一、笔记资源下载地址:[首页](javascript:void(0)😉 > 导航 > 笔记下载
https://www.kuangstudy.com/app/code
Web UI 组件库:https://www.layui.com/
博客笔记资源:
https://www.cnblogs.com/yaolicheng/p/13689710.html
绘图:https://www.processon.com/diagrams
https://www.bootcss.com/p/layoutit/
前端组件:https://www.layui.com/
Bootstrap
简洁、直观、强悍的前端开发框架,让web开发更迅速、简单。
甚至可以直接引入网上的css样式来美化组件
https://www.bootcss.com/
SpringBoot
相关资源
艺术字网站:https://www.bootschool.net/ascii-art
狂神说SpringBoot连载中:
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/mp/homepage?__biz=Mzg2NTAzMTExNg==&hid=1&sn=3247dca1433a891523d9e4176c90c499
springboot日志
https://www.cnblogs.com/yaolicheng/p/13689796.html
介绍
微服务
什么是微服务:
https://martinfowler.com/articles/microservices.html#CharacteristicsOfAMicroserviceArchitecture
回顾
什么是Spring
Spring是一个开源框架,2003 年兴起的一个轻量级的Java 开发框架,作者:Rod Johnson 。
Spring是为了解决企业级应用开发的复杂性而创建的,简化开发。
**
**
如何简化
Spring是如何简化Java开发的
为了降低Java开发的复杂性,Spring采用了以下4种关键策略:
1、基于POJO的轻量级和最小侵入性编程,所有东西都是bean;
2、通过IOC,依赖注入(DI)和面向接口实现松耦合;
3、基于切面(AOP)和惯例进行声明式编程;
4、通过切面和模版减少样式代码,RedisTemplate,xxxTemplate;
SpringBoot
什么是SpringBoot
学过javaweb的同学就知道,开发一个web应用,从最初开始接触Servlet结合Tomcat, 跑出一个Hello Wolrld程序,是要经历特别多的步骤;后来就用了框架Struts,再后来是SpringMVC,到了现在的SpringBoot,过一两年又会有其他web框架出现;你们有经历过框架不断的演进,然后自己开发项目所有的技术也在不断的变化、改造吗?建议都可以去经历一遍;
言归正传,什么是SpringBoot呢,就是一个javaweb的开发框架,和SpringMVC类似,对比其他javaweb框架的好处,官方说是简化开发,约定大于配置, you can “just run”,能迅速的开发web应用,几行代码开发一个http接口。
所有的技术框架的发展似乎都遵循了一条主线规律:从一个复杂应用场景 衍生 一种规范框架,人们只需要进行各种配置而不需要自己去实现它,这时候强大的配置功能成了优点;发展到一定程度之后,人们根据实际生产应用情况,选取其中实用功能和设计精华,重构出一些轻量级的框架;之后为了提高开发效率,嫌弃原先的各类配置过于麻烦,于是开始提倡“约定大于配置”,进而衍生出一些一站式的解决方案。
是的这就是Java企业级应用->J2EE->spring->springboot的过程。
随着 Spring 不断的发展,涉及的领域越来越多,项目整合开发需要配合各种各样的文件,慢慢变得不那么易用简单,违背了最初的理念,甚至人称配置地狱。Spring Boot 正是在这样的一个背景下被抽象出来的开发框架,目的为了让大家更容易的使用 Spring 、更容易的集成各种常用的中间件、开源软件;
Spring Boot 基于 Spring 开发,Spirng Boot 本身并不提供 Spring 框架的核心特性以及扩展功能,只是用于快速、敏捷地开发新一代基于 Spring 框架的应用程序。也就是说,它并不是用来替代 Spring 的解决方案,而是和 Spring 框架紧密结合用于提升 Spring 开发者体验的工具。Spring Boot 以约定大于配置的核心思想,默认帮我们进行了很多设置,多数 Spring Boot 应用只需要很少的 Spring 配置。同时它集成了大量常用的第三方库配置(例如 Redis、MongoDB、Jpa、RabbitMQ、Quartz 等等),Spring Boot 应用中这些第三方库几乎可以零配置的开箱即用。
简单来说就是SpringBoot其实不是什么新的框架,它默认配置了很多框架的使用方式,就像maven整合了所有的jar包,spring boot整合了所有的框架 。
Spring Boot 出生名门,从一开始就站在一个比较高的起点,又经过这几年的发展,生态足够完善,Spring Boot 已经当之无愧成为 Java 领域最热门的技术。
Spring Boot的主要优点:
- 为所有Spring开发者更快的入门
- 开箱即用,提供各种默认配置来简化项目配置
- 内嵌式容器简化Web项目
- 没有冗余代码生成和XML配置的要求
真的很爽,我们快速去体验开发个接口的感觉吧!
Hello
Hello,SpringBoot!
准备工作
我们将学习如何快速的创建一个Spring Boot应用,并且实现一个简单的Http请求处理。通过这个例子对Spring Boot有一个初步的了解,并体验其结构简单、开发快速的特性。
我的环境准备:
- java version “1.8.0_181”
- Maven-3.6.1
- SpringBoot 2.x 最新版
开发工具:
- IDEA
说明
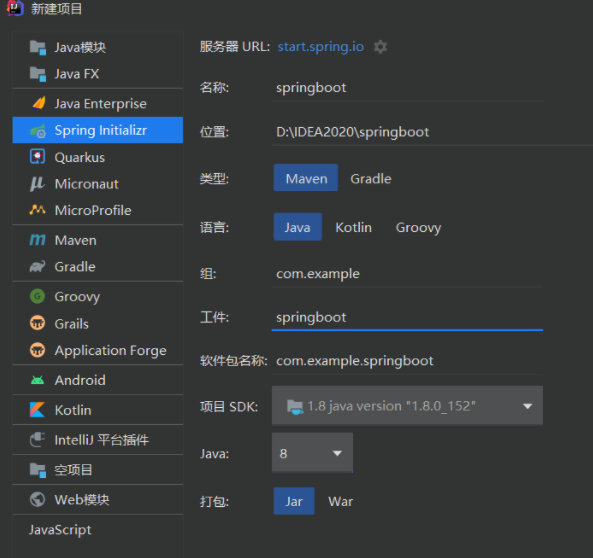
创建基础项目说明
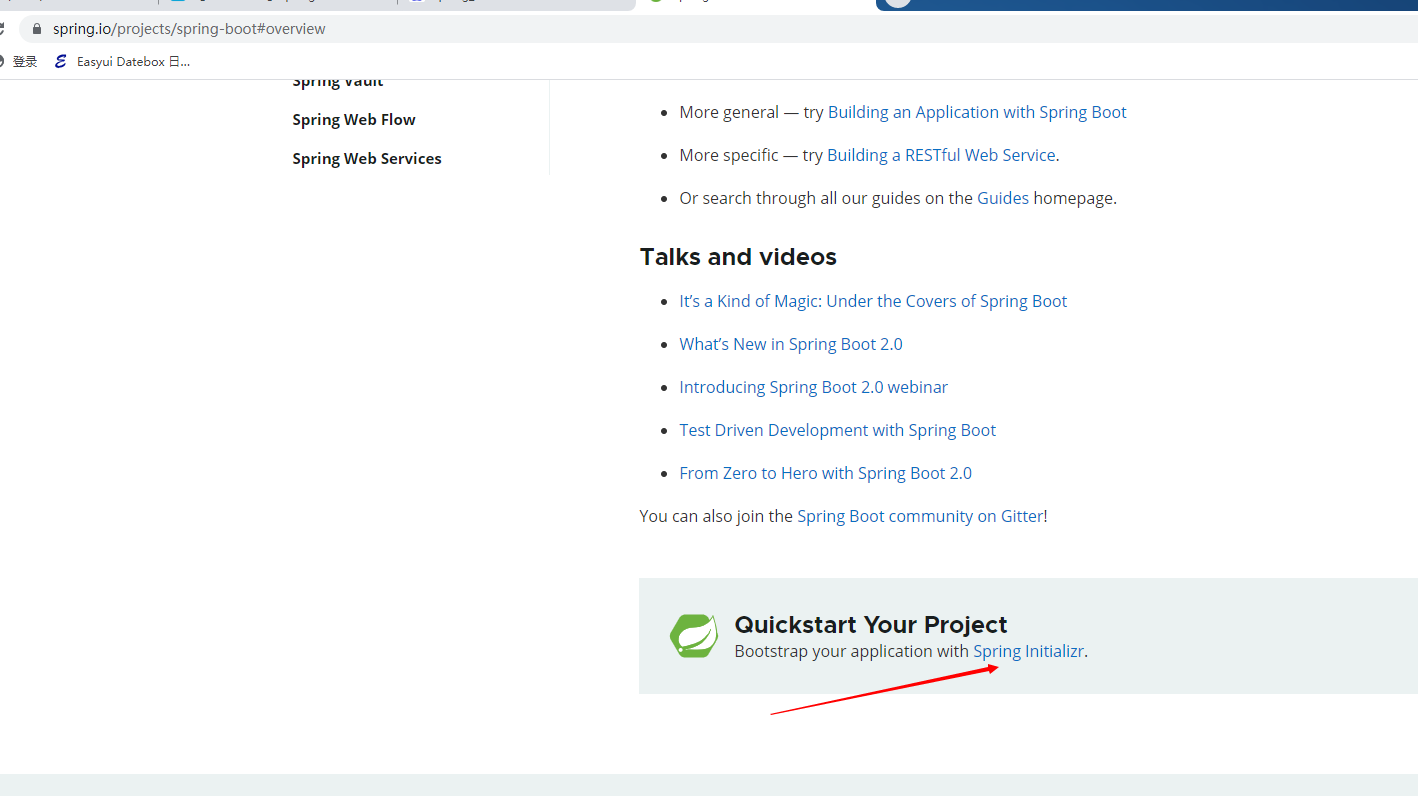
Spring官方提供了非常方便的工具让我们快速构建应用
Spring Initializr:https://start.spring.io/
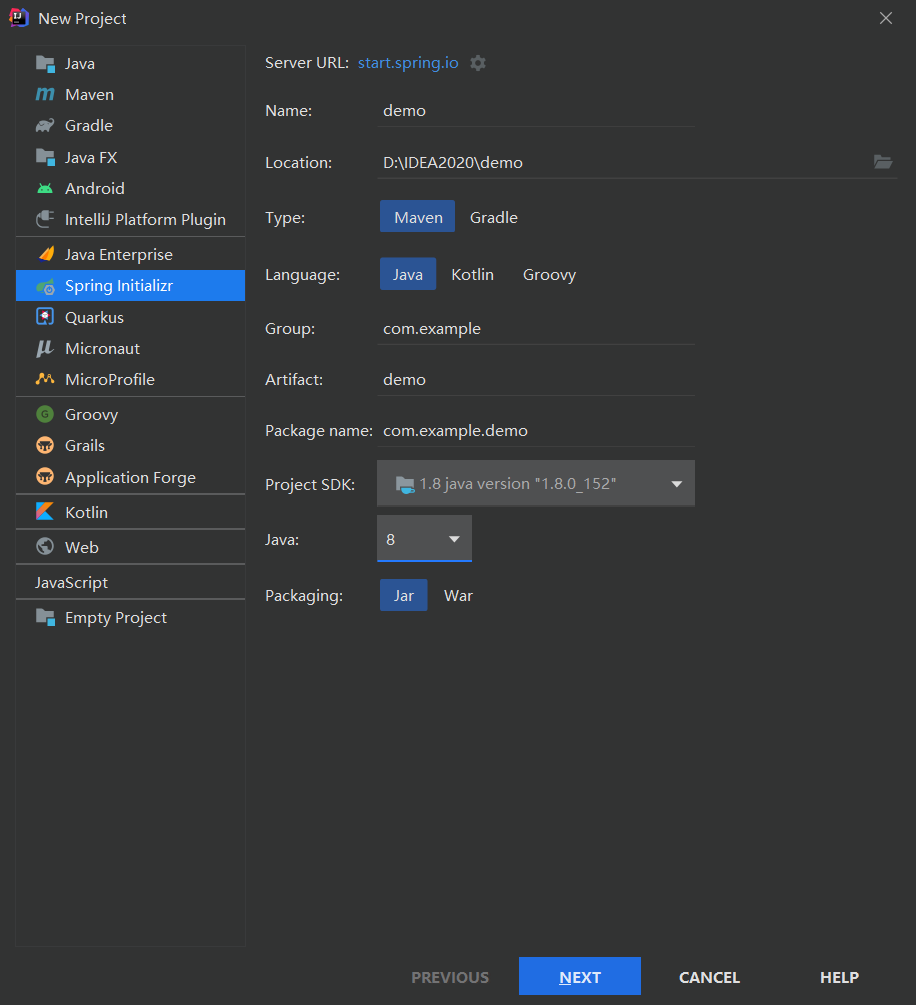
项目创建方式一
项目创建方式一:**使用Spring Initializr 的 Web页面创建项目
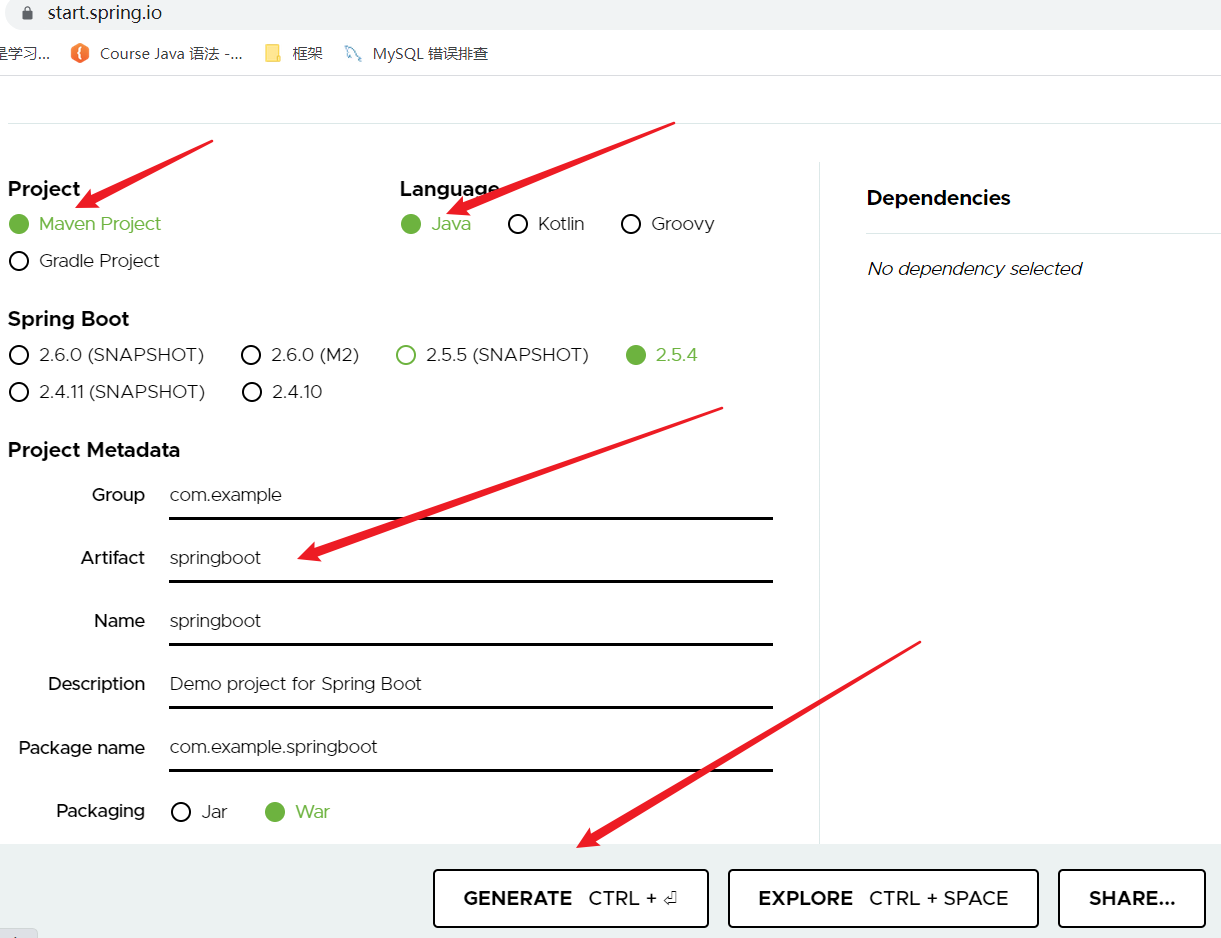
1、打开 https://start.spring.io/
2、填写项目信息
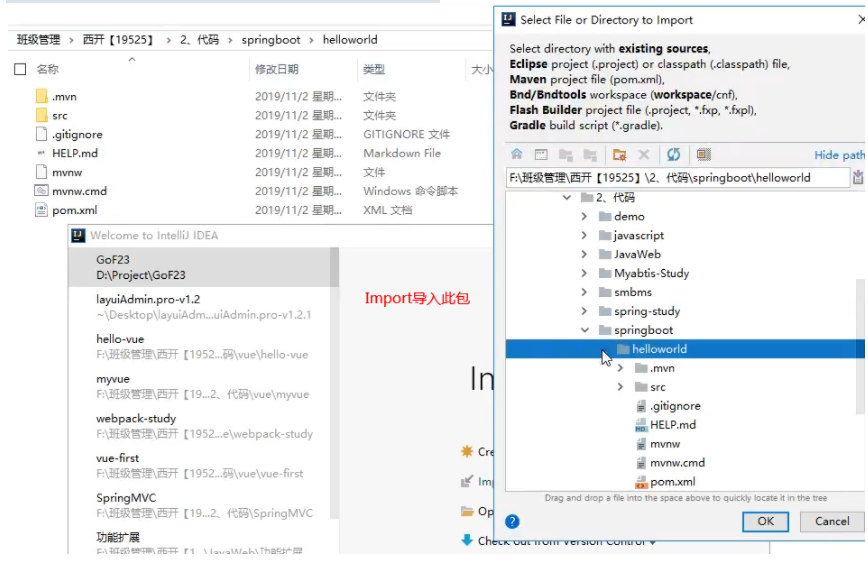
3、点击”Generate Project“按钮生成项目;下载此项目
4、解压项目包,并用IDEA以Maven项目导入,一路下一步即可,直到项目导入完毕。
5、如果是第一次使用,可能速度会比较慢,包比较多、需要耐心等待一切就绪。
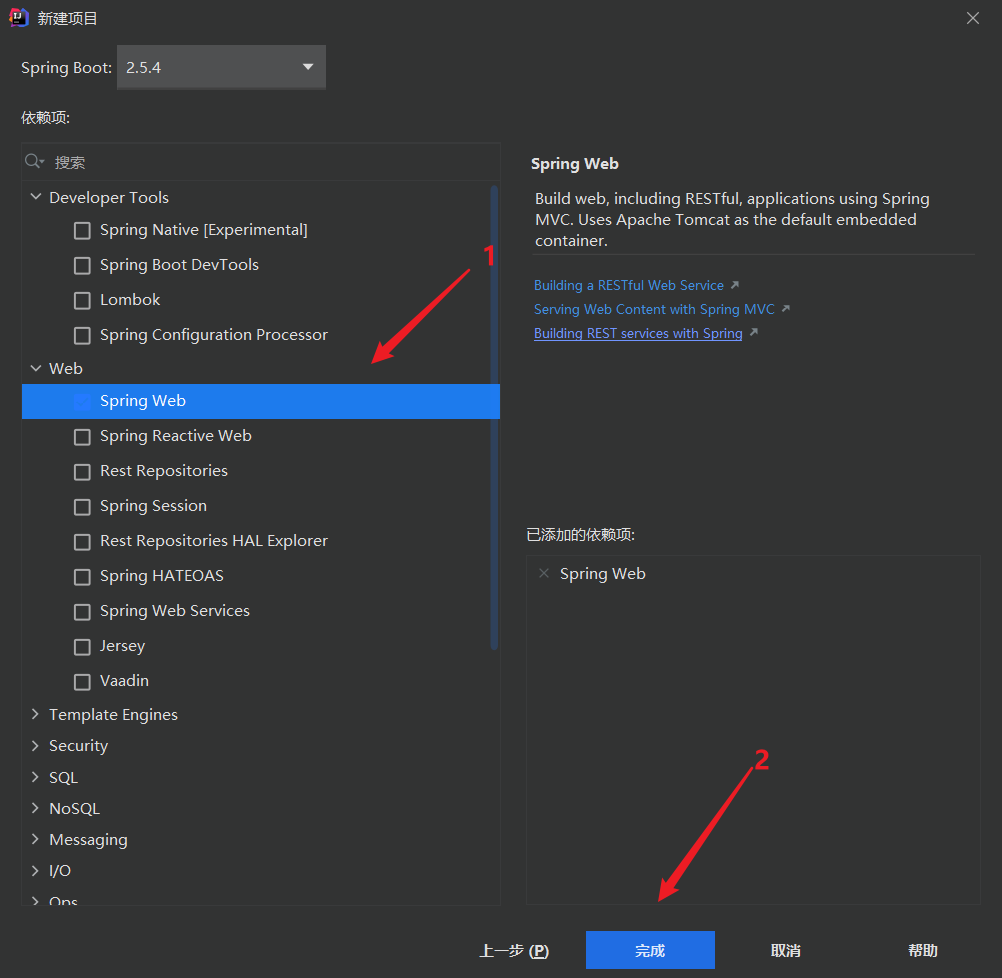
项目创建方式二
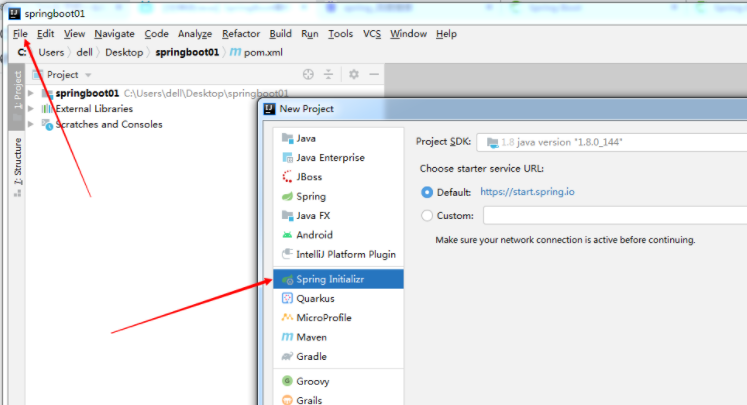
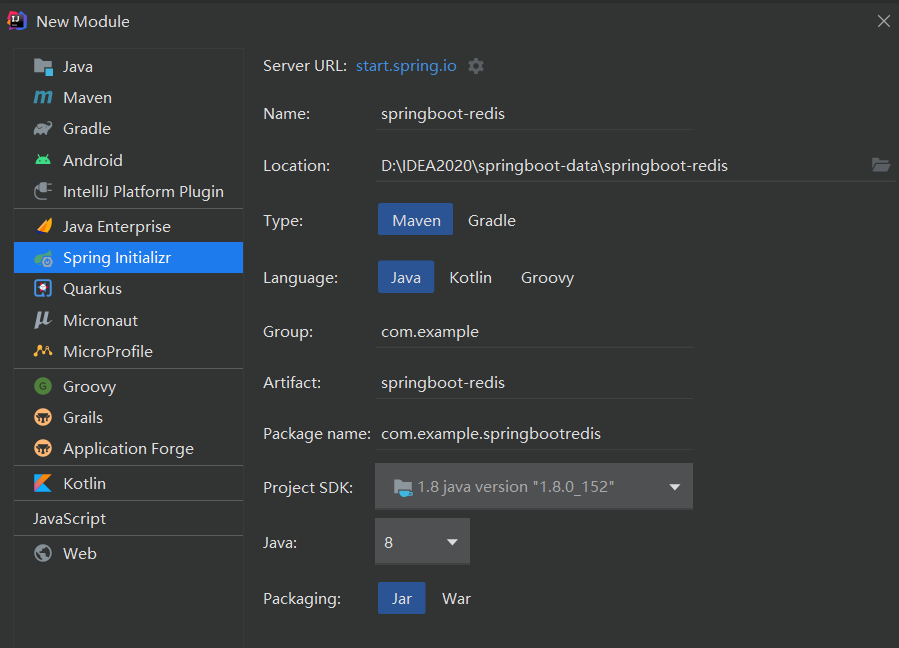
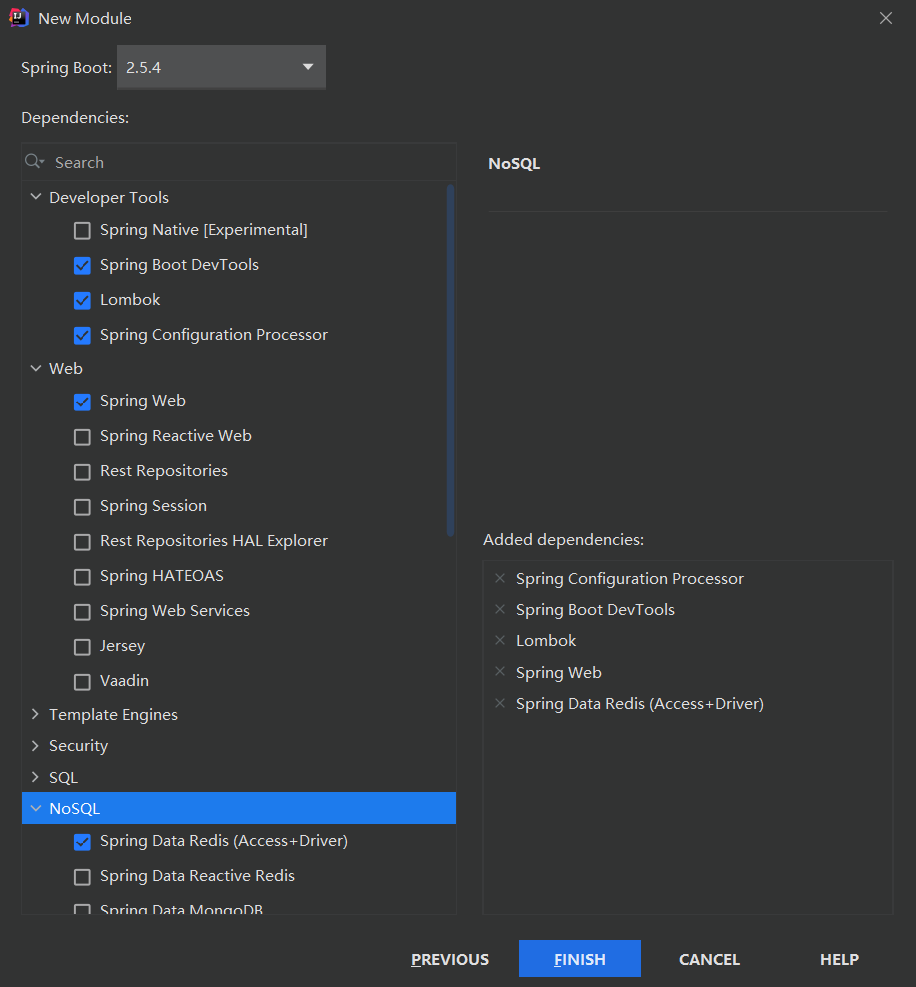
项目创建方式二:使用 IDEA 直接创建项目
1、创建一个新项目
2、选择spring initalizr , 可以看到默认就是去官网的快速构建工具那里实现
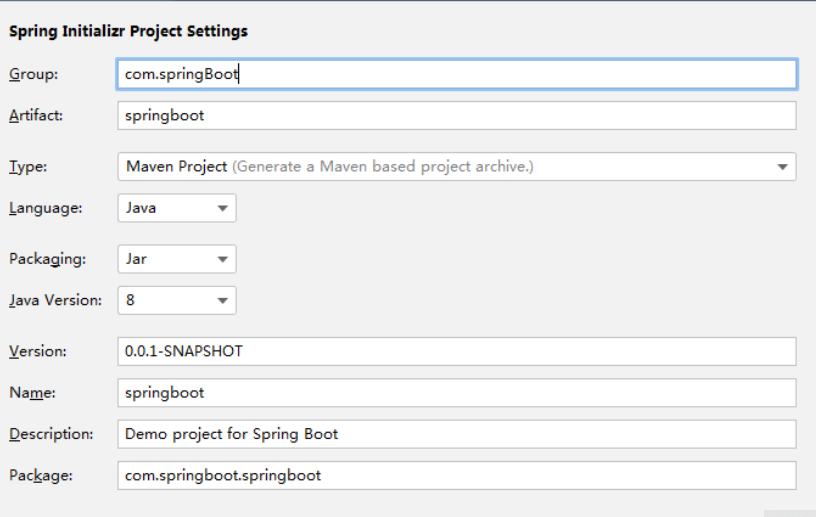
3、填写项目信息
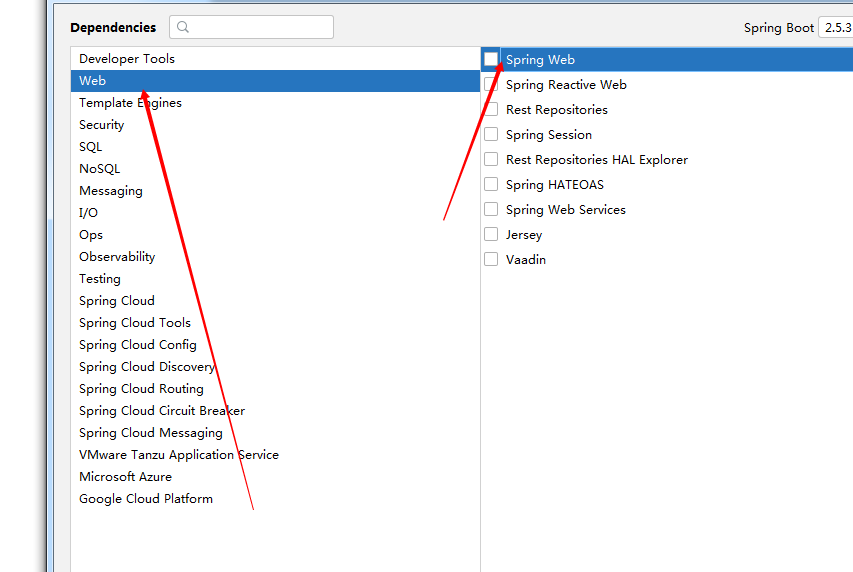
4、选择初始化的组件(初学勾选 Web 即可)
5、填写项目路径
6、等待项目构建成功
开发环境:
https://spring.io/projects/spring-boot#learn
一般的创建过程为:
官方:提供了一个快速生成的网站!IDEA集成了这个网站
可以在官网直接下载后,导入idea开发(上述官网在哪)
接下来直接使用IDEA创建一个springboot项目(一般开发都是直接在IDEA中创建的)。
目录介绍:
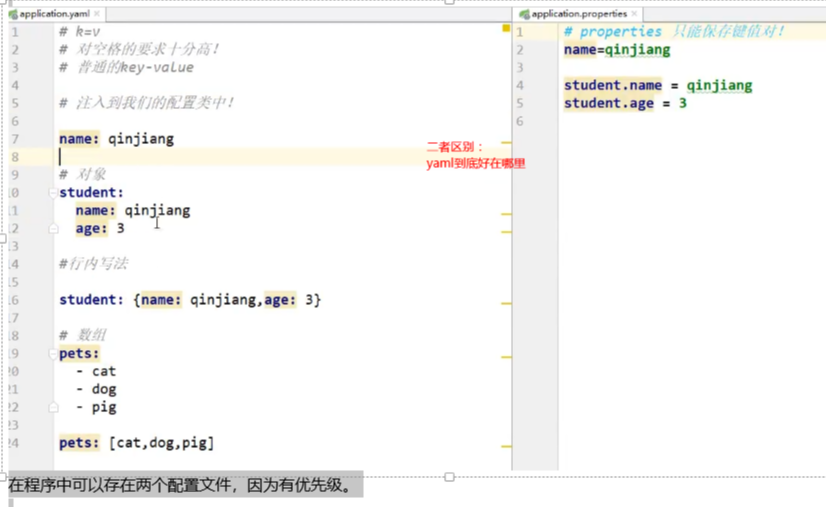
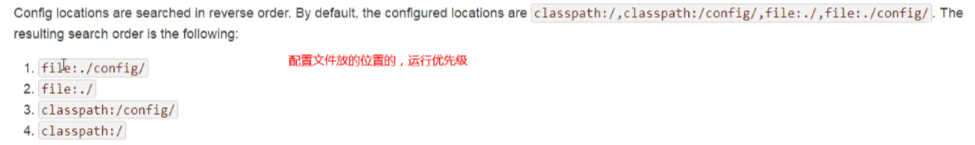
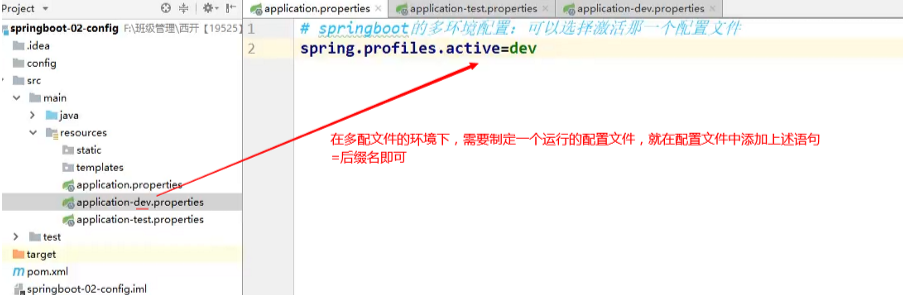
在程序中可以存在两个配置文件,因为有优先级。
添加依赖即可解决,主要会有一些提示的功能,问题不大。
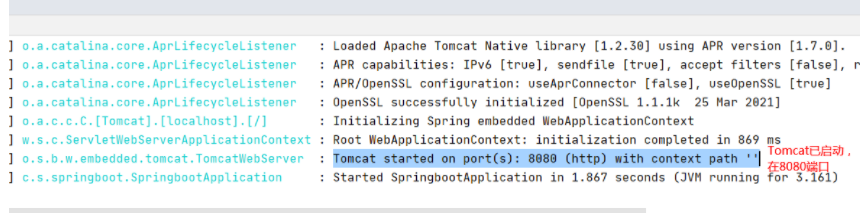
http://localhost:8080/hello
初始化标准的pom.xml文件
<?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?>
<projectxmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
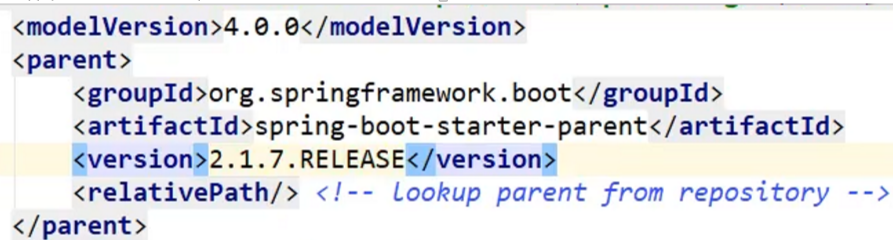
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<!--有一个父项目-->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.5.3</version>
<relativePath/><!--lookupparentfromrepository-->
</parent>
<groupId>com.springBoot</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springboot</name>
<description>DemoprojectforSpringBoot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!--web依赖:tomcat,dispatcherSerbvlet,xml....---->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--spring-boot-starter所有的springboot依赖都是使用这个开头的-->
<!--单元测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<!--打jar包插件-->
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
打jar包的使用
在左边的target下就找得到,就是一个可执行jar接口
更改端口号
项目结构分析:
通过上面步骤完成了基础项目的创建。就会自动生成以下文件。
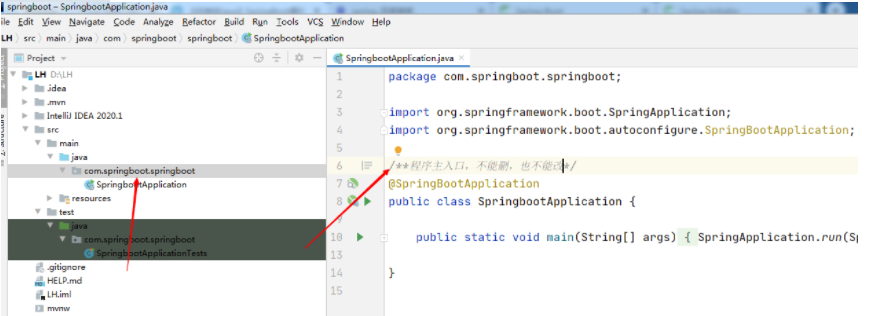
1、程序的主启动类
2、一个 application.properties 配置文件
3、一个 测试类
4、一个 pom.xml
pom.xml 分析
打开pom.xml,看看Spring Boot项目的依赖:
<!-- 父依赖 -->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.5.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<!-- web场景启动器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- springboot单元测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<!-- 剔除依赖 -->
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<!-- 打包插件 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
http接口
编写一个http接口
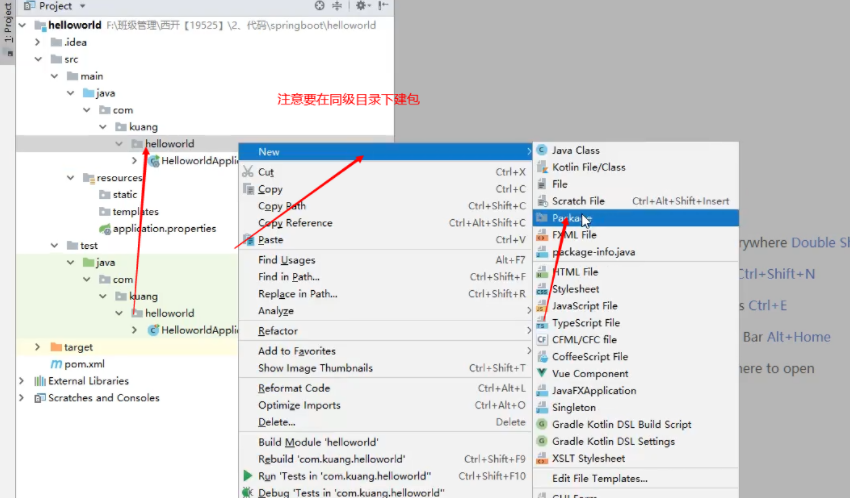
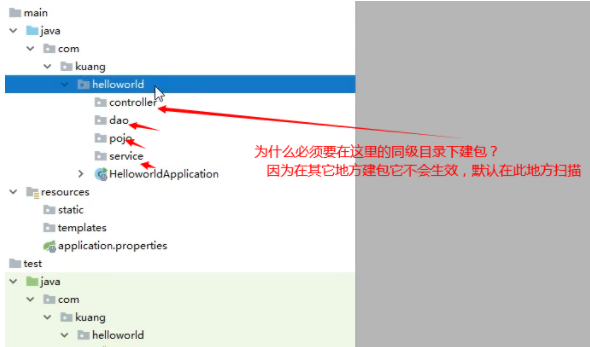
1、在主程序的同级目录下,新建一个controller包,一定要在同级目录下,否则识别不到
2、在包中新建一个HelloController类
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "Hello World";
}
}
3、编写完毕后,从主程序启动项目,浏览器发起请求,看页面返回;控制台输出了 Tomcat 访问的端口号!
自动装配
自动配置
Pom.xml
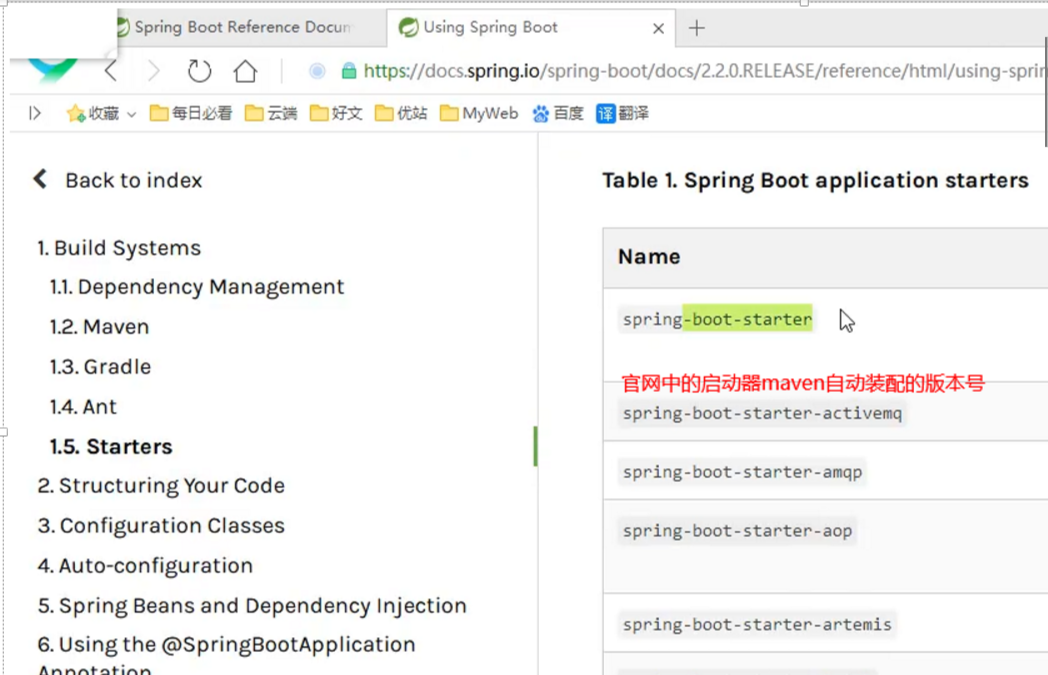
Spring-boot-dependencies:核心依赖在父工程中!
我们在写或者引入一些SpringBoot依赖的时候,不需要指定版本,因为有这些版本仓库。
启动器
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
启动器:就是springboot的启动场景
比如spring-boot-starter-web,他就会帮我们自动导入web环境所有的依赖!
springboot会将所有的功能场景,都变成一个个的启动器。
运行原理
SpringApplication
这个类主要做了以下四件事情:
1、推断应用的类型是普通的项目还是Web项目
2、查找并加载所有可用初始化器 , 设置到initializers属性中
3、找出所有的应用程序监听器,设置到listeners属性中
4、推断并设置main方法的定义类,找到运行的主类
运行原理初探
通俗易懂,基于SpringBoot2.2.5版本
运行原理探究
我们之前写的HelloSpringBoot,到底是怎么运行的呢,Maven项目,我们一般从pom.xml文件探究起;
pom.xml
父依赖
其中它主要是依赖一个父项目,主要是管理项目的资源过滤及插件!
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.5.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
点进去,发现还有一个父依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.2.5.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath>../../spring-boot-dependencies</relativePath>
</parent>
这里才是真正管理SpringBoot应用里面所有依赖版本的地方,SpringBoot的版本控制中心;
以后我们导入依赖默认是不需要写版本;但是如果导入的包没有在依赖中管理着就需要手动配置版本了;
启动器
启动器 spring-boot-starter
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
springboot-boot-starter-xxx:就是spring-boot的场景启动器
spring-boot-starter-web:帮我们导入了web模块正常运行所依赖的组件;
SpringBoot将所有的功能场景都抽取出来,做成一个个的starter (启动器),只需要在项目中引入这些starter即可,所有相关的依赖都会导入进来 , 我们要用什么功能就导入什么样的场景启动器即可 ;我们未来也可以自己自定义 starter;
主启动类
分析完了 pom.xml 来看看这个启动类
主启动类
默认的主启动类
//@SpringBootApplication 来标注一个主程序类
//说明这是一个Spring Boot应用
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//以为是启动了一个方法,没想到启动了一个服务
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args);
}
}
但是**一个简单的启动类并不简单!**我们来分析一下这些注解都干了什么
@SpringBootApplication
作用:标注在某个类上说明这个类是SpringBoot的主配置类 , SpringBoot就应该运行这个类的main方法来启动SpringBoot应用;
进入这个注解:可以看到上面还有很多其他注解!
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(
excludeFilters = {@Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class}
), @Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class}
)}
)
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
// ......
}
@ComponentScan
这个注解在Spring中很重要 ,它对应XML配置中的元素。
作用:自动扫描并加载符合条件的组件或者bean , 将这个bean定义加载到IOC容器中
@SpringBootConfiguration
作用:SpringBoot的配置类 ,标注在某个类上 , 表示这是一个SpringBoot的配置类;
我们继续进去这个注解查看
// 点进去得到下面的 @Component
@Configuration
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {}
@Component
public @interface Configuration {}
这里的 @Configuration,说明这是一个配置类 ,配置类就是对应Spring的xml 配置文件;
里面的 @Component 这就说明,启动类本身也是Spring中的一个组件而已,负责启动应用!
我们回到 SpringBootApplication 注解中继续看。
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration :开启自动配置功能
以前我们需要自己配置的东西,而现在SpringBoot可以自动帮我们配置 ;@EnableAutoConfiguration告诉SpringBoot开启自动配置功能,这样自动配置才能生效;
点进注解接续查看:
@AutoConfigurationPackage :自动配置包
@Import({Registrar.class})
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
}
@import :Spring底层注解@import , 给容器中导入一个组件
Registrar.class 作用:将主启动类的所在包及包下面所有子包里面的所有组件扫描到Spring容器 ;
这个分析完了,退到上一步,继续看
@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}) :给容器导入组件 ;
AutoConfigurationImportSelector :自动配置导入选择器,那么它会导入哪些组件的选择器呢?我们点击去这个类看源码:
1、这个类中有一个这样的方法
// 获得候选的配置
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
//这里的getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass()方法
//返回的就是我们最开始看的启动自动导入配置文件的注解类;EnableAutoConfiguration
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
2、这个方法又调用了 SpringFactoriesLoader 类的静态方法!我们进入SpringFactoriesLoader类loadFactoryNames() 方法
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
//这里它又调用了 loadSpringFactories 方法
return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList());
}
3、我们继续点击查看 loadSpringFactories 方法
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
//获得classLoader , 我们返回可以看到这里得到的就是EnableAutoConfiguration标注的类本身
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = (MultiValueMap)cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
} else {
try {
//去获取一个资源 "META-INF/spring.factories"
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories") : ClassLoader.getSystemResources("META-INF/spring.factories");
LinkedMultiValueMap result = new LinkedMultiValueMap();
//将读取到的资源遍历,封装成为一个Properties
while(urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next();
String factoryClassName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] var9 = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue());
int var10 = var9.length;
for(int var11 = 0; var11 < var10; ++var11) {
String factoryName = var9[var11];
result.add(factoryClassName, factoryName.trim());
}
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
} catch (IOException var13) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var13);
}
}
}
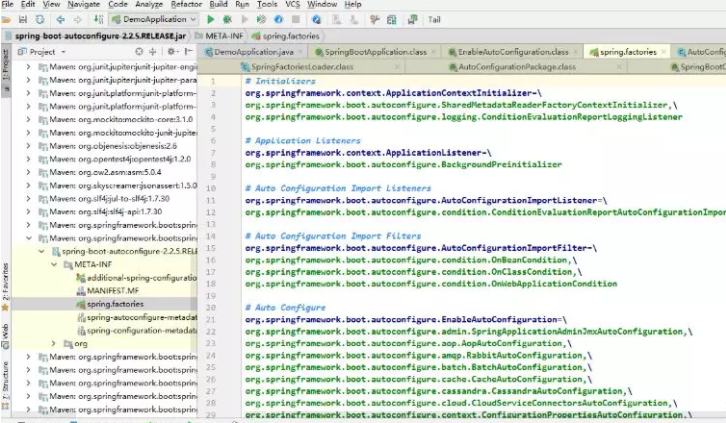
4、发现一个多次出现的文件:spring.factories,全局搜索它
spring.factories
我们根据源头打开spring.factories , 看到了很多自动配置的文件;这就是自动配置根源所在!
WebMvcAutoConfiguration
我们在上面的自动配置类随便找一个打开看看,比如 :WebMvcAutoConfiguration
可以看到这些一个个的都是JavaConfig配置类,而且都注入了一些Bean,可以找一些自己认识的类,看着熟悉一下!
所以,自动配置真正实现是从classpath中搜寻所有的META-INF/spring.factories配置文件 ,并将其中对应的 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure. 包下的配置项,通过反射实例化为对应标注了 @Configuration的JavaConfig形式的IOC容器配置类 , 然后将这些都汇总成为一个实例并加载到IOC容器中。
| 结论 |
|---|
| 1.SpringBoot在启动的时候从类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories中获取EnableAutoConfiguration指定的值 |
| 2.将这些值作为自动配置类导入容器 , 自动配置类就生效 , 帮我们进行自动配置工作; |
| 3.整个J2EE的整体解决方案和自动配置都在springboot-autoconfigure的jar包中; |
| 4.它会给容器中导入非常多的自动配置类 (xxxAutoConfiguration), 就是给容器中导入这个场景需要的所有组件 , 并配置好这些组件 ; |
| 5.有了自动配置类 , 免去了我们手动编写配置注入功能组件等的工作; |
现在大家应该大概的了解了下,SpringBoot的运行原理,后面我们还会深化一次!
SpringApplication
main=服务
不简单的方法
我最初以为就是运行了一个main方法,没想到却开启了一个服务;
@SpringBootApplicationpublic class SpringbootApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args); }}
SpringApplication.run分析
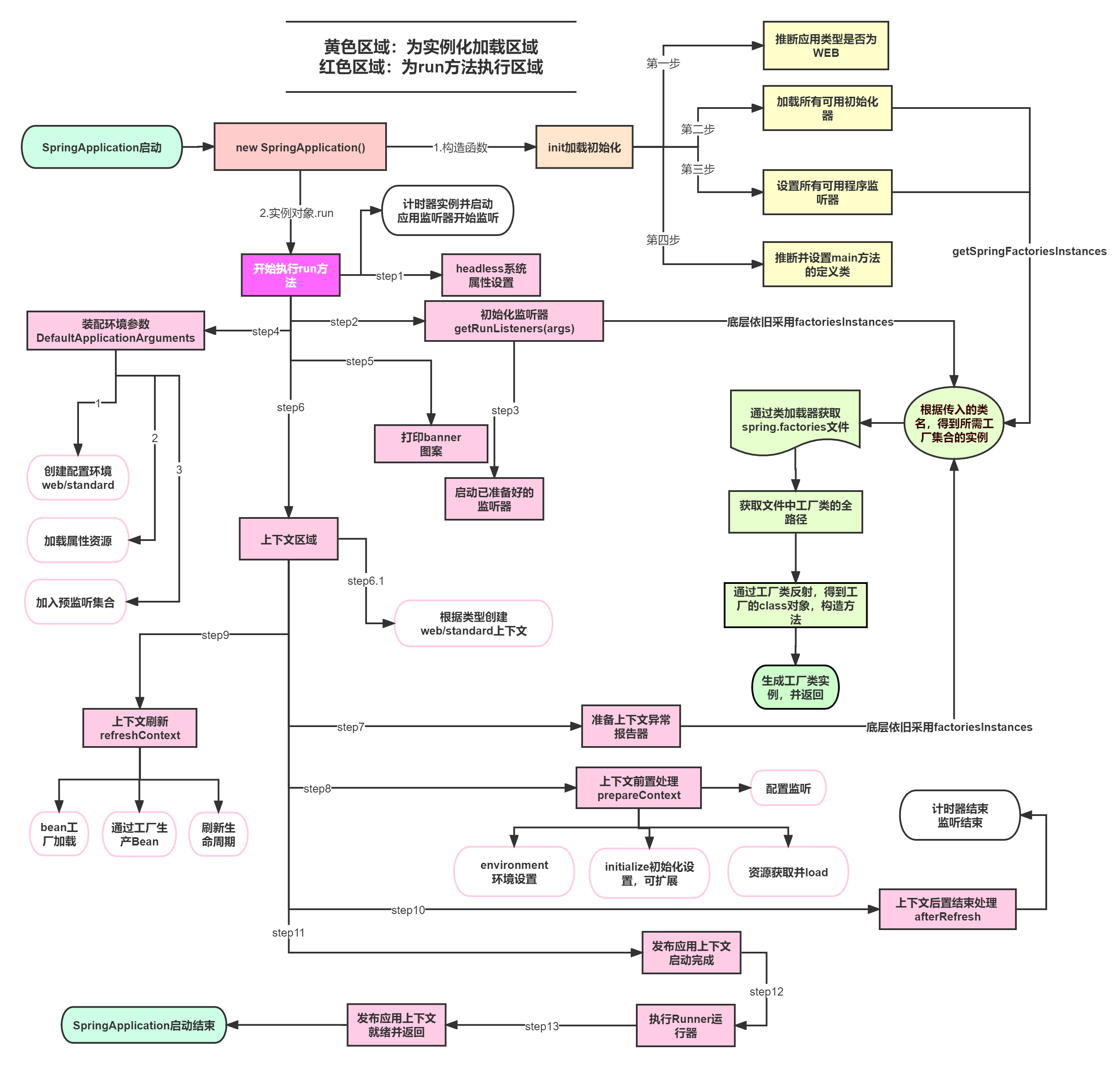
分析该方法主要分两部分,一部分是SpringApplication的实例化,二是run方法的执行;
SpringApplication
这个类主要做了以下四件事情:
1、推断应用的类型是普通的项目还是Web项目
2、查找并加载所有可用初始化器 , 设置到initializers属性中
3、找出所有的应用程序监听器,设置到listeners属性中
4、推断并设置main方法的定义类,找到运行的主类
查看构造器:
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class... primarySources) {
// ......
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
this.setInitializers(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances();
this.setListeners(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
run方法流程分析
跟着源码和这幅图就可以一探究竟了!
yaml
yaml语法学习
添加依赖即可解决,主要会有一些提示的功能,问题不大。
校验
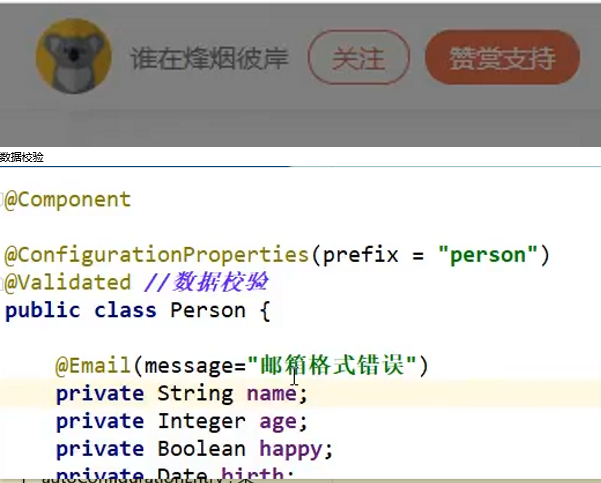
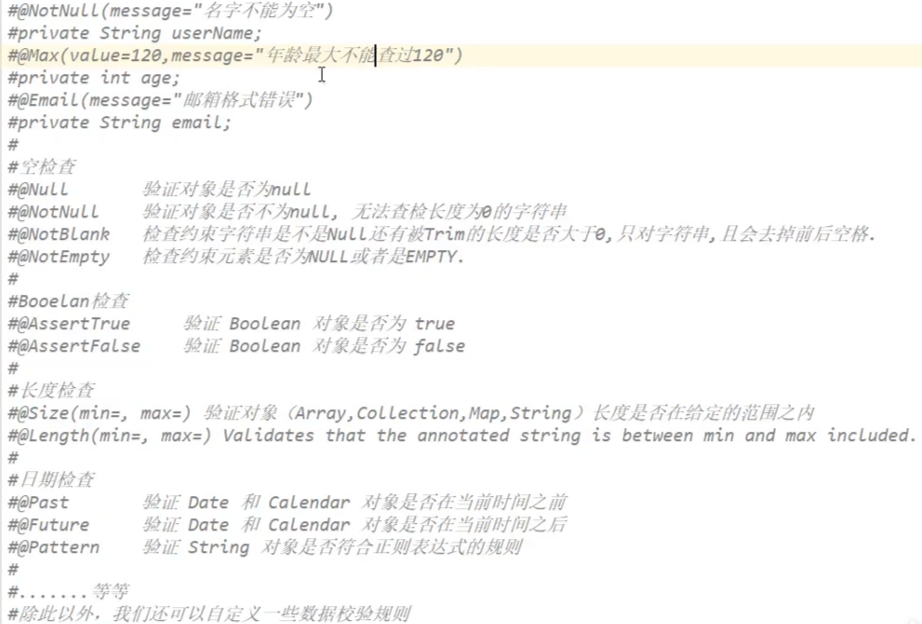
实现校验功能
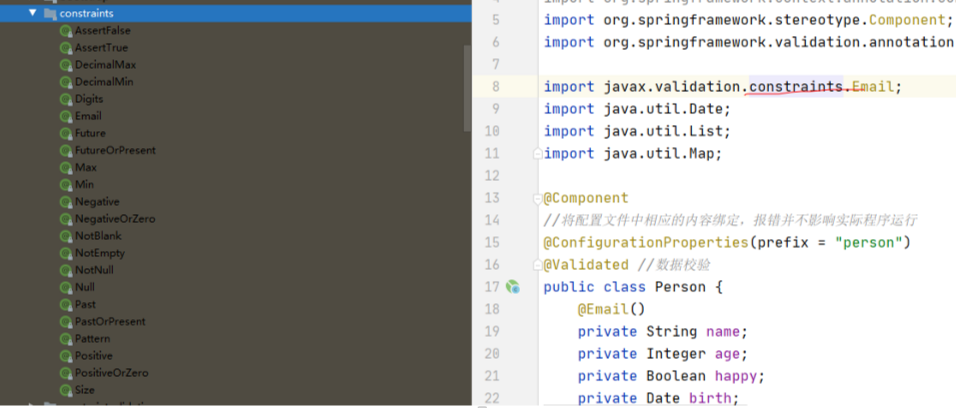
第一步,在需要校验的类名上面加上@Validated*//*数据校验
然后在@需要校验的变量上面加上Email()
需要不同的提示信息语句Email(message=“自己需要的提示信息。”)
常用
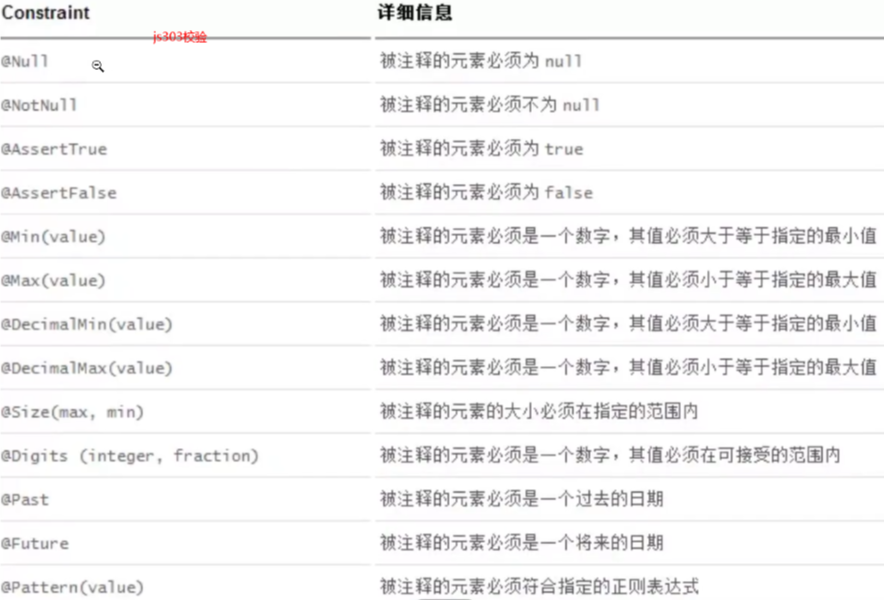
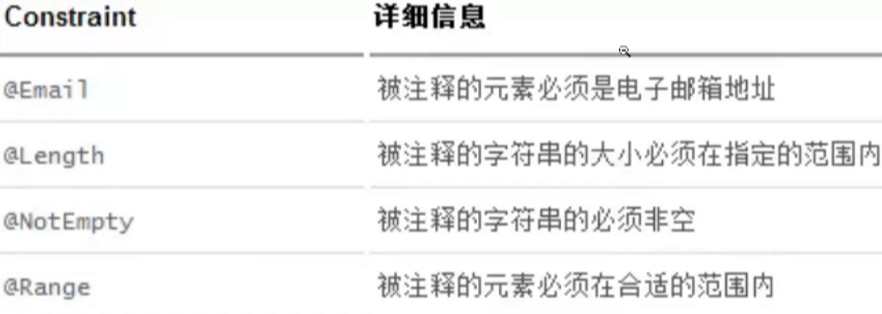
JSR303校验
配置文件
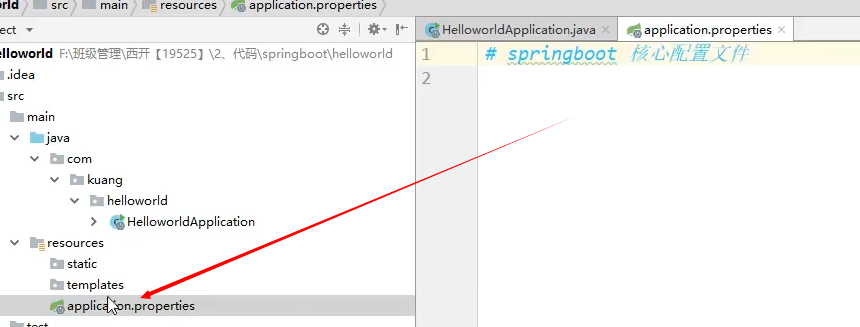
SpringBoot使用一个全局的配置文件 , 配置文件名称是固定的
-
application.properties
-
- 语法结构 :key=value
-
application.yml
-
- 语法结构 :key:空格 value
**配置文件的作用 :**修改SpringBoot自动配置的默认值,因为SpringBoot在底层都给我们自动配置好了;
比如我们可以在配置文件中修改Tomcat 默认启动的端口号!测试一下!
server.port=8081
概述
yaml概述
YAML是 “YAML Ain’t a Markup Language” (YAML不是一种标记语言)的递归缩写。在开发的这种语言时,YAML 的意思其实是:“Yet Another Markup Language”(仍是一种标记语言)
这种语言以数据作为中心,而不是以标记语言为重点!
以前的配置文件,大多数都是使用xml来配置;比如一个简单的端口配置,我们来对比下yaml和xml
传统xml配置:
<server>
<port>8081<port>
</server>
yaml配置:
server:
prot: 8080
基础语法
yaml基础语法
说明:语法要求严格!
1、空格不能省略
2、以缩进来控制层级关系,只要是左边对齐的一列数据都是同一个层级的。
3、属性和值的大小写都是十分敏感的。
字面量
字面量:普通的值 [ 数字,布尔值,字符串 ]
字面量直接写在后面就可以 , 字符串默认不用加上双引号或者单引号;
k: v
注意:
-
“ ” 双引号,不会转义字符串里面的特殊字符 , 特殊字符会作为本身想表示的意思;
比如 :name: “kuang \n shen” 输出 :kuang 换行 shen
-
‘’ 单引号,会转义特殊字符 , 特殊字符最终会变成和普通字符一样输出
比如 :name: ‘kuang \n shen’ 输出 :kuang \n shen
对象
对象、Map(键值对)
#对象、Map格式
k:
v1:
v2:
在下一行来写对象的属性和值得关系,注意缩进;比如:
student:
name: qinjiang
age: 3
行内写法
student: {name: qinjiang,age: 3}
数组
数组( List、set )
用 - 值表示数组中的一个元素,比如:
pets:
- cat
- dog
- pig
行内写法
pets: [cat,dog,pig]
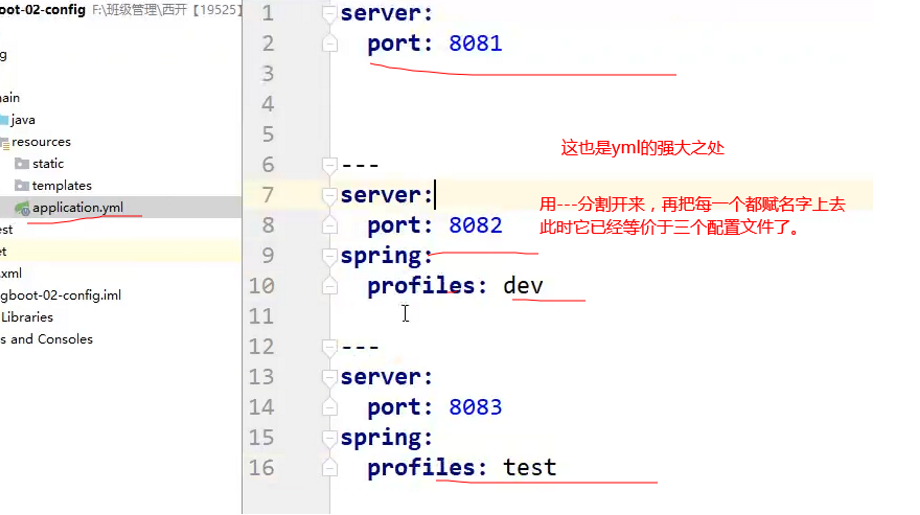
修改SpringBoot的默认端口号
配置文件中添加,端口号的参数,就可以切换端口;
server:
port: 8082
注入配置
yaml文件更强大的地方在于,他可以给我们的实体类直接注入匹配值!
yaml注入配置文件
1、在springboot项目中的resources目录下新建一个文件 application.yml
2、编写一个实体类 Dog;
package com.kuang.springboot.pojo;
@Component //注册bean到容器中
public class Dog {
private String name;
private Integer age;
//有参无参构造、get、set方法、toString()方法
}
3、思考,我们原来是如何给bean注入属性值的!@Value,给狗狗类测试一下:
@Component //注册bean
public class Dog {
@Value("阿黄")
private String name;
@Value("18")
private Integer age;
}
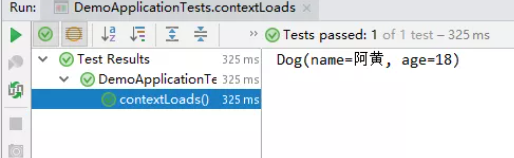
4、在SpringBoot的测试类下注入狗狗输出一下;
@SpringBootTest
class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired //将狗狗自动注入进来
Dog dog;
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(dog); //打印看下狗狗对象
}
}
结果成功输出,@Value注入成功,这是我们原来的办法对吧。
5、我们在编写一个复杂一点的实体类:Person 类
@Component //注册bean到容器中
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Boolean happy;
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
//有参无参构造、get、set方法、toString()方法
}
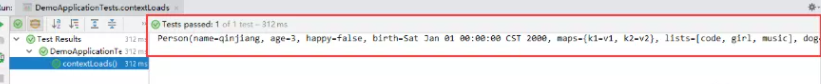
6、我们来使用yaml配置的方式进行注入,大家写的时候注意区别和优势,我们编写一个yaml配置!
person:
name: qinjiang
age: 3
happy: false
birth: 2000/01/01
maps: {k1: v1,k2: v2}
lists:
- code
- girl
- music
dog:
name: 旺财
age: 1
7、我们刚才已经把person这个对象的所有值都写好了,我们现在来注入到我们的类中!
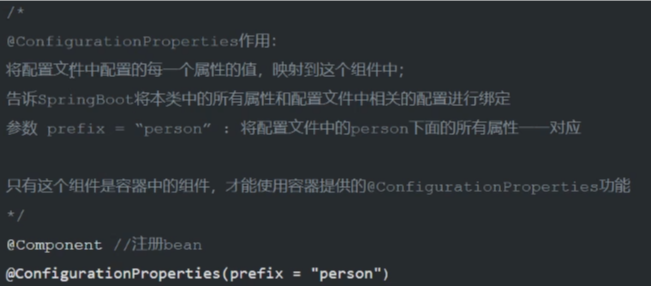
/*
@ConfigurationProperties作用:
将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中;
告诉SpringBoot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定
参数 prefix = “person” : 将配置文件中的person下面的所有属性一一对应
*/
@Component //注册bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Boolean happy;
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
}
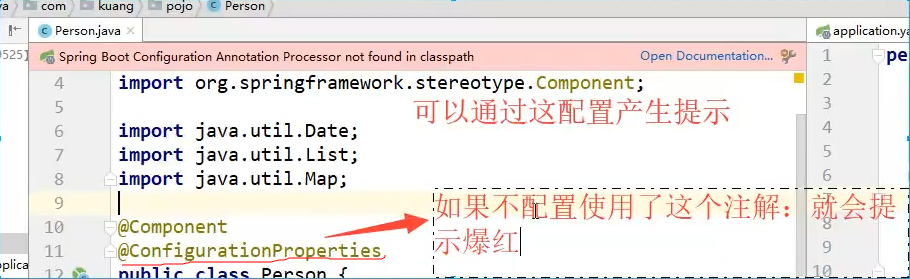
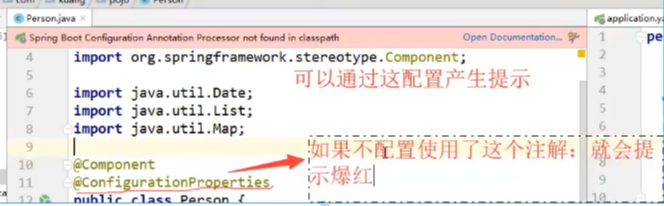
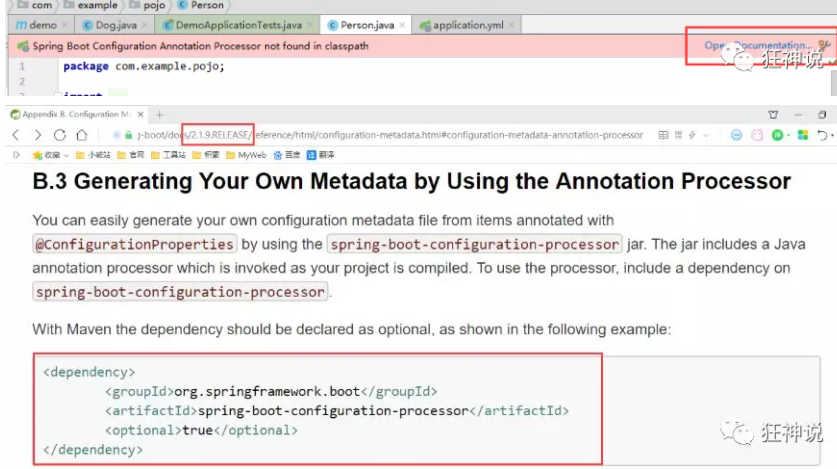
8、IDEA 提示,springboot配置注解处理器没有找到,让我们看文档,我们可以查看文档,找到一个依赖!
<!-- 导入配置文件处理器,配置文件进行绑定就会有提示,需要重启 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
9、确认以上配置都OK之后,我们去测试类中测试一下:
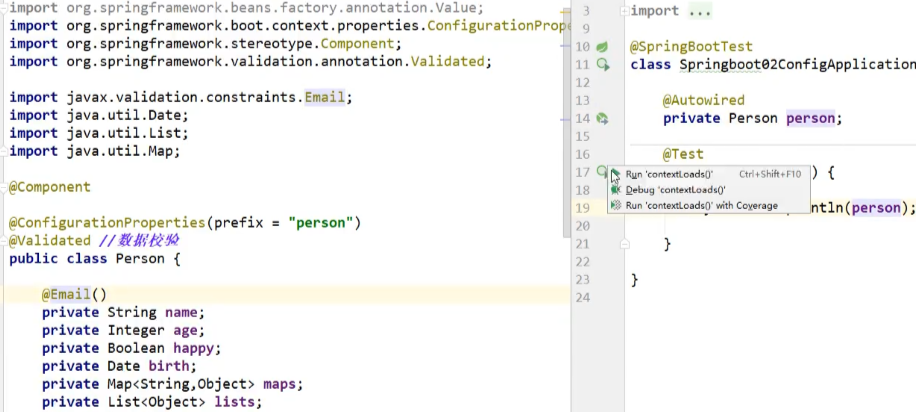
@SpringBootTest
class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
Person person; //将person自动注入进来
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(person); //打印person信息
}
}
结果:所有值全部注入成功!
yaml配置注入到实体类完全OK!
课堂测试:
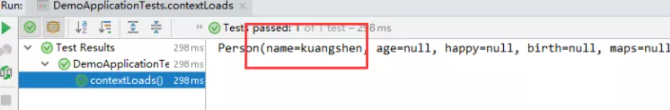
1、将配置文件的key 值 和 属性的值设置为不一样,则结果输出为null,注入失败
2、在配置一个person2,然后将 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “person2”) 指向我们的person2;
加载指定的配置文件
**@PropertySource :**加载指定的配置文件;
@configurationProperties:默认从全局配置文件中获取值;
1、我们去在resources目录下新建一个person.properties文件
name=kuangshen
2、然后在我们的代码中指定加载person.properties文件
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:person.properties")
@Component //注册bean
public class Person {
@Value("${name}")
private String name;
......
}
3、再次输出测试一下:指定配置文件绑定成功!
配置文件占位符
配置文件还可以编写占位符生成随机数
person:
name: qinjiang${random.uuid} # 随机uuid
age: ${random.int} # 随机int
happy: false
birth: 2000/01/01
maps: {k1: v1,k2: v2}
lists:
- code
- girl
- music
dog:
name: ${person.hello:other}_旺财
age: 1
回顾配置
回顾properties配置
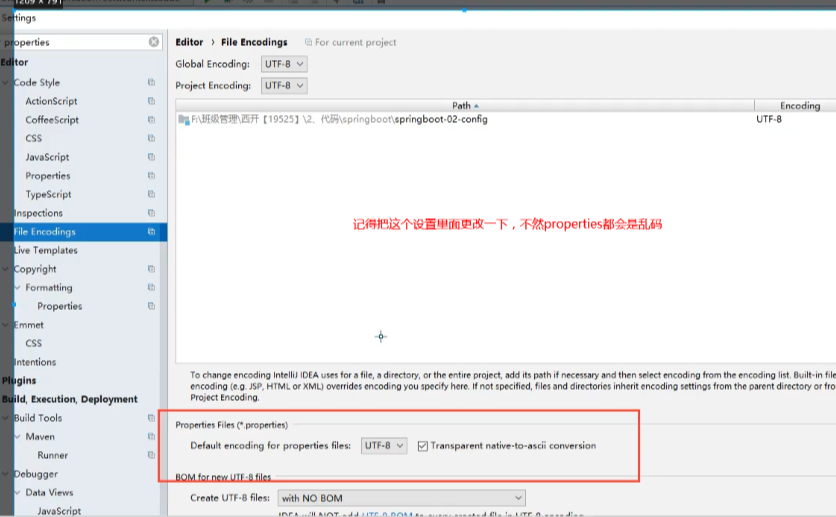
我们上面采用的yaml方法都是最简单的方式,开发中最常用的;也是springboot所推荐的!那我们来唠唠其他的实现方式,道理都是相同的;写还是那样写;配置文件除了yml还有我们之前常用的properties , 我们没有讲,我们来唠唠!
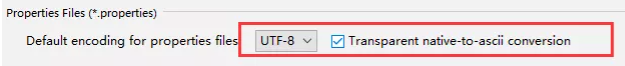
【注意】properties配置文件在写中文的时候,会有乱码 , 我们需要去IDEA中设置编码格式为UTF-8;
settings–>FileEncodings 中配置;
测试步骤:
1、新建一个实体类User
@Component //注册bean
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
}
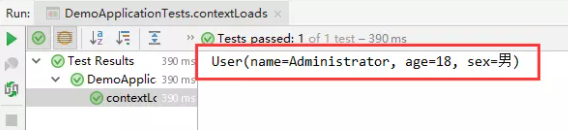
2、编辑配置文件 user.properties
user1.name=kuangshen
user1.age=18
user1.sex=男
3、我们在User类上使用@Value来进行注入!
@Component //注册bean
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:user.properties")
public class User {
//直接使用@value
@Value("${user.name}") //从配置文件中取值
private String name;
@Value("#{9*2}") // #{SPEL} Spring表达式
private int age;
@Value("男") // 字面量
private String sex;
}
4、Springboot测试
@SpringBootTest
class DemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
User user;
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
正常输出结果
对比小结
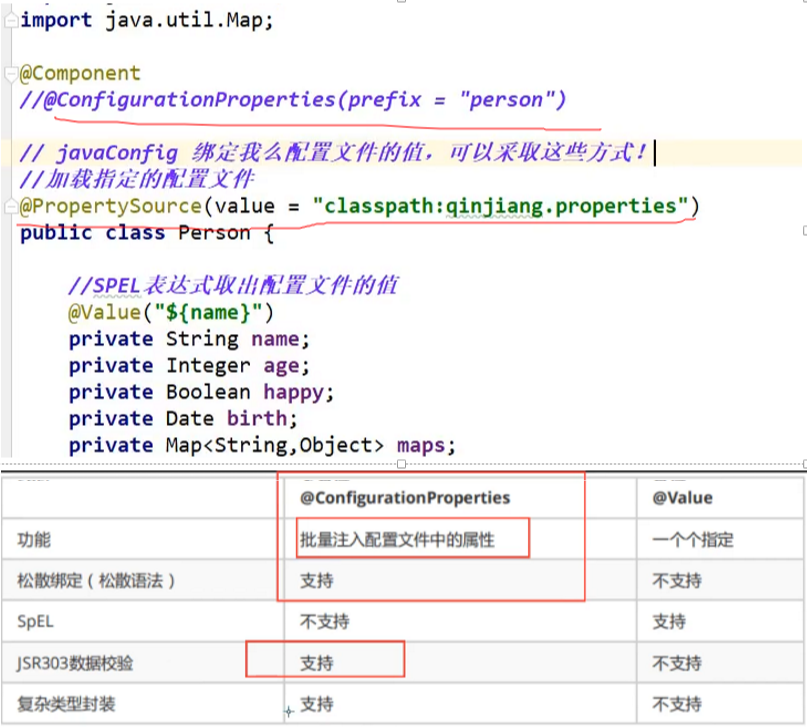
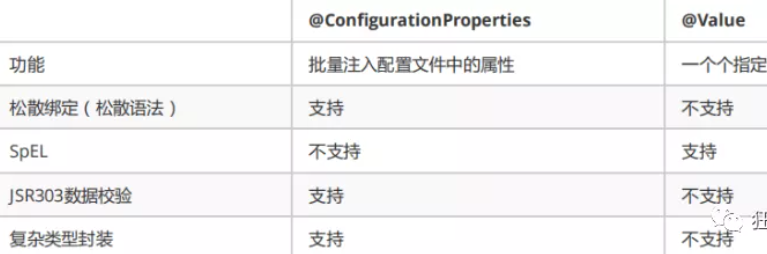
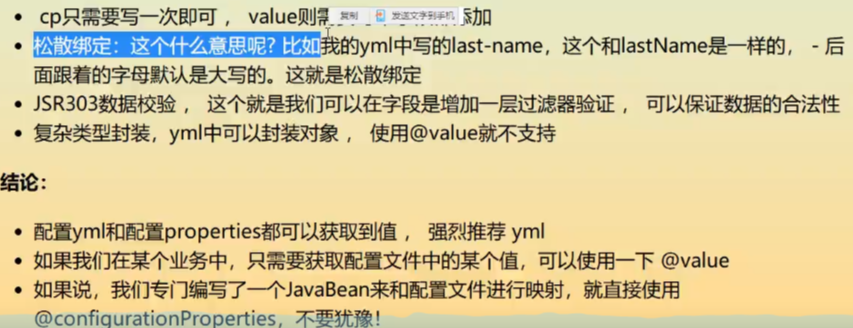
@Value这个使用起来并不友好!我们需要为每个属性单独注解赋值,比较麻烦;我们来看个功能对比图
1、@ConfigurationProperties只需要写一次即可 , @Value则需要每个字段都添加
2、松散绑定:这个什么意思呢? 比如我的yml中写的last-name,这个和lastName是一样的, - 后面跟着的字母默认是大写的。这就是松散绑定。可以测试一下
3、JSR303数据校验 , 这个就是我们可以在字段是增加一层过滤器验证 , 可以保证数据的合法性
4、复杂类型封装,yml中可以封装对象 , 使用value就不支持
结论
配置yml和配置properties都可以获取到值 , 强烈推荐 yml;
如果我们在某个业务中,只需要获取配置文件中的某个值,可以使用一下 @value;
Web开发
SpringBoot Web开发
自动装配
1.创建应用
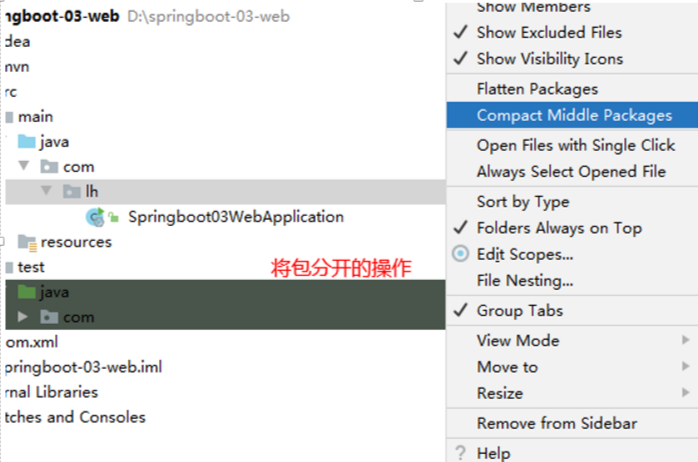
将包分开
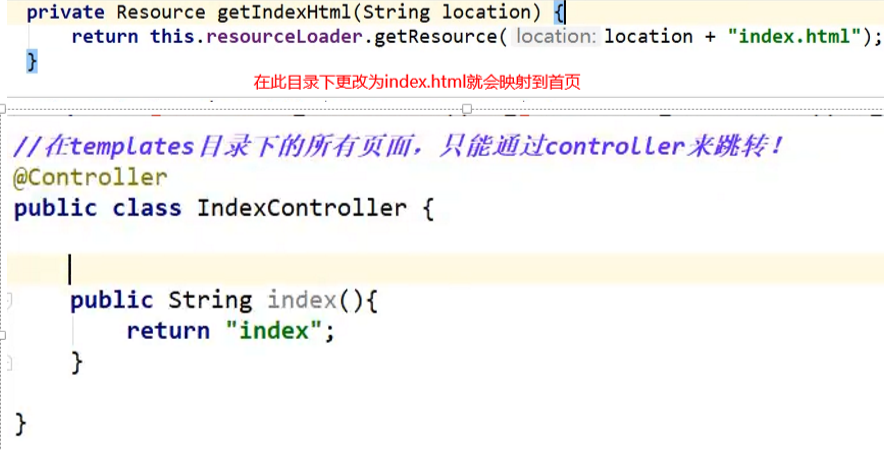
解释意思是:@RestController注解相当于@ResponseBody+ @Controller合在一起的作用。
1)如果只是使用@RestController注解Controller,则Controller中的方法无法返回jsp页面或者html页面,配置的视图解析器InternalResourceViewResolver不起作用,返回的内容就是Return里的内容。
例如:
本来应该到index.html页面的,则其显示index。
2)如果需要返回到指定页面,则需要用@Controller配合视图解析器InternalResourceViewResolver才行。
3)如果需要返回JSON,XML或自定义mediaType内容到页面,则需要在对应的方法上加上@ResponseBody注解。
注解 @ResponseBody
1、概念
注解 @ResponseBody,使用在控制层(controller)的方法上。
2、作用
作用:将方法的返回值,以特定的格式写入到response的body区域,进而将数据返回给客户端。
当方法上面没有写ResponseBody,底层会将方法的返回值封装为ModelAndView对象
如果返回值是字符串,那么直接将字符串写到客户端;如果是一个对象,会将对象转化为json串,然后写到客户端。
3、注意编码
注解中我们可以手动修改编码格式,例如@RequestMapping(value=“/cat/query”,produces=“text/html;charset=utf-8”),前面是请求的路径,后面是编码格式。
4、原理
控制层方法的返回值是如何转化为json格式的字符串的?其实是通过HttpMessageConverter中的方法实现的,它本是一个接口,在其实现类完成转换。如果是bean对象,会调用对象的getXXX()方法获取属性值并且以键值对的形式进行封装,进而转化为json串。如果是map集合,采用get(key)方式获取value值,然后进行封装。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/jiahao1186/article/details/91980316
| SpringMVC中Controller常用注解的理解 一、简介:在SpringMVC 中,控制器Controller 负责处理,由DispatcherServlet 分发的请求,它把用户请求的数据经过业务处理层处理之后封装成一个Model ,然后再把该Model 返回给对应的View 进行展示。在SpringMVC 中提供了一个非常简便的定义Controller 的方法,你无需继承特定的类或实现特定的接口,只需使用@Controller 标记一个类是Controller ,然后使用@RequestMapping 和@RequestParam 等一些注解用以定义URL 请求和Controller 方法之间的映射,这样的Controller 就能被外界访问到。此外Controller 不会直接依赖于HttpServletRequest 和HttpServletResponse 等HttpServlet 对象,它们可以通过Controller 的方法参数灵活的获取到。 二、@Controller : @Controller 是标记在Controller 类(包和类名之间)上面的。用于指示Spring类的实例是一个控制器。Controller接口的实现类只能处理一个单一请求动作,而@Controller注解的控制器可以支持同时处理多个请求动作,更加灵活。Spring使用 扫描机制 查找应用程序中所有基于注解的控制器类。分发处理器 会扫描使用了该注解的类的方法,并检测该方法是否使用了@RequestMapping注解,而使用@RequestMapping注解的方法才是真正处理请求的处理器。为了保证能找到控制器,需要完成两件事情: ①在Spring MVC的配置文件中,使用context:component-scan/元素,该元素的功能为:启动包扫描功能,以便注册带有@Controller,@Service,@repository,@Component等注解的类成为SPring的Bean。 ②<context:component-scan base-package=“包路径”> 应该 将所有控制器类都在基本包下,并且指定扫描该包 三、@ResponseBody: @ResponseBody注解是springmvc中用于方便json与string,实体对象之间转换的一个注解。在controller类中我们可以在方法上面添加@ResponseBody注解,这样我们返回实体对象或者字符串时,就会自动转换成json对象传给前端。在spring4.0后,@ResponseBody又可以加在类上,表示该类中的所有方法都加有@ResponseBody,很方便。 使用@RestController注解在类上,作用等于@Controller与@ResponseBody同时加在类上 要让@ResponseBody在类上也起作用,需要在springmvc配置文件中加上<mvc:annotation-driven />这一行配置才可以。而@ResponseBody使用在方法上,则不用添加该配置也可以使用。也就是说springmvc默认只支持@ResponseBody在方法上使用,不支持在类上的使用。 四、@RequestMapping :在Spring MVC 中使用 @RequestMapping 来映射请求,也就是通过它来指定控制器可以处理哪些URL请求, 可以在方法和类的声明中使用。 ①将 @RequestMapping 注解在类中方法上,而Controller类上不添加 @RequestMapping 注解,这时的请求 URL 是相对于 Web 根目录。 ②将 @RequestMapping 注解在Controller 类上,这时类的注解是相对于 Web 根目录,而方法上的是相对于类上的路径。 @RequestMapping 中的 value 和 path 属性(这两个属性作用相同,可以互换),@PathVariable 将 URL 中的占位符绑定到控制器的处理方法的参数中,占位符使用{}括起来。 @RequestMapping 中的 method 主要用来定义接收浏览器发来的何种请求。在Spring中,使用枚举类 org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod来定义浏览器请求的方式。 Http规范定义了多种请求资源的方式,最基本的有四种,分别为:GET(查)、POST(增)、PUT(改)、DELETE(删),而URL则用于定位网络上的资源相当于地址的作用,配合四种请求方式,可以实现对URL对应的资源的增删改查操作。 在实际应用中,很多人并没有按照这个规范做,因为使用GET/POST同样可以完成PUT和DELETE操作,甚至GET也可以完成POST操作,因为GET不需要用到表单,而POST却需要通过表单来发送。 由于在 RequestMapping 注解类中 method() 方法返回的是 RequestMethod 数组,所以可以给 method 同时指定多个请求方式。 @RequestMapping 的 params 属性,该属性表示请求参数,也就是追加在URL上的键值对,多个请求参数以&隔开。 @RequestMapping 的 headers 属性,该属性表示请求头。 用于HTTP协义交互的信息被称为HTTP报文,客户端发送的HTTP报文被称为请求报文,服务器发回给客户端的HTTP报文称为响应报文,报文由报文头部和报文体组成。 请求头部(Request Headers):请求头包含许多有关客户端环境和请求正文的信息,例如浏览器支持的语言、请求的服务器地址、客户端的操作系统等。响应头部(Rsponse Headers):响应头也包含许多有用的信息,包括服务器类型、日期、响应内容的类型及编码,响应内容的长度等等。 原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/l358366885/article/details/79485497 |
|---|
总结
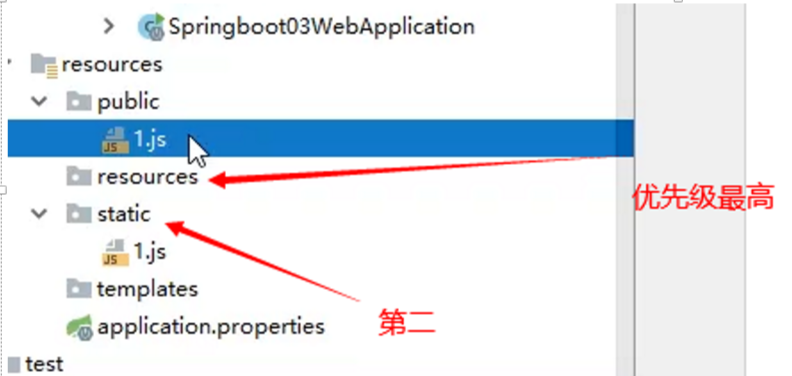
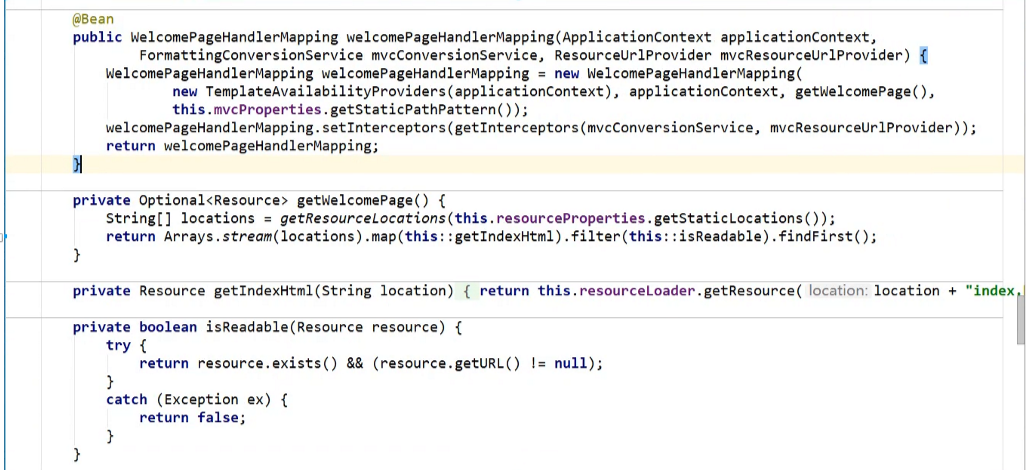
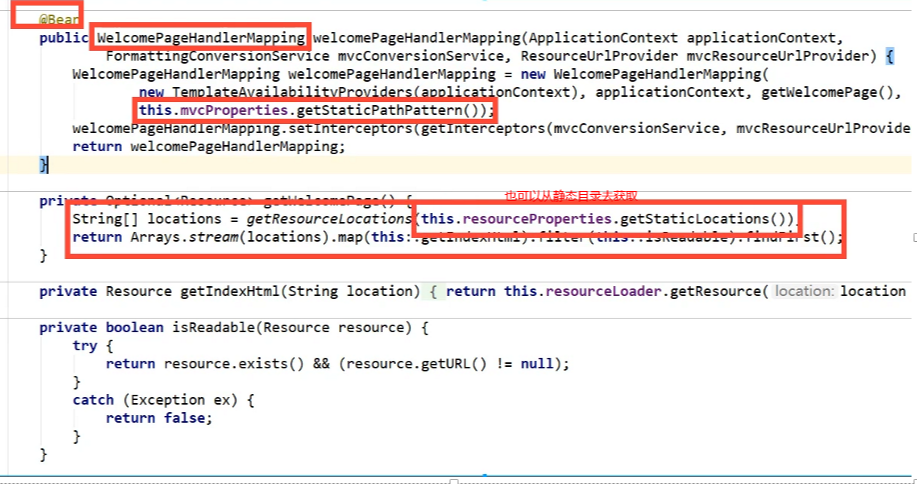
如何定义首页
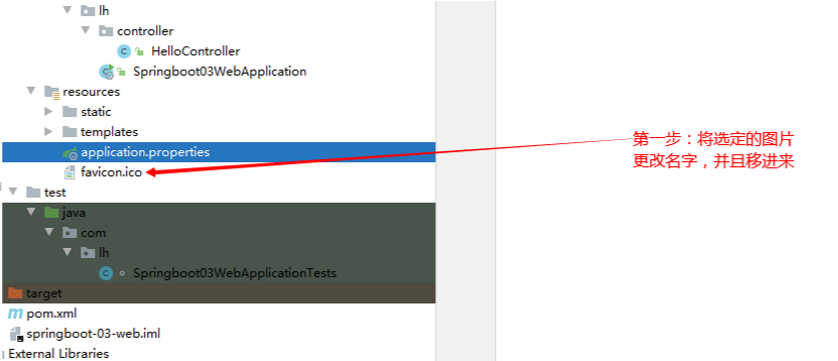
设置默认图标
设置默认图标(新版本就没有,只有2.1.7才有)
publicFaviconConfiguration(ResourcePropertiesresourceProperties){
this.resourceProperties=resourceProperties;
}
@Override
publicvoidsetResourceLoader(ResourceLoaderresourceLoader){
this.resourceLoader=resourceLoader;
}
@Bean
publicSimpleUrlHandlerMappingfaviconHandlerMapping(){
SimpleUrlHandlerMappingmapping=newSimpleUrlHandlerMapping();
mapping.setOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE+1);
//将图标定义成favicon.ico
mapping.setUrlMap(Collections.singletonMap("**/favicon.ico",
faviconRequestHandler()));
returnmapping;
}
@Bean
publicResourceHttpRequestHandlerfaviconRequestHandler(){
ResourceHttpRequestHandlerrequestHandler=newResourceHttpRequestHandler();
requestHandler.setLocations(resolveFaviconLocations());
returnrequestHandler;
}
步骤
root@d853b59f31dd:/# java -version
openjdk version "1.8.0_111"
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_111-8u111-b14-2~bpo8+1-b14)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.111-b14, mixed mode)
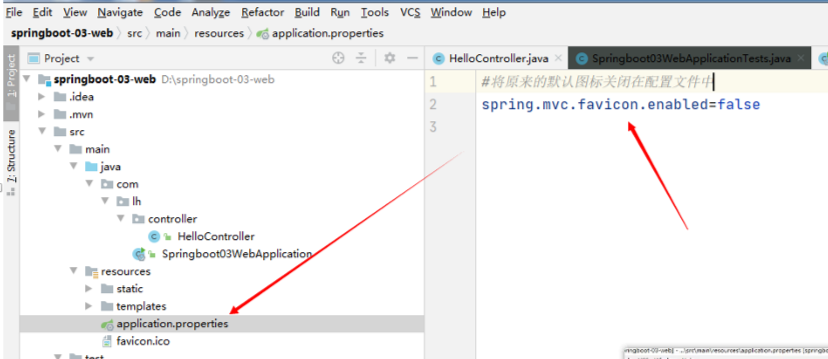
#将原来的默认图标关闭在配置文件中
spring.mvc.favicon.enabled=false
清理浏览器缓存
再重新运行
Thymeleaf
Thymeleaf模板引擎
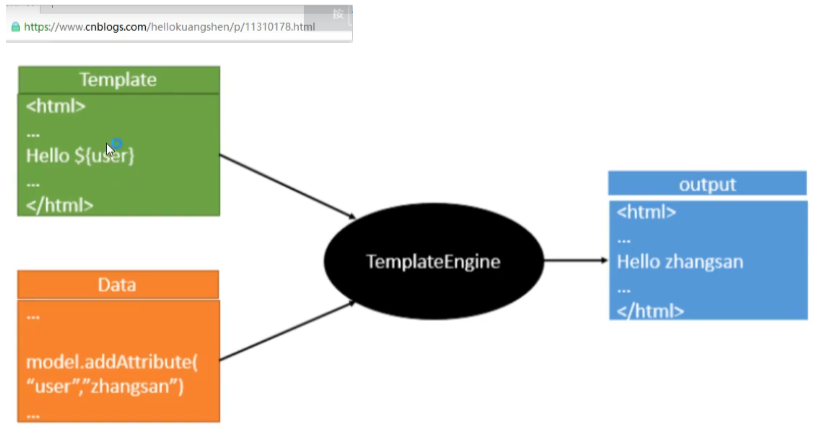
模板引擎
前端交给我们的页面,是html页面。如果是我们以前开发,我们需要把他们转成jsp页面,jsp好处就是当我们查出一些数据转发到JSP页面以后,我们可以用jsp轻松实现数据的显示,及交互等。
jsp支持非常强大的功能,包括能写Java代码,但是呢,我们现在的这种情况,SpringBoot这个项目首先是以jar的方式,不是war,像第二,我们用的还是嵌入式的Tomcat,所以呢,他现在默认是不支持jsp的。
那不支持jsp,如果我们直接用纯静态页面的方式,那给我们开发会带来非常大的麻烦,那怎么办呢?
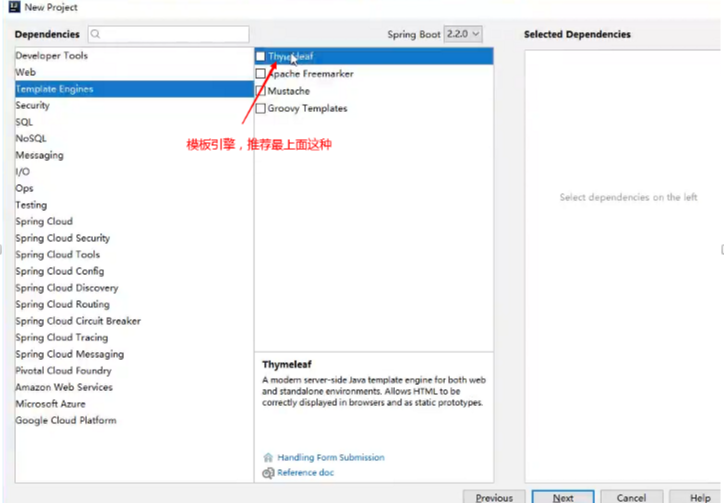
SpringBoot推荐你可以来使用模板引擎:
模板引擎,我们其实大家听到很多,其实jsp就是一个模板引擎,还有用的比较多的freemarker,包括SpringBoot给我们推荐的Thymeleaf,模板引擎有非常多,但再多的模板引擎,他们的思想都是一样的,什么样一个思想呢我们来看一下这张图:
模板引擎的作用就是我们来写一个页面模板,比如有些值呢,是动态的,我们写一些表达式。而这些值,从哪来呢,就是我们在后台封装一些数据。然后把这个模板和这个数据交给我们模板引擎,模板引擎按照我们这个数据帮你把这表达式解析、填充到我们指定的位置,然后把这个数据最终生成一个我们想要的内容给我们写出去,这就是我们这个模板引擎,不管是jsp还是其他模板引擎,都是这个思想。只不过呢,就是说不同模板引擎之间,他们可能这个语法有点不一样。其他的我就不介绍了,我主要来介绍一下SpringBoot给我们推荐的Thymeleaf模板引擎,这模板引擎呢,是一个高级语言的模板引擎,他的这个语法更简单。而且呢,功能更强大。
我们呢,就来看一下这个模板引擎,那既然要看这个模板引擎。首先,我们来看SpringBoot里边怎么用。
引入
引入Thymeleaf
怎么引入呢,对于springboot来说,什么事情不都是一个start的事情嘛,我们去在项目中引入一下。给大家三个网址:
Thymeleaf 官网:https://www.thymeleaf.org/
Thymeleaf 在Github 的主页:https://github.com/thymeleaf/thymeleaf
Spring官方文档:找到我们对应的版本
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.2.5.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#using-boot-starter
找到对应的pom依赖:可以适当点进源码看下本来的包!
<!--thymeleaf-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
Maven会自动下载jar包,我们可以去看下下载的东西;
分析
Thymeleaf分析
前面呢,我们已经引入了Thymeleaf,那这个要怎么使用呢?
我们首先得按照SpringBoot的自动配置原理看一下我们这个Thymeleaf的自动配置规则,在按照那个规则,我们进行使用。
我们去找一下Thymeleaf的自动配置类:ThymeleafProperties
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.thymeleaf"
)
public class ThymeleafProperties {
private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING;
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";
private boolean checkTemplate = true;
private boolean checkTemplateLocation = true;
private String prefix = "classpath:/templates/";
private String suffix = ".html";
private String mode = "HTML";
private Charset encoding;
}
我们可以在其中看到默认的前缀和后缀!
我们只需要把我们的html页面放在类路径下的templates下,thymeleaf就可以帮我们自动渲染了。
使用thymeleaf什么都不需要配置,只需要将他放在指定的文件夹下即可!
测试
1、编写一个TestController
@Controller
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/t1")
public String test1(){
//classpath:/templates/test.html
return "test";
}
}
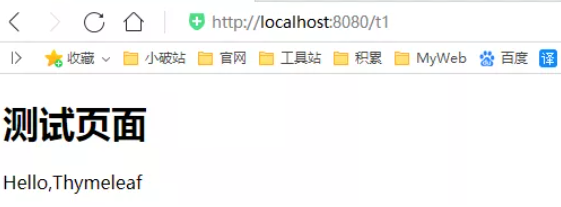
2、编写一个测试页面 test.html 放在 templates 目录下
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>测试页面</h1>
</body>
</html>
3、启动项目请求测试
语法学习
Thymeleaf 语法学习
要学习语法,还是参考官网文档最为准确,我们找到对应的版本看一下;
Thymeleaf 官网:https://www.thymeleaf.org/ , 简单看一下官网!我们去下载Thymeleaf的官方文档!
我们做个最简单的练习 :我们需要查出一些数据,在页面中展示
1、修改测试请求,增加数据传输;
@RequestMapping("/t1")
public String test1(Model model){
//存入数据
model.addAttribute("msg","Hello,Thymeleaf");
//classpath:/templates/test.html
return "test";
}
2、我们要使用thymeleaf,需要在html文件中导入命名空间的约束,方便提示。
我们可以去官方文档的#3中看一下命名空间拿来过来:
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
3、我们去编写下前端页面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>狂神说</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>测试页面</h1>
<!--th:text就是将div中的内容设置为它指定的值,和之前学习的Vue一样-->
<div th:text="${msg}"></div>
</body>
</html>
4、启动测试!
OK,入门搞定,我们来认真研习一下Thymeleaf的使用语法!
1、我们可以使用任意的 th:attr 来替换Html中原生属性的值!
2、我们能写哪些表达式呢?
Simple expressions:(表达式语法)
Variable Expressions: ${...}:获取变量值;OGNL;
1)、获取对象的属性、调用方法
2)、使用内置的基本对象:#18
#ctx : the context object.
#vars: the context variables.
#locale : the context locale.
#request : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletRequest object.
#response : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletResponse object.
#session : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpSession object.
#servletContext : (only in Web Contexts) the ServletContext object.
3)、内置的一些工具对象:
#execInfo : information about the template being processed.
#uris : methods for escaping parts of URLs/URIs
#conversions : methods for executing the configured conversion service (if any).
#dates : methods for java.util.Date objects: formatting, component extraction, etc.
#calendars : analogous to #dates , but for java.util.Calendar objects.
#numbers : methods for formatting numeric objects.
#strings : methods for String objects: contains, startsWith, prepending/appending, etc.
#objects : methods for objects in general.
#bools : methods for boolean evaluation.
#arrays : methods for arrays.
#lists : methods for lists.
#sets : methods for sets.
#maps : methods for maps.
#aggregates : methods for creating aggregates on arrays or collections.
==================================================================================
Selection Variable Expressions: *{...}:选择表达式:和${}在功能上是一样;
Message Expressions: #{...}:获取国际化内容
Link URL Expressions: @{...}:定义URL;
Fragment Expressions: ~{...}:片段引用表达式
Literals(字面量)
Text literals: 'one text' , 'Another one!' ,…
Number literals: 0 , 34 , 3.0 , 12.3 ,…
Boolean literals: true , false
Null literal: null
Literal tokens: one , sometext , main ,…
Text operations:(文本操作)
String concatenation: +
Literal substitutions: |The name is ${name}|
Arithmetic operations:(数学运算)
Binary operators: + , - , * , / , %
Minus sign (unary operator): -
Boolean operations:(布尔运算)
Binary operators: and , or
Boolean negation (unary operator): ! , not
Comparisons and equality:(比较运算)
Comparators: > , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le )
Equality operators: == , != ( eq , ne )
Conditional operators:条件运算(三元运算符)
If-then: (if) ? (then)
If-then-else: (if) ? (then) : (else)
Default: (value) ?: (defaultvalue)
Special tokens:
No-Operation: _
练习测试:
1、 我们编写一个Controller,放一些数据
@RequestMapping("/t2")
public String test2(Map<String,Object> map){
//存入数据
map.put("msg","<h1>Hello</h1>");
map.put("users", Arrays.asList("qinjiang","kuangshen"));
//classpath:/templates/test.html
return "test";
}
2、测试页面取出数据
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>狂神说</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>测试页面</h1>
<div th:text="${msg}"></div>
<!--不转义-->
<div th:utext="${msg}"></div>
<!--遍历数据-->
<!--th:each每次遍历都会生成当前这个标签:官网#9-->
<h4 th:each="user :${users}" th:text="${user}"></h4>
<h4>
<!--行内写法:官网#12-->
<span th:each="user:${users}">[[${user}]]</span>
</h4>
</body>
</html>
3、启动项目测试!
我们看完语法,很多样式,我们即使现在学习了,也会忘记,所以我们在学习过程中,需要使用什么,根据官方文档来查询,才是最重要的,要熟练使用官方文档!
构思网站
回顾
此上必须要掌握的点
-
SpringBoot是什么?
1、SpringBoot是什么? 在Spring框架这个大家族中,产生了很多衍生框架,比如 Spring、SpringMvc框架等,Spring的核心内容在于控制反转(IOC)和依赖注入(DI),所谓控制反转并非是一种技术,而是一种思想,在操作方面是指在spring配置文件中创建<bean>,依赖注入即为由spring容器为应用程序的某个对象提供资源,比如 引用对象、常量数据等。 SpringBoot是一个框架,一种全新的编程规范,他的产生简化了框架的使用,所谓简化是指简化了Spring众多框架中所需的大量且繁琐的配置文件,所以 SpringBoot是一个服务于框架的框架,服务范围是简化配置文件。 2、SpringBoot可以做什么? 最明显的特点是,让文件配置变的相当简单、让应用部署变的简单(SpringBoot内置服务器,并装备启动类代码),可以快速开启一个Web容器进行开发。 3、SpringBoot工程的使用特点 (1)一个简单的SpringBoot工程是不需要在pom.xml手动添加什么配置的,如果与其他技术合用 比如postMan(文档在线自动生成、开发功能测试的一套工具)、Swagger(文档在线自动生成、开发功能测试的一套工具),则需要在pom.xml中添加依赖,由程序自动加载依赖jar包等配置文件。 (2)我们之前在利用SSM或者SSH开发的时候,在resources中储存各种对应框架的配置文件,而现在我们只需要一个配置文件即可,配置内容也大体有 服务器端口号、数据库连接的地址、用户名、密码。这样,虽然简单 但在一定问题上而言,这也是极不安全的,将所有配置,放在一个文件里,是很危险的,但对于一般项目而言并不会有太大影响。 (3)在SpringBoot创建时会自动创建Bootdemo1Application启动类,代表着本工程项目和服务器的启动加载,在springBoot中是内含服务器的,所以不需手动配置Tomact,但注意端口号冲突问题。 -
微服务的概念
“微服务是一种用于构建应用的架构方案。微服务架构有别于更为传统的单体式方案,可将应用拆分成多个核心功能。每个功能都被称为一项服务,可以单独构建和部署,这意味着各项服务在工作(和出现故障)时不会相互影响。”
-
HelloWorld~
-
探究源码~自动装配的原理
-
配置yaml
-
多文档环境切换
-
静态资源映射
-
Thymeleaf的基本语法及使用 th:xxx
-
SpringBoot如何扩展MVC javaconfig~
-
如何修改SpringBoot的默认配置
-
CRUD
-
国际化
-
拦截器
-
定制首页,错误页~
整合JDBC
准备
新建项目
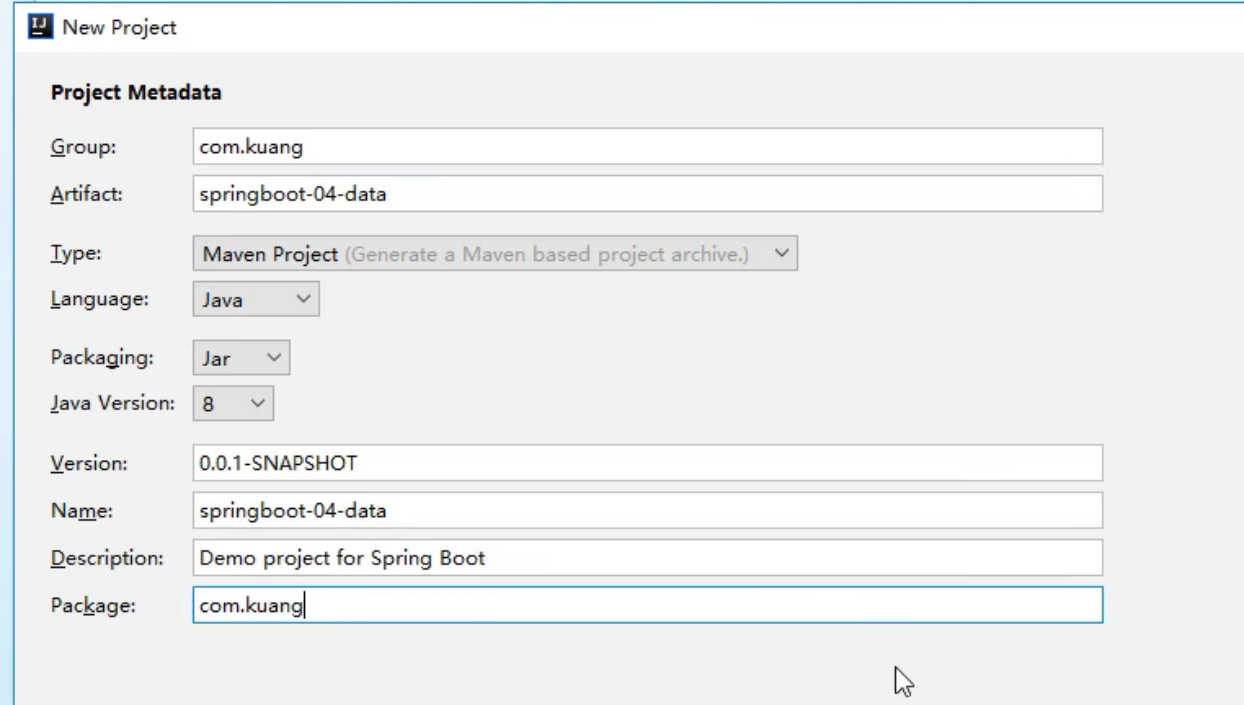
2.导入依赖
检查依赖是否正确导入
检查目录
3.配置yaml文件
基本目录整理以及配置yaml
username:root
password:123456
url:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driver-cl
对于数据访问层,无论是 SQL(关系型数据库) 还是 NOSQL(非关系型数据库),Spring Boot 底层都是采用 Spring Data 的方式进行统一处理。
Spring Boot 底层都是采用 Spring Data 的方式进行统一处理各种数据库,Spring Data 也是 Spring 中与 Spring Boot、Spring Cloud 等齐名的知名项目。
Sping Data 官网:https://spring.io/projects/spring-data
数据库相关的启动器 :可以参考官方文档:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.2.5.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#using-boot-starter
整合JDBC
创建测试项目测试数据源
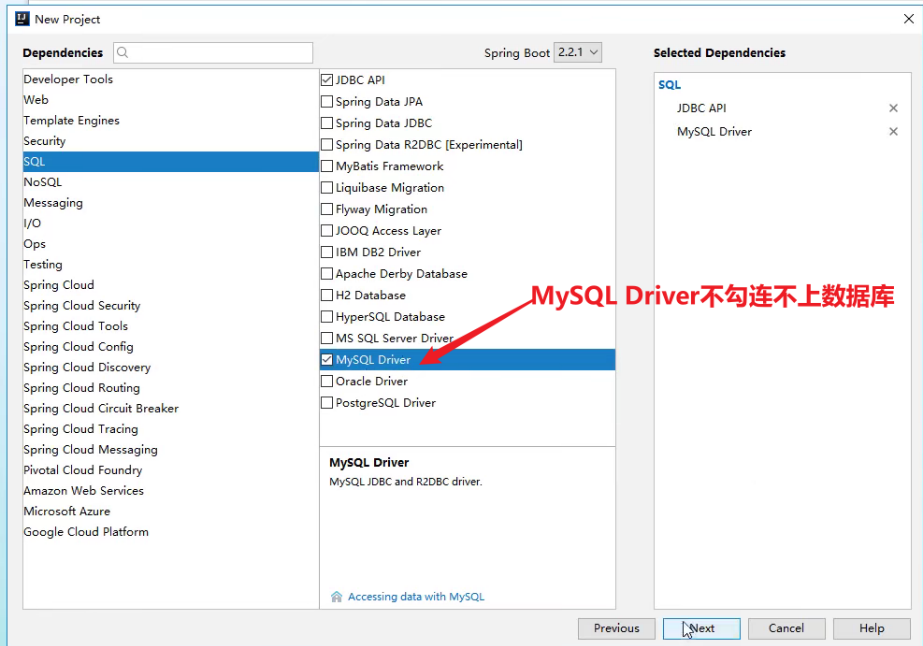
1、我去新建一个项目测试:springboot-data-jdbc ; 引入相应的模块!基础模块
2、项目建好之后,发现自动帮我们导入了如下的启动器:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
3、编写yaml配置文件连接数据库;
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
#?serverTimezone=UTC解决时区的报错
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
4、配置完这一些东西后,我们就可以直接去使用了,因为SpringBoot已经默认帮我们进行了自动配置;去test测试类测试一下
package com.Hao;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
@SpringBootTest
class SpringbootDataJdbcApplicationTests {
//DI注入数据源
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource;
@Test
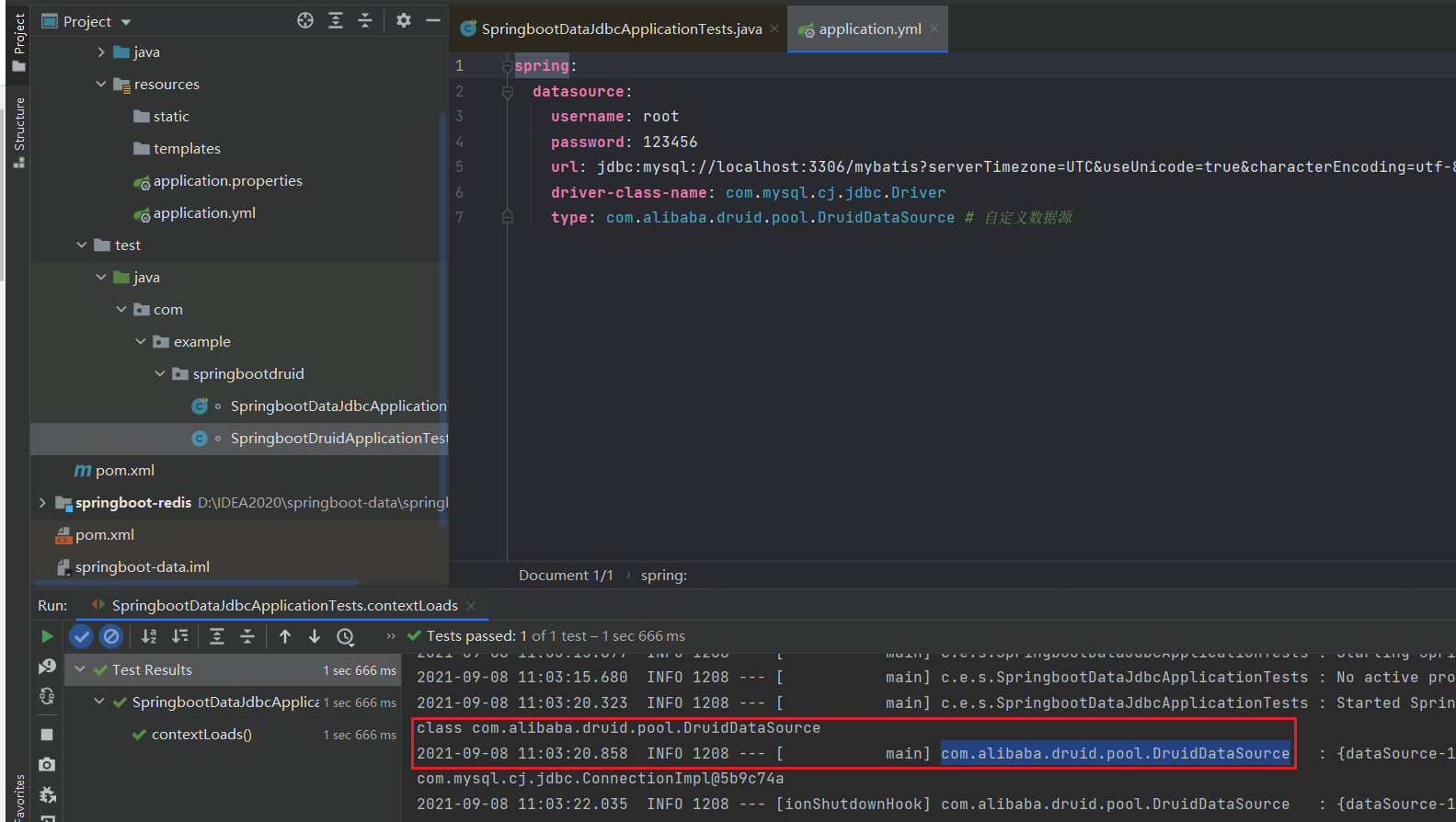
public void contextLoads() throws SQLException {
//看一下默认数据源
System.out.println(dataSource.getClass());
//获得连接
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
//关闭连接默认操作
connection.close();
}
}
结果:我们可以看到他默认给我们配置的数据源为 : class com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource , 我们并没有手动配置
我们来全局搜索一下,找到数据源的所有自动配置都在 :DataSourceAutoConfiguration文件:
@Import(
{Hikari.class, Tomcat.class, Dbcp2.class, Generic.class, DataSourceJmxConfiguration.class}
)
protected static class PooledDataSourceConfiguration {
protected PooledDataSourceConfiguration() {
}
}
这里导入的类都在 DataSourceConfiguration 配置类下,可以看出 Spring Boot 2.2.5 默认使用HikariDataSource 数据源,而以前版本,如 Spring Boot 1.5 默认使用 org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource 作为数据源;
HikariDataSource 号称 Java WEB 当前速度最快的数据源,相比于传统的 C3P0 、DBCP、Tomcat jdbc 等连接池更加优秀;
可以使用 spring.datasource.type 指定自定义的数据源类型,值为 要使用的连接池实现的完全限定名。
关于数据源我们并不做介绍,有了数据库连接,显然就可以 CRUD 操作数据库了。但是我们需要先了解一个对象 JdbcTemplate
JDBCTemplate
1、有了数据源(com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource),然后可以拿到数据库连接(java.sql.Connection),有了连接,就可以使用原生的 JDBC 语句来操作数据库;
2、即使不使用第三方第数据库操作框架,如 MyBatis等,Spring 本身也对原生的JDBC 做了轻量级的封装,即JdbcTemplate。
3、数据库操作的所有 CRUD 方法都在 JdbcTemplate 中。
4、Spring Boot 不仅提供了默认的数据源,同时默认已经配置好了 JdbcTemplate 放在了容器中,程序员只需自己注入即可使用
5、JdbcTemplate 的自动配置是依赖 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc 包下的 JdbcTemplateConfiguration 类
JdbcTemplate主要提供以下几类方法:
- execute方法:可以用于执行任何SQL语句,一般用于执行DDL语句;
- update方法及batchUpdate方法:update方法用于执行新增、修改、删除等语句;batchUpdate方法用于执行批处理相关语句;
- query方法及queryForXXX方法:用于执行查询相关语句;
- call方法:用于执行存储过程、函数相关语句。
测试
在com.Hao.controller包下编写一个Controller,注入 jdbcTemplate,编写测试方法进行访问测试;
package com.Hao.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/jdbc")
public class JDBCController {
/**
* Spring Boot 默认提供了数据源,默认提供了 org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate
* JdbcTemplate 中会自己注入数据源,用于简化 JDBC操作
* 还能避免一些常见的错误,使用起来也不用再自己来关闭数据库连接
*/
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
//查询user表中所有数据
//List 中的1个 Map 对应数据库的 1行数据
//Map 中的 key 对应数据库的字段名,value 对应数据库的字段值
@GetMapping("/list")
public List<Map<String, Object>> userList(){
String sql = "select * from mybatis.user";
List<Map<String, Object>> maps = jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql);
return maps;
}
//新增一个用户
@GetMapping("/add")
public String addUser(){
//插入语句,注意时间问题
String sql = "insert into mybatis.user(id, name,pwd)" +
" values ('6','狂说','24736743')";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql);
//查询
return "addOk";
}
//修改用户信息
@GetMapping("/update/{id}")
public String updateUser(@PathVariable("id") int id){
//插入语句
String sql = "update mybatis.user set name=?,pwd=? where id="+id;
//数据
Object[] objects = new Object[2];
objects[0] = "秦疆";
objects[1] = "24736743";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,objects);
//查询
return "updateOk";
}
//删除用户
@GetMapping("/delete/{id}")
public String delUser(@PathVariable("id") int id){
//插入语句
String sql = "delete from mybatis.user where id=?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,id);
//查询
return "deleteOk";
}
}
这个才是访问地址,一定要注意前面是否加上了@RequestMapping注解
http://localhost:8080/jdbc/delete/5
包文件扫不到的问题
添加@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages=“controller”)
在你的启动的Demo01Application类中,添加注释,指定你的controller的位置,就可以指定加载,成功解决问题。
整合Druid
整合Druid数据源
Druid简介
Java程序很大一部分要操作数据库,为了提高性能操作数据库的时候,又不得不使用数据库连接池。
Druid 是阿里巴巴开源平台上一个数据库连接池实现,结合了 C3P0、DBCP 等 DB 池的优点,同时加入了日志监控。
Druid 可以很好的监控 DB 池连接和 SQL 的执行情况,天生就是针对监控而生的 DB 连接池。
Druid已经在阿里巴巴部署了超过600个应用,经过一年多生产环境大规模部署的严苛考验。
Spring Boot 2.0 以上默认使用 Hikari 数据源,可以说 Hikari 与 Driud 都是当前 Java Web 上最优秀的数据源,我们来重点介绍 Spring Boot 如何集成 Druid 数据源,如何实现数据库监控。
Github地址:https://github.com/alibaba/druid/
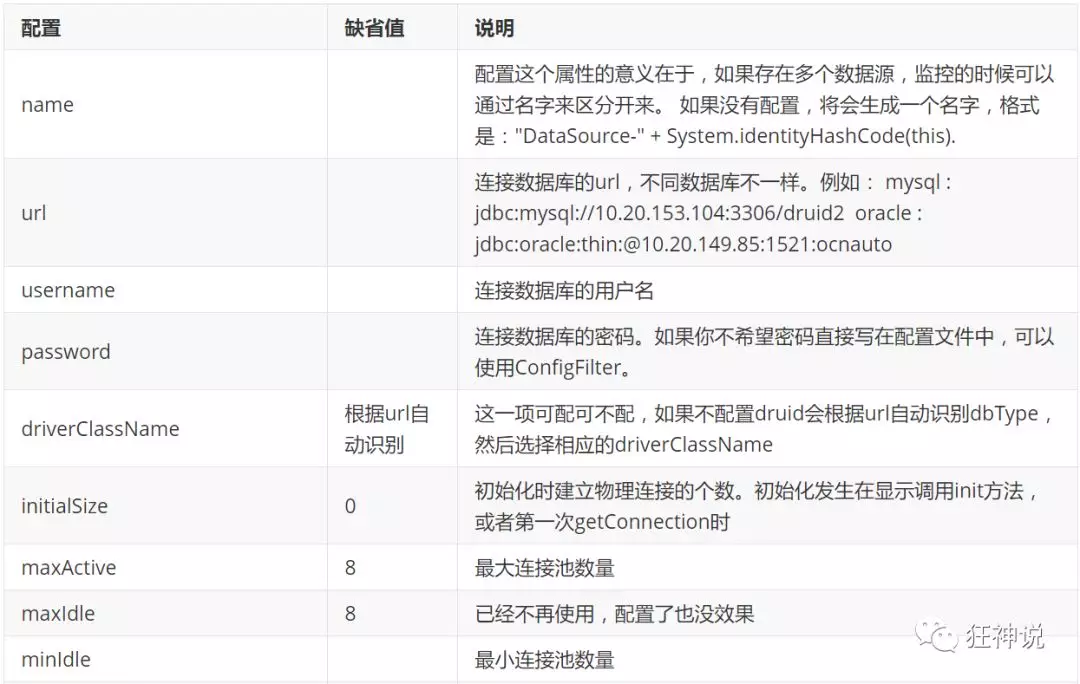
com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource 基本配置参数如下:
配置数据源
依赖
1、添加上 Druid 数据源依赖。
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba/druid -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.21</version>
</dependency>
<!--Log4j,在druid中需要用到log4j就必须要导入这个包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
切换
2、切换数据源;之前已经说过 Spring Boot 2.0 以上默认使用 com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource 数据源,但可以 通过 spring.datasource.type 指定数据源。
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource # 自定义数据源
注意:当自定义数据源出现错误,可能是thymeleaf模板引擎未添加此支持框架,yaml并没有加载。
测试
3、数据源切换之后,在Test测试类中注入 DataSource,然后获取到它,输出一看便知是否成功切换;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
@SpringBootTest
class SpringbootDataJdbcApplicationTests {
//DI注入数据源
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource;
@Test
public void contextLoads() throws SQLException {
//看一下默认数据源
System.out.println(dataSource.getClass());
//获得连接
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
//关闭连接
connection.close();
}
}
配置
4、切换成功!既然切换成功,就可以设置数据源连接初始化大小、最大连接数、等待时间、最小连接数 等设置项;可以查看源码
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
#?serverTimezone=UTC解决时区的报错
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
#Spring Boot 默认是不注入这些属性值的,需要自己绑定
#druid 数据源专有配置
initialSize: 5
minIdle: 5
maxActive: 20
maxWait: 60000
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000
validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
testWhileIdle: true
testOnBorrow: false
testOnReturn: false
poolPreparedStatements: true
#配置监控统计拦截的filters,stat:监控统计、log4j:日志记录、wall:防御sql注入
#如果允许时报错 java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.log4j.Priority
#则导入 log4j 依赖即可,Maven 地址:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/log4j
filters: stat,wall,log4j
maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20
useGlobalDataSourceStat: true
connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500
5.controller
package com.Hao.controller;
/**
* @Project_Name springboot-data
* @Author LH
* @Date 2021/9/8 11:11
* @TODO:绑定yml
* @Thinking:
*/
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 现在需要程序员自己为 DruidDataSource 绑定全局配置文件中的参数,再添加到容器中,而不再使用 Spring Boot 的自动生成了;
* 我们需要 自己添加 DruidDataSource 组件到容器中,并绑定属性;
*/
@Configuration//对应原来的xml配置文件
public class DruidConfig {
/*
将自定义的 Druid数据源添加到容器中,不再让 Spring Boot 自动创建
绑定全局配置文件中的 druid 数据源属性到 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource从而让它们生效
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource"):作用就是将 全局配置文件中
前缀为 spring.datasource的属性值注入到 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource 的同名参数中
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
@Bean
public DataSource druidDataSource() {
return new DruidDataSource();
}
//后台监控功能配置Druid数据源监控,直接放在这里即可
//配置 Druid 监控管理后台的Servlet;
//内置 Servlet 容器时没有web.xml文件,所以使用 Spring Boot 的注册 Servlet 方式
// @Bean
// public ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet() {
// ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new StatViewServlet(), "/druid/*");
//
// // 这些参数可以在 com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet
// // 的父类 com.alibaba.druid.support.http.ResourceServlet 中找到
// Map<String, String> initParams = new HashMap<>();
// initParams.put("loginUsername", "admin"); //后台管理界面的登录账号
// initParams.put("loginPassword", "123456"); //后台管理界面的登录密码
//
// //后台允许谁可以访问
// //initParams.put("allow", "localhost"):表示只有本机可以访问
// //initParams.put("allow", ""):为空或者为null时,表示允许所有访问
// initParams.put("allow", "");
// //deny:Druid 后台拒绝谁访问
// //initParams.put("kuangshen", "192.168.1.20");表示禁止此ip访问
//
// //设置初始化参数
// bean.setInitParameters(initParams);
// return bean;
}
}
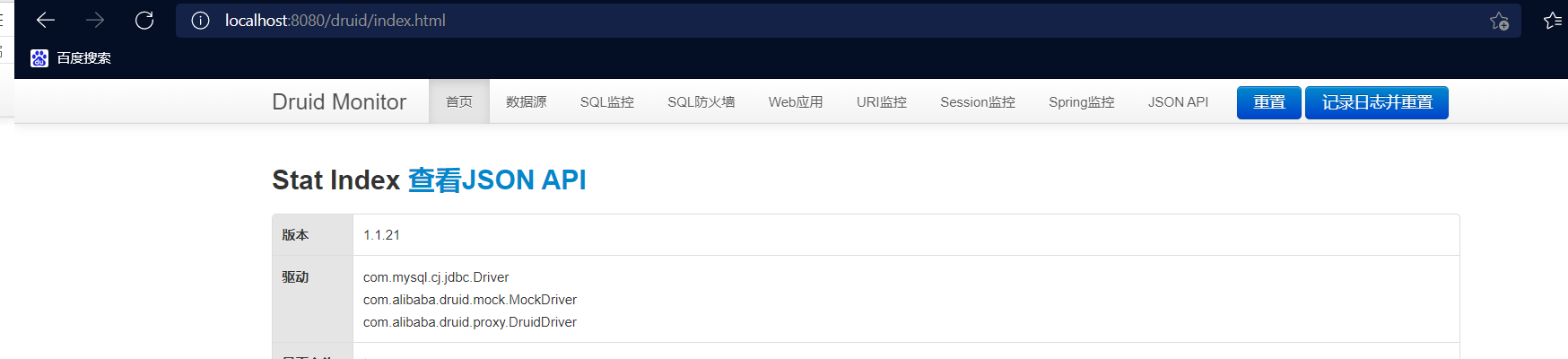
Druid数据源监控
Druid 数据源具有监控的功能,并提供了一个 web 界面方便用户查看,类似安装 路由器 时,人家也提供了一个默认的 web 页面。
所以第一步需要设置 Druid 的后台管理页面,比如 登录账号、密码 等;配置后台管理;
//配置 Druid 监控管理后台的Servlet;
//内置 Servlet 容器时没有web.xml文件,所以使用 Spring Boot 的注册 Servlet 方式
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet() {
ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new StatViewServlet(), "/druid/*");
// 这些参数可以在 com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet
// 的父类 com.alibaba.druid.support.http.ResourceServlet 中找到
Map<String, String> initParams = new HashMap<>();
initParams.put("loginUsername", "admin"); //后台管理界面的登录账号
initParams.put("loginPassword", "123456"); //后台管理界面的登录密码
//后台允许谁可以访问
//initParams.put("allow", "localhost"):表示只有本机可以访问
//initParams.put("allow", ""):为空或者为null时,表示允许所有访问
initParams.put("allow", "");
//deny:Druid 后台拒绝谁访问
//initParams.put("kuangshen", "192.168.1.20");表示禁止此ip访问
//设置初始化参数
bean.setInitParameters(initParams);
return bean;
}
测试
上述Druid数据源监控功能实现测试
1.输入http://localhost:8080/druid自动跳转到druid monitor页面
2.输入自己配置的账户admin,和123456,注意,这里的账户密码是自己任意设定的即可
配置 Druid web 监控 filter 过滤器
//配置 Druid 监控 之 web 监控的 filter
//WebStatFilter:用于配置Web和Druid数据源之间的管理关联监控统计
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean webStatFilter() {
FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
bean.setFilter(new WebStatFilter());
//exclusions:设置哪些请求进行过滤排除掉,从而不进行统计
Map<String, String> initParams = new HashMap<>();
initParams.put("exclusions", "*.js,*.css,/druid/*,/jdbc/*");
bean.setInitParameters(initParams);
//"/*" 表示过滤所有请求
bean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/*"));
return bean;
}
平时在工作中,按需求进行配置即可,主要用作监控!=
整合mybatis
官方文档:http://mybatis.org/spring-boot-starter/mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigure/
Maven仓库地址:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis.spring.boot/mybatis-spring-boot-starter/2.1.1
整合测试
新建springboot项目(不是maven)
1、导入 MyBatis 所需要的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1</version>
</dependency>
2、配置数据库连接信息(不变)
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
#?serverTimezone=UTC解决时区的报错
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
#Spring Boot 默认是不注入这些属性值的,需要自己绑定
#druid 数据源专有配置
initialSize: 5
minIdle: 5
maxActive: 20
maxWait: 60000
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000
validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
testWhileIdle: true
testOnBorrow: false
testOnReturn: false
poolPreparedStatements: true
#配置监控统计拦截的filters,stat:监控统计、log4j:日志记录、wall:防御sql注入
#如果允许时报错 java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.log4j.Priority
#则导入 log4j 依赖即可,Maven 地址:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/log4j
filters: stat,wall,log4j
maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20
useGlobalDataSourceStat: true
connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500
3、测试数据库是否连接成功!
4、创建实体类,导入 Lombok!
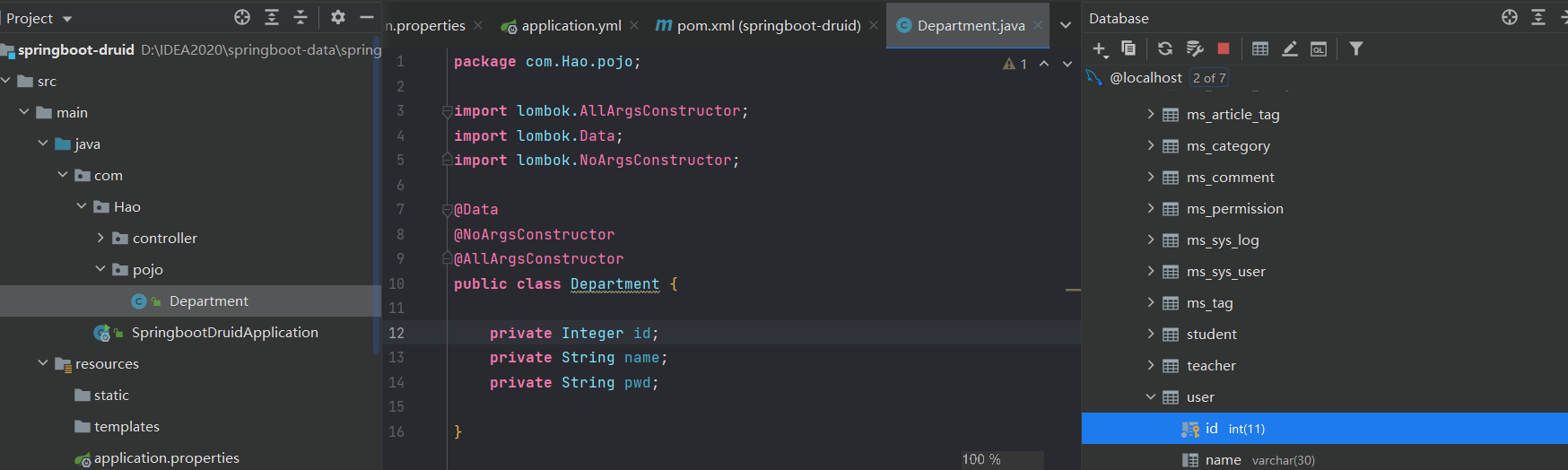
在pojo包下创建实体类User.java对应数据库表中的字段
package com.Hao.pojo;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String pwd;
}
5、创建mapper目录以及对应的 Mapper 接口
UserMapper.java
package com.Hao.mapper;
import com.Hao.pojo.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.List;
//@Mapper : 表示本类是一个 MyBatis 的 Mapper
@Mapper
@Repository
public interface UserMapper {
// 获取所有用户信息
List<User> getUsers();
// 通过id获得用户信息
User getUser(Integer id);
Integer addUser(User user);
Integer updateUser(User user);
Integer deleteUser(int id);
}
6.在application.properties中配置mybatis重点
注意想配置什么,点开MybatisProperties的源码,都有
#整合mybatis的配置
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.Hao.pojo
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml
7.对应的Mapper映射文件,注意,现在由于上述配置xml位置,直接写在resources目录下新建mapper目录下的
UserMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.Hao.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="getUsers" resultType="com.Hao.pojo.User">
select * from mybatis.user;
</select>
<select id="getUser" resultType="com.Hao.pojo.User" parameterType="int">
select * from mybatis.user where id = #{id};
</select>
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="com.Hao.pojo.User">
insert into user (id,name,pwd) value (#{id},#{name},#{pwd})
</insert>
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="com.Hao.pojo.User">
update user set name =#{name},pwd=#{pwd} where id = #{id}
</update>
<delete id="deleteUser" parameterType="int">
delete from user where id = #{id}
</delete>
</mapper>
package com.Hao.controller;
import com.Hao.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.Hao.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Project_Name springboot-data
* @Author LH
* @Date 2021/9/8 12:51
* @TODO:整合mybatis
* @Thinking:
*/
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@GetMapping("/getUsers")//名称尽量与sql查询使用的方法名一致
public List<User> getUsers(){
//只测试一个
List<User> userList = userMapper.getUsers();
for (User user : userList){
System.out.println(user);
}
return userList;
}
//这里只测试一个,接下来的几个方法都可以在这里测试
}
SpringSecurity(安全)
官网地址
https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/5.2.12.RELEASE/reference/html/overall-architecture.html#what-is-authentication-in-spring-security
博文地址:
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/FLdC-24_pP8l5D-i7kEwcg
安全简介
在 Web 开发中,安全一直是非常重要的一个方面。
安全虽然属于应用的非功能性需求,但是应该在应用开发的初期就考虑进来。
如果在应用开发的后期才考虑安全的问题,就可能陷入一个两难的境地:
一方面,应用存在严重的安全漏洞,无法满足用户的要求,并可能造成用户的隐私数据被攻击者窃取;
另一方面,应用的基本架构已经确定,要修复安全漏洞,可能需要对系统的架构做出比较重大的调整,因而需要更多的开发时间,影响应用的发布进程。因此,从应用开发的第一天就应该把安全相关的因素考虑进来,并在整个应用的开发过程中。
市面上存在比较有名的:Shiro,Spring Security !
这里需要阐述一下的是,每一个框架的出现都是为了解决某一问题而产生了,那么Spring Security框架的出现是为了解决什么问题呢?
首先我们看下它的官网介绍:Spring Security官网地址
Spring Security is a powerful and highly customizable authentication and access-control framework. It is the de-facto standard for securing Spring-based applications.
Spring Security is a framework that focuses on providing both authentication and authorization to Java applications. Like all Spring projects, the real power of Spring Security is found in how easily it can be extended to meet custom requirements
Spring Security是一个功能强大且高度可定制的身份验证和访问控制框架。它实际上是保护基于spring的应用程序的标准。
Spring Security是一个框架,侧重于为Java应用程序提供身份验证和授权。与所有Spring项目一样,Spring安全性的真正强大之处在于它可以轻松地扩展以满足定制需求
从官网的介绍中可以知道这是一个权限框架。想我们之前做项目是没有使用框架是怎么控制权限的?对于权限 一般会细分为功能权限,访问权限,和菜单权限。代码会写的非常的繁琐,冗余。
怎么解决之前写权限代码繁琐,冗余的问题,一些主流框架就应运而生而Spring Scecurity就是其中的一种。
Spring 是一个非常流行和成功的 Java 应用开发框架**。**
Spring Security 基于 Spring 框架,提供了一套 Web 应用安全性的完整解决方案。一般来说,Web 应用的安全性包括用户认证(Authentication)和用户授权(Authorization)两个部分。
| 用户认证 | 指的是验证某个用户是否为系统中的合法主体,也就是说用户能否访问该系统。用户认证一般要求用户提供用户名和密码。系统通过校验用户名和密码来完成认证过程。 |
|---|---|
| 用户授权 | 指的是验证某个用户是否有权限执行某个操作。在一个系统中,不同用户所具有的权限是不同的。比如对一个文件来说,有的用户只能进行读取,而有的用户可以进行修改。一般来说,系统会为不同的用户分配不同的角色,而每个角色则对应一系列的权限。 |
对于上面提到的两种应用情景,Spring Security 框架都有很好的支持。
在用户认证方面,Spring Security 框架支持主流的认证方式,包括 HTTP 基本认证、HTTP 表单验证、HTTP 摘要认证、OpenID 和 LDAP 等。
在用户授权方面,Spring Security 提供了基于角色的访问控制和访问控制列表(Access Control List,ACL),可以对应用中的领域对象进行细粒度的控制。
环境搭建
创建Wed项目
1.在项目中创建springboot项目,再选择web即可
2.导包
<!--security-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--security-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--web-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--thymeleaf模板-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-spring5</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf.extras</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-java8time</artifactId>
</dependency>
3.导入素材文件
导入静态资源
welcome.html
|views
|level1
1.html
2.html
3.html
|level2
1.html
2.html
3.html
|level3
1.html
2.html
3.html
Login.html
4.在controller包下创建RouterController测试页面
package com.example.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
/**
* @Project_Name springboot
* @Author LH
* @Date 2021/9/23 12:09
* @TODO:测试跳转页面
* @Thinking:
*/
public class RouterController {
@RequestMapping({"/","/index"})
public String index(){
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping({"/toLogin"})
public String toLogin(){
return "views/login";
}
@RequestMapping("/level1/{id}")
public String level1(@PathVariable("id") int id){
return "views/level1/"+id;
}
@RequestMapping("/level2/{id}")
public String level2(@PathVariable("id") int id){
return "views/level2/"+id;
}
@RequestMapping("/level3/{id}")
public String level3(@PathVariable("id") int id){
return "views/level3/"+id;
}
}
5.新建config包,在config包下建立SecurityConfig
package com.Hao.config;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
/**
* @Project_Name springboot
* @Author LH
* @Date 2021/9/23 16:04
* @TODO:Security配置
* @Thinking:
*/
@EnableWebSecurity // 开启WebSecurity模式
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//定制请求的授权规则
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//hasRole只有这个拥有vip1权限的才能进入到对应/level1/**目录下相关内容进行访问,hasAll就是所有对应目录都能访问
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/level1/**").hasRole("vip1")
.antMatchers("/level2/**").hasRole("vip2")
.antMatchers("/level3/**").hasRole("vip3");
//开启自动配置的登录功能:如果没有权限,就会跳转到登录页面!
// /login 请求来到登录页
// /login?error 重定向到这里表示登录失败
http.formLogin()
.usernameParameter("username")
.passwordParameter("password")
.loginPage("/toLogin")
.loginProcessingUrl("/login"); // 登陆表单提交请求
//开启自动配置的注销的功能
// /logout 注销请求
// .logoutSuccessUrl("/"); 注销成功来到首页
http.csrf().disable();//关闭csrf功能:跨站请求伪造,默认只能通过post方式提交logout请求
http.logout().logoutSuccessUrl("/");
//记住我
http.rememberMe().rememberMeParameter("remember");
}
//定义认证规则
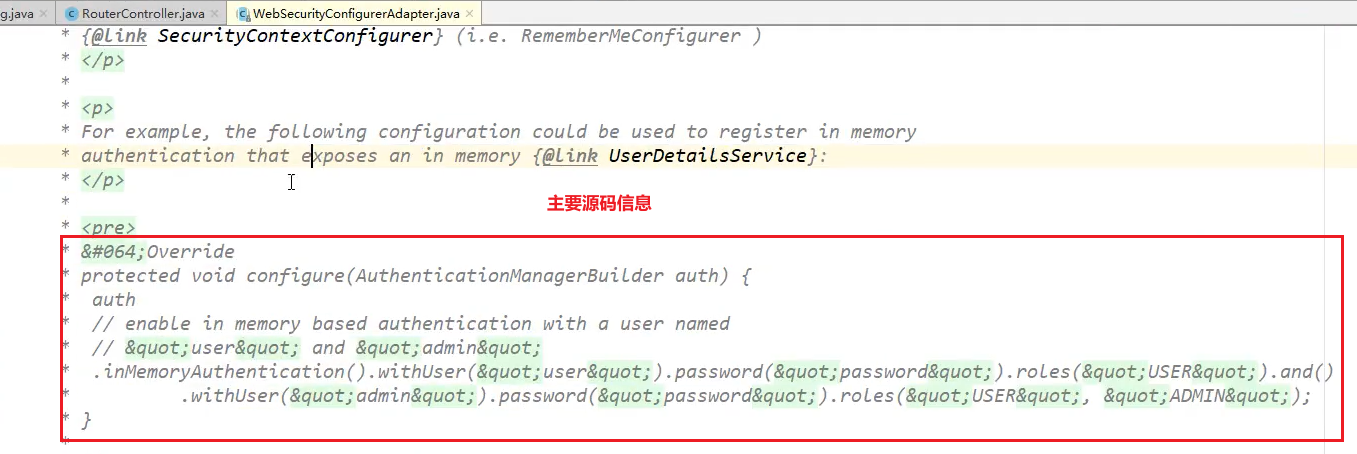
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
//在内存中定义,也可以在jdbc中去拿....
//Spring security 5.0中新增了多种加密方式,也改变了密码的格式。
//要想我们的项目还能够正常登陆,需要修改一下configure中的代码。我们要将前端传过来的密码进行某种方式加密
//spring security 官方推荐的是使用bcrypt加密方式。
//new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode(加密的内容),使用此方法加密,在新版本的的Security定义认证规则是需要将密码加密
//否则会报无法解析的错误,在java中也可以使用md5加密
//参数介绍:虚拟用户名(lihao),密码roles("权限名"),注意:由于是链式编程,可以使用and()连接需要指定的所有虚拟用户
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder())
.withUser("lihao").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("vip2","vip3")
.and()
.withUser("root").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("vip1","vip2","vip3")
.and()
.withUser("guest").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("vip1","vip2");
}
}
可以查看一下WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter类的源码
注意:这里在前端需要实现页面功能(注册之后显示登录页面,登录之后显示用户名…)样式得将spirngboot版本降级到2.0.9左右才可!但现在版本太低了。
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.7</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
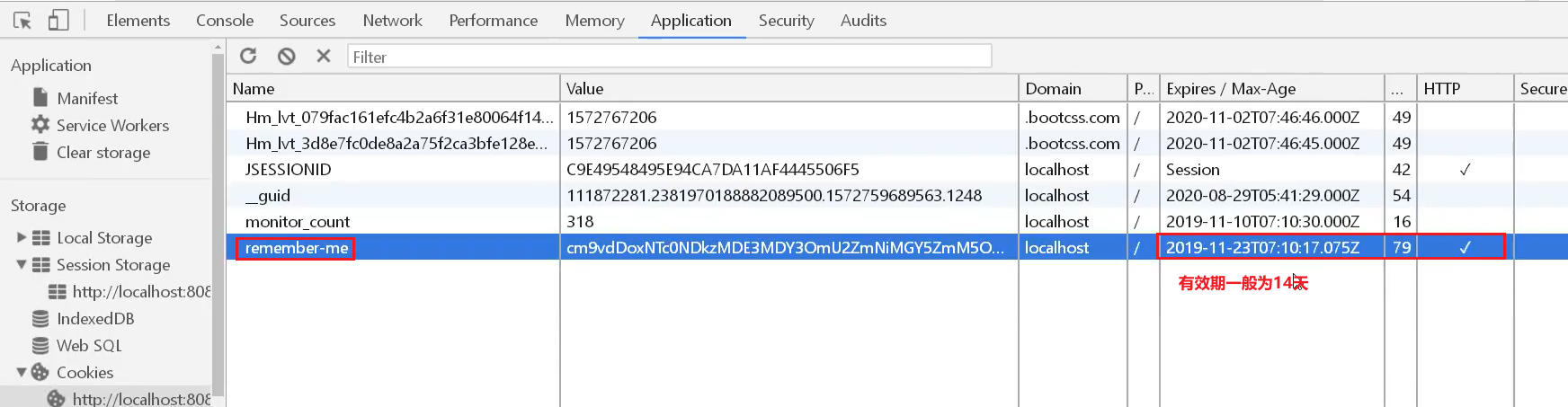
记住我cookie一般在浏览器的有效期为14天
认证和授权
目前,我们的测试环境,是谁都可以访问的,我们使用 Spring Security 增加上认证和授权的功能
1、引入 Spring Security 模块
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、编写 Spring Security 配置类
参考官网:https://spring.io/projects/spring-security
查看我们自己项目中的版本,找到对应的帮助文档:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/5.3.0.RELEASE/reference/html5 #servlet-applications 8.16.4
Shiro
什么是Shiro?
- Apache Shiro 是一个Java 的安全(权限)框架。
- Shiro 可以非常容易的开发出足够好的应用,其不仅可以用在JavaSE环境,也可以用在JavaEE环 境。
- Shiro可以完成,认证,授权,加密,会话管理,Web集成,缓存等。
- 下载地址:http://shiro.apache.org/
Apache Shiro™是一个功能强大且易于使用的 Java 安全框架,可执行身份验证、授权、加密和会话管理。借助 Shiro 易于理解的 API,您可以快速轻松地保护任何应用程序——从最小的移动应用程序到最大的 Web 和企业应用程序。
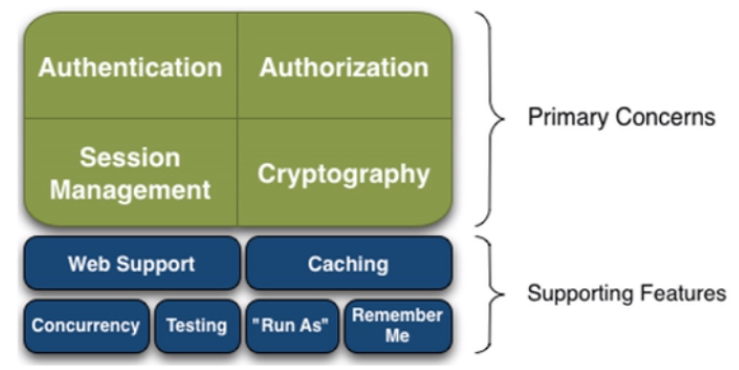
有哪些功能?
-
Authentication:身份认证、登录,验证用户是不是拥有相应的身份;
-
Authorization:授权,即权限验证,验证某个已认证的用户是否拥有某个权限,即判断用户能否 进行什么操作,如:验证某个用户是否拥有某个角色,或者细粒度的验证某个用户对某个资源是否 具有某个权限!
-
Session Manager:会话管理,即用户登录后就是第一次会话,在没有退出之前,它的所有信息都 在会话中;会话可以是普通的JavaSE环境,也可以是Web环境;
-
Cryptography:加密,保护数据的安全性,如密码加密存储到数据库中,而不是明文存储;
-
Web Support:Web支持,可以非常容易的集成到Web环境;
-
Caching:缓存,比如用户登录后,其用户信息,拥有的角色、权限不必每次去查,这样可以提高 效率
-
Concurrency:Shiro支持多线程应用的并发验证,即,如在一个线程中开启另一个线程,能把权限自动的传播过去
-
Testing:提供测试支持;
-
Run As:允许一个用户假装为另一个用户(如果他们允许)的身份进行访问;
-
Remember Me:记住我,这个是非常常见的功能,即一次登录后,下次再来的话不用登录了
Shiro架构(外部)
从外部来看Shiro,即从应用程序角度来观察如何使用shiro完成工作:
核心概念
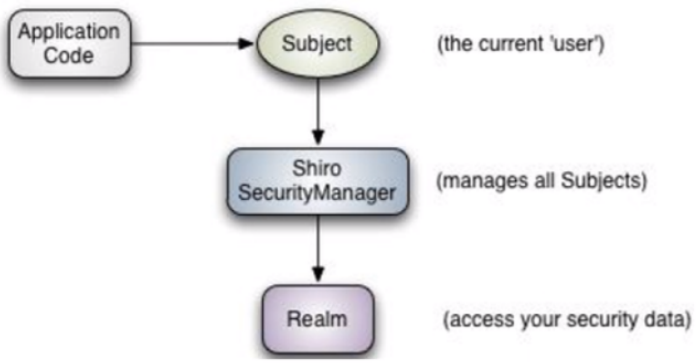
Subject、SecurityManager 和 Realms
-
subject: 应用代码直接交互的对象是Subject,也就是说Shiro的对外API核心就是Subject, Subject代表了当前的用户,这个用户不一定是一个具体的人,与当前应用交互的任何东西都是 Subject,如网络爬虫,机器人等,与Subject的所有交互都会委托给SecurityManager;Subject其实是一个门面,SecurityManageer 才是实际的执行者
-
SecurityManager:安全管理器,即所有与安全有关的操作都会与SercurityManager交互,并且它 管理着所有的Subject,可以看出它是Shiro的核心,它负责与Shiro的其他组件进行交互,它相当于 SpringMVC的DispatcherServlet的角色
-
Realm:Shiro从Realm获取安全数据(如用户,角色,权限),就是说SecurityManager 要验证 用户身份,那么它需要从Realm 获取相应的用户进行比较,来确定用户的身份是否合法;也需要从 Realm得到用户相应的角色、权限,进行验证用户的操作是否能够进行,可以把Realm看成 DataSource;
Shiro架构(内部)
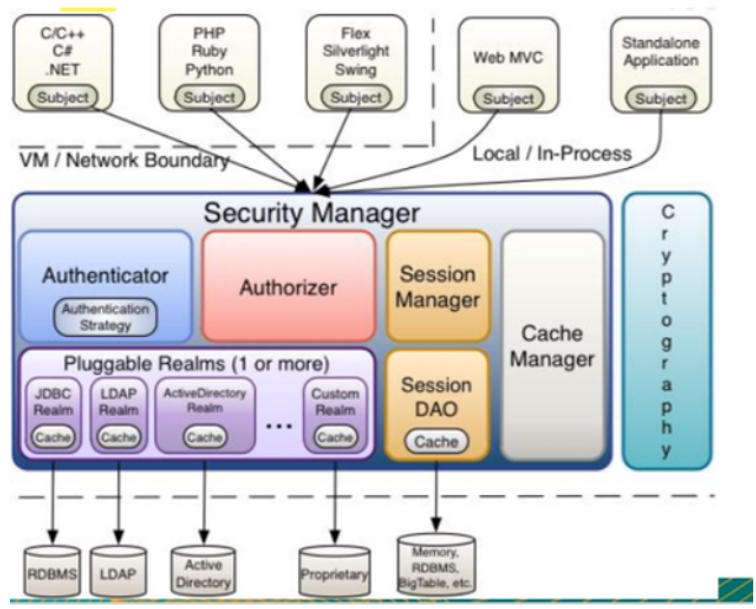
-
Subject:任何可以与应用交互的 ‘用户’;
-
Security Manager:相当于SpringMVC中的DispatcherServlet;是Shiro的心脏,所有具体的交互 都通过Security Manager进行控制,它管理者所有的Subject,且负责进行认证,授权,会话,及 缓存的管理。
-
Authenticator:负责Subject认证,是一个扩展点,可以自定义实现;可以使用认证策略 (Authentication Strategy),即什么情况下算用户认证通过了;
-
Authorizer:授权器,即访问控制器,用来决定主体是否有权限进行相应的操作;即控制着用户能 访问应用中的那些功能;
-
Realm:可以有一个或者多个的realm,可以认为是安全实体数据源,即用于获取安全实体的,可 以用JDBC实现,也可以是内存实现等等,由用户提供;所以一般在应用中都需要实现自己的realm
-
SessionManager:管理Session生命周期的组件,而Shiro并不仅仅可以用在Web环境,也可以用 在普通的JavaSE环境中
-
CacheManager:缓存控制器,来管理如用户,角色,权限等缓存的;因为这些数据基本上很少改 变,放到缓存中后可以提高访问的性能;
-
Cryptography:密码模块,Shiro 提高了一些常见的加密组件用于密码加密,解密等
HelloWorld
快速实践
查看官网文档:http://shiro.apache.org/tutorial.html
官方的quickstart:https://github.com/apache/shiro/tree/master/samples/quickstart/
- 创建一个maven父工程,用于学习Shiro,删掉不必要的东西
- 创建一个普通的Maven子工程:shiro-01-helloworld
- 根据官方文档,导入Shiro的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-core</artifactId>
<version>1.4.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Shiro uses SLF4J for logging. We'll use the 'simple' binding
in this example app. See http://www.slf4j.org for more info. -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-simple</artifactId>
<version>1.7.21</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>jcl-over-slf4j</artifactId>
<version>1.7.21</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
- 编写Shiro配置 ———log4j.properties
log4j.rootLogger=INFO, stdout
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%d %p [%c] - %m %n
# General Apache libraries
log4j.logger.org.apache=WARN
# Spring
log4j.logger.org.springframework=WARN
# Default Shiro logging
log4j.logger.org.apache.shiro=INFO
# Disable verbose logging
log4j.logger.org.apache.shiro.util.ThreadContext=WARN
log4j.logger.org.apache.shiro.cache.ehcache.EhCache=WARN
Shiro 的
SecurityManager实现和所有支持组件都与 JavaBeans 兼容。这允许使用几乎任何配置格式配置 Shiro,例如 XML(Spring、JBoss、Guice 等)、YAML、JSON、Groovy Builder 标记等。INI 只是 Shiro 的“公分母”格式,允许在任何环境中进行配置,以防其他选项不可用。
shiro.ini
使用一个 INI 文件来SecurityManager为这个简单的应用程序配置 Shiro 。首先,**src/main/resources**在与 相同的目录中创建一个目录pom.xml。然后shiro.ini在该新目录中创建一个包含以下内容的文件:
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
-------
# Users and their assigned roles
#
# Each line conforms to the format defined in the
1
2
3
4
5. 编写我们的QuickStrat
# org.apache.shiro.realm.text.TextConfigurationRealm#setUserDefinitions
JavaDoc
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
-------
[users]
# user 'root' with password 'secret' and the 'admin' role
root = secret, admin
# user 'guest' with the password 'guest' and the 'guest' role
guest = guest, guest
# user 'presidentskroob' with password '12345' ("That's the same
combination on
# my luggage!!!" ;)), and role 'president'
presidentskroob = 12345, president
# user 'darkhelmet' with password 'ludicrousspeed' and roles 'darklord'
and 'schwartz'
darkhelmet = ludicrousspeed, darklord, schwartz
# user 'lonestarr' with password 'vespa' and roles 'goodguy' and
'schwartz'
lonestarr = vespa, goodguy, schwartz
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
-------
# Roles with assigned permissions
#
# Each line conforms to the format defined in the
# org.apache.shiro.realm.text.TextConfigurationRealm#setRoleDefinitions
JavaDoc
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
-------
[roles]
# 'admin' role has all permissions, indicated by the wildcard '*'
admin = *
# The 'schwartz' role can do anything (*) with any lightsaber:
schwartz = lightsaber:*
# The 'goodguy' role is allowed to 'drive' (action) the winnebago (type)
with
# license plate 'eagle5' (instance specific id)
goodguy = winnebago:drive:eagle5
- 编写我们的Tutorial
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.*;
import org.apache.shiro.config.IniSecurityManagerFactory;
import org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager;
import org.apache.shiro.session.Session;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
import org.apache.shiro.util.Factory;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class Tutorial {
private static final transient Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Tutorial.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
log.info("My First Apache Shiro Application");
/**使用 Shiro 的IniSecurityManagerFactory实现来摄取shiro.ini位于类路径根目录的文件。这个实现反映了 Shiro 对工厂方法设计模式的支持。
classpath:前缀是一个资源指示符,告诉shiro哪里加载从ini文件(其他前缀,如url:和file:以及支持)。*/
Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini");
//factory.getInstance()方法被调用,它解析 INI 文件并返回一个SecurityManager反映配置的实例
SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
/**设置SecurityManager为静态(内存)单例,可跨 JVM 访问。但是请注意,如果您将在单个 JVM 中拥有多个启用 Shiro 的应用程序,则这是不可取的。对于这个简单的例子,没问题,但是更复杂的应用程序环境通常会将 放在SecurityManager特定于应用程序的内存中(例如在 Web 应用程序ServletContext或 Spring、Guice 或 JBoss DI 容器实例中)。*/
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
//到此SecurityManager 已经设置并准备就绪 现在可以——执行安全操作了
/**在几乎所有环境中,您都可以通过以下调用获取当前正在执行的用户
可以将其Subject视为 Shiro 的“用户”概念
getSubject()独立应用程序中的调用可能会返回Subject特定于应用程序位置的用户数据,而在服务器环境(例如 Web 应用程序)中,它会Subject根据与当前线程或传入请求关联的用户数据获取。*/
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
/**现在有了一个Subject,如果您想在用户与应用程序的当前会话期间向其提供内容,您可以获取他们的会话
Session是一个特定于 Shiro 的实例,它提供了您习惯于使用常规 HttpSessions 的大部分内容,但还有一些额外的好处和一个很大的区别:它不需要 HTTP 环境!*/
Session session = currentUser.getSession();
session.setAttribute("someKey", "aValue");
String value = (String) session.getAttribute("someKey");
/**只能对已知用户进行这些检查。我们Subject上面的实例代表当前用户,但当前用户是谁?嗯,他们是匿名的——也就是说,直到他们至少登录一次*/
if (value.equals("aValue")) {
log.info("Retrieved the correct value! [" + value + "]");
}
// let's login the current user so we can check against roles and permissions:
if (!currentUser.isAuthenticated()) {
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("lonestarr", "vespa");
token.setRememberMe(true);
/**如果他们的登录尝试失败了?您可以捕获各种特定的异常,这些异常会准确地告诉您发生了什么,并允许您进行相应的处理和反应,可以检查许多不同类型的异常,或者为 Shiro 可能无法解释的自定义条件抛出您自己的异常。
*/
try {
currentUser.login(token);
} catch (UnknownAccountException uae) {
log.info("There is no user with username of " + token.getPrincipal());
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) {
log.info("Password for account " + token.getPrincipal() + " was incorrect!");
} catch (LockedAccountException lae) {
log.info("The account for username " + token.getPrincipal() + " is locked. " +
"Please contact your administrator to unlock it.");
}
// ... catch more exceptions here (maybe custom ones specific to your application?
catch (AuthenticationException ae) {
//unexpected condition? error?
}
}
//告诉他们是谁:
//print their identifying principal (in this case, a username):
log.info("User [" + currentUser.getPrincipal() + "] logged in successfully.");
//test a role:测试它们是否具有特定的作用,也是看它是什么角色,具有哪些权限
if (currentUser.hasRole("schwartz")) {
log.info("May the Schwartz be with you!");
} else {
log.info("Hello, mere mortal.");
}
//test a typed permission (not instance-level):查看他们是否有权对某种类型的实体采取行动:
if (currentUser.isPermitted("lightsaber:wield")) {
log.info("You may use a lightsaber ring. Use it wisely.");
} else {
log.info("Sorry, lightsaber rings are for schwartz masters only.");
}
//a (very powerful) Instance Level permission:
//我们可以执行极其强大的实例级权限检查——查看用户是否有能力访问某个类型的特定实例
if (currentUser.isPermitted("winnebago:drive:eagle5")) {
log.info("You are permitted to 'drive' the winnebago with license plate (id) 'eagle5'. " +
"Here are the keys - have fun!");
} else {
log.info("Sorry, you aren't allowed to drive the 'eagle5' winnebago!");
}
//all done - log out!
//当用户使用完应用程序后,他们可以注销
currentUser.logout();
System.exit(0);
}
}
附:抛出异常信息类型文档:参阅AuthenticationException JavaDoc
-
测试运行一下
-
报错,则导入一下 commons-logging 的依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/commons-logging/commons-logging -
->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
- 发现,执行完毕什么都没有,可能是maven依赖中的作用域问题,我们需要将scope作用域删掉, 默认是在test,然后重启,那么我们的Tutorial就结束了,默认的日志消息!
[main] INFO org.apache.shiro.session.mgt.AbstractValidatingSessionManager
- Enabling session validation scheduler...
[main] INFO Tutorial - Retrieved the correct value! [aValue]
[main] INFO Tutorial - User [lonestarr] logged in successfully.
[main] INFO Tutorial - May the Schwartz be with you!
[main] INFO Tutorial - You may use a lightsaber ring. Use it wisely.
[main] INFO Tutorial - You are permitted to 'drive' the winnebago with
license plate (id) 'eagle5'. Here are the keys - have fun!
代码块说明
-
导入了一堆包!
-
类的描述
/**
* Simple Quickstart application showing how to use Shiro's API.
* 简单的快速启动应用程序,演示如何使用Shiro的API。
*/
- 通过工厂模式创建SecurityManager的实例对象
// The easiest way to create a Shiro SecurityManager with configured
// realms, users, roles and permissions is to use the simple INI config.
// We'll do that by using a factory that can ingest a .ini file and
// return a SecurityManager instance:
// 使用类路径根目录下的shiro.ini文件
// Use the shiro.ini file at the root of the classpath
// (file: and url: prefixes load from files and urls respectively):
Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new
IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini");
SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
// for this simple example quickstart, make the SecurityManager
// accessible as a JVM singleton. Most applications wouldn't do this
// and instead rely on their container configuration or web.xml for
// webapps. That is outside the scope of this simple quickstart, so
// we'll just do the bare minimum so you can continue to get a feel
// for things.
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
// 现在已经建立了一个简单的Shiro环境,让我们看看您可以做什么:
// Now that a simple Shiro environment is set up, let's see what you can
//do:
- 获取当前的Subject
// get the currently executing user: 获取当前正在执行的用户
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
- session的操作
// 用会话做一些事情(不需要web或EJB容器!!!)
// Do some stuff with a Session (no need for a web or EJB container!!!)
Session session = currentUser.getSession(); //获得session
session.setAttribute("someKey", "aValue"); //设置Session的值!
String value = (String) session.getAttribute("someKey"); //从session中获取值
if (value.equals("aValue")) { //判断session中是否存在这个值!
log.info("==Retrieved the correct value! [" + value + "]");
}
- 用户认证功能
// 测试当前的用户是否已经被认证,即是否已经登录!
// let's login the current user so we can check against roles andpermissions:
if (!currentUser.isAuthenticated()) { // isAuthenticated();是否认证
//将用户名和密码封装为 UsernamePasswordToken ;
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("lonestarr","vespa");
token.setRememberMe(true); //记住我功能
try {
currentUser.login(token); //执行登录,可以登录成功的!
} catch (UnknownAccountException uae) { //如果没有指定的用户,则
UnknownAccountException异常
log.info("There is no user with username of " +
token.getPrincipal());
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) { //密码不对的异常!
log.info("Password for account " + token.getPrincipal() + " wasincorrect!");
} catch (LockedAccountException lae) { //用户被锁定的异常
log.info("The account for username " + token.getPrincipal() + "is locked. " +"Please contact your administrator to unlock it.");
}
// ... catch more exceptions here (maybe custom ones specific toyour application?
catch (AuthenticationException ae) { //认证异常,上面的异常都是它的子类
//unexpected condition? error?
}
}
//说出他们是谁:
//say who they are:
//打印他们的标识主体(在本例中为用户名):
//print their identifying principal (in this case, a username):
log.info("User [" + currentUser.getPrincipal() + "] logged insuccessfully.");
- 角色检查
//test a role:
//是否存在某一个角色
if (currentUser.hasRole("schwartz")) {
log.info("May the Schwartz be with you!");
} else {
log.info("Hello, mere mortal.");
}
- 权限检查,粗粒度
//测试用户是否具有某一个权限,行为
//test a typed permission (not instance-level)
if (currentUser.isPermitted("lightsaber:wield")) {
log.info("You may use a lightsaber ring. Use it wisely.");
} else {
log.info("Sorry, lightsaber rings are for schwartz masters only.");
}
- 权限检查,细粒度
//测试用户是否具有某一个权限,行为,比上面更加的具体!
//a (very powerful) Instance Level permission:
if (currentUser.isPermitted("winnebago:drive:eagle5")) {
log.info("You are permitted to 'drive' the winnebago with licenseplate (id) 'eagle5'. " +"Here are the keys - have fun!");
} else {
log.info("Sorry, you aren't allowed to drive the 'eagle5'winnebago!");
}
- 注销操作
//执行注销操作!
//all done - log out!
currentUser.logout();
- 退出系统
System.exit(0);
Shiro整合
回顾核心API:
- Subject:用户主体
- SecurityManager:安全管理器
- Realm:Shiro 连接数据
步骤
1.创建springboot项目勾选web模块
2.删除不必要的目录之后导入相关的依赖
<!--
Subject 用户
SecurityManager 管理所有用户
Realm 连接数据
-->
<!--shiro整合spring的包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.4.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--thymeleaf模板-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-spring5</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf.extras</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-java8time</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--web-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
注意:在html文件中使用thymeleaf还需要导入命名空间的约束,方便提示
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
3.编写一个页面 index.html templates包下
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>首页</h1>
<p th:text="${msg}"></p>
</body>
</html>
4.编写controller进行访问测试
4.编写Shiro 配置类 config包
package com.Hao.config;
import org.apache.shiro.spring.web.ShiroFilterFactoryBean;
import org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @Project_Name springboot
* @Author LH
* @Date 2021/9/24 21:31
* @TODO:核心配置类
* @Thinking:
*/
@Configuration
public class ShiroConfig {
//ShiroFilterFactoryBean:第3步
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(@Qualifier("securityManager") DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager){
ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
//设置安全管理器
bean.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
return bean;
}
//DafaultWebSecurityManager:第2步
@Bean(name = "securityManager")//在这里也可以给这个类设置这个别名
public DefaultWebSecurityManager getDefaultWebSecurityManager(@Qualifier("userRealm") UserRealm userRealm){
DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
return securityManager;
}
//创建 realm 对象 ,需要自定义类 : 第1步
@Bean
public UserRealm userRealm(){
return new UserRealm();
}
}
4.倒着来,先创建一个 realm 对象
5.需要自定义一个 realm 的类,用来编写一些查询的方法,或者认证与授权的逻辑
Swagger
集成Redis
1.新建springboot项目
勾选包含redis的工具
1.导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.配置application.properties
# SpringBoot 所有的配置类,都有一个自动配置类
# 自动配置类都会绑定一个 properties 配置文件
#host源码默认就是localhost,如果是远程就需要配置
spring.redis.host=localhost
spring.redis.port=6379
3.测试