路径规划算法—Astar C++实现及显示
以下均为原创的内容,转载请著名出处,谢谢。
1.主函数
main.cpp
主函数主要提供实现算法的对外接口,这里主要的流程是
1.调用MapData(mapPath)来读取地图数据
2.调用astar.PathPoint()进行Astar路径查找
3.Display(astarPath, mapData, xStart, yStart, xStop, yStop, “Astar”, true)函数进行最终路径的可视化显示
/*
@Function:Astar External Implementation
@Time:2022-01-10
@Author:Tang Gu Jie
@E-Mail:[email protected]
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include "Astar.h"
#include "map.h"
#include "display.h"
int main()
{
//string mapPath = "map_small.txt"; //地图路径
//int xStart = 4;
//int yStart = 0; //起点
//int xStop = 2;
//int yStop = 6; //终点
string mapPath = "map_big.txt"; //地图路径
int xStart = 25;
int yStart = 4; //起点
int xStop = 3;
int yStop = 16; //终点
//f=a*g+b*h
float weightA = 1.0; //权重a
float weightB = 1.0; //权重b
//地图数据
vector<vector<int>> mapData(MapData(mapPath));
/***
*@函数功能 初始化A星算法
------------------------------------------------
*@参数 mapData 地图数据
*@参数 xStart 起点x值
*@参数 yStart 起点y值
*@参数 xStop 终点x值
*@参数 yStop 终点y值
*@参数 weightA 权重a值
*@参数 weightA 权重b值
*@参数 PathType 路径寻找的结果,初始化时赋为NOFINDPATHPOINT
*@参数 DistanceType 距离类型,EUCLIDEAN欧式距离,MANHANTTAN曼哈顿距离
------------------------------------------------
*@返回值 无
*/
ASTAR::CAstar astar(mapData, xStart, yStart, xStop, yStop, weightA, weightB,ASTAR::CAstar::PathType::NOFINDPATHPOINT,ASTAR::CAstar::DistanceType::EUCLIDEAN);
//A星算法路径寻找函数
std::vector<std::pair<int, int> >astarPath = astar.PathPoint();
if (astar.m_noPathFlag == ASTAR::CAstar::PathType::NOFINDPATHPOINT)
{
std::cout << "A星算法没能找到路径!!!" << std::endl;
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < astarPath.size(); i++)
{
std::cout << astarPath[i].first << "," << astarPath[i].second << std::endl;
}
/***
*@函数功能 显示路径结果,蓝色起点,红色终点,黑色障碍物
------------------------------------------------
*@参数 mapData 地图数据
*@参数 xStart 起点x值
*@参数 yStart 起点y值
*@参数 xStop 终点x值
*@参数 yStop 终点y值
*@参数 "Astar" 图片的标题
*@参数 true 是否保存图片,ture保存,false不保存
------------------------------------------------
*@返回值 无
*/
Display(astarPath, mapData, xStart, yStart, xStop, yStop, "Astar", true);
}
return 0;
}
2.地图数据的读取
map.h
/*
@Function:Map Data Read
@Time:2022-01-10
@Author:Tang Gu Jie
@E-Mail:[email protected]
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef __MAP__
#define __MAP
#include <vector>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
vector<vector<int>> MapData(std::string _mapPath);
#endif
map.cpp
/*该函数是读取map_big.txt形成一个二维数组num,其中num里面0表示可自由通行区域,1表示障碍物*/
/*
@Function:Map Data Read
@Time:2022-01-10
@Author:Tang Gu Jie
@E-Mail:[email protected]
*/
#include "map.h"
#include<fstream>
#include<sstream>
vector<vector<int>>MapData(std::string _mapPath)
{
ifstream f;
//f.open("map_media.txt");
f.open(_mapPath);
//f.open("map.txt");
string str;
vector<vector<int> > num;
while (getline(f, str)) //读取1行并将它赋值给字符串str
{
istringstream input(str); // c++风格的串流的输入操作
vector<int> tmp;
int a;
while (input >> a) //通过input将第一行的数据一个一个的输入给a
tmp.push_back(a);
num.push_back(tmp);
}
return num;
}
地图数据的读取主要采用C++文件读取流的方式。 0表示自由通行区域,1表示障碍物,以下是map_big.txt
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
3.Astar算法的实现
Astar.h
在这头文件中,对外只提供了PathPoint()接口,该接口就是Astar算法入口函数,其次在该文件中,使用命名空间的机制,防止以后写其他的路径规划算法会用到相同的名字。通过枚举类型DistanceType已达到距离函数传参时见名之意的作用,此外还在构造函数中加入权重a和权重b,对应理论部分的 f ( n ) = a × g ( n ) + b × g ( n ) f(n)=a \times g(n)+b \times g(n) f(n)=a×g(n)+b×g(n),以此实现Astar算法的变形。
/*
@Function:Astar Algorithm Implementation
@Time:2022-01-10
@Author:Tang Gu Jie
@E-Mail:[email protected]
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef __ASTAR__
#define __ASTAR__
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <map>
//命名空间 ASTAR
namespace ASTAR
{
//节点结构体
struct Node
{
int SnodeX; //节点X值
int SnodeY; //节点Y值
int SparentX; //父节点X值
int SparentY; //父节点Y值
float Sgn;; //节点的g值
float Shn; //节点的h值
float Sfn; //节点的f值
};
class CAstar
{
public:
//路径类型的枚举类型,NOFINDPATHPOINT表示没找到路径点,FINDPATHPOINT找到路径点
enum PathType {NOFINDPATHPOINT=0, FINDPATHPOINT =1};
//距离类型 EUCLIDEAN欧式距离,MANHANTTAN曼哈顿距离
enum DistanceType {EUCLIDEAN=0,MANHANTTAN=1};
PathType m_noPathFlag;
public:
/*初始化函数*/
CAstar(std::vector<std::vector<int>>_mapData, //地图数据,以二维数据存储
int _xStart, //起始点X值
int _yStart, //起始点Y值
int _xStop, //目标点X值
int _yStop, //目标点Y值
float _weightA, //权重a值
float _weightB, //权重b值
PathType _noPathFlag, //路径是否生成标志)
DistanceType _distanceType, //距离类型
);
/*生成路径点*/
std::vector<std::pair<int, int>> PathPoint();
private:
/*两点之间的欧式距离*/
//float EuclideanDistance(int _xNode, int _yNode, int _xTarget, int _yTarget);
/*向OpenList插入数据*/
Node InsertOpen(int _xVal, int _yVal, int _parentXval, int _parentYval, float _hn, float _gn, float _fn);
/*扩展一个节点的周围邻居*/
std::vector<Node> ExpandArray(int _xNodeExpanded, int _yNodeExpanded, float _gNodeExpanded, int _xTarget, int _yTarget,
std::vector<std::vector<int>> _mapData, std::vector<Node>_closeList);
/*该节点在openList-->multimap中的索引*/
float NodeIndex(std::multimap<float, Node> _openList, int _xNode, int _yNode);
/*该节点在closeList-->vector中的索引*/
int CloseNodeIndex(std::vector<Node> _closeList, int _xNode, int _yNode);
/*Astar的核心函数*/
void AstarCoreFunction();
/*获得A星算法的路径*/
std::vector<std::pair<int, int>> FindPath(std::vector<Node>_closeList, int _xStart, int _yStart, int _xStop, int _yStop);
private:
std::multimap<float, Node> m_openList; //openList列表,multimap类型(默认Key是从小到大排序)
std::vector<Node> m_closeList; //closeList列表,vector列表
std::vector<std::vector<int>> m_mapData; //地图数据,双vector类型
float m_weightA; //权重a
float m_weightB; //权重b
int m_xStart; //起点x值
int m_yStart; //起点y值
int m_xStop; //终点x值
int m_yStop; //终点y值
};
}
#endif
Astar.cpp
/*
@Function:Astar Algorithm Implementation
@Time:2022-01-10
@Author:Tang Gu Jie
@E-Mail:[email protected]
*/
#include "Astar.h"
#include <functional>
std::function<float(int, int, int, int)>Distance;
/***
*@函数功能 计算两点间的欧式距离
------------------------------------------------
*@参数 _xNode 节点的x值
*@参数 _yNode 节点的y值
*@参数 _xTarget 终点的y值
*@参数 _yTarget 终点的y值
------------------------------------------------
*@返回值 欧式距离值:根号√((x2-x1)^2+(y2-y1)^2)
*/
float EuclideanDistance(int _xNode, int _yNode, int _xTarget, int _yTarget)
{
float d = sqrt(pow(_xNode - _xTarget, 2) + pow(_yNode - _yTarget, 2));
return d;
}
/***
*@函数功能 计算两点间的曼哈顿距离
------------------------------------------------
*@参数 _xNode 节点的x值
*@参数 _yNode 节点的y值
*@参数 _xTarget 终点的y值
*@参数 _yTarget 终点的y值
------------------------------------------------
*@返回值 曼哈顿距离值:|(x2-x1)+(y2-y1)|
*/
float ManhattanDistance(int _xNode, int _yNode, int _xTarget, int _yTarget)
{
float d = std::abs(_xNode - _xTarget) + std::abs(_yNode - _yTarget);
return d;
}
ASTAR::CAstar::CAstar(std::vector<std::vector<int>>_mapData, //地图数据,以二维数据存储
int _xStart, //起始点X值
int _yStart, //起始点Y值
int _xStop, //目标点X值
int _yStop, //目标点Y值
float _weightA, //权重a值
float _weightB, //权重b值
PathType _noPathFlag, //路径是否生成标志)
DistanceType _distanceType //距离类型
) :m_mapData(_mapData), m_xStart(_xStart), m_yStart(_yStart),m_xStop(_xStop), m_yStop(_yStop), m_noPathFlag(_noPathFlag),m_weightA(_weightA),m_weightB(_weightB)
{
switch (_distanceType)
{
case ASTAR::CAstar::EUCLIDEAN:
{
std::cout << "使用欧式距离!!!" << std::endl;
Distance = EuclideanDistance;
break;
}
case ASTAR::CAstar::MANHANTTAN:
{
std::cout << "使用曼哈顿距离!!!" << std::endl;
Distance = ManhattanDistance;
break;
}
default:
break;
}
}
/***
*@函数功能 向openList插入新的节点
------------------------------------------------
*@参数 _xVal 当前节点的x值
*@参数 _yVal 当前节点的y值
*@参数 _parentXval 当前节点的父节点的x值
*@参数 _parentYval 当前节点的父节点的y值
*@参数 _hn 当前节点的h值(当前节点与终点的关系)
*@参数 _gn 当前节点的g值(当前节点与上一个的关系)
*@参数 _fn 当前节点的f值(f=g+h)
------------------------------------------------
*@返回值 Node 赋有上述参数的节点
*/
ASTAR::Node ASTAR::CAstar::InsertOpen(int _xVal, int _yVal, int _parentXval, int _parentYval, float _hn, float _gn, float _fn)
{
Node node;
node.SnodeX = _xVal;
node.SnodeY = _yVal;
node.SparentX = _parentXval;
node.SparentY = _parentYval;
node.Shn = _hn;
node.Sgn = _gn;
node.Sfn = _fn;
return node;
}
/***
*@函数功能 扩展一个节点的周围邻居节点
------------------------------------------------
*@参数 _xNodeExpanded 要扩展邻居的节点x值
*@参数 _yNodeExpanded 要扩展邻居的节点y值
*@参数 _gNodeExpanded 要扩展邻居的节点g值
*@参数 _xTarget 终点x值
*@参数 _yTarget 终点y值
*@参数 _mapData 地图数据
*@参数 _closeList 关闭列表
------------------------------------------------
*@返回值 none
*/
std::vector<ASTAR::Node> ASTAR::CAstar::ExpandArray(int _xNodeExpanded, int _yNodeExpanded, float _gNodeExpanded, int _xTarget, int _yTarget,std::vector<std::vector<int>> _mapData, std::vector<ASTAR::Node>_closeList)
{
//节点的8领域,顺序为右下、下、左下、右、左、右上、上、左上
int mapHeight = _mapData.size();
int mapWidth = _mapData[1].size();
Node node;
std::vector<Node> nodeList;
bool expandFlag = false;
for (int k = 1; k >= -1; k--)
{
for (int j = 1; j >= -1; j--)
{
if (k != j || j != 0)
{
int sx = _xNodeExpanded + k;
int sy = _yNodeExpanded + j;
if ((sx >= 0 && sx < mapHeight) && (sy >= 0 && sy < mapWidth) && _mapData[sx][sy] != 1)
{
expandFlag = true;
for (int i = 0; i < _closeList.size(); i++)
{
if (sx == _closeList[i].SnodeX && sy == _closeList[i].SnodeY)
{
expandFlag = false;
break;
}
}
if (expandFlag == true)
{
node.SnodeX = sx;
node.SnodeY = sy;
node.SparentX = -1; //这个随便填
node.SparentY = -1; //这个随便填
node.Sgn = (_gNodeExpanded + EuclideanDistance(_xNodeExpanded, _yNodeExpanded, sx, sy));
node.Shn = (Distance(_xTarget, _yTarget, sx, sy));
node.Sfn = m_weightA*node.Sgn + m_weightB*node.Shn;
nodeList.emplace_back(node);
}
}
}
}
}
return nodeList;
}
/***
*@函数功能 查询节点(x,y)在openList中的Key索引
------------------------------------------------
*@参数 _openList 开启列表
*@参数 _xNode 节点x值
*@参数 _yNode 节点y值
------------------------------------------------
*@返回值 key值索引,注意因为在multimap中,Key可能是重复的,-1.0表示没找到
*/
float ASTAR::CAstar::NodeIndex(std::multimap<float, Node> _openList, int _xNode, int _yNode)
{
for (std::multimap<float, Node>::iterator it = _openList.begin(); it != _openList.end(); it++)
{
if (it->second.SnodeX == _xNode && it->second.SnodeY == _yNode)
{
return it->first;
}
}
return -1.0;
}
/***
*@函数功能 查询节点(x,y)在closeList中的索引
------------------------------------------------
*@参数 _closeList 关闭列表
*@参数 _xNode 节点x值
*@参数 _yNode 节点y值
------------------------------------------------
*@返回值 i表示节点在vector中的索引,-1表示没有找到
*/
int ASTAR::CAstar::CloseNodeIndex(std::vector<Node> _closeList, int _xNode, int _yNode)
{
for (int i = 0; i < _closeList.size(); i++)
{
if (_closeList[i].SnodeX == _xNode && _closeList[i].SnodeY == _yNode)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
/***
*@函数功能 Astar的核心函数,所有的数据处理在这里完成
------------------------------------------------
*@参数 无
*@参数 无
------------------------------------------------
*@返回值 无,其实有一个隐藏的输出closeList,最终函数完成后,会完善closeList,最后根据closeList来逆变路径点
*/
void ASTAR::CAstar::AstarCoreFunction()
{
float goalDistance = EuclideanDistance(m_xStart, m_yStart, m_xStop, m_yStop);
float pathCost =0.0;
float f_ = m_weightA*goalDistance + m_weightB*pathCost;
//将起点放入到openList中
Node node = InsertOpen(m_xStart, m_yStart, m_xStart, m_yStart, goalDistance, pathCost, f_);
m_openList.insert(std::make_pair(goalDistance, node));
while (true)
{
//对应伪代码-->if the queue(openList) is empty, return False; break;
if (m_openList.size() == 0)
break;
//对应伪代码-->Remove the node "n" with the lowest f(n) from the priority queue.
std::multimap<float, Node>::iterator pos = m_openList.begin(); //multimap键值默认是从小到大排布
int xNodeExpanded = pos->second.SnodeX;
int yNodeExpanded = pos->second.SnodeY;
float gNodeExpanded = pos->second.Sgn;
// 对应伪代码-->Mark node "n" as expanded
Node closeNode = pos->second;
m_closeList.emplace_back(closeNode);
m_openList.erase(pos);
//对应伪代码-->if the node "n" is the goal state, return TRUE; break;
if (xNodeExpanded == m_xStop && yNodeExpanded == m_yStop)
{
m_noPathFlag = FINDPATHPOINT;
break;
}
//获得所有节点n的所有“可用”邻居集合
std::vector<Node> nodeList = ExpandArray(xNodeExpanded, yNodeExpanded, gNodeExpanded, m_xStop, m_yStop, m_mapData, m_closeList);
for (int i = 0; i < nodeList.size(); i++)
{
int xNode = nodeList[i].SnodeX;
int yNode = nodeList[i].SnodeY;
float nodeIndex = NodeIndex(m_openList, xNode, yNode);
if (nodeIndex == -1.0)
{
//对应伪代码-->If node m is not in openList, push node m into openList
float gn = gNodeExpanded + EuclideanDistance(xNode, yNode, xNodeExpanded, yNodeExpanded);
float hn = Distance(xNode, yNode, m_xStop, m_yStop);
float fn = m_weightA*gn+ m_weightB*hn;
Node node_ = InsertOpen(xNode, yNode, xNodeExpanded, yNodeExpanded, hn, gn, fn);
m_openList.insert(std::make_pair(fn, node_));
}
else
{
//对应伪代码-->If g(m)>g(n)+Cnm
//lower_bound返回查找结果第一个迭代器,upper_bound返回最后一个查找结果的下一个位置的迭代器
std::multimap<float, Node>::iterator indexLow = m_openList.lower_bound(nodeIndex);
std::multimap<float, Node>::iterator indexUpper = m_openList.upper_bound(nodeIndex);
indexUpper--;
if (indexLow == indexUpper)
{
//表示没有重复的键值
if (indexLow->second.Sgn > (gNodeExpanded + EuclideanDistance(xNode, yNode, xNodeExpanded, yNodeExpanded)))
{
indexLow->second.SparentX = xNodeExpanded;
indexLow->second.SparentY = yNodeExpanded;
indexLow->second.Sgn = gNodeExpanded + EuclideanDistance(xNode, yNode, xNodeExpanded, yNodeExpanded);
indexLow->second.Sfn = m_weightA*indexLow->second.Sgn + m_weightB*indexLow->second.Shn;
}
}
else
{
//表示有重复的键值
while (indexLow != indexUpper)
{
if (indexLow->second.SnodeX == xNode && indexLow->second.SnodeY == yNode)
break;
indexLow++;
}
if (indexLow->second.Sfn > (gNodeExpanded + EuclideanDistance(xNode, yNode, xNodeExpanded, yNodeExpanded)))
{
indexLow->second.SparentX = xNodeExpanded;
indexLow->second.SparentY = yNodeExpanded;
indexLow->second.Sgn = gNodeExpanded + EuclideanDistance(xNode, yNode, xNodeExpanded, yNodeExpanded);
indexLow->second.Sfn = m_weightA*indexLow->second.Sgn + m_weightB*indexLow->second.Shn;
}
}
}
}
}
}
/***
*@函数功能 路径寻找函数
------------------------------------------------
*@参数 _closeList 关闭列表
*@参数 _xStart 起点X值
*@参数 _yStart 起点Y值
*@参数 _xStop 终点X值
*@参数 _yStop 终点Y值
------------------------------------------------
*@返回值 路径节点 类型[(first,second),(),()...]
*/
std::vector<std::pair<int, int>> ASTAR::CAstar::FindPath(std::vector<Node>_closeList, int _xStart, int _yStart, int _xStop, int _yStop)
{
std::pair<int, int>path;
std::vector<std::pair<int, int>>findPath;
path.first = _xStop;
path.second = _yStop;
findPath.emplace_back(path);
int index = CloseNodeIndex(_closeList, _xStop, _yStop);
while (true)
{
if (_closeList[index].SparentX == _xStart && _closeList[index].SparentY == _yStart)
{
break;
}
int nodeX = _closeList[index].SparentX;
int nodeY = _closeList[index].SparentY;
path.first = nodeX;
path.second = nodeY;
findPath.emplace_back(path);
index = CloseNodeIndex(_closeList, nodeX, nodeY);
}
return findPath;
}
/***
*@函数功能 对外的A星算法的接口
------------------------------------------------
*@参数 无
------------------------------------------------
*@返回值 路径节点 类型[(first,second),(),()...]
*/
std::vector<std::pair<int, int>> ASTAR::CAstar::PathPoint()
{
//AstarCoreFunction完善openList与closeList
AstarCoreFunction();
//FindPath通过closeList进行寻找路径点
std::vector<std::pair<int, int> > pathPoint = FindPath(m_closeList, m_xStart, m_yStart, m_xStop, m_yStop);
return pathPoint;
}
特别说明如下:
- 在构造函数中使用函数包装器function,可以在编译的时候将一个函数与另外一个函数进行绑定(当然这样说并不是特别准确,大家理解就可以了),这样只要通过函数传参的不同,调用不同的函数。**其实要实现上述的功能最简单方法就是构造函数中设置一个标志位,再在另外一个函数 f f f中通过标志位的不同来调用不同的函数,这样的话确实可以实现上述的功能,但是每次调用 f f f函数都会进行一个标志位的判断,这样做并不是特别好,下面是自己写的一个伪代码,希望有助于大家理解。**于是就产生函数包装器,这玩意就相当于写了很多函数,通过构造函数的传参不同,可以动态绑定不同的函数。
"头文件"
class A
{
...
public:
A(string a)
{
switch(a)
{
case "a":
flag1=true;
break;
case "b":
flag2=true;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
public:
bool flag1=false;
bool flag2=false;
....
};
"源文件"
void test1()
{
...
}
void test2()
{
...
}
void f()
{
if (flag1==true)
test1();
else if(flag2==true)
test2();
...
}
-
openLIst的设计使用std::multimap,以Astar中的 f f f作为键, N o d e Node Node为值,这样就可以巧妙的使用multimap默认是按照键值进行排序的(默认从小到大)。必须使用迭代器取multimap的第一个元素,此时就是 f f f最小的节点。这样的好处,就是在插入节点的时候,节点就已经按照键值 f f f进行排序了。
-
关于函数距离的选择,其实不管欧式距离还是曼哈顿距离,其实改变的都是估计成本** h ( n ) h(n) h(n)**,对于 g ( n ) g(n) g(n)还是采用欧式距离,可以参考Dijkstra的方法,这个大家注意,我在这当时卡了很长时间,仿真效果也特别奇怪;对于权重a,b的变化,改变的只是 f ( n ) f(n) f(n)值,并不没有改变 g ( n ) g(n) g(n)和 h ( n ) h(n) h(n)。
-
一个节点的邻居节点使用8领域的方法,依此为右下,下,坐下;右,左;右上,上,左上。
-
函数的运行部分为PathPoint → \to → AstarCoreFunction+FindPath,具体的函数功能已在程序中标注上,大家可以自行理解。
4.显示功能的实现
display.h
/*
@Function:Astar Algorithm Display
@Time:2022-01-10
@Author:Tang Gu Jie
@E-Mail:[email protected]
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef __DISPLAY__
#define __DISPLAY__
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <string>
#define Size 30
#define Menu Size/2
#define Width 1200
#define Height 1200
using namespace std;
void Display(vector<pair<int,int> >_pathPoint,vector<vector<int>> _mapData, int _xStart, int _yStart, int _xStop, int _yStop,string _pictureName,bool _saveFlag);
#endif
display.cpp
/*
@Function:Astar Algorithm Display
@Time:2022-01-10
@Author:Tang Gu Jie
@E-Mail:[email protected]
*/
#include "display.h"
//#include "fit.h"
void Display(vector<pair<int, int> >_pathPoint, vector<vector<int>>_mapData,int _xStart,int _yStart,int _xStop,int _yStop,string _pictureName,bool _saveFlag)
{
int ROWS = _mapData.size();
int COLS = _mapData[1].size();
cv::Mat img(Height, Width, CV_8UC3, cv::Scalar(255, 255, 255));
cv::Point left_up, right_bottom;
cv::Point point_first, point_second;
//中间路径点--->黄色
for (int i = 0; i < _pathPoint.size(); i++)
{
left_up.x = _pathPoint[i].second * Size;
left_up.y = _pathPoint[i].first * Size;
right_bottom.x = left_up.x + Size;
right_bottom.y = left_up.y + Size;
cv::rectangle(img, left_up, right_bottom, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 255), CV_FILLED, 8, 0);//path yellow(full)
}
//障碍物--->黑色,起点--->蓝色,终点--->红色
for (int i = 0; i<ROWS; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j<COLS; j++)
{
left_up.x = j * Size; //存储数组的列(j)对应矩形的x轴
left_up.y = i * Size;
right_bottom.x = left_up.x + Size;
right_bottom.y = left_up.y + Size;
if (_mapData[i][j])
{
cv::rectangle(img, left_up, right_bottom, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), CV_FILLED, 8, 0);//obstacles balck
}
else
{
if (i == _xStart&&j == _yStart)
cv::rectangle(img, left_up, right_bottom, cv::Scalar(255, 0, 0), CV_FILLED, 8, 0);//start point blue(full)
else if (i == _xStop&&j == _yStop)
cv::rectangle(img, left_up, right_bottom, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255), CV_FILLED, 8, 0);//goal point red(full)
}
}
}
//中间线--->黄色
for (int i = 1; i < COLS; i++)
{
point_first.x = i * Size;
point_first.y = 1 * Size;
point_second.x = i *Size;
point_second.y = (ROWS - 1) * Size;
cv::line(img, point_first, point_second, cv::Scalar(141,238,238), 2, 2);
}
for (int i = 1; i < ROWS;i++)
{
point_first.x = 1 * Size;
point_first.y = i * Size;
point_second.x = (COLS - 1) * Size;
point_second.y = i * Size;
cv::line(img, point_first, point_second, cv::Scalar(141,238,238), 2, 2);
}
//路径线--->黄色
point_first.x = _yStop * Size + Menu;
point_first.y = _xStop * Size + Menu;
for (int i = 0; i < _pathPoint.size(); i++)
{
left_up.x = _pathPoint[i].second * Size;
left_up.y = _pathPoint[i].first * Size;
point_second.x = left_up.x + Menu;
point_second.y = left_up.y + Menu;
cv::line(img, point_first, point_second, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), 2, 4);
point_first = point_second;
}
if (_saveFlag)
{
string str1 = ".png";
_pictureName.append(str1);
cv::imwrite(_pictureName, img);
cout << "save png success" << endl;
}
cv::imshow(_pictureName, img);
cv::waitKey(0);
}
显示的实现是基于OpenCV3.4的,传入路径节点即可。C++下面的显示没有matlab或者python的方便,这是我借鉴一个网上博主写的,ROS下路径规划的插件底层使用C++实现的,其实最后还是需要C++来实现。
5.算法仿真
其中蓝色表示起点,红色表示终点,黑色为障碍物,白色为可通行部分,黑色的线为Astar得到的路径。
仿真一
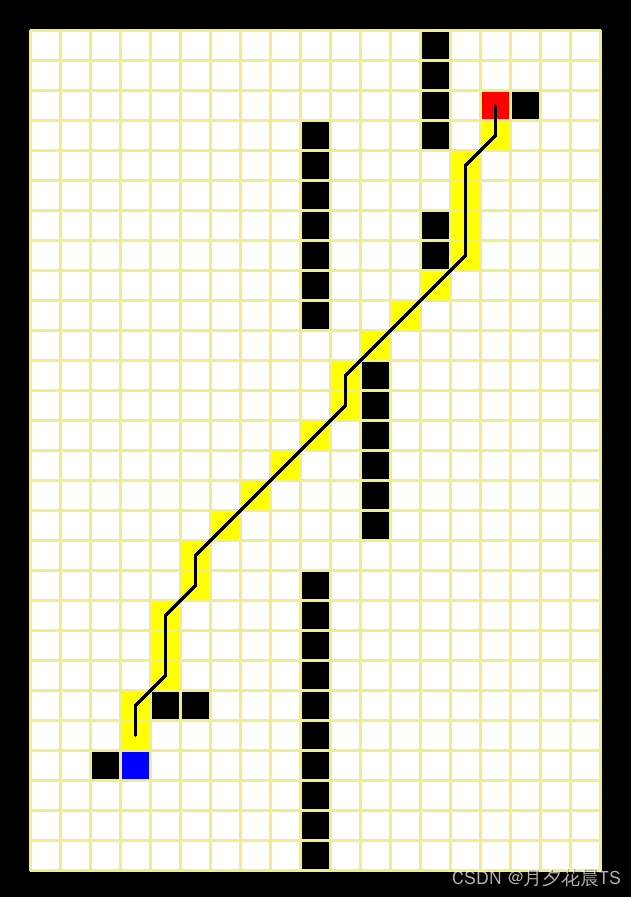 Astar(a=1.0,b=1.0)
Astar(a=1.0,b=1.0)
|
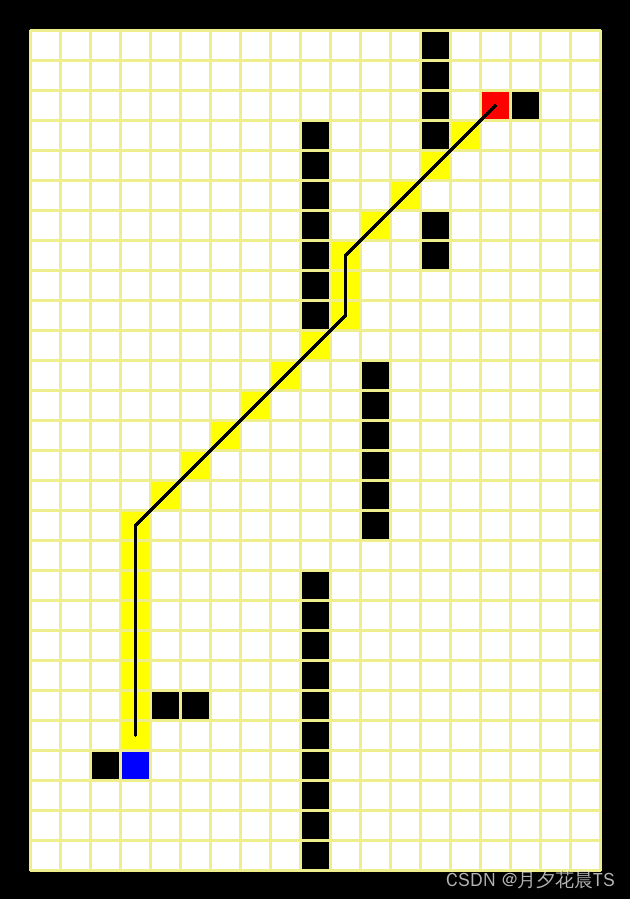 Dijkstra(a=1.0,b=0)
Dijkstra(a=1.0,b=0)
|
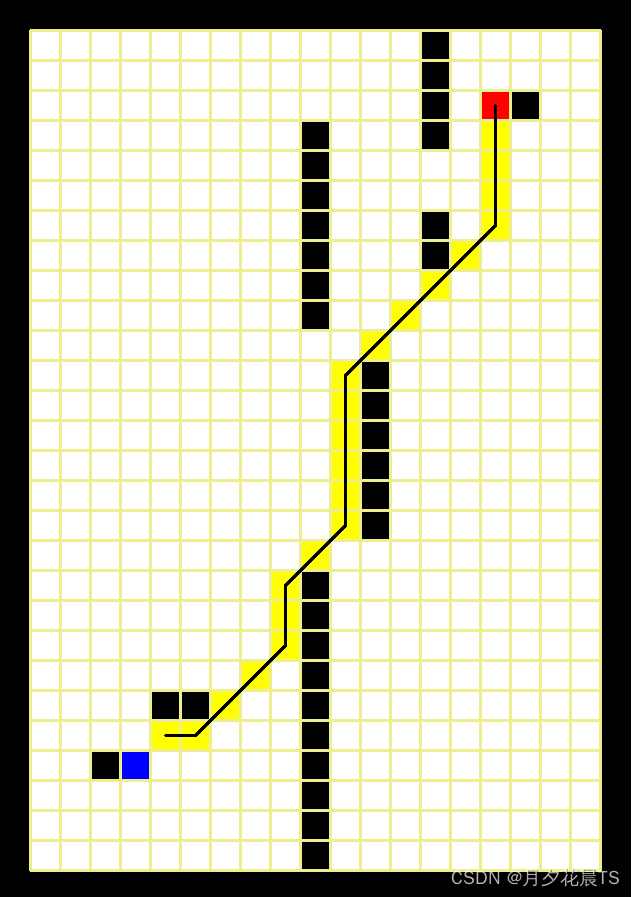 Greedy(a=0,b=1.0)
Greedy(a=0,b=1.0)
|
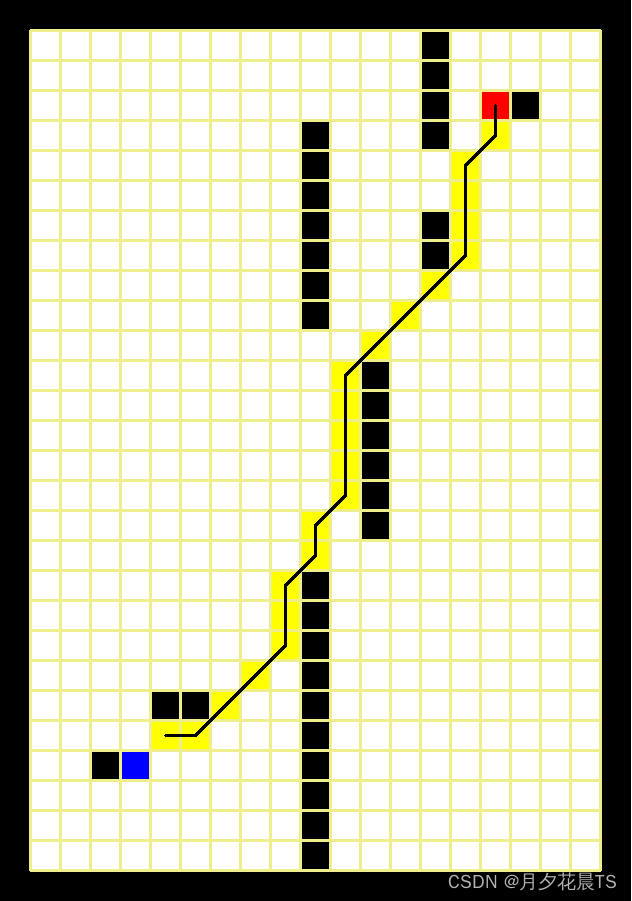 Weight Astar(a=1.0,b=1.1)
Weight Astar(a=1.0,b=1.1)
|
仿真二
 Astar 欧式距离
Astar 欧式距离
|
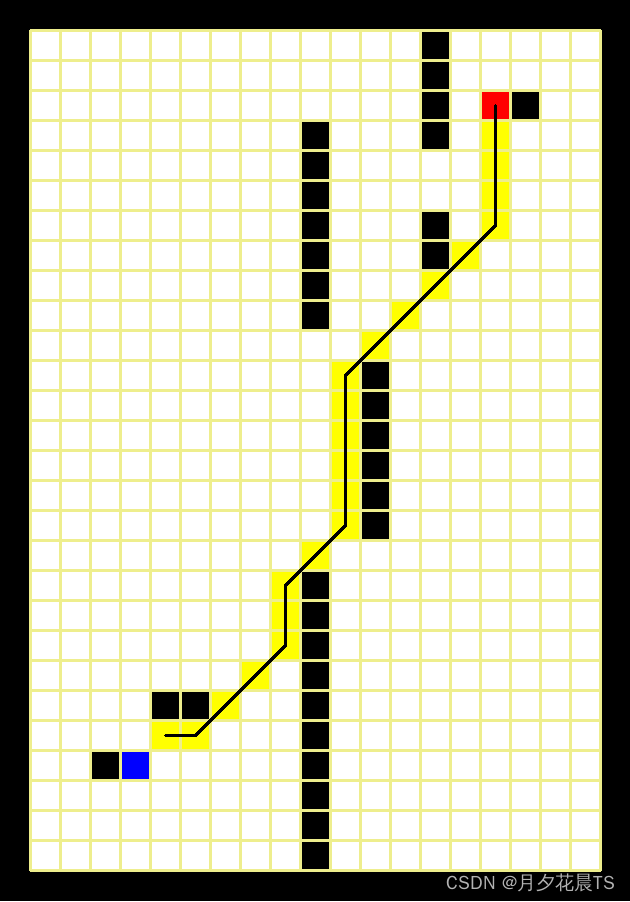 Astar 曼哈顿距离
Astar 曼哈顿距离
|
上述代码都是自己慢慢调试出来的,可能存在一些问题,发现问题的小伙伴加我QQ:2822902808,大家一起交流进步,谢谢。
理论部分参考我的上一篇博客:(一)路径规划算法—Graph Search Basis