1.什么是Semaphore
Semaphore也是Java中的同步器,与CountDownLatch和CyclicBarrier不同的是,他的内部计数器是递增的,而CountDownLatch和CyclicBarrier内部是递减的。在一开始我们不需要知道有多少个需要同步的线程,只需要在需要同步的地方调用acquire方法指定需要同步的线程个数。
2.Semaphore的基本使用
public class SemaphoreTest {
// 创建Semaphore实例
private static Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(0);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
// 将线程A添加到线程池
executorService.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "over");
// 该方法会将计数器加1
semaphore.release();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
// 将线程B添加到线程池
executorService.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "over");
// 该方法会将计数器加1
semaphore.release();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
// 调用该方法主线程会阻塞在这里直到计数器为2
semaphore.acquire(2);
System.out.println("all child thread over!");
// 关闭线程池
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
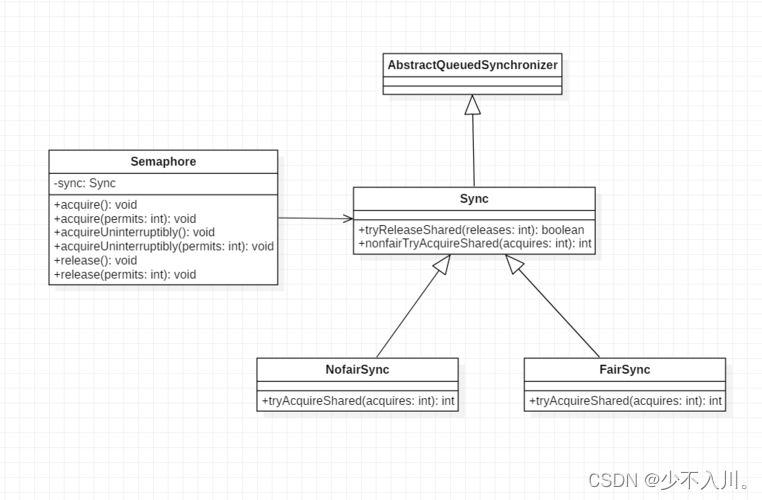
3.Semaphore类图
通过类图我们可以得知,Semaphore还是基于AQS实现的,并且Sync有公平策略和非公平策略。
4.实现原理探究
构造方法
public Semaphore(int permits) {
// 默认使用非公平锁
sync = new NonfairSync(permits);
}
public Semaphore(int permits, boolean fair) {
// 传入boolean值可以手动选择公平锁还是非公平锁实现
sync = fair ? new FairSync(permits) : new NonfairSync(permits);
}
Sync(int permits) {
setState(permits);
}
通过构造方法我们可以知道,Semaphore默认使用非公平策略,在后面acquire()方法中我们可以大概明白Semaphore是如何实现公平性策略的。通过内部类Sync的构造方法我们可以明白,state也表示当前持有的信号量个数。
acquire()
调用acquire的目的是想获取一个信号量资源,如果state>0,那么会减一并返回,如果当前信号量等于0,那么当前线程就会被放入AQS的阻塞队列。
public void acquire() throws InterruptedException {
// 传递参数为1,表示获取一个信号量
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);
}
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
// 如果当前线程被中断,则直接抛出异常
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
// 调用Sync子类中的tryAcquireShared方法试图获取信号量资源,如果失败则被放入阻塞队列
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}
从类图我们可知,Sync有两种策略的实现,下面我们从两方面讨论tryAcquireShared()都干了什么。
首先讨论非公平策略NonfairSync类的tryAcquireShared方法
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquireShared(acquires);
}
final int nonfairTryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
for (;;) {
// 得到当前信号量的值
int available = getState();
// 计算操作信号量后的剩余值
int remaining = available - acquires;
// 在这个判断中,只有两种情况会返回
// 1.remaining<0,返回负数或0表示获取资源量失败
// 2.remaining>0且CAS对信号量做修改成功返回,此时remaining>0,返回正数意味着获取资源量成功
if (remaining < 0 ||
compareAndSetState(available, remaining))
return remaining;
}
}
再来讨论公平策略FairSync类的tryAcquireShared方法
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
for (;;) {
// hasQueuedPredecessors方法的逻辑是如果当前线程前面有一个排队的线程,则为 true;如果当前线程位于队列的头部或队列为空,则为 false。
if (hasQueuedPredecessors())
return -1;
// 至此我们就知道了公平策略是如何保证公平性的
// 接下来的操作与非公平策略差不多
int available = getState();
int remaining = available - acquires;
if (remaining < 0 ||
compareAndSetState(available, remaining))
return remaining;
}
}
Semaphore中还有两个与acquire()方法类似的方法:acquire(int permits)、acquireUninterruptibly()、acquireUninterruptibly(int permits)
带有参数permits的方法表示获取permits个信号量。以Uninterruptibly为后缀的方法表示对中断不做出响应。
release()
该方法的作用是将当前semaphore对象的信号值量增加1,具体逻辑我们来看下面的代码实现。
public void release() {
// arg=1
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
// AQS中的releaseShared方法
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
// 尝试释放资源
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
// 释放成功则调用park方法唤醒AQS队列中最先被挂起的线程
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
for (;;) {
// 获取当前信号量值
int current = getState();
// 信号量增加releases(当前是1)
int next = current + releases;
// 溢出处理
if (next < current)
throw new Error("Maximum permit count exceeded");
// 对state做cas更新操作,因为这段程序被前面的for包着,所以如果失败不会返回,而是一直重试
if (compareAndSetState(current, next))
return true;
}
}
同样类似acquire()与acquire(int permits),也有release(int releases)方法。