1.最基础的使用示例
诉求:存在一份甲方公司的数据库表,需要当前公司项目可以直接进行读取到所需数据,需要用到多数据源时——这里的需求属于自编,目的是了解配置多数据源以及配置使用
-
所需依赖
mysql,mybatis,springboot就不添加了,这里只做相关多数据源配置的依赖。aop 用于后面进阶的切面
<dependency> <groupId>com.baomidou</groupId> <artifactId>dynamic-datasource-spring</artifactId> <version>4.2.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId> </dependency> -
数据库相关的配置文件 .yml
spring: datasource: middle: username: root password: root jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sour_one?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useUnicode=true@characterEncoding=utf-8 driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver master: username: root password: root jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sour_two?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useUnicode=true@characterEncoding=utf-8 driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver注意:数据库配置的 url 改为了 jdbc-url。这里做的是不同的库,如果是 SQL Server、Oracle 等的也是同理使用方式
-
数据表
这里不做复杂的,只做简单,两张表只是库不同以及表名不同,结构是相同的
-
数据源配置类
import javax.sql.DataSource; @Data @Configuration public class DataSourceConfig { // 默认数据源-master @Bean(name = "master") @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.master") public DataSource dataSourceDevOps() { return DataSourceBuilder.create().build(); } // 中间表数据源-middle @Bean(name = "middle") @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.middle") public DataSource dataSourceHNSX() { return DataSourceBuilder.create().build(); } // 配置动态数据源 @Bean @Primary // 注解指定一个默认数据源。 @DependsOn({"master", "middle"}) // 指定加载顺序 public DynamicDataSource dataSource(@Qualifier("master") DataSource master, @Qualifier("middle") DataSource middle) { DynamicDataSource dataSource = new DynamicDataSource(); // 设置默认的数据源,在没有明确指定数据源时使用。 dataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(master); // 多个数据源注册到 targetDataSources 中 Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources = new HashMap<>(); targetDataSources.put("master", master); targetDataSources.put("middle", middle); // 设置所有目标数据源 dataSource.setTargetDataSources(targetDataSources); return dataSource; } }
DynamicDataSource在下面的配置
-
动态切换数据源配置
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource; public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource { // 存储当前线程的数据源标识,确保每个线程都有自己的独立副本 public static final ThreadLocal<String> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<>(); // 设置数据源 public static void setDataSource(String key) { contextHolder.set(key); System.out.println("切换到数据源:" + contextHolder.get()); } // 清除数据源 public static void clearDataSource() { contextHolder.remove(); } // 确定当前数据源 @Override protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() { return contextHolder.get(); } }
1.1、代码示例演示
-
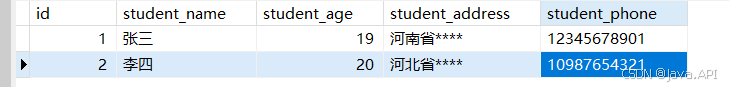
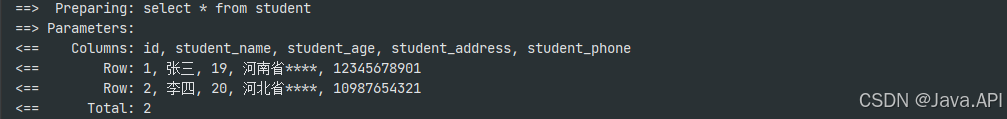
主表数据内容
-
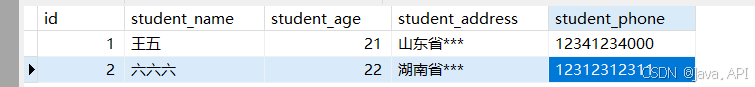
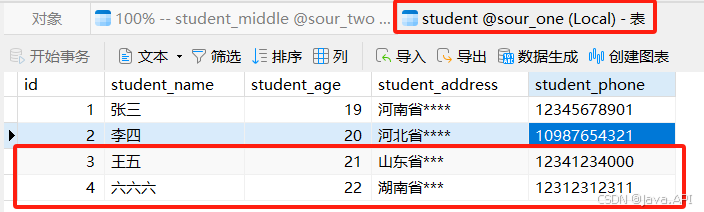
中间表数据内容
-
StudentServiceImpl
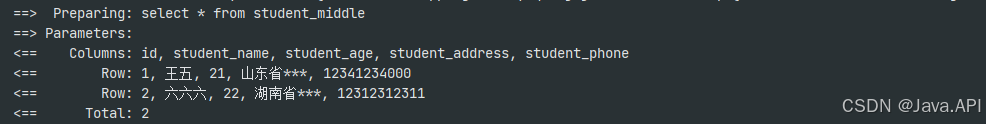
这里只展示实现层代码,控制层代码只是用来访问接口,下方的结果图也是访问接口 MySQL 打印的 SQL 日志
@Service @RequiredArgsConstructor public class StudentServiceImpl implements IStudentService { private final StudentMapper studentMapper; @Override public R<List<Student>> readMiddleData() { // 切换数据源读取中间表数据 DynamicDataSource.setDataSource("middle"); List<Student> students = studentMapper.findMiddleData(); // 清除数据源 DynamicDataSource.clearDataSource(); return R.createBySuccess(students); } @Override public R<List<Student>> readLocalData() { // 切换本地数据源,也可以不进行切换,因为存在着默认数据源 - master DynamicDataSource.setDataSourceKey("master"); List<Student> students = studentMapper.findLocalData(); // 清除数据源 DynamicDataSource.clearDataSource(); return R.createBySuccess(students); } } -
StudentMppaer
<mapper namespace="com.coding.mapper.StudentMapper"> <select id="findMiddleData" resultType="com.coding.entity.Student"> select * from student_middle </select> <select id="findLocalData" resultType="com.coding.entity.Student"> select * from student </select> </mapper>
两条 SQL 都同在一个 mapper 文件中,这并不影响,也有的可以通过两个不同的数据源文件来配置对应的 mapper 来实现,这里就不做补充了,后续可能会有
2.进阶:通过自定义注解 + AOP 来实现动态切换数据源
-
annotation 注解
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface UseSource { // 要使用的数据库名称 String value(); } -
aspect 切面
@Aspect @Component public class UseDBAspect { // 定义切面 @Pointcut(value = "@annotation(com.sesami.datacollectproject.annotations.UseDB)") private void getAnnounce(){} @Around("getAnnounce()") public Object logPostMapping(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable { // 获取自定义注解中的value值 MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature(); UseDB annotation = signature.getMethod().getAnnotation(UseDB.class); String dataSourceKey = annotation.value(); // 将dataSource的key设置到ThreadLocal DynamicDataSource.setDataSource(dataSourceKey); // 执行目标方法,也就是service方法 Object result = joinPoint.proceed(); // 执行方法后,记得清除ThreadLocal,避免内存泄漏 DynamicDataSource.clearDataSource(); // 返回方法返回值 return result; } }
使用 AOP 后效果是相同的,这里就不粘贴图费眼睛了,简单放下业务层的
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class StudentServiceImpl implements IStudentService {
private final StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Override
@UseSource("middle")
public R<List<Student>> readMiddleData() {
List<Student> students = studentMapper.findMiddleData();
return R.createBySuccess(students);
}
@Override
@UseSource("master")
public R<List<Student>> readLocalData() {
List<Student> students = studentMapper.findLocalData();
return R.createBySuccess(students);
}
}
下面是可能遇到的问题和延伸
3.在一个 service 方法调用另一个使用了不同数据源的 service 方法数据源切换失败
- 业务需求是:需要吧甲方公司提供的数据库表里的数据进行查询并且放入本地数据库(可以说当前项目数据库),这就需要在一个 service 方法调用查询甲方公司数据库后,紧接着使用本地数据源进行添加操作,导致数据源切换失败的问题
问题未解决调用前的实现层代码
-
StudentServiceImpl
@Override @UseSource("middle") public R<String> readMiddleInsertLocal() { List<Student> students = studentMapper.findMiddleData(); return insertLocalSource(students); } // 添加至本地数据库 @UseSource("master") public R<String> insertLocalSource(List<Student> students){ // 这里就不做批量插入了简单的来主要针对多数据源,数据量大的情况下一般是需要使用批量加入,而不是一条条循环加入 for (Student student : students) { int result = studentMapper.insertStudent(student); if(result == 0){ return R.createByErrorMessage("添加异常"); } } return R.createBySuccess("添加成功"); } -
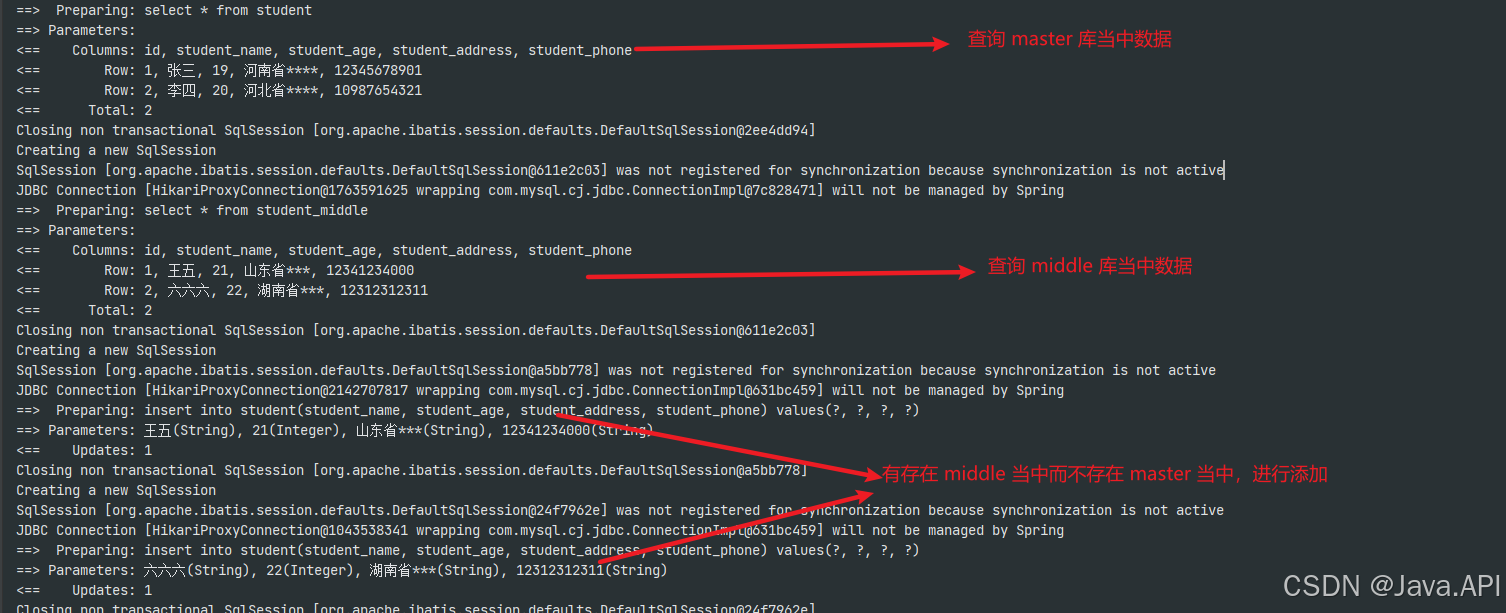
运行 readMiddleInsertLocal 后报错:
也就是说在 middle(对应的 sour_two 数据库) 使用查询后,切换数据源调用了 insertLocalSource 方法并没有成功切换 master 数据源
-
原因:是因为AOP实现代理时,类的内部调用默认不走代理方法,当调用另一个使用了不同数据源 service 方法时,默认不走 AOP 动态代理,这就导致了数据源并没有被切换回来
-
解决方案
- 开启exposeProxy=true的配置,将类内部引用也走AOP代理,在启动类上进行标注
@SpringBootApplication @EnableAspectJAutoProxy(exposeProxy = true) public class CodeGeneratorApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(CodeGeneratorApplication.class, args); } }- StudentServiceImpl:获取到代理对象,通过代理对象调用另外的 service 层方法
@Override @UseSource("middle") public R<String> readMiddleInsertLocal() { List<Student> students = studentMapper.findMiddleData(); // 获取到代理对象,通过代理对象来调用另外的 service 层方法 StudentServiceImpl studentService = (StudentServiceImpl) AopContext.currentProxy(); return studentService.insertLocalSource(students); } // 添加至本地数据库 @UseSource("master") public R<String> insertLocalSource(List<Student> students){ // 这里就不做批量插入了简单的来主要针对多数据源,数据量大的情况下一般是需要使用批量加入,而不是一条条循环加入 for (Student student : students) { int result = studentMapper.insertStudent(student); if(result == 0){ return R.createByErrorMessage("添加异常"); } } return R.createBySuccess("添加成功"); }
结果将甲方数据库 sour_two 当中的 student_middle 表中的数据添加至本地库 sour_one 当中的 student 表中
4.补充:在同一个 service 层中调用另外一个不同数据源的 service 方法后需要再使用最初的数据源的bug
这样的情况会导致在调用内层的 service(也就是另外一个不同数据源的 service 方法) 时,切面会去使用DynamicDataSource.clearDataSource() 清除数据源,这样就导致了没有指定走的数据源会执行默认数据源,如果是刚好最外层使用的是默认的,那还好如果是多个或者不是默认的就会导致执行了默认数据源的问题.
我们要解决的就是,外层方法使用外层的数据源,内层 service 调用使用内层的,方法执行一个清楚一个,不影响外层的数据源。这样的形式为先进后出,可以使用栈 Stack 来进行存储
-
修改 DynamicDataSource
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource; import java.util.Objects; import java.util.Stack; public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource { // 存储当前线程的数据源标识,确保每个线程都有自己的独立副本 public static final ThreadLocal<Stack<String>> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<>(); // 将 DataSource 的 key 添加到 ThreadLocal 的 Stack 中,效果等同直接交给 ThreadLocal public static void setDataSource(String key) { // 判断是否为空,初始状态时为 null 需要进行创建 Stack if (Objects.isNull(contextHolder.get())){ contextHolder.set(new Stack<String>()); } // 将给定的数据源参数放入 Stack 中 contextHolder.get().push(key); } // 清除数据源:将 DataSource 的 key 删除,不一定删除ThreadLocal,只有最后一个 key 被 Stack 出栈后才删除 ThreadLocal public static void clearDataSource() { contextHolder.get().pop(); // 如果此时栈中没有数据了,则将 ThreadLocal 清除 if (contextHolder.get().empty()) { contextHolder.remove(); } } // 确定当前数据源 @Override protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() { return contextHolder.get().peek(); } }
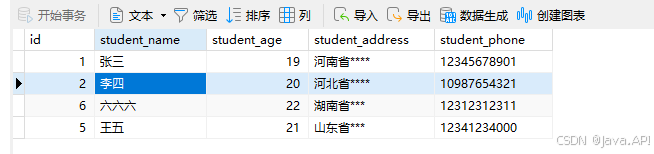
这里做个示例,外层 service 走 master 数据源进行查询数据,然后再通过调用不同数据源的 middle 来进行查询,如果 middle 中存在的学生而 master 中不存在,则进行添加【这里先将之前的“王五”、“六六六”数据进行删除】
-
实现层
// 外层 service 走 master 数据源进行查询数据,然后再通过调用不同数据源的 middle 来进行查询,如果 middle 中存在而 master 中不存在,则进行添加 @Override @UseSource("master") public R<String> readMiddleAndInsertDifferent() { // 获取到代理对象 StudentServiceImpl studentService = (StudentServiceImpl) AopContext.currentProxy(); // master 中学生名称的数据,这里使用 stream 的方式进行只获取学生名字 List<String> studentLocalNames = studentMapper.findLocalData().stream().map(Student::getStudentName).collect(Collectors.toList()); // middle 中数据 List<Student> studentMiddle = studentService.readMiddleData().getData(); // 循环便利判断是否存在本地库中没有添加的学生 for (Student student : studentMiddle) { // 如果 master 内不存在该学生,则进行添加操作 if(!studentLocalNames.contains(student.getStudentName())){ studentService.insertSingleStudent(student); } } return null; } @UseSource("master") public R<String> insertSingleStudent(Student student){ int result = studentMapper.insertStudent(student); if(result == 0){ return R.createByErrorMessage("添加失败"); } return R.createBySuccess("添加成功"); }
这里做的例子,其实本身可以不用使用 Stack 来进行存储指定的数据源,因为清楚后会走默认的,还是 master,大家意会即可
-
结果图
4.遇到@Transactional 无法切换数据源的问题
是因为在进行切换数据源的时候是在事务开启之前进行的,如果给定了 Transcational 注解就会导致数据源还没有进行切换,事务就已经开启了,这就导致了数据源切换失败的原因
解决方案
- 使用 mybatis-plus 的 @DSTransactional
- 使用事物传播行为 Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW:@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW),事务生效
事务的相关可以参考:https://blog.csdn.net/Onstduy/article/details/106093994
如果有问题或者是需要补充说明的地方,可以进行评论和私信我,个人很乐于解决,需要上面示例代码的也可以私信