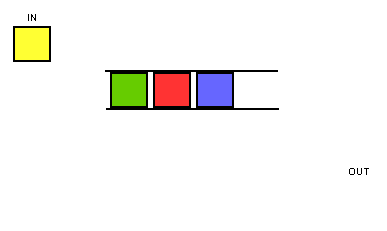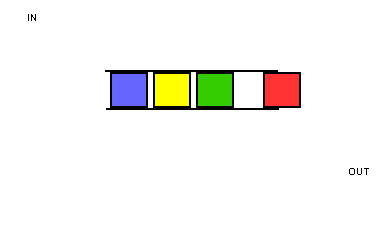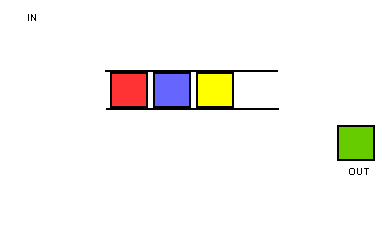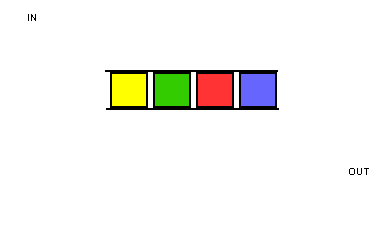1. 基本概念
队列是最常见的概念,日常生活经常需要排队,仔细观察队列会发现,队列是一种逻辑结构,是一种特殊的线性表。特殊在:
- 只能在固定的两端操作线性表
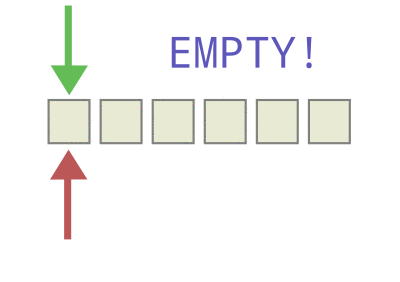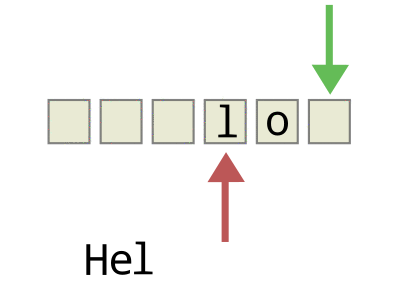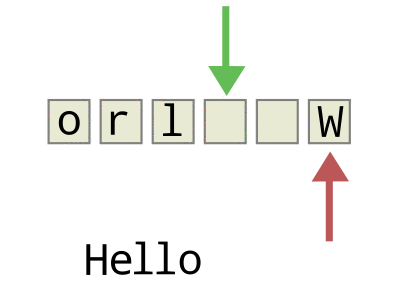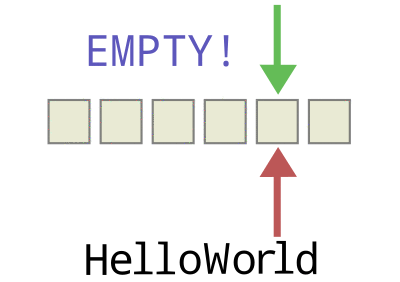
只要满足上述条件,那么这种特殊的线性表就会呈现一种“先进先出”的逻辑,这种逻辑就被称为队列。
由于约定了只能在线性表固定的两端进行操作,于是给队列这种特殊的线性表的插入删除,起个特殊的名称:
- 队头:可以删除节点的一端
- 队尾:可以插入节点的一端
- 入队:将节点插入到队尾之后,函数名通常为enQueue()
- 出队:将队头节点从队列中剔除,函数名通常为outQueue()
- 取队头:取得队头元素,但不出队,函数名通常为front()
由于这种固定两端操作的简单约定,队列获得了“先进先出”的基本特性,如下图所示:
2.顺序存储的队列:循环队列
与其他的逻辑结构类似,队列可以采用顺序存储形成循环队列,也可以采用链式存储形成链式队列。顺序存储的队列之所以被称为循环队列,是因为可以利用更新队头队尾的下标信息,来循环地利用整个数组,出队入队时也不必移动当中的数据。循环队列示意图如下所示:
从上述动图中可以观察到,需要牺牲至少数组中的一个存储位置,来区分循环队列中的满队和空队。满队和空队的约定如下:
- 当front与rear相等时,队列为空
- 当rear循环加一与front相等时,队列为满
与其他数据结构一样,管理循环队列除了需要一块连续的内存之外,还需要记录队列的总容量、当前队列的元素个数、当前队头、队尾元素位置,如果有多线程还需要配互斥锁和信号量等信息,为了便于管理,通常将这些信息统一于在一个管理结构体之中:
struct seqQueue
{
datatype *data; // 循环队列入口
int capacity; // 循环队列总容量
int front; // 循环队列队头元素下标
int rear; // 循环队列队头元素下标
};
-
循环队列的基本操作
// 初始化空队列 seqQueue * initQueue(int cap) { *pq = (sequeue *)malloc(sizeof(sequeue)); (*pq)->front = (*pq)->rear = MAXSIZE - 1; } // 判断队列是否为空 bool isEmpty(seqQueue *q) { return q->front == q->rear; } // 判断队列是否已满 bool isFull(seqQueue *q) { return (q->rear+1)%q->capacity == q->front; } // 出队 bool outQueue(seqQueue *q, datatype *pm) { if(isEmpty(q)) return false; *pm = q->data[q->front]; q->front = (q->front + 1) % q->capacity; return true; } // 入队 bool enQueue(seqQueue *q, datatype data) { if(isFull(q)) return false; q->data[q->rear] = data; q->rear = (q->rear + 1) % q->capacity; return true; }注意:
循环队列中,需要牺牲一个存储位置来区分空队和满队「课堂练习3」
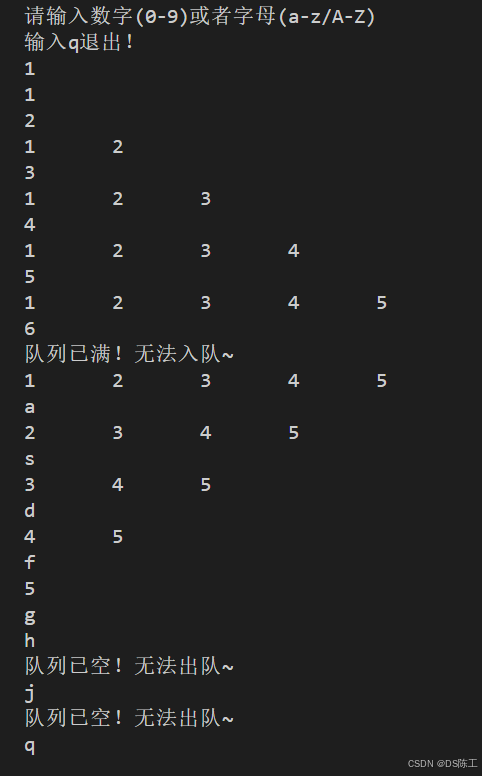
构建一个顺序存储的循环队列,当用户输入数字时,将数字入队,当用户输入字母时,将队头元素出队。每次操作队列之后,将队列中的元素显示出来。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <ctype.h>
typedef int dataType;
// 队列管理结构体
typedef struct seqQueue
{
dataType *data; // 指向数据域数组的首元素地址
int cap; // 数组大小
int front; // 队头
int rear; // 队尾
} seqQueue;
// 初始化队
seqQueue *init_queue(int cap)
{
seqQueue *queue = malloc(sizeof(seqQueue));
if (queue == NULL)
return NULL;
queue->data = calloc(cap, sizeof(dataType));
if (queue->data == NULL)
{
free(queue);
return NULL;
}
queue->cap = cap;
queue->front = 0;
queue->rear = 0;
return queue;
}
// 判断队列是否满
bool isFull(seqQueue *queue)
{
return (queue->rear + 1) % queue->cap == queue->front;
}
// 入队
bool enQueue(seqQueue *queue, dataType data)
{
if (isFull(queue))
{
return false;
}
// 入队--尾进
queue->data[queue->rear] = data;
queue->rear = (queue->rear + 1) % queue->cap;
return true;
}
bool isEmpty(seqQueue *queue)
{
return queue->rear == queue->front;
}
// 出队
bool outQueue(seqQueue *queue)
{
if (isEmpty(queue))
return false;
// 出队————头出
queue->front = (queue->front + 1) % queue->cap;
return true;
}
//显示
void show(seqQueue *q)
{
if (q == NULL || isEmpty(q))
return;
for(int i = q->front; i != q->rear; i = (i+1)%q->cap)
{
printf("%d\t", q->data[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//销毁
void destory(seqQueue *queue)
{
// 判断队列是否为空,如果为空直接返回
if (queue == NULL)
return;
// 释放数据域数组
free(queue->data);
// 释放队列结构体
free(queue);
printf("销毁成功!\n");
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
seqQueue *queue = init_queue(6);
if (queue == NULL)
{
perror("初始化失败!");
return -1;
}
//构建一个顺序存储的循环队列,当用户输入数字时,将数字入队,当用户输入字母时,将队头元素出队。每次操作队列之后,将队列中的元素显示出来
printf("请输入数字(0-9)或者字母(a-z/A-Z)\n输入q退出!\n");
while (1)
{
char input;
scanf("%c", &input);
while(getchar()!='\n');
if (input == 'q' ) //q退出
{
break;
}
else if(isdigit(input))
{
int num = input - '0';
if(!enQueue(queue,num))
printf("队列已满!无法入队~\n");
}
else if(isalpha(input))
{
dataType data;
if(!outQueue(queue))
printf("队列已空!无法出队~\n");
}
else
printf("无效输入!请输入数字或者字母!\n");
show(queue);
}
printf("\n");
// while (1)
// {
// dataType data;
// if(scanf("%d",&data) == 1)
// {
// if(!enQueue(queue,data))
// {
// printf("队满!无法入队!\n");
// break;
// }
// }
// else
// {
// while(getchar()!= '\n');
// if( ! outQueue(queue))
// {
// printf("队空!无法出队!\n");
// break;
// }
// }
// show(queue);
// }
// destory(queue);
return 0;
}
3.链式队列
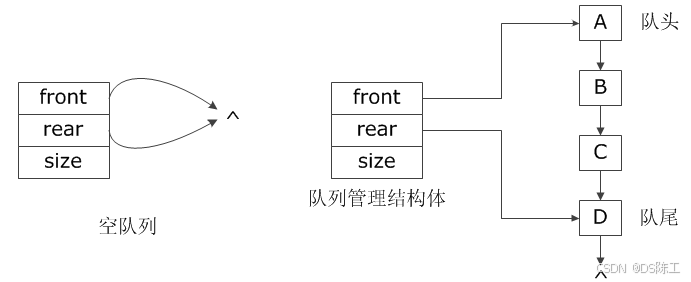
链式队列的组织形式与链表无异,只不过插入删除被约束在固定的两端。为了便于操作,通常也会创建所谓管理结构体,用来存储队头指针、队尾指针、队列元素个数等信息:
从上图可以看到,链式队列主要控制队头和队尾,由于管理结构体中保存了当前队列元素个数size,因此可以不必设计链表的头节点,初始化空队列时只需要让队头队尾指针同时指向空即可。
以下是队列链表节点设计和管理结构体设计的示例代码:
// 链式队列节点
typedef struct node
{
datatype data;
struct node *next;
}node;
// 链式队列管理结构体
typedef struct
{
node *front; // 队头指针
node *rear; // 队尾指针
int size; // 队列当前元素个数
}linkQueue;
-
链式队列的基本操作
// 初始化空队列 linkQueue *initQueue() { linkQueue *q = (linkQueue *)malloc(sizeof(linkQueue)) if(q != NULL) { q->front = NULL; q->rear = NULL; q->size = 0; } return q; } // 判断队列是否为空 bool isEmpty(linkQueue *q) { return q->size == 0; } // 入队 bool enQueue(linkQueue *q, datatype data) { // 创建新节点 node *new = malloc(sizeof(node)); if(new == NULL) return false; new->data = data; new->next = NULL; // 入队分两种情况: // 1. 当前队列为空,则新节点是队列的唯一节点 if(isEmpty(q)) q->front = q->rear = new; // 2. 否则队列不为空,将新节点拼接到队尾之后 else { q->rear->next = new; q->rear = new; } q->size++; return true; } // 出队 bool outQueue(linkQueue *q, datatype *pm) { if(isEmpty(q)) return false; // 返回用户数据 *pm = q->front->data; // 更新队头队尾指针,分两种情况: // 1. 当前队列只有一个元素,出队后队列为空,此时队头队尾指针都必须更新 if(q->size == 1) { free(q->front); q->front = NULL; q->rear = NULL; } // 2. 否则,只需更新队头指针即可 else { node *tmp = q->front; q->front = q->front->next; tmp->next = NULL; free(tmp); } q->size--; return true; } // 取队头元素 bool front(linkQueue *q, datatype *pm) { if(isEmpty(q)) return false; *pm = q->front->data; return true; }「课堂练习4」
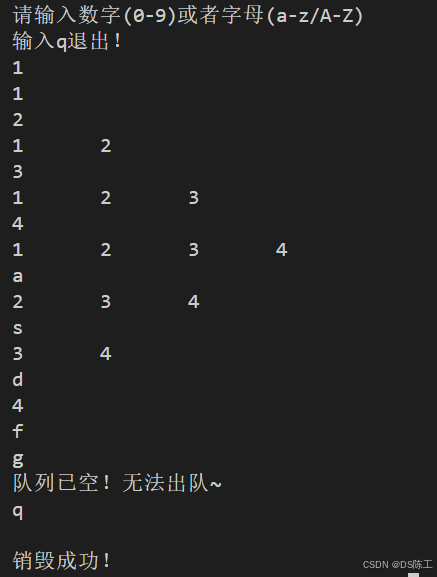
构建一个链式队列,当用户输入数字时,将数字入队,当用户输入字母时,将队头元素出队。每次操作队列之后,将队列中的元素显示出来。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <ctype.h>
typedef int dataType;
// 链式队列节点
typedef struct node
{
dataType data;
struct node *next;
} node;
// 链式队列管理结构体
typedef struct
{
node *front; // 队头指针
node *rear; // 队尾指针
int size; // 队列当前元素个数
} linkQueue;
// 初始化空队列
linkQueue *initQueue()
{
linkQueue *q = (linkQueue *)malloc(sizeof(linkQueue));
if (q != NULL)
{
q->front = NULL;
q->rear = NULL;
q->size = 0;
}
return q;
}
// 判断队列是否为空
bool isEmpty(linkQueue *q)
{
return q->size == 0;
}
// 入队
bool enQueue(linkQueue *q, dataType data)
{
// 创建新节点
node *pnew = malloc(sizeof(node));
if (pnew == NULL)
return false;
pnew->data = data;
pnew->next = NULL;
// 入队分两种情况:
// 1. 当前队列为空,则新节点是队列的唯一节点
if (isEmpty(q))
q->front = q->rear = pnew;
// 2. 否则队列不为空,将新节点拼接到队尾之后
else
{
q->rear->next = pnew;
q->rear = pnew;
}
q->size++;
return true;
}
// 出队
bool outQueue(linkQueue *q)
{
if (isEmpty(q))
return false;
// 更新队头队尾指针,分两种情况:
// 1. 当前队列只有一个元素,出队后队列为空,此时队头队尾指针都必须更新
if (q->size == 1)
{
free(q->front);
q->front = NULL;
q->rear = NULL;
}
// 2. 否则,只需更新队头指针即可
else
{
node *tmp = q->front;
q->front = tmp->next;
tmp->next = NULL;
free(tmp);
}
q->size--;
return true;
}
// 取队头元素
bool front(linkQueue *q, dataType *pm)
{
if (isEmpty(q))
return false;
*pm = q->front->data;
return true;
}
// 显示
void show(linkQueue *q)
{
if (q == NULL || isEmpty(q))
return;
node *p = q->front;
while (p != NULL)
{
printf("%d\t", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
// 销毁
void destory(linkQueue *q)
{
// 判断队列是否为空,如果为空直接返回
if (q == NULL)
return;
node *p = q->front;
while (p != NULL)
{
node *tmp = p->next;
printf("%d\t", p->data);
free(p);
p = tmp;
}
q->front = NULL;
q->rear = NULL;
printf("销毁成功!\n");
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
linkQueue *queue = initQueue();
if (queue == NULL)
{
perror("初始化失败!");
return -1;
}
// 构建一个链式队列,当用户输入数字时,将数字入队,当用户输入字母时,将队头元素出队。每次操作队列之后,将队列中的元素显示出来。
printf("请输入数字(0-9)或者字母(a-z/A-Z)\n输入q退出!\n");
while (1)
{
char input;
scanf("%c", &input);
// 清除输入缓冲区
while (getchar() != '\n');
if (input == 'q') // q退出
{
break;
}
else if (isdigit(input))
{
int num = input - '0';
if (!enQueue(queue, num))
printf("队列已满!无法入队~\n");
}
else if (isalpha(input))
{
if (!outQueue(queue))
printf("队列已空!无法出队~\n");
}
else
printf("无效输入!请输入数字或者字母!\n");
show(queue);
}
printf("\n");
destory(queue);
return 0;
}