6.5.1 fdisk 命令
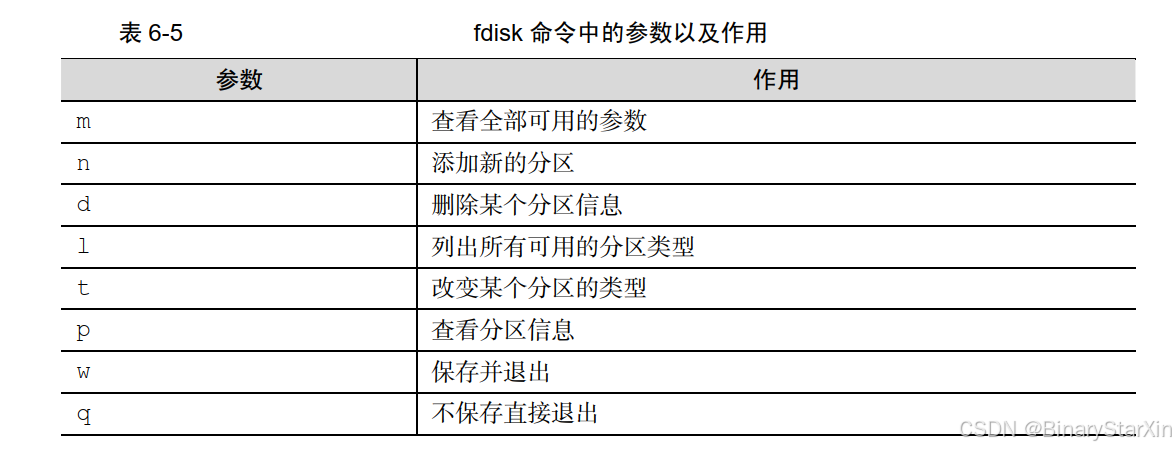
在 Linux 系统中,管理硬盘设备最常用的方法就当属 fdisk 命令了。 fdisk 命令用于管理磁盘分区,格式为“fdisk [磁盘名称]”,它提供了集添加、删除、转换分区等功能于一身的“一站式分区服务”。不过与前面讲解的直接写到命令后面的参数不同,这条命令的参数(见表 6-5)是交互式的,因此在管理硬盘设备时特别方便,可以根据需求动态调整。
我们首先使用 fdisk 命令来尝试管理/dev/sdb 硬盘设备。在看到提示信息后输入参数 p 来查看硬盘设备内已有的分区信息,其中包括了硬盘的容量大小、扇区个数等信息:
[root@linuxprobe ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Device does not contain a recognized partition table
Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x47d24a34.
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes, 41943040 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x47d24a34
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System输入参数 n 尝试添加新的分区。系统会要求您是选择继续输入参数 p 来创建主分区,还是输入参数 e 来创建扩展分区。这里输入参数 p 来创建一个主分区:
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended
Select (default p): p在确认创建一个主分区后,系统要求您先输入主分区的编号。我们在前文得知,主分区的编号范围是 1~4,因此这里输入默认的 1 就可以了。接下来系统会提示定义起始的扇区位置,这不需要改动,我们敲击回车键保留默认设置即可,系统会自动计算出最靠前的空闲扇区的位置。最后,系统会要求定义分区的结束扇区位置,这其实就是要去定义整个分区的大小是多少。我们不用去计算扇区的个数,只需要输入+2G 即可创建出一个容量为 2GB 的硬盘分区。
Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1
First sector (2048-41943039, default 2048):此处敲击回车
Using default value 2048
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-41943039, default 41943039): +2G
Partition 1 of type Linux and of size 2 GiB is set再次使用参数 p 来查看硬盘设备中的分区信息。果然就能看到一个名称为/dev/sdb1、起始扇区位置为 2048、结束扇区位置为 4196351 的主分区了。这时候千万不要直接关闭窗口,而应该敲击参数 w 后回车,这样分区信息才是真正的写入成功啦。
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes, 41943040 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x47d24a34
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 4196351 2097152 83 Linux
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.在上述步骤执行完毕之后, Linux 系统会自动把这个硬盘主分区抽象成/dev/sdb1 设备文件。我们可以使用 file 命令查看该文件的属性,但是刘遄老师在讲课和工作中发现,有些时候系统并没有自动把分区信息同步给 Linux 内核,而且这种情况似乎还比较常见(但不能算作是严重的 bug)。我们可以输入 partprobe 命令手动将分区信息同步到内核,而且一般推荐连续两次执行该命令,效果会更好。如果使用这个命令都无法解决问题,那么就重启计算机吧,这个杀手锏百试百灵,一定会有用的。
[root@linuxprobe ]# file /dev/sdb1
/dev/sdb1: cannot open (No such file or directory)
[root@linuxprobe ]# partprobe
[root@linuxprobe ]# partprobe
[root@linuxprobe ]# file /dev/sdb1
/dev/sdb1: block special如果硬件存储设备没有进行格式化,则 Linux 系统无法得知怎么在其上写入数据。因此,在对存储设备进行分区后还需要进行格式化操作。在 Linux 系统中用于格式化操作的命