系列文章目录
前言
本文通过动手实现demo和分析源码来介绍Springboot中的监听器
参考资料:https://www.imooc.com/
参考文章:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34886352/article/details/105188150
一、监听器模式例子
1.1 创建抽象类WeatherEvent
public abstract class WeatherEvent {
public abstract String getWeather();
}
创建下雨、下雪事件继承WeatherEvent
下雨事件
public class RainEvent extends WeatherEvent{
@Override
public String getWeather() {
return "rain";
}
}
下雪事件
public class SnowEvent extends WeatherEvent{
@Override
public String getWeather() {
return "snow";
}
}
1.2 创建天气监听器接口WeatherListener
public interface WeatherListener{
void onWeatherEvent(WeatherEvent event);
}
创建监听器实现WeatherListener接口
下雨监听器
@Component
public class RainListener implements WeatherListener {
@Override
public void onWeatherEvent(WeatherEvent event) {
if (event instanceof RainEvent){
System.out.println("hello "+event.getWeather());
}
}
}
下雪监听器
@Component
public class SnowListener implements WeatherListener {
@Override
public void onWeatherEvent(WeatherEvent event) {
if (event instanceof SnowEvent){
System.out.println("hello "+event.getWeather());
}
}
}
1.3 创建广播器接口
public interface EventMulticaster {
//广播事件
void multicastEvent(WeatherEvent event);
//添加监听器
void addListener(WeatherListener weatherListener);
//删除监听器
void removeListener(WeatherListener weatherListener);
}
创建抽象类实现广播器接口
@Component
public abstract class AbstractEventMulticaster implements EventMulticaster {
@Autowired
private List<WeatherListener> listenerList;
@Override
public void multicastEvent(WeatherEvent event) {
doStart();
//遍历所有监听器,调用onWeatherEvent方法
listenerList.forEach(i -> i.onWeatherEvent(event));
doEnd();
}
@Override
public void addListener(WeatherListener weatherListener) {
listenerList.add(weatherListener);
}
@Override
public void removeListener(WeatherListener weatherListener) {
listenerList.remove(weatherListener);
}
abstract void doStart();
abstract void doEnd();
}
实现天气事件广播
@Component
public class WeatherEventMulticaster extends AbstractEventMulticaster {
@Override
void doStart() {
System.out.println("begin broadcast weather event");
}
@Override
void doEnd() {
System.out.println("end broadcast weather event");
}
}
1.4 创建天气监听器代理
@Component
public class WeatherRunListener {
@Autowired
private WeatherEventMulticaster weatherEventMulticaster;
public void snow() {
weatherEventMulticaster.multicastEvent(new SnowEvent());
}
public void rain() {
weatherEventMulticaster.multicastEvent(new RainEvent());
}
}
1.5 在test中进行测试
@SpringBootTest
class Sb2ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private WeatherRunListener weatherRunListener;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
weatherRunListener.rain();
weatherRunListener.snow();
}
}
结果:
1.6 总结
实现的天气事件监听主要流程:
- 首先创建事件(rainEvent、snowEvent)
- 然后创建事件监听器(snowListener、rainListener)实现onApplicationEvent方法,在方法内嗅探当前事件是否为感兴趣的事件。
- 添加广播事件,包括添加监听器(addListener)、删除监听器(removeListener)、广播方法(multicastEvent、doStart、doEnd)
- 最后注入到WeatherRunListener类中,实现对外低耦合
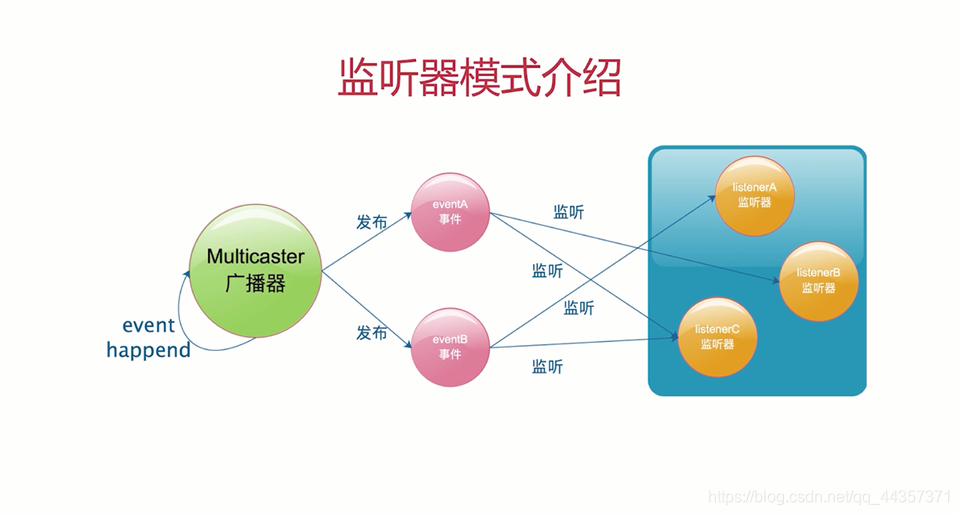
1.7 附:监听器模式图解(图源:慕课网)
二、SpringBoot事件监听器源码剖析
2.1 监听器模式四要素
- 事件 ==》 对应RainEvent、SnowEvent
- 监听器 ==》对应RainListener、SnowListener
- 广播器 ==》对应WeatherEventMulticaster
- 触发机制 ==》对应test里面的方法调用
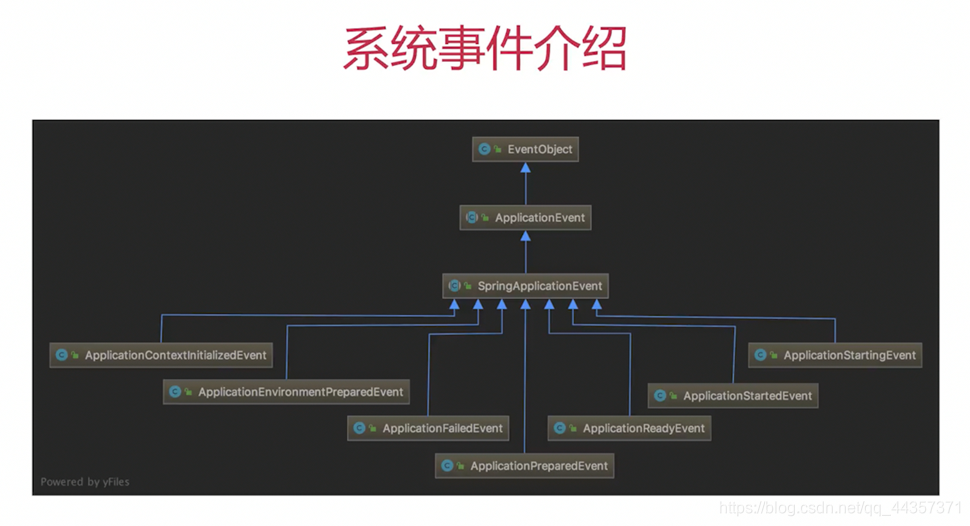
2.2 SpringBoot七大事件(图源:慕课网)
- EventObject:事件顶级对象,所有事件对象的根对象
- ApplicationEvent:应用事件
- SpringApplicationEvent:Spring自己的事件,Spring框架自身的事件都会实现这个接口
- ApplicationStartingEvent:启动事件,框架刚刚启动就会发出这个事件
- ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent:环境在变完成,系统属性和用户指定已经加载完成
- ApplicationContextInitializedEvent:已经创建好了上下文,并且还没有加载任何bean之前发出这个事件
- ApplicationPreparedEvent:在Bean定义开始加载之后,尚未完全加载之前,刷新上下文之前触发
- ApplicationStartedEvent:bean已经创建完成,上下文已经刷新完成,但是ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunne两个扩展接口并未执行
- ApplicationReadyEvent:ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunne两个扩展接口执行完成之后触发
- ApplicationFailedEvent:在启动发生异常时触发
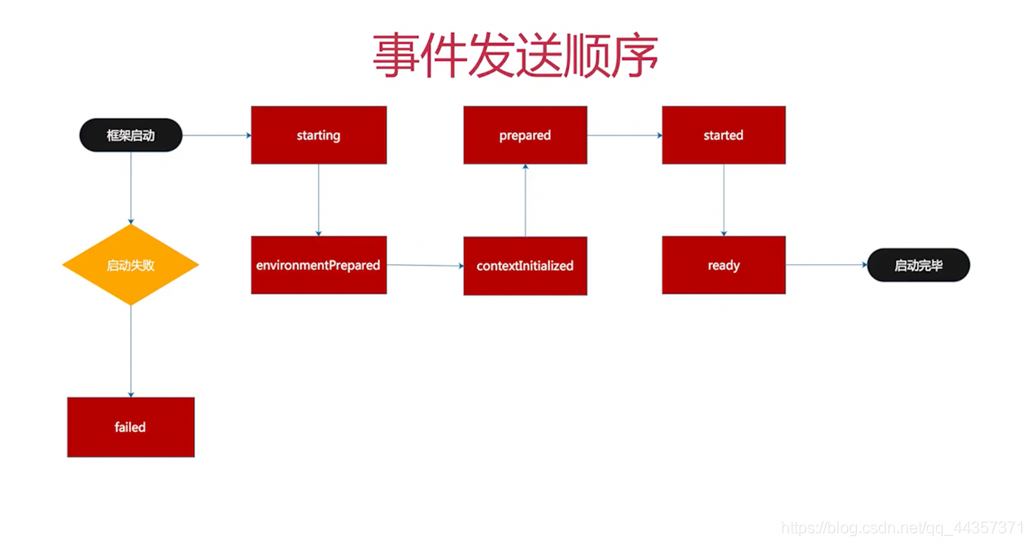
2.3 事件的启动顺序
2.4 SpringBoot监听器源码剖析
2.4.1 监听器注册
public static void main(String[] args) {
//进入run方法
SpringApplication.run(Sb2Application.class, args);
}
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
//进入同名run方法
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
//进入SpringApplication构造方法
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources) {
//点this查看构造函数
this(null, primarySources);
}
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
//setListeners就是将找到的监听器对象注册,同上面系统初始化器类似
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
监听器注册流程
2.4.2 监听器事件触发机制
public static void main(String[] args) {
//进入run方法
SpringApplication.run(Sb2Application.class, args);
}
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
//进入同名run方法
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
//进入run()方法
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
//进入SpringApplicationRunListeners
//里面包含七大事件:starting、environmentPrepared、contextPrepared、contextLoaded、started、running、failed
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
//进入starting方法
listeners.starting();
···
void starting() {
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
//listener.starting()方法的一个实现类是EventPublishingRunListener,找到该类中的starting方法
listener.starting();
}
}
@Override
public void starting() {
//initialMulticaster是广播器
//进入multicastEvent
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args));
}
@Override
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
//这里的resolveDefaultEventType是指获取事件的类型
multicastEvent(event, resolveDefaultEventType(event));
}
①resolveDefaultEventType:获取事件的类型(比如前面的例子中,分为下雨事件和下雪事件两种类型)
首先进入此方法:
private ResolvableType resolveDefaultEventType(ApplicationEvent event) {
//从代码含义上看,此步就是将获取到的event的类型转化为ResolvableType并返回
return ResolvableType.forInstance(event);
}
进入forInstance方法:
public static ResolvableType forInstance(Object instance) {
//若instance为空,就停止SpringBoot的启动,并报错
Assert.notNull(instance, "Instance must not be null");
//ResolvableTypeProvider接口,表明这个类的事件类型可以被解析
//对于实现了ResolvableTypeProvider的类型,可以直接获取到type
if (instance instanceof ResolvableTypeProvider) {
ResolvableType type = ((ResolvableTypeProvider) instance).getResolvableType();
if (type != null) {
return type;
}
}
//对于无法识别的类型:将instance用ResolvableType包装后再返回
return ResolvableType.forClass(instance.getClass());
}
②multicastEvent:广播
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
//先确保事件类型不为空,如果为空,就回到前面的方法用ResolvableType包装一下
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
//获取任务执行的线程池(null)
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
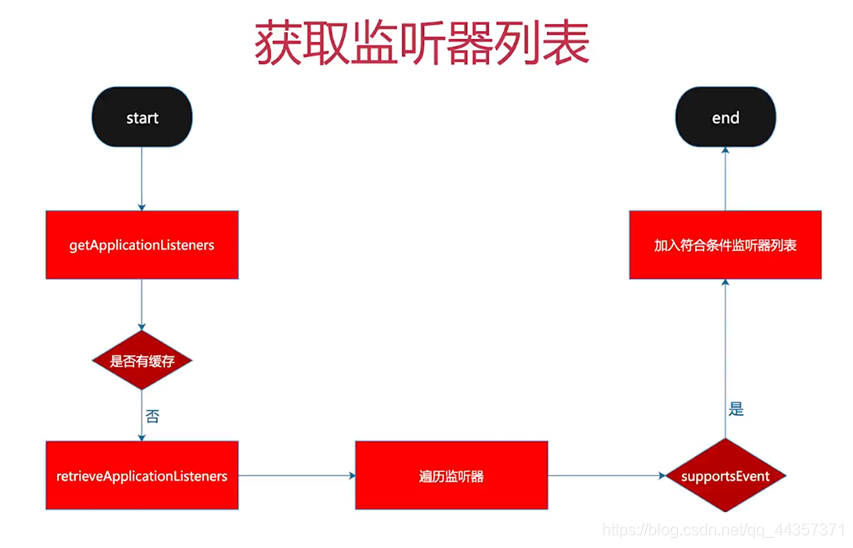
//getApplicationListeners:获取对当前事件感兴趣的监听器
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
if (executor != null) {
//在指定线程上触发
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
//用默认的方式触发
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
getApplicationListeners:获取对当前事件感兴趣的监听器列表
protected Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> getApplicationListeners(
ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {
//获取事件发生的源头类,这里就是SpringApplication
Object source = event.getSource();
//获取源头类的类型
Class<?> sourceType = (source != null ? source.getClass() : null);
//获取缓存的key,下面通过key值来获取监听器
ListenerCacheKey cacheKey = new ListenerCacheKey(eventType, sourceType);
// Quick check for existing entry on ConcurrentHashMap...
ListenerRetriever retriever = this.retrieverCache.get(cacheKey);
if (retriever != null) {
//若缓存中存在值,就直接返回对应事件的监听器
return retriever.getApplicationListeners();
}
if (this.beanClassLoader == null ||
(ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(event.getClass(), this.beanClassLoader) &&
(sourceType == null || ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(sourceType, this.beanClassLoader)))) {
// Fully synchronized building and caching of a ListenerRetriever
//上锁后再检查看有没有其他地方触发了当前事件并把监听器列表放入了缓存
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
retriever = this.retrieverCache.get(cacheKey);
if (retriever != null) {
//又从缓存中读到了
return retriever.getApplicationListeners();
}
retriever = new ListenerRetriever(true);
//真正的查找逻辑retrieveApplicationListeners
Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners =
retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, retriever);
//查到了之后就把结果放入缓存中
this.retrieverCache.put(cacheKey, retriever);
return listeners;
}
}
else {
// No ListenerRetriever caching -> no synchronization necessary
return retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, null);
}
}
retrieveApplicationListeners真正的检索逻辑
private Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> retrieveApplicationListeners(
ResolvableType eventType, @Nullable Class<?> sourceType, @Nullable ListenerRetriever retriever) {
List<ApplicationListener<?>> allListeners = new ArrayList<>();
Set<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners;
Set<String> listenerBeans;
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
//获取所有监听器的实例
listeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners);
//获取所有监听器的beanName
listenerBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListenerBeans);
}
// Add programmatically registered listeners, including ones coming
// from ApplicationListenerDetector (singleton beans and inner beans).
//遍历监听器
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : listeners) {
//判断当前监听器对当前事件是否感兴趣
if (supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)) {
if (retriever != null) {
//如果监听器存在缓存,就存进缓存中
retriever.applicationListeners.add(listener);
}
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
····
//对监听器按照Order值进行排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(allListeners);
//刷新缓存
if (retriever != null && retriever.applicationListenerBeans.isEmpty()) {
retriever.applicationListeners.clear();
retriever.applicationListeners.addAll(allListeners);
}
return allListeners;
}
获取对当前事件感兴趣的监听器的列表流程图
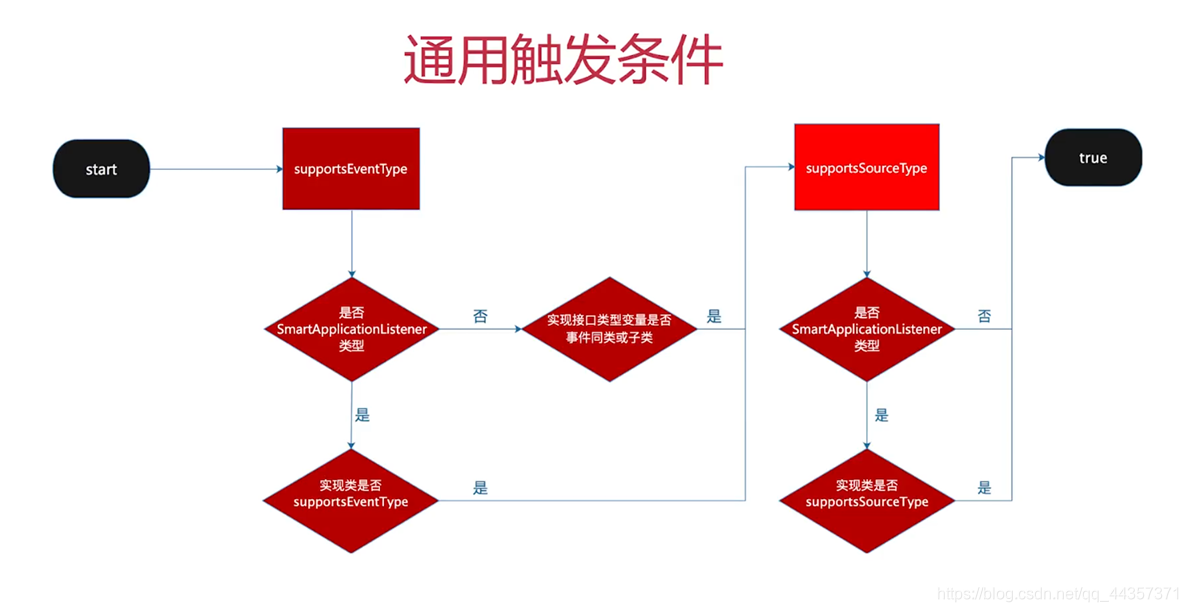
supportsEvent:判断监听器对当前事件是否感兴趣
protected boolean supportsEvent(
ApplicationListener<?> listener, ResolvableType eventType, @Nullable Class<?> sourceType) {
//判断监听器是否是GenericApplicationListener 的子类,并把它转为GenericApplicationListener类型
GenericApplicationListener smartListener = (listener instanceof GenericApplicationListener ?
(GenericApplicationListener) listener : new GenericApplicationListenerAdapter(listener));
//返回 : 判断
//1、supportsEventType监听器是否支持这个事件
//并且
//2、supportsSourceType对当前的事件来源感兴趣
return (smartListener.supportsEventType(eventType) && smartListener.supportsSourceType(sourceType));
}
三、自定义SpringBoot监听器
方式一: 在spring.factories内填写接口实现
@Order(1)
public class FirstListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationStartedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationStartedEvent event) {
System.out.println("hello first");
}
}
//此文件在resources的META-INFO目录下,后面是实现监听器类的全路径名
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=com.mooc.sb2.listener.FirstListener
方式二: 硬编码方式手动注入
@Order(2)
public class SecondListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationStartedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationStartedEvent event) {
System.out.println("hello second");
}
}
//修改SpringBoot启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.mooc.sb2.mapper")
public class Sb2Application {
SpringApplication springApplication = new SpringApplication(Sb2Application.class);
springApplication.addListeners(new SecondListener());
springApplication.run();
}
}
方式三: application.properties内填写实现接口
//此文件在resources目录下
context.listener.classes=com.mooc.sb2.listener.ThirdListener
@Order(3)
public class ThirdListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationStartedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationStartedEvent event) {
System.out.println("hello third");
}
}
方式四: 实现SmartApplicationListener接口,重写supportsEventType方法
通过重写supportsEventType方法,可以实现对多个事件感兴趣
@Order(4)
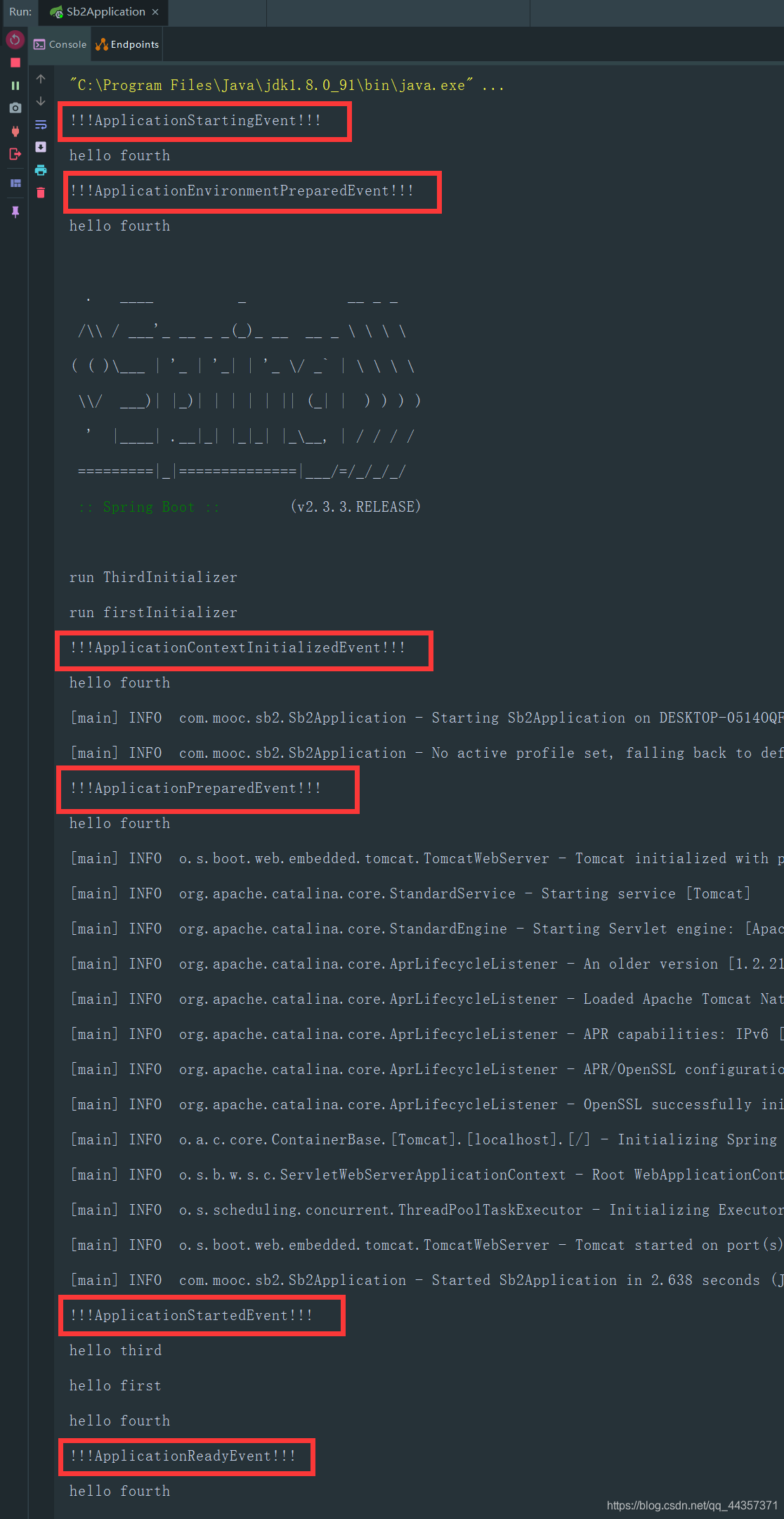
public class FourthListener implements SmartApplicationListener {
@Override
public boolean supportsEventType(Class<? extends ApplicationEvent> eventType) {
if (ApplicationStartingEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(eventType)) {
System.out.println("!!!ApplicationStartingEvent!!!");
}
if (ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(eventType)) {
System.out.println("!!!ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent!!!");
}
if (ApplicationContextInitializedEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(eventType)) {
System.out.println("!!!ApplicationContextInitializedEvent!!!");
}
if (ApplicationPreparedEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(eventType)) {
System.out.println("!!!ApplicationPreparedEvent!!!");
}
if (ApplicationStartedEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(eventType)) {
System.out.println("!!!ApplicationStartedEvent!!!");
}
if (ApplicationReadyEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(eventType)) {
System.out.println("!!!ApplicationReadyEvent!!!");
}
return ApplicationStartingEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(eventType) ||
ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(eventType) ||
ApplicationContextInitializedEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(eventType) ||
ApplicationPreparedEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(eventType) ||
ApplicationStartedEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(eventType) ||
ApplicationReadyEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(eventType);
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
System.out.println("hello fourth");
}
}
这里写了六个事件(除了fail事件),可以通过打印结果,验证上文写的事件的启动顺序
四、面试题总结(图源:慕课网)