四、堆的代码实现
Heap.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int HPDataType;
typedef struct Heap
{
HPDataType* a;
int size;
int capacity;
}Heap;
// 堆的初始化
void HeapInit(Heap* hp);
// 堆的销毁
void HeapDestory(Heap* hp);
// 堆的插入
void HeapPush(Heap* hp, HPDataType x);
// 堆的删除
void HeapPop(Heap* hp);
// 取堆顶的数据
HPDataType HeapTop(Heap* hp);
// 堆的数据个数
int HeapSize(Heap* hp);
// 堆的判空
int HeapEmpty(Heap* hp);
//向上调整算法
void AdjustUp(HPDataType* a, int child);
//向下调整算法
void AdjustDown(HPDataType* a, int n, int parent);
Heap.c
#include "Heap.h"
//交换函数
void Swap(HPDataType* n1, HPDataType* n2)
{
HPDataType* tmp = *n1;
*n1 = *n2;
*n2 = tmp;
}
//初始化
void HeapInit(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
hp->a = NULL;
hp->capacity = hp->size = 0;
}
//销毁
void HeapDestory(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
free(hp->a);
hp->a = NULL;
hp->capacity = hp->size = 0;
}
//入堆
void HeapPush(Heap* hp, HPDataType x)
{
assert(hp);
if(hp->capacity == hp->size)//检查当容量和数据个数相等时
{
int newcapacity = hp->capacity == 0 ? 4 : hp->capacity * 2;
//检查容量是否为0,若为0则赋值newcapacity为4,若不为0则赋值为原来的两倍
HPDataType* tmp = (HPDataType*)realloc(hp->a, newcapacity);
//以newcapacity为大小开辟空间
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
hp->a = tmp;
hp->capacity = newcapacity;
}
hp->a[hp->size] = x;
hp->size++;
AdjustUp(hp->a, hp->size - 1);//向上调整建堆
}
//出堆
void HeapPop(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
assert(!HeapEmpty(hp));
Swap(&hp->a[0], &hp->a[hp->size - 1]);//交换堆顶与最后一个元素
hp->size--;//删除当前的最后一个元素,也就是原堆顶数
AdjustDown(hp->a, hp->size, 0);//向下调整调整堆
}
//堆顶元素
HPDataType HeapTop(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
assert(!HeapEmpty(hp));
return hp->a[0];
}
//堆的元素个数
int HeapSize(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
return hp->size;
}
//判断堆是否为空
int HeapEmpty(Heap* hp)
{
assert(hp);
return hp->size == 0;
}
//向上调整
void AdjustUp(HPDataType* a, int child)
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
//通过子节点找到父节点,这里不管是左孩子还是右孩子都可以找到父节点,因为除法有向下取整的特性
//while (parent >= 0)
while (child > 0)//这里用子节点作为循环条件,因为child可能调整到根节点上
{
if (a[child] > a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}//大于就交换,把此时的父节点变成子节点,父节点的父节点变成父节点,比较上一层的关系
else
{
break;//小于等于直接退出
}
}
}
//向下调整
void AdjustDown(HPDataType* a, int n, int parent)
{
int child = parent * 2 + 1;//通过父节点找到左孩子
while (child < n)
{
// 选出左右孩子中大的那个
if (child + 1 < n && a[child + 1] > a[child])
{
child++;//如果左孩子比右孩子大就把比较的孩子换成右孩子
}
//大于/小于就交换
if (a[child] > a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
test.c
#include "Heap.h"
int main()
{
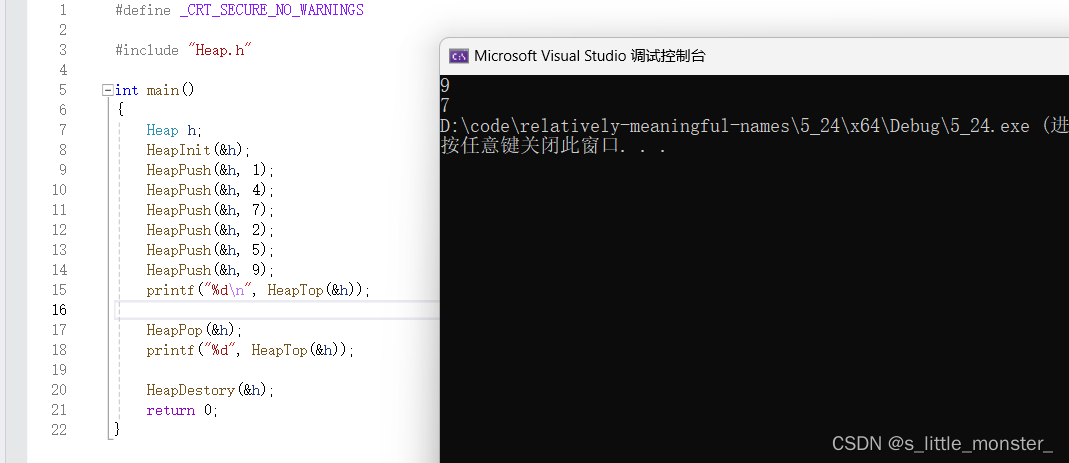
Heap h;
HeapInit(&h);
HeapPush(&h, 1);
HeapPush(&h, 4);
HeapPush(&h, 7);
HeapPush(&h, 2);
HeapPush(&h, 5);
HeapPush(&h, 9);
printf("%d\n", HeapTop(&h));
HeapPop(&h);
printf("%d", HeapTop(&h));
HeapDestory(&h);
return 0;
}
五、堆的应用
堆排序思想进行排序
我们在上面实现了堆,如果想要升序数组就建大堆,降序数组就建小堆
在排序当中,堆排序是一种时间复杂度较低的排序,要远优于冒泡排序,在使用堆排序时,要使用向下调整算法,这样我们就可以最大限度的减少时间的使用
在堆排序中,升序排序建大堆,此时堆顶的元素就是最大的元素,将堆顶元素与最后一个元素交换,再进行向下调整,此时的向下调整的最后一个数字不是最后一个数字,即不是那个最大大的数字,而是倒数第二个,然后再交换,倒数第二个就是第二大的数,以此类推,排序后成为升序数组
在堆排序中有一个很经典的问题就是TopK问题,即一堆数据,个数为n(n>>k),求这堆数据中最大/最小的k个数据
如果是求前k个最大的元素,则用前k个元素建小堆
如果是求前k个最小的元素,则用前k个元素建大堆
然后再用剩下的n-k个元素一次与堆顶元素来比较,不满足则替换堆顶元素
也就是说,我们用求前k个最大数据来举例,我们先将整组数据的前k个元素建一个小堆,小堆的根是整个堆里最小的,用它来和剩余的n-k个元素比较,如果剩余的元素中的某一个比小堆根大,那么就替换掉,再用向下调整算法调整,这样一来,最大的数据都沉底了,堆中最小的数据继续与剩余的数据比较,重复上述步骤,当所有剩余元素都比完了之后,剩下的这个小堆就是前k个最大数
六、二叉树链式结构的实现
BTree.h
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef char BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
BTDataType data;
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
}BTNode;
// 通过前序遍历的数组"ABD##E#H##CF##G##"构建二叉树
BTNode* BinaryTreeCreate(BTDataType* a, int* pi);
// 二叉树销毁
void BinaryTreeDestory(BTNode* root);
// 二叉树节点个数
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root);
// 二叉树叶子节点个数
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root);
// 二叉树第k层节点个数
int BinaryTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k);
// 二叉树查找值为x的节点
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x);
// 二叉树前序遍历
void BinaryTreePrevOrder(BTNode* root);
// 二叉树中序遍历
void BinaryTreeInOrder(BTNode* root);
// 二叉树后序遍历
void BinaryTreePostOrder(BTNode* root);
BTree.c
#include "BTree.h"
BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x)
{
BTNode* new = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (new == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
new->data = x;
new->left = NULL;
new->right = NULL;
return new;
}
BTNode* BinaryTreeCreate(BTDataType* a,int n, int* pi)
{
if (*pi >= n || a[*pi] == '#')//这里我们把#作为空的标识符
{
// 如果到达数组末尾或遇到#,则返回NULL
(*pi)++;
return NULL;
}
BTNode* node = BuyNode(a[*pi]);
(*pi)++; // 移动到下一个节点
node->left = BinaryTreeCreate(a, n, pi); // 递归创建左子树
node->right = BinaryTreeCreate(a, n, pi); // 递归创建右子树
return node;
}
void BinaryTreeDestory(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
BinaryTreeDestory(root->left);
BinaryTreeDestory(root->right);
free(root);
}
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
//return root == NULL ? 0 : BinaryTreeSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeSize(root->right) + 1;
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
return BinaryTreeSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return 1;
return BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
int BinaryTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{
assert(k > 0);
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (k == 1)
return 1;
return BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1) + BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
}
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
if (root->data = x)
return root;
BTNode* ret1 = BinaryTreeFind(root->left, x);
if (ret1)
return ret1;
BTNode* ret2 = BinaryTreeFind(root->right, x);
if (ret2)
return ret2;
return NULL;
}
void BinaryTreePrevOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("N ");
return;
}
printf("%c ", root->data);
BinaryTreePrevOrder(root->left);
BinaryTreePrevOrder(root->right);
}
void BinaryTreeInOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("N ");
return;
}
BinaryTreeInOrder(root->left);
printf("%c ", root->data);
BinaryTreeInOrder(root->right);
}
void BinaryTreePostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("N ");
return;
}
BinaryTreeInOrder(root->left);
BinaryTreeInOrder(root->right);
printf("%c ", root->data);
}
test.c
#include "BTree.h"
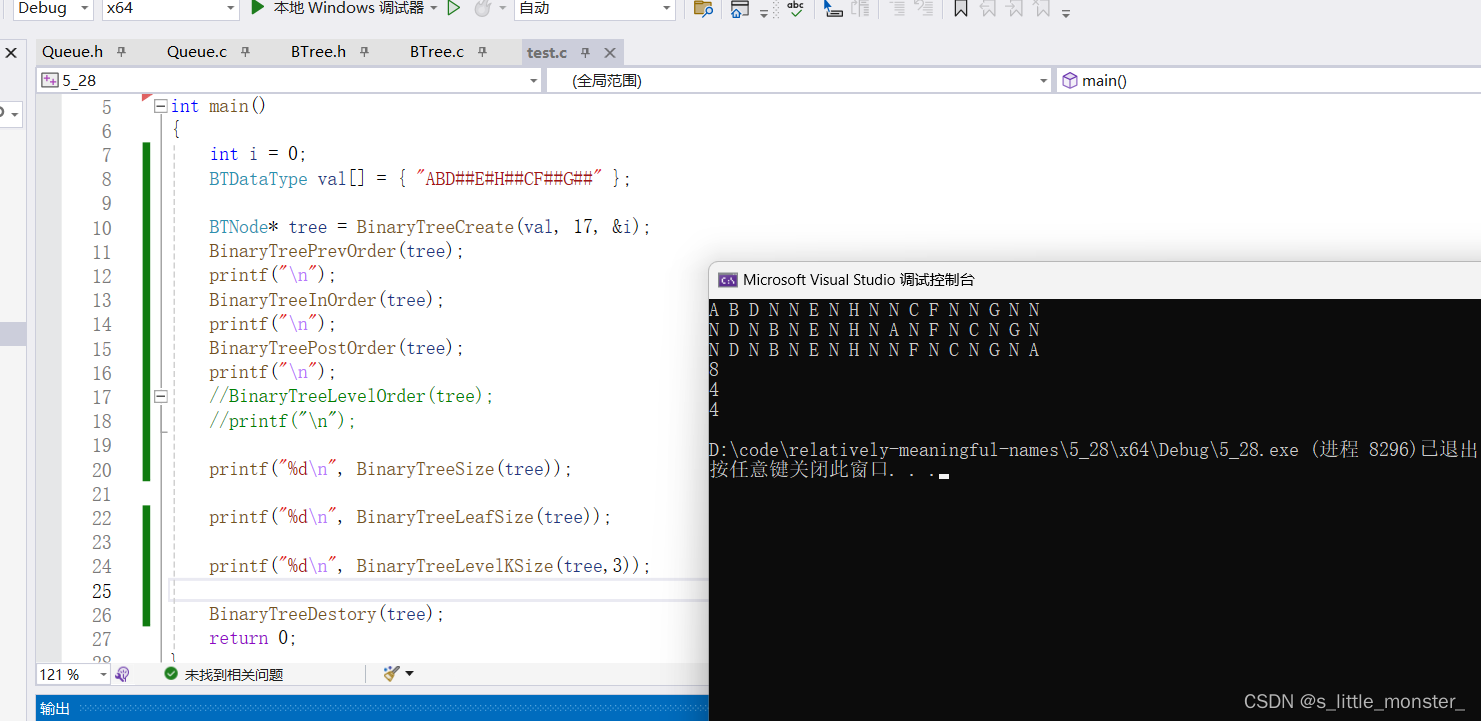
int main()
{
int i = 0;
BTDataType val[] = { "ABD##E#H##CF##G##" };
BTNode* tree = BinaryTreeCreate(val, 17, &i);
BinaryTreePrevOrder(tree);
printf("\n");
BinaryTreeInOrder(tree);
printf("\n");
BinaryTreePostOrder(tree);
printf("\n");
printf("%d\n", BinaryTreeSize(tree));
printf("%d\n", BinaryTreeLeafSize(tree));
printf("%d\n", BinaryTreeLevelKSize(tree,3));
BinaryTreeDestory(tree);
return 0;
}
下一篇我们来详细剖析链式二叉树的实现~