前言
在实际处理过程中,我们使用YOLO V8进行推理时,通常会针对一张图片进行推理。如果需要对多张图片进行推理,则可以通过一个循环来实现对图片逐张进行推理。
单张图片推理时,需要注意图片的尺寸必须是32的倍数,否则可能导致推理失败。在下面的示例中,我们展示了如何使用PyTorch和Ultralytics库进行单张图片的推理:
import torch
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
model = YOLO('yolov8n-seg.pt')
# Create a random torch tensor of BCHW shape (1, 3, 640, 640) with values in range [0, 1] and type float32
source = torch.rand(1, 3, 640, 640, dtype=torch.float32)
# Run inference on the source
results = model(source) # list of Results objects批量图片推理时,也需要注意图片的尺寸必须是32的倍数。在下面的示例中,我们展示了如何使用PyTorch和Ultralytics库进行多张图片的批量推理:
import torch
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
model = YOLO('yolov8n-seg.pt')
# Create a random torch tensor of BCHW shape (1, 3, 640, 640) with values in range [0, 1] and type float32
source = torch.rand(4, 3, 640, 640, dtype=torch.float32)
# Run inference on the source
results = model(source) # list of Results objects需要注意的是,在批量推理时,虽然一次推理了多张图片,但实际处理方式仍然是通过循环进行的。在后续的文章中,我们将介绍如何使用更高效的方式进行批量推理,以获得更快的推理速度和更好的性能。
下面我们介绍如何将检测推理代码给单独提取出来,进行推理。
一、YOLO V8-Segment 预测
在官方中,进行推理时,直接使用两行代码就能实现目标检测的功能。
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a model
model = YOLO('yolov8n-seg.pt')
# Run batched inference on a list of images
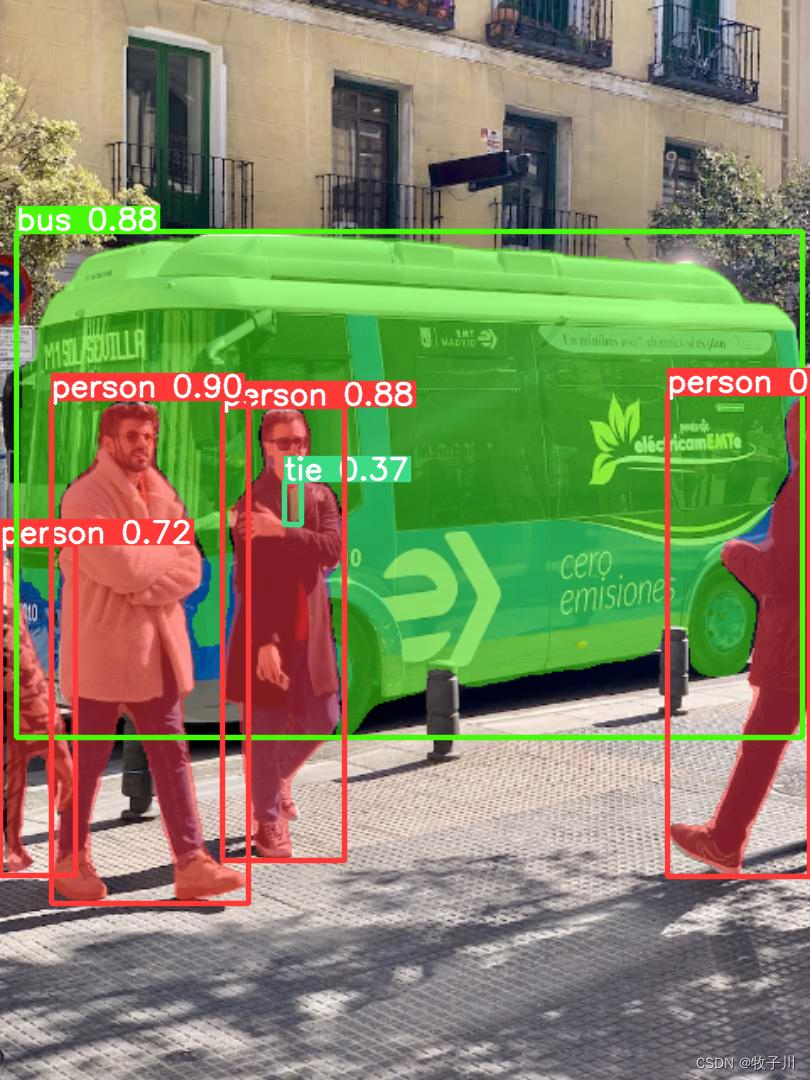
model.predict("./ultralytics/assets/bus.jpg", imgsz=640, save=True, device=0)模型推理保存的结果图像如下所示:
模型预测成功,我们就需要自己动手来写下 YOLOv8-Seg 的模型加载、预处理和后处理,以便我们进行相关的操作,我们先来看看预处理的实现
二、YOLO V8-Segmnt 模型加载
原始加载方式
模型文件:ultralytics\engine\model.py
def _load(self, weights: str, task=None):
"""
Initializes a new model and infers the task type from the model head.
Args:
weights (str): model checkpoint to be loaded
task (str | None): model task
"""
suffix = Path(weights).suffix
if suffix == ".pt":
self.model, self.ckpt = attempt_load_one_weight(weights)
self.task = self.model.args["task"]
self.overrides = self.model.args = self._reset_ckpt_args(self.model.args)
self.ckpt_path = self.model.pt_path
else:
weights = checks.check_file(weights)
self.model, self.ckpt = weights, None
self.task = task or guess_model_task(weights)
self.ckpt_path = weights
self.overrides["model"] = weights
self.overrides["task"] = self.task模型文件:ultralytics/nn/tasks.py
def attempt_load_one_weight(weight, device=None, inplace=True, fuse=False):
"""Loads a single model weights."""
ckpt, weight = torch_safe_load(weight) # load ckpt
args = {**DEFAULT_CFG_DICT, **(ckpt.get("train_args", {}))} # combine model and default args, preferring model args
model = (ckpt.get("ema") or ckpt["model"]).to(device).float() # FP32 model
# Model compatibility updates
model.args = {k: v for k, v in args.items() if k in DEFAULT_CFG_KEYS} # attach args to model
model.pt_path = weight # attach *.pt file path to model
model.task = guess_model_task(model)
if not hasattr(model, "stride"):
model.stride = torch.tensor([32.0])
model = model.fuse().eval() if fuse and hasattr(model, "fuse") else model.eval() # model in eval mode
# Module updates
for m in model.modules():
t = type(m)
if t in (nn.Hardswish, nn.LeakyReLU, nn.ReLU, nn.ReLU6, nn.SiLU, Detect, Segment, Pose, OBB):
m.inplace = inplace
elif t is nn.Upsample and not hasattr(m, "recompute_scale_factor"):
m.recompute_scale_factor = None # torch 1.11.0 compatibility
# Return model and ckpt
return model, ckpt上述两个代码是加载模型的原始方法,这种方法不仅会加载模型的权重,还会加载一系列相关的配置文件,这个并不是我们想要的。我们只加载模型权重,其余相关的都不需要加载,因此要使用下面这种方式进行加载。
修改后的加载方式
模型文件:ultralytics/nn/autobackend.py
@torch.no_grad()
def __init__(
self,
weights="yolov8n.pt",
device=torch.device("cpu"),
dnn=False,
data=None,
fp16=False,
fuse=True,
verbose=True,
):参数介绍
weights:模型权重文件的路径。默认为 "yolov8n.pt"。device (torch.device):运行模型的设备。默认为 CPU。dnn:使用 OpenCV DNN 模块进行 ONNX 推断。默认为假。data:包含类名的附加 data.yaml 文件的路径。可选。fp16:启用半精度推理。仅在特定后端支持。默认为 False。fuse:融合 Conv2D + BatchNorm 层进行优化。默认为 True。verbose:启用详细日志记录。默认为 True。
.pt 加载方式
elif pt: # PyTorch
from ultralytics.nn.tasks import attempt_load_weights
model = attempt_load_weights(
weights if isinstance(weights, list) else w, device=device, inplace=True, fuse=fuse
)
if hasattr(model, "kpt_shape"):
kpt_shape = model.kpt_shape # pose-only
stride = max(int(model.stride.max()), 32) # model stride
names = model.module.names if hasattr(model, "module") else model.names # get class names
model.half() if fp16 else model.float()
self.model = model # explicitly assign for to(), cpu(), cuda(), half()最终代码
from ultralytics.nn.autobackend import AutoBackend
weights = 'yolov8n-seg.pt'
model = AutoBackend(weights, device=torch.device("cuda:0"))三、YOLO V8-Segment 预处理
原始处理方式
模型文件:ultralytics/engine/predictor.py
from ultralytics.data.augment import LetterBox
@smart_inference_mode()
def stream_inference(self, source=None, model=None, *args, **kwargs):
"""Streams real-time inference on camera feed and saves results to file."""
.
.
.
# Preprocess
with profilers[0]:
im = self.preprocess(im0s)
.
.
.
def pre_transform(self, im):
"""
Pre-transform input image before inference.
Args:
im (List(np.ndarray)): (N, 3, h, w) for tensor, [(h, w, 3) x N] for list.
Returns:
(list): A list of transformed images.
"""
same_shapes = all(x.shape == im[0].shape for x in im)
letterbox = LetterBox(self.imgsz, auto=same_shapes and self.model.pt, stride=self.model.stride)
return [letterbox(image=x) for x in im]
def preprocess(self, im):
"""
Prepares input image before inference.
Args:
im (torch.Tensor | List(np.ndarray)): BCHW for tensor, [(HWC) x B] for list.
"""
not_tensor = not isinstance(im, torch.Tensor)
if not_tensor:
im = np.stack(self.pre_transform(im))
im = im[..., ::-1].transpose((0, 3, 1, 2)) # BGR to RGB, BHWC to BCHW, (n, 3, h, w)
im = np.ascontiguousarray(im) # contiguous
im = torch.from_numpy(im)
im = im.to(self.device)
im = im.half() if self.model.fp16 else im.float() # uint8 to fp16/32
if not_tensor:
im /= 255 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
return im它包含以下步骤:
-
self.pre_transform:即 letterbox 添加灰条
-
im[…,::-1]:BGR → RGB
-
transpose((0, 3, 1, 2)):添加 batch 维度,HWC → CHW
-
torch.from_numpy:to Tensor
-
im /= 255:除以 255,归一化
大家如果对 YOLOv5 的预处理熟悉的话,会发现 YOLOv8 的预处理和 YOLOv5 的预处理一模一样,因此我们不难写出对应的预处理代码,如下所示:
修改后的处理方式
def letterbox(self, im, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(114, 114, 114), auto=True, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True,
stride=32):
# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraints
shape = im.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
if not scaleup: # only scale down, do not scale up (for better val mAP)
r = min(r, 1.0)
# Compute padding
ratio = r, r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
if auto: # minimum rectangle
dw, dh = np.mod(dw, stride), np.mod(dh, stride) # wh padding
elif scaleFill: # stretch
dw, dh = 0.0, 0.0
new_unpad = (new_shape[1], new_shape[0])
ratio = new_shape[1] / shape[1], new_shape[0] / shape[0] # width, height ratios
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
im = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return im, ratio, (dw, dh)
def precess_image(self, img_src, img_size, stride, half, device):
# Padded resize
img = self.letterbox(img_src, img_size, stride=stride)[0]
# Convert
img = img.transpose((2, 0, 1))[::-1] # HWC to CHW, BGR to RGB
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(device)
img = img.half() if half else img.float() # uint8 to fp16/32
img = img / 255 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
if len(img.shape) == 3:
img = img[None] # expand for batch dim
return img四、YOLO V8-Segment 后处理
原始处理方式
模型文件:ultralytics/engine/predictor.py
@smart_inference_mode()
def stream_inference(self, source=None, model=None, *args, **kwargs):
"""Streams real-time inference on camera feed and saves results to file."""
.
.
.
# Postprocess
with profilers[2]:
self.results = self.postprocess(preds, im, im0s)
.
.
.模型文件:ultralytics/models/yolo/segment/predict.py
def postprocess(self, preds, img, orig_imgs):
"""Applies non-max suppression and processes detections for each image in an input batch."""
p = ops.non_max_suppression(
preds[0],
self.args.conf,
self.args.iou,
agnostic=self.args.agnostic_nms,
max_det=self.args.max_det,
nc=len(self.model.names),
classes=self.args.classes,
)
if not isinstance(orig_imgs, list): # input images are a torch.Tensor, not a list
orig_imgs = ops.convert_torch2numpy_batch(orig_imgs)
results = []
proto = preds[1][-1] if isinstance(preds[1], tuple) else preds[1] # tuple if PyTorch model or array if exported
for i, pred in enumerate(p):
orig_img = orig_imgs[i]
img_path = self.batch[0][i]
if not len(pred): # save empty boxes
masks = None
elif self.args.retina_masks:
pred[:, :4] = ops.scale_boxes(img.shape[2:], pred[:, :4], orig_img.shape)
masks = ops.process_mask_native(proto[i], pred[:, 6:], pred[:, :4], orig_img.shape[:2]) # HWC
else:
masks = ops.process_mask(proto[i], pred[:, 6:], pred[:, :4], img.shape[2:], upsample=True) # HWC
pred[:, :4] = ops.scale_boxes(img.shape[2:], pred[:, :4], orig_img.shape)
results.append(Results(orig_img, path=img_path, names=self.model.names, boxes=pred[:, :6], masks=masks))
return results可以看到原始的后处理部分一共有两个部分,分别为 nms 处理和 坐标绘图处理这两步。
nms 处理
模型文件:ultralytics/utils/ops.py
def scale_boxes(img1_shape, boxes, img0_shape, ratio_pad=None, padding=True, xywh=False):
"""
Rescales bounding boxes (in the format of xyxy by default) from the shape of the image they were originally
specified in (img1_shape) to the shape of a different image (img0_shape).
Args:
img1_shape (tuple): The shape of the image that the bounding boxes are for, in the format of (height, width).
boxes (torch.Tensor): the bounding boxes of the objects in the image, in the format of (x1, y1, x2, y2)
img0_shape (tuple): the shape of the target image, in the format of (height, width).
ratio_pad (tuple): a tuple of (ratio, pad) for scaling the boxes. If not provided, the ratio and pad will be
calculated based on the size difference between the two images.
padding (bool): If True, assuming the boxes is based on image augmented by yolo style. If False then do regular
rescaling.
xywh (bool): The box format is xywh or not, default=False.
Returns:
boxes (torch.Tensor): The scaled bounding boxes, in the format of (x1, y1, x2, y2)
"""
if ratio_pad is None: # calculate from img0_shape
gain = min(img1_shape[0] / img0_shape[0], img1_shape[1] / img0_shape[1]) # gain = old / new
pad = (
round((img1_shape[1] - img0_shape[1] * gain) / 2 - 0.1),
round((img1_shape[0] - img0_shape[0] * gain) / 2 - 0.1),
) # wh padding
else:
gain = ratio_pad[0][0]
pad = ratio_pad[1]
if padding:
boxes[..., 0] -= pad[0] # x padding
boxes[..., 1] -= pad[1] # y padding
if not xywh:
boxes[..., 2] -= pad[0] # x padding
boxes[..., 3] -= pad[1] # y padding
boxes[..., :4] /= gain
return clip_boxes(boxes, img0_shape)
def clip_boxes(boxes, shape):
"""
Takes a list of bounding boxes and a shape (height, width) and clips the bounding boxes to the shape.
Args:
boxes (torch.Tensor): the bounding boxes to clip
shape (tuple): the shape of the image
Returns:
(torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): Clipped boxes
"""
if isinstance(boxes, torch.Tensor): # faster individually (WARNING: inplace .clamp_() Apple MPS bug)
boxes[..., 0] = boxes[..., 0].clamp(0, shape[1]) # x1
boxes[..., 1] = boxes[..., 1].clamp(0, shape[0]) # y1
boxes[..., 2] = boxes[..., 2].clamp(0, shape[1]) # x2
boxes[..., 3] = boxes[..., 3].clamp(0, shape[0]) # y2
else: # np.array (faster grouped)
boxes[..., [0, 2]] = boxes[..., [0, 2]].clip(0, shape[1]) # x1, x2
boxes[..., [1, 3]] = boxes[..., [1, 3]].clip(0, shape[0]) # y1, y2
return boxes
def xywh2xyxy(x):
"""
Convert bounding box coordinates from (x, y, width, height) format to (x1, y1, x2, y2) format where (x1, y1) is the
top-left corner and (x2, y2) is the bottom-right corner.
Args:
x (np.ndarray | torch.Tensor): The input bounding box coordinates in (x, y, width, height) format.
Returns:
y (np.ndarray | torch.Tensor): The bounding box coordinates in (x1, y1, x2, y2) format.
"""
assert x.shape[-1] == 4, f"input shape last dimension expected 4 but input shape is {x.shape}"
y = torch.empty_like(x) if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) else np.empty_like(x) # faster than clone/copy
dw = x[..., 2] / 2 # half-width
dh = x[..., 3] / 2 # half-height
y[..., 0] = x[..., 0] - dw # top left x
y[..., 1] = x[..., 1] - dh # top left y
y[..., 2] = x[..., 0] + dw # bottom right x
y[..., 3] = x[..., 1] + dh # bottom right y
return y
def non_max_suppression(
prediction,
conf_thres=0.25,
iou_thres=0.45,
classes=None,
agnostic=False,
multi_label=False,
labels=(),
max_det=300,
nc=0, # number of classes (optional)
max_time_img=0.05,
max_nms=30000,
max_wh=7680,
rotated=False,
):
"""
Perform non-maximum suppression (NMS) on a set of boxes, with support for masks and multiple labels per box.
Args:
prediction (torch.Tensor): A tensor of shape (batch_size, num_classes + 4 + num_masks, num_boxes)
containing the predicted boxes, classes, and masks. The tensor should be in the format
output by a model, such as YOLO.
conf_thres (float): The confidence threshold below which boxes will be filtered out.
Valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0.
iou_thres (float): The IoU threshold below which boxes will be filtered out during NMS.
Valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0.
classes (List[int]): A list of class indices to consider. If None, all classes will be considered.
agnostic (bool): If True, the model is agnostic to the number of classes, and all
classes will be considered as one.
multi_label (bool): If True, each box may have multiple labels.
labels (List[List[Union[int, float, torch.Tensor]]]): A list of lists, where each inner
list contains the apriori labels for a given image. The list should be in the format
output by a dataloader, with each label being a tuple of (class_index, x1, y1, x2, y2).
max_det (int): The maximum number of boxes to keep after NMS.
nc (int, optional): The number of classes output by the model. Any indices after this will be considered masks.
max_time_img (float): The maximum time (seconds) for processing one image.
max_nms (int): The maximum number of boxes into torchvision.ops.nms().
max_wh (int): The maximum box width and height in pixels
Returns:
(List[torch.Tensor]): A list of length batch_size, where each element is a tensor of
shape (num_boxes, 6 + num_masks) containing the kept boxes, with columns
(x1, y1, x2, y2, confidence, class, mask1, mask2, ...).
"""
# Checks
assert 0 <= conf_thres <= 1, f"Invalid Confidence threshold {conf_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0"
assert 0 <= iou_thres <= 1, f"Invalid IoU {iou_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0"
if isinstance(prediction, (list, tuple)): # YOLOv8 model in validation model, output = (inference_out, loss_out)
prediction = prediction[0] # select only inference output
bs = prediction.shape[0] # batch size
nc = nc or (prediction.shape[1] - 4) # number of classes
nm = prediction.shape[1] - nc - 4
mi = 4 + nc # mask start index
xc = prediction[:, 4:mi].amax(1) > conf_thres # candidates
# Settings
# min_wh = 2 # (pixels) minimum box width and height
time_limit = 0.5 + max_time_img * bs # seconds to quit after
multi_label &= nc > 1 # multiple labels per box (adds 0.5ms/img)
prediction = prediction.transpose(-1, -2) # shape(1,84,6300) to shape(1,6300,84)
if not rotated:
prediction[..., :4] = xywh2xyxy(prediction[..., :4]) # xywh to xyxy
t = time.time()
output = [torch.zeros((0, 6 + nm), device=prediction.device)] * bs
for xi, x in enumerate(prediction): # image index, image inference
# Apply constraints
# x[((x[:, 2:4] < min_wh) | (x[:, 2:4] > max_wh)).any(1), 4] = 0 # width-height
x = x[xc[xi]] # confidence
# Cat apriori labels if autolabelling
if labels and len(labels[xi]) and not rotated:
lb = labels[xi]
v = torch.zeros((len(lb), nc + nm + 4), device=x.device)
v[:, :4] = xywh2xyxy(lb[:, 1:5]) # box
v[range(len(lb)), lb[:, 0].long() + 4] = 1.0 # cls
x = torch.cat((x, v), 0)
# If none remain process next image
if not x.shape[0]:
continue
# Detections matrix nx6 (xyxy, conf, cls)
box, cls, mask = x.split((4, nc, nm), 1)
if multi_label:
i, j = torch.where(cls > conf_thres)
x = torch.cat((box[i], x[i, 4 + j, None], j[:, None].float(), mask[i]), 1)
else: # best class only
conf, j = cls.max(1, keepdim=True)
x = torch.cat((box, conf, j.float(), mask), 1)[conf.view(-1) > conf_thres]
# Filter by class
if classes is not None:
x = x[(x[:, 5:6] == torch.tensor(classes, device=x.device)).any(1)]
# Check shape
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n: # no boxes
continue
if n > max_nms: # excess boxes
x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)[:max_nms]] # sort by confidence and remove excess boxes
# Batched NMS
c = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classes
scores = x[:, 4] # scores
if rotated:
boxes = torch.cat((x[:, :2] + c, x[:, 2:4], x[:, -1:]), dim=-1) # xywhr
i = nms_rotated(boxes, scores, iou_thres)
else:
boxes = x[:, :4] + c # boxes (offset by class)
i = torchvision.ops.nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres) # NMS
i = i[:max_det] # limit detections
# # Experimental
# merge = False # use merge-NMS
# if merge and (1 < n < 3E3): # Merge NMS (boxes merged using weighted mean)
# # Update boxes as boxes(i,4) = weights(i,n) * boxes(n,4)
# from .metrics import box_iou
# iou = box_iou(boxes[i], boxes) > iou_thres # iou matrix
# weights = iou * scores[None] # box weights
# x[i, :4] = torch.mm(weights, x[:, :4]).float() / weights.sum(1, keepdim=True) # merged boxes
# redundant = True # require redundant detections
# if redundant:
# i = i[iou.sum(1) > 1] # require redundancy
output[xi] = x[i]
if (time.time() - t) > time_limit:
LOGGER.warning(f"WARNING ⚠️ NMS time limit {time_limit:.3f}s exceeded")
break # time limit exceeded
return output
def process_mask(protos, masks_in, bboxes, shape, upsample=False):
"""
Apply masks to bounding boxes using the output of the mask head.
Args:
protos (torch.Tensor): A tensor of shape [mask_dim, mask_h, mask_w].
masks_in (torch.Tensor): A tensor of shape [n, mask_dim], where n is the number of masks after NMS.
bboxes (torch.Tensor): A tensor of shape [n, 4], where n is the number of masks after NMS.
shape (tuple): A tuple of integers representing the size of the input image in the format (h, w).
upsample (bool): A flag to indicate whether to upsample the mask to the original image size. Default is False.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor): A binary mask tensor of shape [n, h, w], where n is the number of masks after NMS, and h and w
are the height and width of the input image. The mask is applied to the bounding boxes.
"""
c, mh, mw = protos.shape # CHW
ih, iw = shape
masks = (masks_in @ protos.float().view(c, -1)).sigmoid().view(-1, mh, mw) # CHW
width_ratio = mw / iw
height_ratio = mh / ih
downsampled_bboxes = bboxes.clone()
downsampled_bboxes[:, 0] *= width_ratio
downsampled_bboxes[:, 2] *= width_ratio
downsampled_bboxes[:, 3] *= height_ratio
downsampled_bboxes[:, 1] *= height_ratio
masks = crop_mask(masks, downsampled_bboxes) # CHW
if upsample:
masks = F.interpolate(masks[None], shape, mode="bilinear", align_corners=False)[0] # CHW
return masks.gt_(0.5)
def crop_mask(masks, boxes):
"""
It takes a mask and a bounding box, and returns a mask that is cropped to the bounding box.
Args:
masks (torch.Tensor): [n, h, w] tensor of masks
boxes (torch.Tensor): [n, 4] tensor of bbox coordinates in relative point form
Returns:
(torch.Tensor): The masks are being cropped to the bounding box.
"""
_, h, w = masks.shape
x1, y1, x2, y2 = torch.chunk(boxes[:, :, None], 4, 1) # x1 shape(n,1,1)
r = torch.arange(w, device=masks.device, dtype=x1.dtype)[None, None, :] # rows shape(1,1,w)
c = torch.arange(h, device=masks.device, dtype=x1.dtype)[None, :, None] # cols shape(1,h,1)
return masks * ((r >= x1) * (r < x2) * (c >= y1) * (c < y2))图片绘制
模型文件:ultralytics/engine/results.py
class Boxes(BaseTensor):
"""
A class for storing and manipulating detection boxes.
Args:
boxes (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): A tensor or numpy array containing the detection boxes,
with shape (num_boxes, 6) or (num_boxes, 7). The last two columns contain confidence and class values.
If present, the third last column contains track IDs.
orig_shape (tuple): Original image size, in the format (height, width).
Attributes:
xyxy (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): The boxes in xyxy format.
conf (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): The confidence values of the boxes.
cls (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): The class values of the boxes.
id (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): The track IDs of the boxes (if available).
xywh (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): The boxes in xywh format.
xyxyn (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): The boxes in xyxy format normalized by original image size.
xywhn (torch.Tensor | numpy.ndarray): The boxes in xywh format normalized by original image size.
data (torch.Tensor): The raw bboxes tensor (alias for `boxes`).
Methods:
cpu(): Move the object to CPU memory.
numpy(): Convert the object to a numpy array.
cuda(): Move the object to CUDA memory.
to(*args, **kwargs): Move the object to the specified device.
"""
def __init__(self, boxes, orig_shape) -> None:
"""Initialize the Boxes class."""
if boxes.ndim == 1:
boxes = boxes[None, :]
n = boxes.shape[-1]
assert n in (6, 7), f"expected 6 or 7 values but got {n}" # xyxy, track_id, conf, cls
super().__init__(boxes, orig_shape)
self.is_track = n == 7
self.orig_shape = orig_shape
@property
def xyxy(self):
"""Return the boxes in xyxy format."""
return self.data[:, :4]
@property
def conf(self):
"""Return the confidence values of the boxes."""
return self.data[:, -2]
@property
def cls(self):
"""Return the class values of the boxes."""
return self.data[:, -1]
@property
def id(self):
"""Return the track IDs of the boxes (if available)."""
return self.data[:, -3] if self.is_track else None
@property
@lru_cache(maxsize=2) # maxsize 1 should suffice
def xywh(self):
"""Return the boxes in xywh format."""
return ops.xyxy2xywh(self.xyxy)
@property
@lru_cache(maxsize=2)
def xyxyn(self):
"""Return the boxes in xyxy format normalized by original image size."""
xyxy = self.xyxy.clone() if isinstance(self.xyxy, torch.Tensor) else np.copy(self.xyxy)
xyxy[..., [0, 2]] /= self.orig_shape[1]
xyxy[..., [1, 3]] /= self.orig_shape[0]
return xyxy
@property
@lru_cache(maxsize=2)
def xywhn(self):
"""Return the boxes in xywh format normalized by original image size."""
xywh = ops.xyxy2xywh(self.xyxy)
xywh[..., [0, 2]] /= self.orig_shape[1]
xywh[..., [1, 3]] /= self.orig_shape[0]
return xywh
class Masks(BaseTensor):
"""
A class for storing and manipulating detection masks.
Attributes:
xy (list): A list of segments in pixel coordinates.
xyn (list): A list of normalized segments.
Methods:
cpu(): Returns the masks tensor on CPU memory.
numpy(): Returns the masks tensor as a numpy array.
cuda(): Returns the masks tensor on GPU memory.
to(device, dtype): Returns the masks tensor with the specified device and dtype.
"""
def __init__(self, masks, orig_shape) -> None:
"""Initialize the Masks class with the given masks tensor and original image shape."""
if masks.ndim == 2:
masks = masks[None, :]
super().__init__(masks, orig_shape)
@property
@lru_cache(maxsize=1)
def xyn(self):
"""Return normalized segments."""
return [
ops.scale_coords(self.data.shape[1:], x, self.orig_shape, normalize=True)
for x in ops.masks2segments(self.data)
]
@property
@lru_cache(maxsize=1)
def xy(self):
"""Return segments in pixel coordinates."""
return [
ops.scale_coords(self.data.shape[1:], x, self.orig_shape, normalize=False)
for x in ops.masks2segments(self.data)
]
class Results(SimpleClass):
.
.
.
def plot(
self,
conf=True,
line_width=None,
font_size=None,
font="Arial.ttf",
pil=False,
img=None,
im_gpu=None,
kpt_radius=5,
kpt_line=True,
labels=True,
boxes=True,
masks=True,
probs=True,
):
# Plot Segment results
if pred_masks and show_masks:
if im_gpu is None:
img = LetterBox(pred_masks.shape[1:])(image=annotator.result())
im_gpu = (
torch.as_tensor(img, dtype=torch.float16, device=pred_masks.data.device)
.permute(2, 0, 1)
.flip(0)
.contiguous()
/ 255
)
idx = pred_boxes.cls if pred_boxes else range(len(pred_masks))
annotator.masks(pred_masks.data, colors=[colors(x, True) for x in idx], im_gpu=im_gpu)
# Plot Detect results
if pred_boxes is not None and show_boxes:
for d in reversed(pred_boxes):
c, conf, id = int(d.cls), float(d.conf) if conf else None, None if d.id is None else int(d.id.item())
name = ("" if id is None else f"id:{id} ") + names[c]
label = (f"{name} {conf:.2f}" if conf else name) if labels else None
box = d.xyxyxyxy.reshape(-1, 4, 2).squeeze() if is_obb else d.xyxy.squeeze()
annotator.box_label(box, label, color=colors(c, True), rotated=is_obb)
.
.
.模型文件:ultralytics/utils/plotting.py
def masks(self, masks, colors, im_gpu, alpha=0.5, retina_masks=False):
"""
Plot masks on image.
Args:
masks (tensor): Predicted masks on cuda, shape: [n, h, w]
colors (List[List[Int]]): Colors for predicted masks, [[r, g, b] * n]
im_gpu (tensor): Image is in cuda, shape: [3, h, w], range: [0, 1]
alpha (float): Mask transparency: 0.0 fully transparent, 1.0 opaque
retina_masks (bool): Whether to use high resolution masks or not. Defaults to False.
"""
if self.pil:
# Convert to numpy first
self.im = np.asarray(self.im).copy()
if len(masks) == 0:
self.im[:] = im_gpu.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous().cpu().numpy() * 255
if im_gpu.device != masks.device:
im_gpu = im_gpu.to(masks.device)
colors = torch.tensor(colors, device=masks.device, dtype=torch.float32) / 255.0 # shape(n,3)
colors = colors[:, None, None] # shape(n,1,1,3)
masks = masks.unsqueeze(3) # shape(n,h,w,1)
masks_color = masks * (colors * alpha) # shape(n,h,w,3)
inv_alpha_masks = (1 - masks * alpha).cumprod(0) # shape(n,h,w,1)
mcs = masks_color.max(dim=0).values # shape(n,h,w,3)
im_gpu = im_gpu.flip(dims=[0]) # flip channel
im_gpu = im_gpu.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous() # shape(h,w,3)
im_gpu = im_gpu * inv_alpha_masks[-1] + mcs
im_mask = im_gpu * 255
im_mask_np = im_mask.byte().cpu().numpy()
self.im[:] = im_mask_np if retina_masks else ops.scale_image(im_mask_np, self.im.shape)
if self.pil:
# Convert im back to PIL and update draw
self.fromarray(self.im)
def box_label(self, box, label="", color=(128, 128, 128), txt_color=(255, 255, 255), rotated=False):
"""Add one xyxy box to image with label."""
if isinstance(box, torch.Tensor):
box = box.tolist()
if self.pil or not is_ascii(label):
if rotated:
p1 = box[0]
# NOTE: PIL-version polygon needs tuple type.
self.draw.polygon([tuple(b) for b in box], width=self.lw, outline=color)
else:
p1 = (box[0], box[1])
self.draw.rectangle(box, width=self.lw, outline=color) # box
if label:
w, h = self.font.getsize(label) # text width, height
outside = p1[1] - h >= 0 # label fits outside box
self.draw.rectangle(
(p1[0], p1[1] - h if outside else p1[1], p1[0] + w + 1, p1[1] + 1 if outside else p1[1] + h + 1),
fill=color,
)
# self.draw.text((box[0], box[1]), label, fill=txt_color, font=self.font, anchor='ls') # for PIL>8.0
self.draw.text((p1[0], p1[1] - h if outside else p1[1]), label, fill=txt_color, font=self.font)
else: # cv2
if rotated:
p1 = [int(b) for b in box[0]]
# NOTE: cv2-version polylines needs np.asarray type.
cv2.polylines(self.im, [np.asarray(box, dtype=int)], True, color, self.lw)
else:
p1, p2 = (int(box[0]), int(box[1])), (int(box[2]), int(box[3]))
cv2.rectangle(self.im, p1, p2, color, thickness=self.lw, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
if label:
w, h = cv2.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=self.sf, thickness=self.tf)[0] # text width, height
outside = p1[1] - h >= 3
p2 = p1[0] + w, p1[1] - h - 3 if outside else p1[1] + h + 3
cv2.rectangle(self.im, p1, p2, color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA) # filled
cv2.putText(
self.im,
label,
(p1[0], p1[1] - 2 if outside else p1[1] + h + 2),
0,
self.sf,
txt_color,
thickness=self.tf,
lineType=cv2.LINE_AA,
)它包含以下步骤:
-
ops.non_max_suppression:非极大值抑制,即 NMS
-
ops.scale_boxes:框的解码,即 decode boxes
-
annotator.box_label:绘制矩形框到原图上
-
annotator.masks:绘制分割掩码图到原图上
修改后的处理方式
proto = preds[1][-1]
for i, pred in enumerate(det):
lw = max(round(sum(img_src.shape) / 2 * 0.003), 2) # line width
tf = max(lw - 1, 1) # font thickness
sf = lw / 3 # font scale
# 6, 640, 480
masks = ops.process_mask(proto[i], pred[:, 6:], pred[:, :4], img.shape[2:], upsample=True) # HWC
pred[:, :4] = ops.scale_boxes(img.shape[2:], pred[:, :4], img_src.shape)
pred_bbox = pred[:, :6].cpu().detach().numpy()
self.draw_masks(img_src, masks.data, colors=[colors(x, True) for x in pred[:, 5]], im_gpu=img.squeeze(0))
for bbox in pred_bbox:
self.draw_box(img_src, bbox[:4], bbox[4], self.names[bbox[5]], lw, sf, tf)五、YOLO V8-Segment 推理
通过上面的解析,我们了解了 YOLOv8-Segment 的整个处理过程,以及使用到的模型文件和模型函数。
完整的推理代码如下:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# @author: 牧锦程
# @微信公众号: AI算法与电子竞赛
# @Email: [email protected]
# @VX:fylaicai
import os
import random
import cv2
import numpy as np
import torch
from ultralytics.nn.autobackend import AutoBackend
from ultralytics.utils import ops
from ultralytics.utils.plotting import colors
class YOLOV8SegmentInfer:
def __init__(self, weights, cuda, conf_thres, iou_thres) -> None:
self.imgsz = 640
self.device = cuda
self.model = AutoBackend(weights, device=torch.device(cuda))
self.model.eval()
self.names = self.model.names
self.half = False
self.conf = conf_thres
self.iou = iou_thres
self.color = {"font": (255, 255, 255)}
self.color.update(
{self.names[i]: (random.randint(0, 255), random.randint(0, 255), random.randint(0, 255))
for i in range(len(self.names))})
def infer(self, img_src, save_path):
img = self.precess_image(img_src)
preds = self.model(img) # shape [1, 116, 6300]
det = ops.non_max_suppression(preds[0], self.conf, self.iou, classes=None, agnostic=False, max_det=300, nc=len(self.names))
proto = preds[1][-1]
for i, pred in enumerate(det):
lw = max(round(sum(img_src.shape) / 2 * 0.003), 2) # line width
tf = max(lw - 1, 1) # font thickness
sf = lw / 3 # font scale
# 6, 640, 480
masks = ops.process_mask(proto[i], pred[:, 6:], pred[:, :4], img.shape[2:], upsample=True) # HWC
pred[:, :4] = ops.scale_boxes(img.shape[2:], pred[:, :4], img_src.shape)
pred_bbox = pred[:, :6].cpu().detach().numpy()
self.draw_masks(img_src, masks.data, colors=[colors(x, True) for x in pred[:, 5]], im_gpu=img.squeeze(0))
for bbox in pred_bbox:
self.draw_box(img_src, bbox[:4], bbox[4], self.names[bbox[5]], lw, sf, tf)
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(save_path, os.path.split(img_path)[-1]), img_src)
def draw_box(self, img_src, box, conf, cls_name, lw, sf, tf):
color = self.color[cls_name]
label = f'{cls_name} {conf}'
p1, p2 = (int(box[0]), int(box[1])), (int(box[2]), int(box[3]))
# 绘制矩形框
cv2.rectangle(img_src, p1, p2, color, thickness=lw, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
# text width, height
w, h = cv2.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=sf, thickness=tf)[0]
# label fits outside box
outside = box[1] - h - 3 >= 0
p2 = p1[0] + w, p1[1] - h - 3 if outside else p1[1] + h + 3
# 绘制矩形框填充
cv2.rectangle(img_src, p1, p2, color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA)
# 绘制标签
cv2.putText(img_src, label, (p1[0], p1[1] - 2 if outside else p1[1] + h + 2),
0, sf, self.color["font"], thickness=2, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
def draw_masks(self, img_src, masks, colors, im_gpu, alpha=0.5):
# maks [6, 640, 480]
if len(masks) == 0:
img_src[:] = im_gpu.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous().cpu().numpy() * 255
if im_gpu.device != masks.device:
im_gpu = im_gpu.to(masks.device)
colors = torch.tensor(colors, device=masks.device, dtype=torch.float32) / 255.0 # shape(n,3)
colors = colors[:, None, None] # shape(n,1,1,3)
masks = masks.unsqueeze(3) # shape(n,h,w,1)
masks_color = masks * (colors * alpha) # shape(n,h,w,3)
inv_alpha_masks = (1 - masks * alpha).cumprod(0) # shape(n,h,w,1)
mcs = masks_color.max(dim=0).values # shape(h,w,3)
im_gpu = im_gpu.flip(dims=[0]) # flip channel
im_gpu = im_gpu.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous() # shape(h,w,3)
im_gpu = im_gpu * inv_alpha_masks[-1] + mcs
im_mask = im_gpu * 255
im_mask_np = im_mask.byte().cpu().numpy()
img_src[:] = ops.scale_image(im_mask_np, img_src.shape)
@staticmethod
def letterbox(im, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(114, 114, 114), scaleup=True, stride=32):
# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraints
shape = im.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
if not scaleup: # only scale down, do not scale up (for better val mAP)
r = min(r, 1.0)
# Compute padding
ratio = r, r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
# minimum rectangle
dw, dh = np.mod(dw, stride), np.mod(dh, stride) # wh padding
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
im = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return im, ratio, (dw, dh)
def precess_image(self, img_src):
# Padded resize
img = self.letterbox(img_src, self.imgsz)[0]
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
# Convert
img = img[..., ::-1].transpose((0, 3, 1, 2)) # BGR to RGB, BHWC to BCHW, (n, 3, h, w)
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img) # contiguous
img = torch.from_numpy(img)
img = img.to(self.device)
img = img.half() if self.half else img.float() # uint8 to fp16/32
img = img / 255 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
return img
if __name__ == '__main__':
weights = r'./weights/yolov8n-seg.pt'
cuda = 'cuda:0'
save_path = "./runs"
if not os.path.exists(save_path):
os.mkdir(save_path)
model = YOLOV8SegmentInfer(weights, cuda, 0.25, 0.7)
img_path = r'./img/bus.jpg'
img_src = cv2.imread(img_path)
model.infer(img_src, save_path)
六、书籍推荐
书籍推荐:《深度学习---Caffe之经典模型详解与实战》
本书首先介绍了深度学习相关的理论和主流的深度学习框,从深度学习框架为切入点介绍了Caffe的安装、配置、编泽和接口运行环境,剖析Caffe网络模型的构成要素和常用的层类型和Solver方法。通过LeNet网络模型的Mnist手写实例介绍其样本训练和识别过程,进一步详细解读了AlexNet 、VGGNet、GoogLeNet、Siamese和SqueezeNet网络模型,并出了这些模于Caffe的训练实战方法。然后,本书解读了利用深度学习进行目标定位的经典网络模型:FCN,R-CNN、Fast-RCNN、Faster-RCNN和SSD,并进行目标定位Caffe实战。本书的最后,从著名的Kaggle网站引入了两个经典的实战项目,并进行了有针对性的原始数据分析、网络模型设计和Caffe训练策略实战,以求带给读者从问题提出到利用Caffe求解的完整工程经历,从而使读者能尽快掌握Caffe框架的使用技巧和实战经验。
针对Caffe和深度学习领域的初学者,本书是一本不可多得的参考资料。本书的内容既有易懂的理论背景,又有丰富的应用实践,是深度学习初学者的指导手册,也可作为深度学习相关领域上工程师和爱好者的参考用书。
关注下方公众号:@AI算法与电子竞赛,回复关键字“PDF”获取下载地址
七、链接作者
欢迎关注我的公众号:@AI算法与电子竞赛
硬性的标准其实限制不了无限可能的我们,所以啊!少年们加油吧!