通过Gazebo仿真和RViz仿真的学习后,本文将通过Gazebo与RViz联合仿真实现机器人在Gazebo仿真环境中运动。
目录
前言
URDF文件改写
Gazebo与RViz联合仿真
前言
机器人操作系统(ROS)提供了Gazebo与RViz两个仿真环境其各有各的用处,Gazebo多用于仿真环境的搭建如房间、马路等, RViz多用于传感器的配置如摄像头、激光雷达等。
URDF文件改写
URDF 文件是一个标准的 XML 文件,在 ROS 中预定义了一系列的标签用于描述机器人模型,主要包含以下部分:
- < robot> 根标签
- < link > 连杆标签
- < joint > 关节标签
- < gazebo > 仿真标签
其中< gazebo >仿真标签是联合仿真所必须的,接下来将参考Gazebo Sim官方文档来配置二轮差速机器人运动控制器(Controller)以改写URDF文件适用于Gazebo与RViz联合仿真。
step1.新建xacro文件
在urdf文件夹中新建文件controller.xaro并输入:【Ctrl+S保存】
<robot name="controller" xmlns:xacro="http://wiki.ros.org/xacro">
<xacro:macro name="joint_trans" params="joint_name">
<!-- Transmission is important to link the joints and the controller -->
<transmission name="${joint_name}_trans">
<type>transmission_interface/SimpleTransmission</type>
<joint name="${joint_name}">
<hardwareInterface>hardware_interface/VelocityJointInterface</hardwareInterface>
</joint>
<actuator name="${joint_name}_motor">
<hardwareInterface>hardware_interface/VelocityJointInterface</hardwareInterface>
<mechanicalReduction>1</mechanicalReduction>
</actuator>
</transmission>
</xacro:macro>
<xacro:joint_trans joint_name="left_wheel_joint" />
<xacro:joint_trans joint_name="right_wheel_joint" />
<gazebo>
<plugin name="differential_drive_controller" filename="libgazebo_ros_diff_drive.so">
<rosDebugLevel>Debug</rosDebugLevel>
<publishWheelTF>true</publishWheelTF>
<robotNamespace>/</robotNamespace>
<publishTf>1</publishTf>
<publishWheelJointState>true</publishWheelJointState>
<alwaysOn>true</alwaysOn>
<updateRate>100.0</updateRate>
<legacyMode>true</legacyMode>
<leftJoint>left_wheel_joint</leftJoint>
<!--left_joint-->
<rightJoint>right_wheel_joint</rightJoint>
<!--right_joint-->
<wheelSeparation>0.277</wheelSeparation>
<!--wheel_separation-->
<wheelDiameter>0.073</wheelDiameter>
<!--wheel_diameter-->
<broadcastTF>1</broadcastTF>
<wheelTorque>30</wheelTorque>
<wheelAcceleration>1.8</wheelAcceleration>
<commandTopic>cmd_vel</commandTopic>
<odometryFrame>odom</odometryFrame>
<odometryTopic>odom</odometryTopic>
<robotBaseFrame>base_footprint</robotBaseFrame>
<!--
<odometrySource>world</odometrySource>
<publishTf>1</publishTf>
-->
</plugin>
</gazebo>
</robot>
其中驱动装置关节即车体与车轮的关节标签left(right)_wheel_joint,URDF官方文档解释了<joint>关节标签的含义如下图所示,本文的left(right)_wheel_joint的Parent为车体连杆标签base_link而Child为车轮连杆标签left(right)_wheel_link,读者可细细体会:
step2.xacro转urdf
在urdf文件夹中打开集成终端,如下所示:
在集成终端中输入:
rosrun xacro xacro controller.xacro > controller.urdfstep3.合并urdf文件
将导出的controller.urdf中第七行至倒数第二行复制粘贴到irobot.urdf的倒数第二行中:
这样我们在irobot.urdf文件中添加了<gazebo>仿真标签。
Gazebo与RViz联合仿真
step1.编写gazebo.launch
<launch>
<include
file="$(find gazebo_ros)/launch/empty_world.launch" />
<node
name="spawn_model"
pkg="gazebo_ros"
type="spawn_model"
args="-file $(find irobot)/urdf/irobot.urdf -urdf -model irobot"
output="screen" />
<node
name="fake_joint_calibration"
pkg="rostopic"
type="rostopic"
args="pub /calibrated std_msgs/Bool true" />
</launch>step2.编写rviz.launch
<launch>
<param
name="robot_description"
textfile="$(find irobot)/urdf/irobot.urdf" />
<node
name="joint_state_publisher_gui"
pkg="joint_state_publisher_gui"
type="joint_state_publisher_gui" />
<node
name="robot_state_publisher"
pkg="robot_state_publisher"
type="robot_state_publisher" />
<node
name="rviz"
pkg="rviz"
type="rviz"
args="-d $(find irobot)/config/irobot.rviz" />
</launch>step3.分别运行两个launch文件
终端一输入:
source ./devel/setup.bash
roslaunch irobot gazebo.launch终端二输入:
source ./devel/setup.bash
roslaunch irobot rviz.launchRViz环境配置参考ROS入门教程(五)—— RViz仿真如下所示:
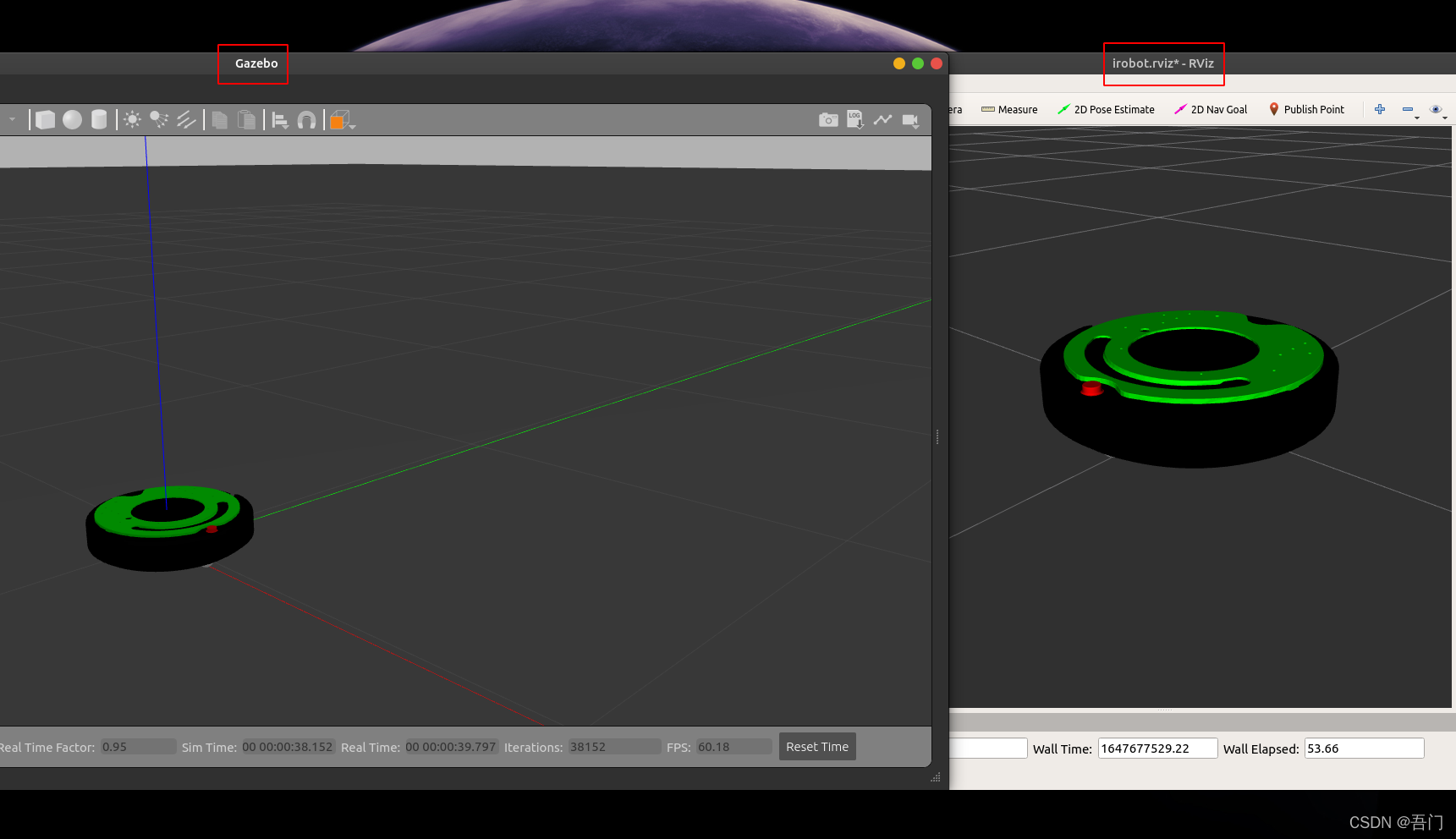
最终结果如下:
step4.发布消息
按Ctrl+Alt+T打开终端输入:
rostopic pub -r 10 /cmd_vel geometry_msgs/Twist "linear:
x: 1.0
y: 0.0
z: 0.0
angular:
x: 0.0
y: 0.0
z: 1.0" 该代码段的旨在10HZ 的频率循环发送运动信息至订阅者,成功结果如下:
Gazebo与RViz联合仿真
文章预告:ROS入门教程(八)—— 传感器