刷题笔记【链表篇】
链表
1、反转链表【LC 206题】
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
维护当前节点cur,前一个节点pre,下一个节点nextNode。每次执行一步有cur.next=pre,并把cur、pre、next都往后移。
注意:
每一次循环最后一步都是更新cur的位置,cur=nextNode,最后cur==null,因此判断返回的时候,需要返回pre,而不是cur。
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur=head,pre=null,nextNode=cur.next;
while (cur!=null){
nextNode=cur.next;
cur.next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=nextNode;
}
return pre;
}
2、回文链表【LC 234题】
给你一个单链表的头节点 head ,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
笔试写法
利用栈先入后出的特性,遍历链表,push节点。判断:从栈中弹出节点,和原来的链表做比对。
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 额外空间复杂度:O(n)
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
Stack<ListNode> stack=new Stack<>();
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
stack.push(cur);
cur=cur.next;
}
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
if(stack.pop().val!=head.val) return false;
head=head.next;
}
return true;
}
面试写法
快慢指针,利用慢指针找到后半段的链表头,反转后半段链表,再分别从原链表头和反转链表头遍历比对。
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 额外空间复杂度:O(1)
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast=head.next,slow=head;
while (fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
ListNode right=reverse(slow.next);
ListNode left=head;
while (right!=null){
if (right.val!=left.val) return false;
right=right.next;
left=left.next;
}
return true;
}
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head){
ListNode cur=head;
ListNode pre=null,next=null;
while (cur!=null){
next=cur.next;
cur.next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=next;
}
return pre;
}
3.0 前置问题 荷兰国旗问题【LC 75题】
给定一个包含红色、白色和蓝色、共 n 个元素的数组 nums ,**原地**对它们进行排序,使得相同颜色的元素相邻,并按照红色、白色、蓝色顺序排列。我们使用整数 0、 1 和 2 分别表示红色、白色和蓝色。
- 用三个变量来维护:下一个
0应该在的位置left,下一个2应该在的位置right,当前遍历位置idx。也就是[0,left-1]为0;[left,right-1]为1,[right,len-1]为2。【idx,r】为待处理区间。- 当nums[idx]==1,表明它已经在正确的位置,因此我们只需要将
idx向右移动。 - 当nums[idx]==0,说明它应该放在数组的左边,因此我们将其与
l位置的元素交换,并将l和idx都向右移动。 - 当nums[idx]==2,说明它应该放在数组的右边,因此我们将其与
r位置的元素交换,并将r向左移动。由于交换后idx位置的新元素还未检查,所以idx暂时不动。
- 当nums[idx]==1,表明它已经在正确的位置,因此我们只需要将
注意:
退出循环条件为idx>right。【idx,r】为待处理区间。退出循环时表明没有待处理的元素。
public class SortColors_75 {
public void sortColors(int[] nums) {
int left=0,idx=0,right=nums.length-1;
while(idx<=right){ //退出循环条件为idx>right
if(nums[idx]==0) {
swap(nums,idx++,left++);
}
else if (nums[idx]==1) idx++;
else swap(nums,idx,right--);
}
}
public void swap(int []nums,int left,int right){
int temp=nums[left];
nums[left]=nums[right];
nums[right]=temp;
}
}
3、单链表荷兰国旗问题
将单向链表按某partition值划分成左边小、中间相等、右边大的形式,并保证节点相对位置不变。
- 需要6个变量构成3个单链表
- 小于partition链表的头指针
- 小于partition链表的尾指针
- 等于partition链表的头指针
- 等于partition链表的尾指针
- 大于partition链表的头指针
- 大于partition链表的尾指针
- 遍历链表,判断当前节点应当插入哪个链表
- 遍历结束,将三个链表依次首尾相接
注意:
需要考虑三个链表中为空的情况,不然可能会出现空指针异常
public static ListNode listPartition(ListNode head,int partition){
ListNode SH=null;
ListNode ST=null;
ListNode EH=null;
ListNode ET=null;
ListNode BH=null;
ListNode BT=null;
ListNode cur;
//遍历链表
while (head!=null){
//下面这两部操作,是为了三个链表的结尾都为null
cur=head.next;
head.next=null;
if (cur.val<partition){
if (SH==null){
SH=cur;
ST=cur;
}else {
ST.next=cur;
ST=cur;
}
} else if (cur.val == partition) {
if (EH==null){
EH=cur;
ET=cur;
}else {
ET.next=cur;
ET=cur;
}
}else {
if (BH==null){
BH=cur;
BT=cur;
}else {
BT.next=cur;
BT=cur;
}
}
head=cur;
}
//连接 三个链表 考虑链表为空的情况
if (ST!=null){
//如果小于partition链表不为空,就先直接赋值
ST.next=EH;
//再考虑等于partition链表是否为空的情况
ET=ET==null? BH :ST;
}
//先连接再说,后面再判断返回什么
if (ET!=null){
ET.next=BH;
}
return SH!=null ? SH : (EH!=null ? EH :BH);
}
4、随机链表的复制【LC 138题】
给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。构造这个链表的 深拷贝。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。接收原链表的头节点,返回复制链表的头节点。
笔试解法
利用HashMap,key放原来的节点,value放新建的节点。再次遍历hashmap,建立next和random指针联系。
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 额外空间复杂度:O(n)
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
HashMap<Node,Node> map=new HashMap<>();
Node cur=head;
// 构建 原节点-新节点的map
while (cur!=null){
map.put(cur,new Node(cur.val));
cur=cur.next;
}
cur=head;
//建立 next和random关系
while (cur!=null){
map.get(cur).next=map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).random=map.get(cur.random);
cur=cur.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
面试解法
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 额外空间复杂度:O(1)
主要分为三步
- 先复制节点 A->B->C 变成 A->A’->B->B’->C->C’
- 建立 random 关系
- split:将A->A’->B->B’->C->C’重新拆分成A->B->C和A’->B’->C’
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head==null) return head;
Node cur=head;
//先复制节点 A->B->C 变成 A->A'->B->B'->C->C'
while (cur!=null){
Node next=cur.next;
cur.next=new Node(cur.val);
cur.next.next=next;
cur=next;
}
//建立 random 关系
cur=head;
while (cur!=null){
cur.next.random=cur.random==null? null : cur.random.next;
cur=cur.next.next;
}
//split
cur=head;
Node headNew=cur.next;
Node curNew=cur.next;
while (cur!=null){
cur.next=cur.next.next;
cur=cur.next;
curNew.next= cur==null? null :cur.next;
curNew=curNew.next;
}
return headNew;
}
5、环形链表【LC 141题】
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
- 使用快慢指针,如果快慢指针相遇了说明链表有环,快指针遇到null说明链表无环
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null) return false;
ListNode fast=head.next;
ListNode slow=head;
while(fast!=slow){
if(fast==null||fast.next==null)
return false;
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return true;
}
6、环形链表【LC142题】
给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
- 和上题类似,使用快慢指针
- 找环的入口时,固定方法:
slow=slow.next,fast=head,然后两者一起往后走,每次走一步,相遇点即为环的入口
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null) return null;
ListNode fast=head.next;
ListNode slow=head;
while(fast!=slow){
if(fast==null || fast.next==null) return null;
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
slow=slow.next;
fast=head;
while(fast!=slow){
fast=fast.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
以上是一些铺垫,考虑 相交链表 这个大问题。
相交链表:两个链表有交点返回交点,无交点返回null。
根据有环、无环分为以下几种情况:
- 两个链表都无环【第七题】
- 一个链表有环,一个链表无环【这样的情况,两个链表不会有交点(如果有交点,就会存在一个节点有两个next指针的情况)】
- 两个链表都有环【第八题】
7、相交链表【LC 160题】
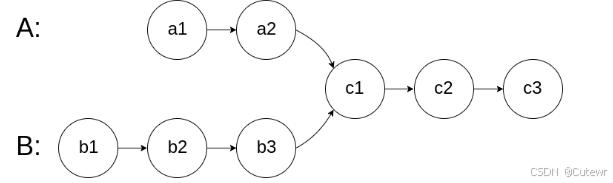
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交
解题思想:
- 求出两个链表的长度差n
- 让长的链表先走n步
- 两个链表一起往后走,如果两链表相交,两者会同时走到交点;如果不相交,两者会同时走到null
//两个链表都无环
public ListNode getIntersectionNode1(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
int n=0;
ListNode curA=headA;
ListNode curB=headB;
//求出链表A和链表B的长度差
while (curA!=null){
curA=curA.next;
n++;
}
while (curB!=null){
curB=curB.next;
n--;
}
curA=n>0?headA:headB; //curA保存长的链表
curB=curA==headA?headB:headA;
n=Math.abs(n);
// 长链表先往前走n步
while (n>0){
curA=curA.next;
}
// 如果两链表相交,两者会同时走到交点;如果不相交,两者会同时走到null
while (curA!=curB){
curA=curA.next;
curB=curB.next;
}
return curA;
}
8、相交链表【两个链表都有环】
分为三种情况:
- 两个有环链表不相交
- 两个链表共用一个入环节点
- 两个链表共用一个环,但是入环节点不一致
解决方案:
传入第一个链表头head1,第一个链表入环节点loop1;第二个链表头head2,第二个链表入环节点loop2;
- 如果loop1==loop2,说明为同一个环,解法和第七题类似,做题时以loop1结尾而不是null结尾
- 如果loop1!=loop2,是1或3情况,这时将loop1再转一圈,如果转的过程碰到loop2了,说明为第三种情况;如果转了一圈没有碰到,说明这两个链表不相交。
//两个链表都有环
public ListNode getIntersectionNode2(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode curA=headA;
ListNode loop1=detectCycle(headA); //链表A的环入口
ListNode curB=headB;
ListNode loop2=detectCycle(headB); //链表B的环入口
if (loop1==loop2){
int n=0;
while(curA!=loop1) n++;
while (curB!=loop2) n--;
curA = n>0 ? headA : headB;
curB = curA==headA ? headB : headA;
n=Math.abs(n);
while (n>0){
curA=curA.next;
n--;
}
while (curA!=curB){
curA=curA.next;
curB=curB.next;
}
return curA;
}else {
curA=loop1.next;
while (curA!=loop1){
if (curA==loop2) return loop2;
curA=curA.next;
}
}
return null;
}