一、引言与概述
1 引言
日期操作是软件开发中的常见需求,如日程管理、数据统计等场景均需处理日期的比较、偏移及合法性校验。为简化此类操作,本文设计了一个高效且类型安全的C++日期类Date。
该类通过构造函数内嵌合法性检查,确保对象初始状态的正确性;借助运算符重载,用户可直观使用d1 > d2、d += 30等语法进行逻辑判断与日期计算,显著提升代码可读性。内部方法GetMonthDay结合静态数组与闰年规则,动态适配不同月份的天数变化,解决了跨月运算的复杂性。
代码结构分为头文件声明与实现文件,测试函数TestDate1和TestDate2覆盖了核心功能的验证,包括运算符逻辑、日期加减及自增行为。本文的实现兼顾效率与安全性(如const引用传参),为日期相关功能提供了可靠的底层支持。
2 概述
本文设计并实现了一个基于C++的日期类Date,支持日期的基本操作与运算。类核心功能包括:
-
日期合法性校验:构造函数自动检测年、月、日的有效性,对非法日期输出警告。
-
运算符重载:提供完整的比较运算符(
==、!=、>、<等)、日期加减运算(+、+=、-、-=)及自增操作(前置/后置++),使日期操作更符合直觉。 -
智能月份天数计算:通过私有方法
GetMonthDay动态判断闰年与各月份天数,确保跨月、跨年运算的准确性。 -
测试验证:包含测试用例
TestDate1和TestDate2,验证比较逻辑、日期增减及边界条件处理的正确性。
代码采用面向对象设计,通过封装与运算符重载提升易用性,适用于需日期处理的应用程序开发。
二、Date头文件的设计
头文件 Date.h 是整个日期类的核心声明文件,其设计遵循面向对象封装原则,通过合理划分公有接口与私有实现,确保类的安全性与易用性。以下从结构、功能与设计细节三个层面详细说明头文件的设计思路。
1. 头文件结构
头文件主要包含以下部分:
-
预处理指令:
#pragma once #include <iostream> using std::cout; using std::endl;-
#pragma once:防止头文件重复包含,保证编译安全性。 -
仅包含必要的输入输出流头文件
<iostream>,避免冗余依赖。 -
使用
using声明简化cout和endl的调用,提升代码简洁性。
-
-
类声明:
class Date { public: // 构造函数与成员函数声明 private: // 成员变量与私有方法声明 };-
明确划分
public与private区域:-
公有接口:暴露构造函数、打印函数及运算符重载,供外部调用。
-
私有实现:隐藏成员变量
_year、_month、_day及辅助方法GetMonthDay,防止外部直接修改内部状态。
-
-
2. 类成员设计
(1) 成员变量
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day; -
命名规范:采用
_前缀标识成员变量(如_year),与构造函数参数year区分,增强可读性。 -
数据封装:私有属性禁止外部直接访问,确保日期状态的完整性,避免非法修改。
(2) 构造函数
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1); -
默认参数:提供默认值(1年1月1日),支持无参构造(如
Date d;)。 -
参数校验:
-
在构造函数内部检查年、月、日的合法性:
if (!(year >= 1 && (month >= 1 && month <= 12) && ... )) cout << "非法日期" << endl; -
确保对象初始状态有效,防止无效日期被创建。
-
(3) 成员函数
-
打印函数:
void Print();提供标准化的日期输出格式(如
2025/3/2),便于调试与展示。 -
运算符重载:
// const 引用参数:提升效率并防止参数被意外修改。 bool operator==(const Date& d); bool operator!=(const Date& d); bool operator>(const Date& d); // d1 > d2 bool operator>=(const Date& d); // d1 >= d2 bool operator<=(const Date& d); bool operator<(const Date& d); Date& operator+=(int day); // d1 += day Date operator+(int day); // d1 + day Date& operator-=(int day); // d1 -= day Date operator-(int day); // d1 - day Date& operator++(); // 前置 Date operator++(int); // 后置-
逻辑运算符(
==、>等):支持日期的直接比较(如d1 > d2)。 -
算术运算符(
+=、+等):实现日期的增减运算(如d1 += 30)。 -
参数传递:使用
const引用(const Date& d)避免拷贝开销,同时防止参数被修改。
-
(4) 私有辅助方法
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month); -
功能:根据年份和月份动态返回当月天数,自动处理闰年二月(29天)。
-
实现细节:
-
静态数组
monthDayArray存储非闰年各月天数,减少重复计算。 -
通过闰年规则判断二月天数,提升计算效率。
-
3. 关键设计细节
-
运算符复用:
-
通过复用已有运算符减少冗余代码。例如:
bool operator!=(const Date& d) { return !(*this == d); } bool operator<=(const Date& d) { return !(*this > d); } -
提高代码可维护性,避免逻辑不一致。
-
-
前置与后置自增:
Date& operator++(); // 前置++(返回引用) Date operator++(int); // 后置++(返回临时对象)-
通过
int参数区分前置与后置运算符,符合C++标准语法。 -
前置自增直接修改对象并返回引用,后置自增返回旧值的副本,保证语义正确性。
-
-
异常处理策略:
-
构造函数检测到非法日期时仅输出警告,未抛出异常,需由调用者确保输入的合法性。
-
可根据需求扩展为抛出异常,增强健壮性。
-
4. 设计优势
-
高内聚低耦合:日期计算逻辑封装在类内部,外部仅通过接口调用,降低依赖。
-
语法直观性:运算符重载使日期操作符接近内置类型(如
d1 == d2),提升代码可读性。 -
效率优化:通过引用传递、静态数组缓存天数,减少运行时开销。
该头文件的设计兼顾功能完备性与代码简洁性,为日期操作提供了高效、安全的抽象层。
三、函数实现
本节详细解析 Date 类的核心函数实现,涵盖运算符重载、日期运算逻辑及关键设计细节,确保代码功能正确性与效率优化。
1. 比较运算符重载
(1) operator== 与 operator!=
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{
return _year == d._year
&& _month == d._month
&& _day == d._day;
}
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d)
{
// 当调用 d1!=d2 时,d1 是调用该成员函数的对象,因此 this 指向 d1。
// 等价于 d1.operator==(d2)
return !(*this == d);
}-
功能:直接比较日期的年、月、日是否全等。
-
设计亮点:通过
operator!=复用operator==逻辑,避免冗余代码。
(2) operator> 与 < 系列运算符
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)
{
if (_year > d._year) return true;
else if (_year == d._year && _month > d._month) return true;
else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day) return true;
else return false;
}
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d)
{
return (*this > d) && (*this == d);
}
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this >= d);
}bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this > d);
}
-
关键逻辑:按年→月→日优先级逐级比较,确保判断顺序正确。
2. 日期加减运算
(1) operator+= 与 operator+
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this -= (-day);
}
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
++_month;
if (_month == 13)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
Date& ret(*this);
ret += day;
return ret;
}-
核心算法:
-
通过循环逐月扣除天数,处理跨月、跨年场景。
-
调用
GetMonthDay动态获取当月天数,适配闰年规则。
-
(2) operator-= 与 operator-
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this += (-day);
}
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
--_month;
if (_month == 0)
{
--_year;
_month = 12;
}
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{
Date& ret(*this);
ret -= day;
return ret;
}-
逆向运算逻辑:逐月回溯天数,处理跨月、跨年问题。
-
边界处理:当
_day减为负数时,调整月份并补足上月天数。
3. 自增运算符
(1) 前置 operator++
Date& Date::operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
-
行为:直接修改对象,日期加1天后返回自身引用。
(2) 后置 operator++
// 后置 -- 多一个int参数主要是为了根前置区分
// 构成函数重载
Date Date::operator++(int)
{
Date tmp(*this);
*this += 1;
return tmp;
}-
行为:先保存原对象状态,再自增,最后返回旧值副本。
-
语法特性:通过
int参数区分前置与后置运算符。
4. 辅助函数 GetMonthDay
// 函数:获取某年某月的天数
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
// 定义静态变量:每月天数
static int monthDayArray[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
// 闰年二月有 29 天
if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0))) return 29;
else return monthDayArray[month];
}-
功能:根据年份和月份返回当月天数,自动处理闰年二月。
-
优化设计:
-
使用静态数组缓存非闰年月份天数,减少重复初始化开销。
-
闰年判断规则符合格里高利历标准。
-
5. 测试函数设计
(1) 测试逻辑运算符(TestDate1)
void TestDate1()
{
/* 测试 == != > >= < <= */
Date d1(2025, 3, 2);
Date d2(d1);
Date d3(2025, 3, 1);
// == 等于
if (d1 == d2) cout << "==" << endl;
else cout << "!==" << endl;
// != 不等于
if (d1 != d3) cout << "!=" << endl;
else cout << "!!=" << endl;
// > 大于
if (d1 > d3) cout << ">" << endl;
else cout << "!>" << endl;
// >= 不大于等于
if (d3 >= d1) cout << ">=" << endl;
else cout << "!>=" << endl;
// < 小于
if (d3 < d1) cout << "<" << endl;
else cout << "!<" << endl;
// < 不小于等于
if (d1 <= d3) cout << "<=" << endl;
else cout << "!<=" << endl;
}-
覆盖场景:相等日期、相邻日期、跨月边界条件。
-
测试结果:
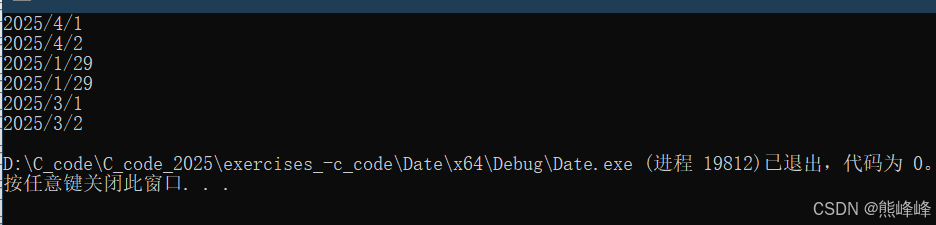
(2) 测试日期运算(TestDate2)
void TestDate2()
{
/* 测试 += + -= - 前置++ 后置++ */
Date d1(2025, 3, 2);
Date d2(d1);
Date d3(2025, 3, 1);
Date d4(d3);
Date d5(2025, 2, 28);
// +=30 2025.4.1
d1 += 30;
d1.Print();
// + 31 2025.4.2
d2 + 31;
d2.Print();
// -= 31 2025.1.29
d3 -= 31;
d3.Print();
// - 31 2025.1.29
d4 - 31;
d3.Print();
// 1 2025.3.1
d5++;
d5.Print();
// 1 2025.3.2
++d5;
d5.Print();
}-
关键测试点:
-
跨月运算(如
+=30导致3月→4月)。 -
闰年二月处理(
d5++从2月28日到3月1日)。 -
运算符链式调用(如
d5++与++d5的区别)。
-
-
测试结果:
四、总结与展望
1. 项目总结
本文设计的 Date 类通过面向对象思想与运算符重载技术,实现了日期的核心操作功能,具有以下特点:
-
语法直观性:通过运算符重载(如
d1 += 30、d1 > d2),使日期操作符的语义接近内置类型,提升代码可读性。 -
高效性与安全性:
-
使用
const引用传递参数,避免不必要的拷贝开销。 -
私有方法
GetMonthDay结合静态数组与闰年规则,高效计算月份天数。
-
-
边界处理能力:支持跨月、跨年的日期运算(如从2月28日加1天到3月1日)。
-
可扩展性:通过封装成员变量与公有接口分离,便于后续功能扩展。
测试验证:
-
TestDate1验证了比较运算符的逻辑正确性。 -
TestDate2覆盖了日期加减、自增运算符的边界场景(如月份进位)。
2. 未来展望
为提升 Date 类的健壮性与功能性,可从以下方向优化:
功能增强:
-
扩展日期运算:
-
实现日期差计算(如
d1 - d2返回相差天数)。 -
支持周数计算、星期获取(如
GetWeekDay()返回周几)。
-
-
格式化输出:
-
支持多种日期格式(如
YYYY-MM-DD、DD/MM/YYYY)。 -
添加国际化支持(如中英文月份名称)。
-
性能优化:
-
缓存优化:将
GetMonthDay的静态数组改为全局常量,避免重复初始化。 -
运算符复用:通过模板或宏进一步减少比较运算符的冗余代码。
兼容性扩展:
-
与标准库集成:兼容
std::chrono库,支持时间戳转换与时区处理。 -
序列化支持:添加
Serialize()与Deserialize()方法,支持日期对象的持久化存储。
测试完善:
-
边界测试:覆盖闰年2月29日、12月31日+1天、1月1日-1天等极端场景。
-
模糊测试:随机生成大规模日期数据,验证运算逻辑的鲁棒性。
3. 结语
本文实现的 Date 类为C++日期操作提供了简洁高效的解决方案,其设计兼顾语法友好性与计算准确性,适用于日历应用、数据分析等场景。通过持续优化异常处理、扩展功能边界,并结合现代C++特性(如移动语义、constexpr 计算),可进一步提升其工程价值。该类的设计思想亦可为其他自定义类型的开发提供参考,体现了面向对象编程在复杂逻辑抽象中的核心优势。
五、完整代码展示
1.Date.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
class Date
{
public:
// 构造函数
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
// _year是类的成员变量用于存储对象的状态, year为构造函数类的参数用于传递外部值到成员变量
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
// 检查日期是否合法
if (!(year >= 1 // 年
&& (month >= 1 && month <= 12) // 月
&& (day >= 1 && day <= GetMonthDay(year, month)))) // 日
{
cout << "非法日期" << endl;
}
}
void Print()
{
cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;
}
// const 引用参数:提升效率并防止参数被意外修改。
bool operator==(const Date& d);
bool operator!=(const Date& d);
bool operator>(const Date& d); // d1 > d2
bool operator>=(const Date& d); // d1 >= d2
bool operator<=(const Date& d);
bool operator<(const Date& d);
Date& operator+=(int day); // d1 += day
Date operator+(int day); // d1 + day
Date& operator-=(int day); // d1 -= day
Date operator-(int day); // d1 - day
Date& operator++(); // 前置
Date operator++(int); // 后置
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
// 函数:获取某年某月的天数
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
// 定义静态变量:每月天数
static int monthDayArray[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
// 闰年二月有 29 天
if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0))) return 29;
else return monthDayArray[month];
}
};2.Date.cpp
#include "Date.h"
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{
return _year == d._year
&& _month == d._month
&& _day == d._day;
}
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d)
{
// 当调用 d1!=d2 时,d1 是调用该成员函数的对象,因此 this 指向 d1。
// 等价于 d1.operator==(d2)
return !(*this == d);
}
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)
{
if (_year > d._year) return true;
else if (_year == d._year && _month > d._month) return true;
else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day) return true;
else return false;
}
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d)
{
return (*this > d) && (*this == d);
}
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this >= d);
}bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this > d);
}
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this -= (-day);
}
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
++_month;
if (_month == 13)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
Date& ret(*this);
ret += day;
return ret;
}
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this += (-day);
}
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
--_month;
if (_month == 0)
{
--_year;
_month = 12;
}
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{
Date& ret(*this);
ret -= day;
return ret;
}
Date& Date::operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
// 后置 -- 多一个int参数主要是为了根前置区分
// 构成函数重载
Date Date::operator++(int)
{
Date tmp(*this);
*this += 1;
return tmp;
}3. Test.cpp
#include "Date.h"
void TestDate1()
{
/* 测试 == != > >= < <= */
Date d1(2025, 3, 2);
Date d2(d1);
Date d3(2025, 3, 1);
// == 等于
if (d1 == d2) cout << "==" << endl;
else cout << "!==" << endl;
// != 不等于
if (d1 != d3) cout << "!=" << endl;
else cout << "!!=" << endl;
// > 大于
if (d1 > d3) cout << ">" << endl;
else cout << "!>" << endl;
// >= 不大于等于
if (d3 >= d1) cout << ">=" << endl;
else cout << "!>=" << endl;
// < 小于
if (d3 < d1) cout << "<" << endl;
else cout << "!<" << endl;
// < 不小于等于
if (d1 <= d3) cout << "<=" << endl;
else cout << "!<=" << endl;
}
void TestDate2()
{
/* 测试 += + -= - 前置++ 后置++ */
Date d1(2025, 3, 2);
Date d2(d1);
Date d3(2025, 3, 1);
Date d4(d3);
Date d5(2025, 2, 28);
// +=30 2025.4.1
d1 += 30;
d1.Print();
// + 31 2025.4.2
d2 + 31;
d2.Print();
// -= 31 2025.1.29
d3 -= 31;
d3.Print();
// - 31 2025.1.29
d4 - 31;
d3.Print();
// 1 2025.3.1
d5++;
d5.Print();
// 1 2025.3.2
++d5;
d5.Print();
}
int main()
{
//TestDate1();
TestDate2();
return 0;
}