") // 将这个对象放入Spring容器中
@Primary // 表示这个数据源是默认数据源
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.test1") // 读取application.properties中的配置参数映射成为一个对象
public DataSource getDateSource1() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean(name = "test1SqlSessionFactory")
@Primary // 表示这个数据源是默认数据源
// @Qualifier表示查找Spring容器中名字为test1DataSource的对象
public SqlSessionFactory test1SqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("test1DataSource") DataSource datasource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(datasource);
bean.setMapperLocations(
// 设置mybatis的xml所在位置
new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath*:mapping/test01/*.xml"));
return bean.getObject();
}
@Bean("test1SqlSessionTemplate")
// 表示这个数据源是默认数据源
@Primary
public SqlSessionTemplate test1sqlsessiontemplate(
@Qualifier("test1SqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sessionfactory) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sessionfactory);
}
}
第二个配置类
@Configuration
@MapperScan(
basePackages = "com.mzd.multipledatasources.mapper.test02",
sqlSessionFactoryRef = "test2SqlSessionFactory")
public class DataSourceConfig2 {
@Bean(name = "test2DataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.test2")
public DataSource getDateSource2() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean(name = "test2SqlSessionFactory")
public SqlSessionFactory test2SqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("test2DataSource") DataSource datasource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(datasource);
bean.setMapperLocations(
new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath*:mapping/test02/*.xml"));
return bean.getObject();
}
@Bean("test2SqlSessionTemplate")
public SqlSessionTemplate test2sqlsessiontemplate(
@Qualifier("test2SqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sessionfactory) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sessionfactory);
}
}
使用这种方式注意下面几个问题:
- @Primary这个注解必须要加,因为不加的话spring将分不清楚那个为主数据源(默认数据源)
- mapper的接口、xml形式以及dao层都需要两个分开
bean.setMapperLocations();,mapper的xml形式文件位置必须要配置,不然将报错- 在service层中根据不同的业务注入不同的dao层
- 如果是主从复制- -读写分离:比如test01中负责增删改,test02中负责查询。但是需要注意的是负责增删改的数据库必须是主库
- 如果是分布式结构的话,不同模块操作各自的数据库就好
3.2:AOP方式实现
用这种方式实现多数据源的前提必须要清楚两个知识点:AOP原理和AbstractRoutingDataSource抽象类
AOP面向切面编程,简单的来说就是拦截器,只要是满足切入点条件的,都会进行拦截增强,然后进行一系列的操作
而AbstractRoutingDataSource是实现多数据源的关键,他的作用就是动态切换数据源
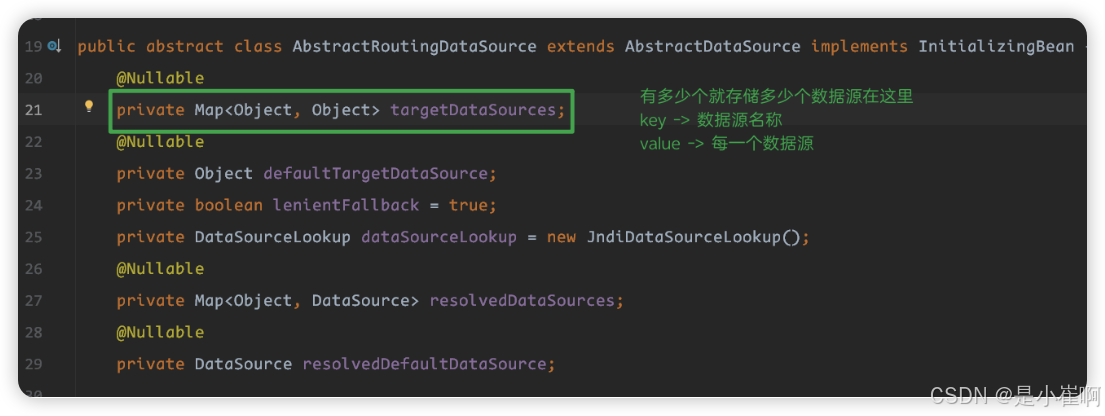
AbstractRoutingDataSource实质:有多少个数据源就存多少个数据源在targetDataSources(是AbstractRoutingDataSource的一个map类型的属性,其中value为每个数据源,key表示每个数据源的名字)这个属性中,然后根据determineCurrentLookupKey获取当前数据源在map中的key值,然后动态获取当前数据源,如果当前数据源不存并且默认数据源也不存在就抛出异常
public abstract class AbstractRoutingDataSource extends AbstractDataSource implements InitializingBean {
//多数据源map集合
private Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources;
//默认数据源
private Object defaultTargetDataSource;
//其实就是targetDataSources,后面的afterPropertiesSet()方法会将targetDataSources赋值给resolvedDataSources
private Map<Object, DataSource> resolvedDataSources;
private DataSource resolvedDefaultDataSource;
public void setTargetDataSources(Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources) {
this.targetDataSources = targetDataSources;
}
protected DataSource determineTargetDataSource() {
Assert.notNull(this.resolvedDataSources, "DataSource router not initialized");
Object lookupKey = this.determineCurrentLookupKey();
DataSource dataSource = (DataSource)this.resolvedDataSources.get(lookupKey);
if (dataSource == null && (this.lenientFallback || lookupKey == null)) {
dataSource = this.resolvedDefaultDataSource;
}
if (dataSource == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot determine target DataSource for lookup key [" + lookupKey + "]");
} else {
return dataSource;
}
}
protected abstract Object determineCurrentLookupKey();
}
- 定义一个动态的数据源
// 继承AbstractRoutingDataSource 抽象类,并重写determineCurrentLookupKey()方法
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource;
/**
* <p>
* 功能描述:定义一个动态数据源
* </p>
*
* @author cui haida
* @date 2024/05/01/15:23
*/
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return DataSourceType.getDataBaseType();
}
}
- 创建一个切换数据源类型的类
/**
* <p>
* 功能描述:创建一个切换数据源类型的类
* </p>
*
* @author cui haida
* @date 2024/05/01/15:25
*/
public class DataSourceType {
public enum DataBaseType {
TEST01, TEST02
}
// 使用ThreadLocal保证线程安全
private static final ThreadLocal<DataBaseType> TYPE = new ThreadLocal<>();
// 往当前线程里设置数据源类型
public static void setDataBaseType(DataBaseType dataBaseType) {
if (dataBaseType == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
System.err.println("[将当前数据源改为]:" + dataBaseType);
TYPE.set(dataBaseType);
}
// 获取数据源类型
public static DataBaseType getDataBaseType() {
DataBaseType dataBaseType = TYPE.get() == null ? DataBaseType.TEST01 : TYPE.get();
System.err.println("[获取当前数据源的类型为]:" + dataBaseType);
return dataBaseType;
}
// 清空数据类型
public static void clearDataBaseType() {
TYPE.remove();
}
}
- 定义多个数据源
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* <p>
* 功能描述:定义多个数据源
* </p>
*
* @author cui haida
* @date 2024/05/01/15:26
*/
@Configuration
@MapperScan(
basePackages = "com.mzd.multipledatasources.mapper", // 扫描的mapper
sqlSessionFactoryRef = "SqlSessionFactory") // 引用的sqlSessionFactory
public class DataSourceConfig {
@Primary // 指定为默认的
@Bean(name = "test1DataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.test1")
public DataSource getDateSource1() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean(name = "test2DataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.test2")
public DataSource getDateSource2() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean(name = "dynamicDataSource")
public DynamicDataSource DataSource(@Qualifier("test1DataSource") DataSource test1DataSource,
@Qualifier("test2DataSource") DataSource test2DataSource) {
Map<Object, Object> targetDataSource = new HashMap<>();
targetDataSource.put(DataSourceType.DataBaseType.TEST01, test1DataSource);
targetDataSource.put(DataSourceType.DataBaseType.TEST02, test2DataSource);
DynamicDataSource dataSource = new DynamicDataSource();
dataSource.setTargetDataSources(targetDataSource);
dataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(test1DataSource);
return dataSource;
}
@Bean(name = "SqlSessionFactory")
public SqlSessionFactory test1SqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("dynamicDataSource") DataSource dynamicDataSource)
throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dynamicDataSource);
bean.setMapperLocations(
new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath*:mapping/*.xml"));
return bean.getObject();
}
}
- AOP切入,进行数据源的切换
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* <p>
* 功能描述:数据源AOP
* </p>
*
* @author cui haida
* @date 2024/05/01/15:29
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class DataSourceAop {
// 在test1包下的使用的是test1数据源
@Before("execution(* com.study.study_demo_of_spring_boot.dynamic..*.test01*(..))")
public void setDataSource2test01() {
System.err.println("test01业务");
DataSourceType.setDataBaseType(DataSourceType.DataBaseType.TEST01);
}
// 在test2包下的使用的是test2数据源
@Before("execution(* com.study.study_demo_of_spring_boot.dynamic..*.test02*(..))")
public void setDataSource2test02() {
System.err.println("test02业务");
DataSourceType.setDataBaseType(DataSourceType.DataBaseType.TEST02);
}
}
六:Mybatis-Plus
1:支持的数据库
任何能使用 MyBatis 进行 CRUD, 并且支持标准 SQL 的数据库,具体支持情况如下:
- MySQL,Oracle,DB2,H2,HSQL,SQLite,PostgreSQL,SQLServer,Phoenix,Gauss,ClickHouse,Sybase,OceanBase,Firebird,Cubrid,Goldilocks,csiidb
- 达梦数据库,虚谷数据库,人大金仓数据库,南大通用(华库)数据库,南大通用数据库,神通数据库,瀚高数据库
2:整体架构
右面是MybatisPlus结构,左边是使用。
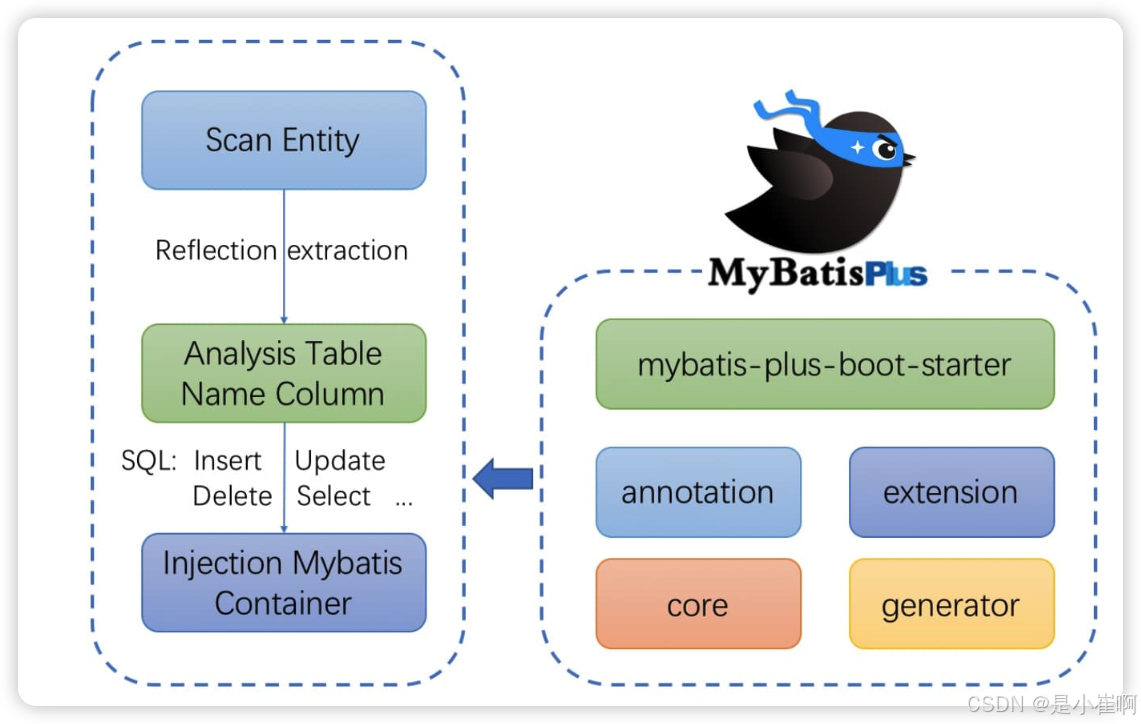
核心工作原理就是 -> 扫描实体类,然后通过反射机制分析表中的字段和实体类的属性的关系,通过调用的方法生成相应的SQL语句。最后注入
3:简单使用
数据使用的是上面的那个User, Role, user-role那个数据
3.1:Maven依赖 & 配置
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.5.2</version>
</dependency>
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: 314159
# mybatis-plus
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
cache-enabled: true # 开启二级缓存
use-generated-keys: true # 主键回填
default-executor-type: reuse # 可重用执行器,相同的SQL只进行一次预处理
use-actual-param-name: true # 默认为true,使用方法名作为参数名称
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
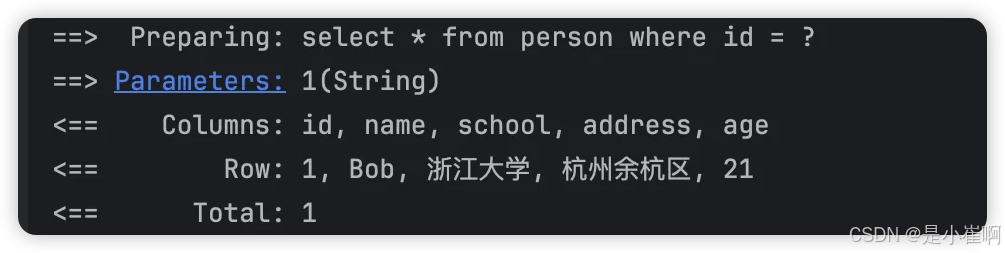
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
# 设置公共前缀
global_config:
db_config:
# 声明表的公共前缀
table_prefix: t_
# 设置主键的生成策略为自增
id_type: auto
3.2:Dao & Mapper
public interface IRoleDao extends BaseMapper<Role> {
}
public interface IUserDao extends BaseMapper<User> {
List<User> findList(UserQueryBean userQueryBean);
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql8.mybatisplus.anno.dao.IUserDao">
<resultMap type="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql8.mybatisplus.anno.entity.User" id="UserResult">
<id property="id" column="id" />
<result property="userName" column="user_name" />
<result property="password" column="password" />
<result property="email" column="email" />
<result property="phoneNumber" column="phone_number" />
<result property="description" column="description" />
<result property="createTime" column="create_time" />
<result property="updateTime" column="update_time" />
<collection property="roles" ofType="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql8.mybatisplus.anno.entity.Role">
<result property="id" column="id" />
<result property="name" column="name" />
<result property="roleKey" column="role_key" />
<result property="description" column="description" />
<result property="createTime" column="create_time" />
<result property="updateTime" column="update_time" />
</collection>
</resultMap>
<sql id="selectUserSql">
select u.id, u.password, u.user_name, u.email, u.phone_number, u.description, u.create_time, u.update_time, r.name, r.role_key, r.description, r.create_time, r.update_time
from tb_user u
left join tb_user_role ur on u.id=ur.user_id
inner join tb_role r on ur.role_id=r.id
</sql>
<select id="findList" parameterType="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql8.mybatisplus.anno.entity.query.UserQueryBean" resultMap="UserResult">
<include refid="selectUserSql"/>
where u.id != 0
<if test="userName != null and userName != ''">
AND u.user_name like concat('%', #{user_name}, '%')
</if>
<if test="description != null and description != ''">
AND u.description like concat('%', #{description}, '%')
</if>
<if test="phoneNumber != null and phoneNumber != ''">
AND u.phone_number like concat('%', #{phoneNumber}, '%')
</if>
<if test="email != null and email != ''">
AND u.email like concat('%', #{email}, '%')
</if>
</select>
</mapper>
3.3:定义Service接口和实现类
User
public interface IUserService extends IService<User> {
List<User> findList(UserQueryBean userQueryBean);
}
@Service
public class UserDoServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<IUserDao, User> implements IUserService {
@Override
public List<User> findList(UserQueryBean userQueryBean) {
return baseMapper.findList(userQueryBean);
}
}
Role
public interface IRoleService extends IService<Role> {
List<Role> findList(RoleQueryBean roleQueryBean);
}
@Service
public class RoleDoServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<IRoleDao, Role> implements IRoleService {
@Override
public List<Role> findList(RoleQueryBean roleQueryBean) {
return lambdaQuery().like(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(roleQueryBean.getName()), Role::getName, roleQueryBean.getName())
.like(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(roleQueryBean.getDescription()), Role::getDescription, roleQueryBean.getDescription())
.like(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(roleQueryBean.getRoleKey()), Role::getRoleKey, roleQueryBean.getRoleKey())
.list();
}
}
3.4:分页配置
通过配置内置的MybatisPlusInterceptor拦截器。
Configuration
public class MyBatisConfig {
@Bean
public PaginationInnerInterceptor paginationInnerInterceptor() {
return new PaginationInnerInterceptor();
}
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor() {
MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
mybatisPlusInterceptor.addInnerInterceptor(paginationInnerInterceptor());
return mybatisPlusInterceptor;
}
}
Page<Person> page = new Page<>(1, 3);
Wrapper<Person> wrapper = new Wrapper<>();
wrapper.like("user_name", "a")
.between("age", 20, 30)
.isNotNull("email")
.orderByASC("age") // 按照年龄升序排序
.orderByDESC("uid"); // 如果年龄相同,按照uid降序排序
Page<Person> page1 = personMapper.selectPage(page, wrapper);
4:较好实践总结
- Mapper层:继承
BaseMapper
public interface IRoleDao extends BaseMapper<Role> {
}
- Service层:继承
ServiceImpl并实现对应接口
public class RoleDoServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<IRoleDao, Role> implements IRoleService {
}
- Lambda函数式查询
@Override
public List<Role> findList(RoleQueryBean roleQueryBean) {
return lambdaQuery().like(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(roleQueryBean.getName()), Role::getName, roleQueryBean.getName())
.like(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(roleQueryBean.getDescription()), Role::getDescription, roleQueryBean.getDescription())
.like(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(roleQueryBean.getRoleKey()), Role::getRoleKey, roleQueryBean.getRoleKey())
.list();
}
- 分页采用内置MybatisPlusInterceptor
/**
* inject pagination interceptor.
*
* @return pagination
*/
@Bean
public PaginationInnerInterceptor paginationInnerInterceptor() {
return new PaginationInnerInterceptor();
}
/**
* add pagination interceptor.
*
* @return MybatisPlusInterceptor
*/
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor() {
MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
mybatisPlusInterceptor.addInnerInterceptor(paginationInnerInterceptor());
return mybatisPlusInterceptor;
}
- 对于复杂的关联查询,可以配置原生xml方式, 在其中自定义ResultMap
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql8.mybatisplus.anno.dao.IUserDao">
<resultMap type="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql8.mybatisplus.anno.entity.User" id="UserResult">
<id property="id" column="id" />
<result property="userName" column="user_name" />
<result property="password" column="password" />
<result property="email" column="email" />
<result property="phoneNumber" column="phone_number" />
<result property="description" column="description" />
<result property="createTime" column="create_time" />
<result property="updateTime" column="update_time" />
<collection property="roles" ofType="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql8.mybatisplus.anno.entity.Role">
<result property="id" column="id" />
<result property="name" column="name" />
<result property="roleKey" column="role_key" />
<result property="description" column="description" />
<result property="createTime" column="create_time" />
<result property="updateTime" column="update_time" />
</collection>
</resultMap>
<sql id="selectUserSql">
select u.id, u.password, u.user_name, u.email, u.phone_number, u.description, u.create_time, u.update_time, r.name, r.role_key, r.description, r.create_time, r.update_time
from tb_user u
left join tb_user_role ur on u.id=ur.user_id
inner join tb_role r on ur.role_id=r.id
</sql>
<select id="findList" parameterType="tech.pdai.springboot.mysql8.mybatisplus.anno.entity.query.UserQueryBean" resultMap="UserResult">
<include refid="selectUserSql"/>
where u.id != 0
<if test="userName != null and userName != ''">
AND u.user_name like concat('%', #{user_name}, '%')
</if>
<if test="description != null and description != ''">
AND u.description like concat('%', #{description}, '%')
</if>
<if test="phoneNumber != null and phoneNumber != ''">
AND u.phone_number like concat('%', #{phoneNumber}, '%')
</if>
<if test="email != null and email != ''">
AND u.email like concat('%', #{email}, '%')
</if>
</select>
</mapper>
除了分页插件之外还提供了哪些插件?
插件都是基于拦截器实现的,MyBatis-Plus提供了如下插件:
- 自动分页: PaginationInnerInterceptor
- 多租户: TenantLineInnerInterceptor
- 动态表名: DynamicTableNameInnerInterceptor
- 乐观锁: OptimisticLockerInnerInterceptor
- sql 性能规范: IllegalSQLInnerInterceptor
- 防止全表更新与删除: BlockAttackInnerInterceptor
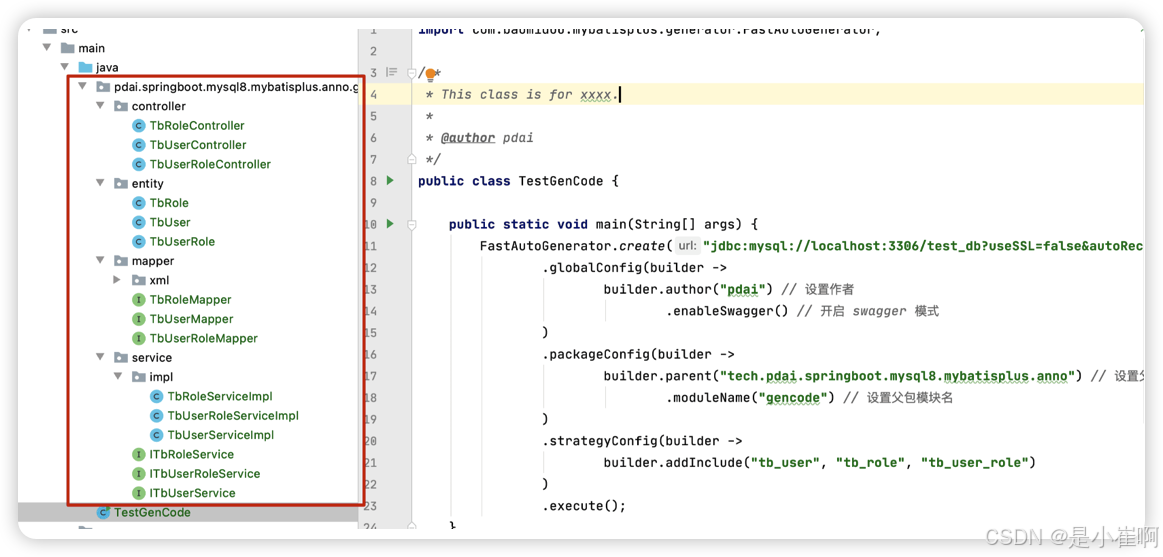
5:代码自动生成
5.1:模板引擎
由于CRUD的工作占了普通开发很多工作,而这些工作是重复的,所以出现了此类的代码生成工具。
这些工具通过模板引擎来生成代码,常见于三方集成工具,IDE插件等等
什么是模板引擎
模板引擎可以在代码生成过程中减少大量机械重复工作,大大提高开发效率,良好的设计使得代码重用,后期维护都降低成本。
一个好的模板引擎的使用要考虑的方面无外乎:功能是否强大,使用是否简单,整合性、扩展性与灵活性,性能。
5.2:简单示例
- 引入依赖:包括mybatis-plus-generator和默认的模板引擎velocity依赖的velocity-engine-core。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-generator</artifactId>
<version>3.5.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.velocity</groupId>
<artifactId>velocity-engine-core</artifactId>
<version>2.0</version>
</dependency>
- 代码生成配置
public class TestGenCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FastAutoGenerator.create("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test_db?useSSL=false&autoReconnect=true&characterEncoding=utf8", "test", "bfXa4Pt2lUUScy8jakXf")
// 全局设置
.globalConfig(builder ->
builder.author("pdai") // 设置作者
.enableSwagger() // 开启 swagger 模式
)
// 包设置
.packageConfig(builder ->
builder.parent("tech.pdai.springboot.mysql8.mybatisplus.anno") // 设置父包名
.moduleName("gencode") // 设置父包模块名
)
// 数据库指定
.strategyConfig(builder ->
builder.addInclude("tb_user", "tb_role", "tb_user_role")
)
.execute();
}
}
下面是全一点的配置说明
package com.example.demo.generator;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.FastAutoGenerator;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.config.rules.NamingStrategy;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.generator.engine.FreemarkerTemplateEngine;
/**
* @author cuihaida
*/
public class CodeGenerator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String dbUrl = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spkcgl_demo?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false";
String user = "root";
String password = "314159";
String outPut = "D:\\project\\test2\\demo\\src\\main\\java";
FastAutoGenerator.create(dbUrl, user, password)
.globalConfig(builder -> {
builder.author("cuihaida") // 设置作者
.disableOpenDir() // 覆盖已生成文件
// .enableSwagger() // 是否允许swagger
.outputDir(outPut); // 指定输出目录
})
.packageConfig(builder -> {
builder.parent("com.example") // 设置父包名
.moduleName("demo") // 设置父包模块名
.entity("dao.po");
})
// 策略配置
.strategyConfig(builder -> {
builder.addInclude("spkcgl_f_xiaosspjl") // 表名
.entityBuilder()
.enableLombok()// 是否使用lombok注解
.enableTableFieldAnnotation()// 生成的实体类字段上是否加注解 @TableField("数据库字段名称")
.naming(NamingStrategy.underline_to_camel) //数据库表映射到实体的命名策略:下划线转驼峰命
.columnNaming(NamingStrategy.underline_to_camel) //数据库表字段映射到实体的命名策略:下划线转驼峰命
; // 设置过滤表前缀
})
// 使用Freemarker引擎模板,默认的是Velocity引擎模板
.templateEngine(new FreemarkerTemplateEngine())
.execute();
}
}
5.3:进一步理解
代码生成的基本原理
配置的装载, FastAutoGenerator本质上就是通过builder注入各种配置,并将它交给代码生成主类:AutoGenerator
public void execute() {
new AutoGenerator(this.dataSourceConfigBuilder.build())
// 全局配置
.global(this.globalConfigBuilder.build())
// 包配置
.packageInfo(this.packageConfigBuilder.build())
// 策略配置
.strategy(this.strategyConfigBuilder.build())
// 注入配置
.injection(this.injectionConfigBuilder.build())
// 模板配置
.template(this.templateConfigBuilder.build())
// 执行
.execute(this.templateEngine);
}
AutoGenerator中execute方法,包括初始化配置和模板引擎(默认是Velocity),然后将配置交给模板引擎初始化执行文件输出
/**
* 生成代码
*
* @param templateEngine 模板引擎
*/
public void execute(AbstractTemplateEngine templateEngine) {
logger.debug("==========================准备生成文件...==========================");
// 初始化配置
if (null == config) {
config = new ConfigBuilder(packageInfo, dataSource, strategy, template, globalConfig, injection);
}
if (null == templateEngine) {
// 为了兼容之前逻辑,采用 Velocity 引擎 【 默认 】
templateEngine = new VelocityTemplateEngine();
}
templateEngine.setConfigBuilder(config);
// 模板引擎初始化执行文件输出
templateEngine.init(config).batchOutput().open();
logger.debug("==========================文件生成完成!!!==========================");
}
模板引擎中batchOuput方法中,包含获取表的信息并根据模板来生成类文件。
@NotNull
public AbstractTemplateEngine batchOutput() {
try {
ConfigBuilder config = this.getConfigBuilder();
List<TableInfo> tableInfoList = config.getTableInfoList();
tableInfoList.forEach(tableInfo -> {
Map<String, Object> objectMap = this.getObjectMap(config, tableInfo);
Optional.ofNullable(config.getInjectionConfig()).ifPresent(t -> {
t.beforeOutputFile(tableInfo, objectMap);
// 输出自定义文件
outputCustomFile(t.getCustomFile(), tableInfo, objectMap);
});
// entity
outputEntity(tableInfo, objectMap);
// mapper and xml
outputMapper(tableInfo, objectMap);
// service
outputService(tableInfo, objectMap);
// controller
outputController(tableInfo, objectMap);
});
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("无法创建文件,请检查配置信息!", e);
}
return this;
}
获取表的列表,由ConfigBuilder完成
public List<TableInfo> getTableInfoList() {
if (tableInfoList.isEmpty()) {
// TODO 暂时不开放自定义
List<TableInfo> tableInfos = new IDatabaseQuery.DefaultDatabaseQuery(this).queryTables();
if (!tableInfos.isEmpty()) {
this.tableInfoList.addAll(tableInfos);
}
}
return tableInfoList;
}
然后获取上述单个表(tableInfo)的具体信息(objectMap)
/**
* 渲染对象 MAP 信息
*
* @param config 配置信息
* @param tableInfo 表信息对象
* @return ignore
*/
@NotNull
public Map<String, Object> getObjectMap(@NotNull ConfigBuilder config, @NotNull TableInfo tableInfo) {
StrategyConfig strategyConfig = config.getStrategyConfig();
Map<String, Object> controllerData = strategyConfig.controller().renderData(tableInfo);
Map<String, Object> objectMap = new HashMap<>(controllerData);
Map<String, Object> mapperData = strategyConfig.mapper().renderData(tableInfo);
objectMap.putAll(mapperData);
Map<String, Object> serviceData = strategyConfig.service().renderData(tableInfo);
objectMap.putAll(serviceData);
Map<String, Object> entityData = strategyConfig.entity().renderData(tableInfo);
objectMap.putAll(entityData);
objectMap.put("config", config);
objectMap.put("package", config.getPackageConfig().getPackageInfo());
GlobalConfig globalConfig = config.getGlobalConfig();
objectMap.put("author", globalConfig.getAuthor());
objectMap.put("kotlin", globalConfig.isKotlin());
objectMap.put("swagger", globalConfig.isSwagger());
objectMap.put("date", globalConfig.getCommentDate());
// 启用 schema 处理逻辑
String schemaName = "";
if (strategyConfig.isEnableSchema()) {
// 存在 schemaName 设置拼接 . 组合表名
schemaName = config.getDataSourceConfig().getSchemaName();
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(schemaName)) {
schemaName += ".";
tableInfo.setConvert(true);
}
}
objectMap.put("schemaName", schemaName);
objectMap.put("table", tableInfo);
objectMap.put("entity", tableInfo.getEntityName());
return objectMap;
}
根据TableInfo和objectMap输出类文件,以输出Entity实体类为例
/**
* 输出实体文件
*
* @param tableInfo 表信息
* @param objectMap 渲染数据
* @since 3.5.0
*/
protected void outputEntity(@NotNull TableInfo tableInfo, @NotNull Map<String, Object> objectMap) {
String entityName = tableInfo.getEntityName();
String entityPath = getPathInfo(OutputFile.entity);
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(entityName) && StringUtils.isNotBlank(entityPath)) {
getTemplateFilePath(template -> template.getEntity(getConfigBuilder().getGlobalConfig().isKotlin())).ifPresent((entity) -> {
String entityFile = String.format((entityPath + File.separator + "%s" + suffixJavaOrKt()), entityName);
outputFile(new File(entityFile), objectMap, entity, getConfigBuilder().getStrategyConfig().entity().isFileOverride());
});
}
}
在outputFile中来确定生成文件的名字和路径
/**
* 输出文件
*
* @param file 文件
* @param objectMap 渲染信息
* @param templatePath 模板路径
* @param fileOverride 是否覆盖已有文件
* @since 3.5.2
*/
protected void outputFile(@NotNull File file, @NotNull Map<String, Object> objectMap, @NotNull String templatePath, boolean fileOverride) {
if (isCreate(file, fileOverride)) {
try {
// 全局判断【默认】
boolean exist = file.exists();
if (!exist) {
File parentFile = file.getParentFile();
FileUtils.forceMkdir(parentFile);
}
writer(objectMap, templatePath, file);
} catch (Exception exception) {
throw new RuntimeException(exception);
}
}
}
最后通过writer方法生成文件
/**
* 将模板转化成为文件
*
* @param objectMap 渲染对象 MAP 信息
* @param templatePath 模板文件
* @param outputFile 文件生成的目录
* @throws Exception 异常
* @since 3.5.0
*/
public void writer(@NotNull Map<String, Object> objectMap, @NotNull String templatePath, @NotNull File outputFile) throws Exception {
this.writer(objectMap, templatePath, outputFile.getPath());
logger.debug("模板:" + templatePath + "; 文件:" + outputFile);
}
本质上就是调用模板引擎来生成
@Override
public void writer(@NotNull Map<String, Object> objectMap, @NotNull String templatePath, @NotNull File outputFile) throws Exception {
Template template = velocityEngine.getTemplate(templatePath, ConstVal.UTF8);
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(outputFile);
OutputStreamWriter ow = new OutputStreamWriter(fos, ConstVal.UTF8);
BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(ow)) {
template.merge(new VelocityContext(objectMap), writer);
}
}
比如Entity,velocityEngine.getTemplate会获取如下entity.vm模板生成Entity的类文件。
package ${package.Entity};
#foreach($pkg in ${table.importPackages})
import ${pkg};
#end
#if(${swagger})
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
#end
/**
* <p>
* $!{table.comment}
* </p>
*
* @author ${author}
* @since ${date}
*/
#if(${table.convert})
@TableName("${schemaName}${table.name}")
#end
#if(${swagger})
@ApiModel(value = "${entity}对象", description = "$!{table.comment}")
#end
#if(${superEntityClass})
class ${entity} : ${superEntityClass}#if(${activeRecord})<${entity}>#end() {
#elseif(${activeRecord})
class ${entity} : Model<${entity}>() {
#elseif(${entitySerialVersionUID})
class ${entity} : Serializable {
#else
class ${entity} {
#end
## ---------- BEGIN 字段循环遍历 ----------
#foreach($field in ${table.fields})
#if(${field.keyFlag})
#set($keyPropertyName=${field.propertyName})
#end
#if("$!field.comment" != "")
#if(${swagger})
@ApiModelProperty(value = "${field.comment}")
#else
/**
* ${field.comment}
*/
#end
#end
#if(${field.keyFlag})
## 主键
#if(${field.keyIdentityFlag})
@TableId(value = "${field.annotationColumnName}", type = IdType.AUTO)
#elseif(!$null.isNull(${idType}) && "$!idType" != "")
@TableId(value = "${field.annotationColumnName}", type = IdType.${idType})
#elseif(${field.convert})
@TableId("${field.annotationColumnName}")
#end
## 普通字段
#elseif(${field.fill})
## ----- 存在字段填充设置 -----
#if(${field.convert})
@TableField(value = "${field.annotationColumnName}", fill = FieldFill.${field.fill})
#else
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.${field.fill})
#end
#elseif(${field.convert})
@TableField("${field.annotationColumnName}")
#end
## 乐观锁注解
#if(${field.versionField})
@Version
#end
## 逻辑删除注解
#if(${field.logicDeleteField})
@TableLogic
#end
#if(${field.propertyType} == "Integer")
var ${field.propertyName}: Int? = null
#else
var ${field.propertyName}: ${field.propertyType}? = null
#end
#end
## ---------- END 字段循环遍历 ----------
#if(${entityColumnConstant})
companion object {
#foreach($field in ${table.fields})
const val ${field.name.toUpperCase()} : String = "${field.name}"
#end
}
#end
#if(${activeRecord})
override fun pkVal(): Serializable? {
#if(${keyPropertyName})
return ${keyPropertyName}
#else
return null
#end
}
#end
override fun toString(): String {
return "${entity}{" +
#foreach($field in ${table.fields})
#if($!{foreach.index}==0)
"${field.propertyName}=" + ${field.propertyName} +
#else
", ${field.propertyName}=" + ${field.propertyName} +
#end
#end
"}"
}
}
同理生成mapper, service, controller等文件
如何看MyBatis-Plus生成代码的功能 -> 食之无味,弃之可惜
- 从上面的源码我们可以看出,生成类只适合单表结构,表的关联无法处理;
- 对于单表的CRUD类,如果可以自动化生成,必然是可以很好的抽象的,而BaseMapper, BaseServiceImpl的封装已经足够了;
- 通常真正可以通过一体化集成前端代码的生成,才有一定的意义;
- 当然少部分情况快速提供接口的可以考虑,不过其实也省不了什么时间。
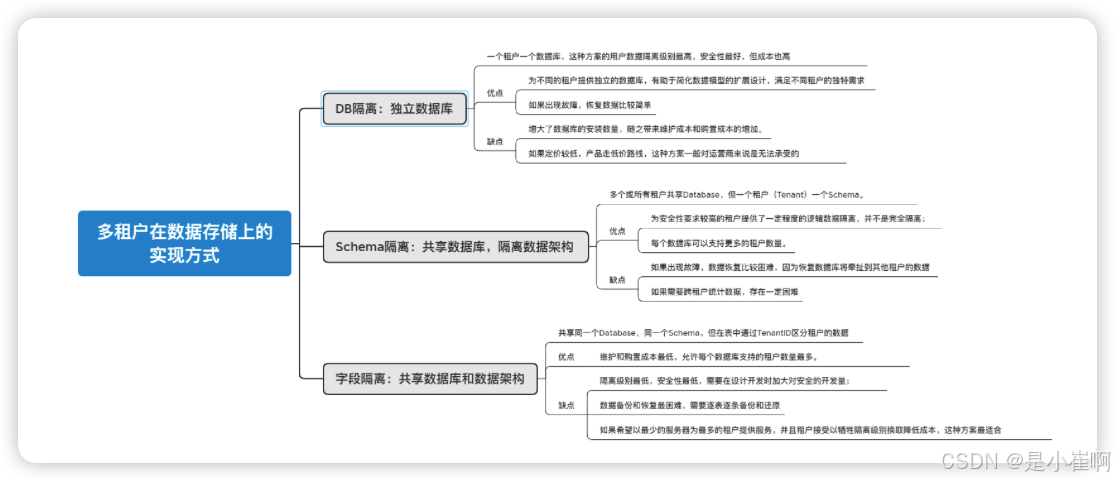
6:基于字段隔离的多租户
6.1:预备知识
什么是多租户?
多租户技术(英语:multi-tenancy technology)或称多重租赁技术,是一种软件架构技术,它是在探讨与实现如何于多用户的环境下共用相同的系统或程序组件,并且仍可确保各用户间数据的隔离性。
多租户简单来说是指一个单独的实例可以为多个组织服务。多租户技术为共用的数据中心内如何以单一系统架构与服务提供多数客户端相同甚至可定制化的服务,并且仍然可以保障客户的数据隔离。
一个支持多租户技术的系统需要在设计上对它的数据和配置进行虚拟分区,从而使系统的每个租户或称组织都能够使用一个单独的系统实例,并且每个租户都可以根据自己的需求对租用的系统实例进行个性化配置。
多租户技术可以实现多个租户之间共享系统实例,同时又可以实现租户的系统实例的个性化定制。
通过使用多租户技术可以保证系统共性的部分被共享,个性的部分被单独隔离。
通过在多个租户之间的资源复用,运营管理维护资源,有效节省开发应用的成本。
而且,在租户之间共享应用程序的单个实例,可以实现当应用程序升级时,所有租户可以同时升级。
同时,因为多个租户共享一份系统的核心代码,因此当系统升级时,只需要升级相同的核心代码即可
多租户在数据存储上有哪些实现方式?
6.2:简单实现
构建表
这里沿用之前的test_db,在表中添加tenant_id,并命名为新的schema test_db_tenant。
-- -------------------- tb_role -----------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `tb_role`;
CREATE TABLE `tb_role` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`tenant_id` int DEFAULT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`role_key` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`description` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`create_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL,
`update_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb3;
LOCK TABLES `tb_role` WRITE;
INSERT INTO `tb_role` VALUES (1,1,'admin','admin','admin','2021-09-08 17:09:15','2021-09-08 17:09:15');
UNLOCK TABLES;
-- -------------------- tb_user -----------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `tb_user`;
CREATE TABLE `tb_user` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`tenant_id` int DEFAULT NULL,
`user_name` varchar(45) NOT NULL,
`password` varchar(45) NOT NULL,
`email` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL,
`phone_number` int DEFAULT NULL,
`description` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`create_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL,
`update_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb3;
LOCK TABLES `tb_user` WRITE;
INSERT INTO `tb_user` VALUES (1,1,'pdai','dfasdf','[email protected]',1212121213,'afsdfsaf','2021-09-08 17:09:15','2021-09-08 17:09:15');
-- -------------------- tb_user_role -----------------------
UNLOCK TABLES;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `tb_user_role`;
CREATE TABLE `tb_user_role` (
`user_id` int NOT NULL,
`role_id` int NOT NULL,
`tenant_id` int NOT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb3;
LOCK TABLES `tb_user_role` WRITE;
INSERT INTO `tb_user_role` VALUES (1,1,1);
UNLOCK TABLES;
依赖和配置
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.28</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
</dependency>
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
cache-enabled: true
use-generated-keys: true
default-executor-type: REUSE
use-actual-param-name: true
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl # 输出SQL log 方便 debug
MyBatis-Plus配置
import java.util.List;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.MybatisPlusInterceptor;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.handler.TenantLineHandler;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.inner.PaginationInnerInterceptor;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.inner.TenantLineInnerInterceptor;
import net.sf.jsqlparser.expression.Expression;
import net.sf.jsqlparser.expression.LongValue;
import net.sf.jsqlparser.schema.Column;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* MyBatis-plus configuration, add pagination interceptor.
*/
@Configuration
public class MyBatisConfig {
@Bean
public PaginationInnerInterceptor paginationInnerInterceptor() {
return new PaginationInnerInterceptor();
}
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor() {
MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
// TenantLineInnerInterceptor
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new TenantLineInnerInterceptor(new TenantLineHandler() {
@Override
public Expression getTenantId() {
// 实际可以将TenantId放在threadLocale中(比如xxxxContext中),并获取。
return new LongValue(1);
}
@Override
public String getTenantIdColumn() {
return "tenant_id";
}
@Override
public boolean ignoreTable(String tableName) {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean ignoreInsert(List<Column> columns, String tenantIdColumn) {
return TenantLineHandler.super.ignoreInsert(columns, tenantIdColumn);
}
}));
// 如果用了分页插件注意先 add TenantLineInnerInterceptor 再 add PaginationInnerInterceptor
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new PaginationInnerInterceptor());
return interceptor;
}
}
七:mybatis plus高级用法
1:日志的优雅打印
在使用MyBatis或者MyBatis-Plus作为ORM框架的时候,会发现默认的日志输出是下面这样的:
在参数少并且SQL简单的情况下,这样的SQL我们能通过手动去替换占位符,来获取到真正执行的SQL。
但是如果是比较复杂的SQL,或者查询参数比较多的话,一个个替换就比较费时费力了。
1.1:MyBatis Plugin
于是我们就可以使用MyBatis对外暴露出的Interceptor接口,来手动实现一个能优雅地打印日志的插件。
平常像用的比较多的PageHelper,就是一个MyBatis的插件,实现原理和我们这次要做的功能十分相似。
最终实现后的效果是下面这样的:
1.2:MyBatis 插件的几个重点模块
@Intercepts 注解
这是 MyBatis 提供的一个注解,用于定义一个拦截器。一个拦截器可以拦截一个或多个方法。
@Signature 注解
这是 @Intercepts 注解的子注解,用于指定要拦截的目标方法。有下面三个参数
- type:指定要拦截的接口类型。
- method:指定要拦截的方法名。
- args:指定要拦截的方法的参数类型列表
1.3:实现一个优雅打日志的功能
首先编写一个Interceptor的实现类,具体代码如下,所有的注释都放在代码上了:
其中类上的Intercepts注解含义为:在 Executor 的 query、update 方法执行前后进行自定义的处理
其中Executor 是最底层的执行器,负责与数据库进行通信。它的职责包括创建和缓存 Statement 对象、执行 SQL 语句、处理结果集等
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.ibatis.cache.CacheKey;
import org.apache.ibatis.executor.Executor;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.BoundSql;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.ParameterMapping;
import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.*;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.MetaObject;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.ResultHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.RowBounds;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.TypeHandlerRegistry;
import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils;
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class}),
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class, CacheKey.class, BoundSql.class}),
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "update", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class})
})
@Slf4j
public class SqlInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// 计算这一次SQL执行钱后的时间,统计一下执行耗时
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object proceed = invocation.proceed();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
String printSql = null;
try {
// 通过generateSql方法拿到最终生成的SQL
printSql = generateSql(invocation);
}catch (Exception exception){
log.error("获取sql异常",exception);
}finally {
// 拼接日志打印过程
long costTime = endTime - startTime;
log.info("\n 执行SQL耗时:{}ms \n 执行SQL:{}",costTime,printSql);
}
return proceed;
}
private static String generateSql(Invocation invocation){
// 获取到BoundSql以及Configuration对象
// BoundSql 对象存储了一条具体的 SQL 语句及其相关参数信息。
// Configuration 对象保存了 MyBatis 框架运行时所有的配置信息
MappedStatement statement = (MappedStatement) invocation.getArgs()[0];
Object parameter = null;
if (invocation.getArgs().length>1){
parameter = invocation.getArgs()[1];
}
Configuration configuration = statement.getConfiguration();
BoundSql boundSql = statement.getBoundSql(parameter);
// 获取参数对象
Object parameterObject = boundSql.getParameterObject();
// 获取参数映射
List<ParameterMapping> params = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
// 获取到执行的SQL
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
// SQL中多个空格使用一个空格代替
sql = sql.replaceAll("[\\s]+", " ");
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(params) && !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(parameterObject)){
// TypeHandlerRegistry 是 MyBatis 用来管理 TypeHandler 的注册器。TypeHandler 用于在 Java 类型和 JDBC 类型之间进行转换
TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry();
// 如果参数对象的类型有对应的 TypeHandler,则使用 TypeHandler 进行处理
if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())){
sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?", Matcher.quoteReplacement(getParameterValue(parameterObject)));
}else {
// 否则,逐个处理参数映射
for (ParameterMapping param : params) {
// 获取参数的属性名
String propertyName = param.getProperty();
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
// 检查对象中是否存在该属性的 getter 方法,如果存在就取出来进行替换
if (metaObject.hasGetter(propertyName)){
Object obj = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?", Matcher.quoteReplacement(getParameterValue(obj)));
// 检查 BoundSql 对象中是否存在附加参数。附加参数可能是在动态 SQL 处理中生成的,有的话就进行替换
}else if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)){
Object obj = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?", Matcher.quoteReplacement(getParameterValue(obj)));
}else {
// 如果都没有,说明SQL匹配不上,带上“缺失”方便找问题
sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?", "缺失");
}
}
}
}
return sql;
}
private static String getParameterValue(Object object) {
String value = "";
if (object instanceof String){
value = "'" + object.toString() + "'";
}else if (object instanceof Date){
DateFormat format = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.DEFAULT, DateFormat.DEFAULT, Locale.CHINA);
value = "'" + format.format((Date) object) + "'";
} else if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(object)) {
value = object.toString();
}
return value;
}
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
// 可以通过properties配置插件参数
}
}
接着编写一个MyBatis的配置类,将这个插件注册进去
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.autoconfigure.ConfigurationCustomizer;
import com.mybatisflex.test.Interceptor.SqlInterceptor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class MyBatisConfig {
@Bean
public ConfigurationCustomizer mybatisConfigurationCustomizer() {
return configuration -> {
configuration.addInterceptor(new SqlInterceptor());
};
}
}
2:类型转换和自动填充
2.1:typeHandler类型转换
主要用到的就是Mybatis-plus中的@TableField注解中的typeHandler属性,下面通过使用TypeHandler对数据进行加解密进行演示
数据库中的用户密码、手机号、邮箱账号等从隐私性考虑,在数据库里进行加密处理,以密文方式存储。
需在存取过程中对隐私数据进行加解密处理。
TypeHandler是MyBatis提供的一个接口,它定义了Java类型和JDBC类型(即数据库类型)之间的转换规则。
如果你想对某个字段进行加解密,你可以创建一个自定义的TypeHandler。
在这个TypeHandler中,你可以在setParameter方法中进行加密,在getResult方法中进行解密。
以下是一个简单的示例:
public class EncryptTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler<String> {
@Override
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, String parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {
// 在这里进行加密
String encryptedData = encrypt(parameter);
ps.setString(i, encryptedData);
}
@Override
public String getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException {
// 在这里进行解密
String encryptedData = rs.getString(columnName);
return decrypt(encryptedData);
}
@Override
public String getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
// 在这里进行解密
String encryptedData = rs.getString(columnIndex);
return decrypt(encryptedData);
}
@Override
public String getNullableResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
// 在这里进行解密
String encryptedData = cs.getString(columnIndex);
return decrypt(encryptedData);
}
// 加密方法
private String encrypt(String data) {
// 实现你的加密逻辑
return data;
}
// 解密方法
private String decrypt(String encryptedData) {
// 实现你的解密逻辑
return encryptedData;
}
}
然后,你可以在你的Mapper XML文件或者Java实体类中使用这个TypeHandler。
public class User {
// 使用自定义的TypeHandler
@TableField(typeHandler = EncryptTypeHandler.class)
private String sensitiveData;
}
2.2:fill自动填充
MyBatis-Plus 支持多种属性自动填充策略,包括创建时间填充、更新时间填充等。以下是一个使用 MyBatis-Plus 实现自动填充的示例
- 首先,在你的实体类中添加自动填充的字段,并使用
@TableField注解指定填充策略。
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableField;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.FieldFill;
public class Entity {
// 其他字段...
// 自动填充创建时间
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private Date createTime;
// 自动填充更新时间
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Date updateTime;
}
- 实现
MetaObjectHandler接口,并重写insertFill和updateFill方法来指定自动填充的值。
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.handlers.MetaObjectHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.MetaObject;
import java.util.Date;
@Component
public class MyMetaObjectHandler implements MetaObjectHandler {
@Override
public void insertFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
this.strictInsertFill(metaObject, "createTime", Date.class, new Date()); // 创建时间
this.strictInsertFill(metaObject, "updateTime", Date.class, new Date()); // 更新时间
}
@Override
public void updateFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
this.strictUpdateFill(metaObject, "updateTime", Date.class, new Date()); // 更新时间
}
}
3:三大注解其他属性说明
3.1:@TableName
- 描述:表名注解,标识实体类对应的表
- 使用位置:实体类
| 属性 | 类型 | 必须指定 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| value | String | 否 | “” | 表名 |
| schema | String | 否 | “” | schema |
| keepGlobalPrefix | boolean | 否 | false | 是否保持使用全局的 tablePrefix 的值(当全局 tablePrefix 生效时) |
| resultMap | String | 否 | “” | xml 中 resultMap 的 id(用于满足特定类型的实体类对象绑定) |
| autoResultMap | boolean | 否 | false | 是否自动构建 resultMap 并使用 如果设置 resultMap 则不会进行 resultMap 的自动构建与注入 |
| excludeProperty | String[] | 否 | {} | 需要排除的属性名 @since 3.3.1 |
3.2:@TableId
- 描述:主键注解,标识实体类中的主键字段
- 使用位置:实体类的主键字段
| 属性 | 类型 | 必须指定 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| value | String | 否 | “” | 表名 |
| type | Enum | 否 | IdType.NONE | 指定主键类型 |
IdType的类型有:
| 值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| AUTO | 数据库 ID 自增 |
| NONE | 无状态,该类型为未设置主键类型(注解里等于跟随全局,全局里约等于 INPUT) |
| INPUT | insert 前自行 set 主键值 |
| ASSIGN_ID | 分配 ID(主键类型为 Number(Long 和 Integer)或 String)(since 3.3.0) 使用接口IdentifierGenerator的方法nextId(默认实现类为DefaultIdentifierGenerator雪花算法) |
| ASSIGN_UUID | 分配 UUID,主键类型为 String(since 3.3.0),使用接口IdentifierGenerator的方法nextUUID(默认 default 方法) |
| ID_WORKER | 分布式全局唯一ID长整型类型(please use ASSIGN_ID) |
| UUID | 32 位 UUID 字符串(please use ASSIGN_UUID) |
| ID_WORKER_STR | 分布式全局唯一 ID 字符串类型(please use ASSIGN_ID) |
这里比较常见的有三种:
AUTO:利用数据库的id自增长INPUT:手动生成idASSIGN_ID:雪花算法生成Long类型的全局唯一id,这是默认的ID策略
3.3:@TableField
描述:普通字段注解
一般情况下我们并不需要给字段添加@TableField注解,一些特殊情况除外:
- 成员变量名与数据库字段名不一致
- 成员变量是以
isXXX命名,按照JavaBean的规范,MybatisPlus识别字段时会把is去除,这就导致与数据库不符。 - 成员变量名与数据库一致,但是与数据库的关键字冲突。使用
@TableField注解给字段名添加转义字符
| 属性 | 类型 | 必填 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| value | String | 否 | “” | 数据库字段名 |
| exist | boolean | 否 | true | 是否为数据库表字段 |
| condition | String | 否 | “” | 字段 where 实体查询比较条件 有值设置则按设置的值为准,没有则为默认全局的 %s=#{%s} |
| update | String | 否 | “” | 字段 update set 部分注入 例如:当在version字段上注解update=“%s+1” 表示更新时会 set version=version+1 (该属性优先级高于EL属性) |
| insertStrategy | Enum | 否 | FieldStrategy.DEFAULT | |
| updateStrategy | Enum | 否 | FieldStrategy.DEFAULT | |
| whereStrategy | Enum | 否 | FieldStrategy.DEFAULT | |
| fill | Enum | 否 | FieldFill.DEFAULT | 字段自动填充策略 |
| select | boolean | 否 | true | 是否进行 select 查询 |
| keepGlobalFormat | boolean | 否 | false | 是否保持使用全局的 format 进行处理 |
| jdbcType | JdbcType | 否 | JdbcType.UNDEFINED | JDBC 类型 (该默认值不代表会按照该值生效) |
| typeHandler | TypeHander | 否 | 类型处理器 (该默认值不代表会按照该值生效) | |
| numericScale | String | 否 | “” | 指定小数点后保留的位数 |
4:常见配置说明
MybatisPlus也支持基于yaml文件的自定义配置,详见官方文档:https://www.baomidou.com/reference/
大多数的配置都有默认值,因此我们都无需配置。但还有一些是没有默认值的,例如:
- 实体类的别名扫描包
- 全局id类型
mybatis-plus:
type-aliases-package: com.itheima.mp.domain.po
global-config:
db-config:
id-type: auto # 全局id类型为自增长
需要注意的是,MyBatisPlus也支持手写SQL的,而mapper文件的读取地址可以自己配置:
mybatis-plus:
mapper-locations: "classpath*:/mapper/**/*.xml" # Mapper.xml文件地址,当前这个是默认值。
八:mybatis-plus-join
详细功能说明见官网:https://ylctmh.com
众所周知,Mybatis Plus 封装的 mapper 不支持 join,如果需要支持就必须自己去实现
这个时候mybatis-plus-join应孕而生
<!-- mybatis plus version >= 3.4.0 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.yulichang</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-join-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.4.4</version>
</dependency>
1:核心类
1.1:MPJLambdaWrapper
class test {
@Resource
private UserMapper userMapper;
void testJoin() {
//和Mybatis plus一致,MPJLambdaWrapper的泛型必须是主表的泛型,并且要用主表的Mapper来调用
MPJLambdaWrapper<UserDO> wrapper = new MPJLambdaWrapper<UserDO>()
.selectAll(UserDO.class)//查询user表全部字段
.select(UserAddressDO::getTel)//查询user_address tel 字段
.selectAs(UserAddressDO::getAddress, UserDTO::getUserAddress)//别名 t.address AS userAddress
.select(AreaDO::getProvince, AreaDO::getCity)
.leftJoin(UserAddressDO.class, UserAddressDO::getUserId, UserDO::getId)
.leftJoin(AreaDO.class, AreaDO::getId, UserAddressDO::getAreaId)
.eq(UserDO::getId, 1)
.like(UserAddressDO::getTel, "1")
.gt(UserDO::getId, 5);
//连表查询 返回自定义ResultType
List<UserDTO> list = userMapper.selectJoinList(UserDTO.class, wrapper);
//分页查询 (需要启用 mybatis plus 分页插件)
Page<UserDTO> listPage = userMapper.selectJoinPage(new Page<>(2, 10), UserDTO.class, wrapper);
}
}
-- 对应SQL如下
SELECT
t.id, t.name, t.sex, t.head_img,
t1.tel, t1.address AS userAddress,
t2.province, t2.city
FROM
user t
LEFT JOIN user_address t1 ON t1.user_id = t.id
LEFT JOIN area t2 ON t2.id = t1.area_id
WHERE (
t.id = ?
AND t1.tel LIKE ?
AND t.id > ?)
MPJLambdaWrapper 还有很多其他的功能
https://gitee.com/best_handsome/mybatis-plus-join/wikis/selectFunc()?sort_id=4082479https://gitee.com/best_handsome/mybatis-plus-join/wikis/leftJoin?sort_id=3496671
多条件示例:
.leftJoin(UserAddressDO.class, on -> on
.eq(UserAddressDO::getUserId,UserDO::getId)
.eq(UserAddressDO::getId,UserDO::getId))
//自定义别名
.leftJoin(UserAddressDO.class, "addr", on -> on
.eq(UserAddressDO::getUserId,UserDO::getId)
.eq(UserAddressDO::getId,UserDO::getId))
LEFT JOIN user_address t1 ON (t1.user_id = t.id AND t1.id = t.id)
LEFT JOIN user_address addr ON (addr.user_id = t.id AND addr.id = t.id)
1.2:String形式用法(MPJQueryWrapper)
简单连表查询
class test {
@Resource
private UserMapper userMapper;
void testJoin() {
MPJQueryWrapper wrapper = new MPJQueryWrapper<UserDO>()
.selectAll(UserDO.class)
.select("addr.tel", "addr.address", "a.province")
.leftJoin("user_address addr on t.id = addr.user_id")
.rightJoin("area a on addr.area_id = a.id")
.like("addr.tel", "1")
.le("a.province", "1");
//列表查询
List<UserDTO> list = userMapper.selectJoinList(UserDTO.class, wrapper);
//分页查询 (需要启用 mybatis plus 分页插件)
Page<UserDTO> listPage = userMapper.selectJoinPage(new Page<>(1, 10), UserDTO.class, wrapper);
}
}
对应的sql如下
SELECT
t.id,
t.name,
t.sex,
t.head_img,
addr.tel,
addr.address,
a.province
FROM
user t
LEFT JOIN user_address addr on t.id = addr.user_id
RIGHT JOIN area a on addr.area_id = a.id
WHERE (
addr.tel LIKE ?
AND a.province <= ?)